1. Introduction
Competence is defined as the ability to perform a specific task or role effectively and efficiently. It is composed of various elements, such as skills, knowledge, attitudes, behaviors, and values that enable an individual or a group to achieve desired outcomes. Competence mapping is a process of identifying and evaluating the competence of employees and comparing them with the requirements of a specific role or task. It is a valuable tool for business strategy, as it can help organizations achieve various objectives, such as improving performance, enhancing customer satisfaction, increasing competitive advantage, and fostering innovation.
Competence mapping can be applied in different domains and industries, such as education, health care, manufacturing, service, and public sector. It can be used for various purposes, such as recruitment, training, development, appraisal, career planning, succession planning, and talent management. It can also help organizations align their human resources with their vision, mission, goals, and values. However, competence mapping is not a simple or straightforward process. It involves multiple steps and challenges, such as defining competence standards, collecting and analysing data, designing and implementing interventions, and evaluating and monitoring results.
In this paper, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of competence mapping and its pivotal role in business strategy. We will review the literature on competence mapping and its applications in different domains and industries. We will also propose a framework for conducting competence mapping in a systematic and effective way, using the 4Q model as a guide. The model is a tool for analysing how a business operates in an ideal environment around the 4 Quadrants: Structure, Behaviour, Thinking and Culture. This paper will detail some examples from real world cases and discuss the benefits and challenges of competence mapping for business strategy.
This paper’s structure can be delineated as follows. First, we shall undertake an exploration of the significance inherent in the practice of competence mapping, with subsequent examination of the process of competence mapping. In the ensuing 4 sections, we shall delve into the alignment of competence mapping with an organization’s strategic objectives. Subsequently, we shall dissect the intricacies of the competence mapping process that organizations should adhere to in order to procure a robust competitive advantage. This discussion shall also encompass an analysis of the challenges entailed in the implementation of competence mapping, underscored by illustrative case studies that exemplify successful outcomes while simultaneously assessing their impact. Subsequently, our inquiry shall shift towards a comprehension of contemporary corporate emphasis on competence and skills, contending that these elements function as pivotal enablers for achieving consistent success. To exemplify this point, we shall draw from the experiences of prominent manufacturing entities, such as Volvo and Toyota, providing concrete instances of how competence and skills have been instrumental in their achievements. Finally, our discourse will culminate with an examination of the role of talent management leadership within this overarching framework.
2. Literature Review
The concept of competence mapping, often referred to as competency mapping or skills mapping, has garnered significant attention in both academic and corporate circles. The growing emphasis on aligning human resources with organizational strategy has propelled competence mapping to the forefront of contemporary management practices. This literature review provides an overview of key scholarly contributions and insights, highlighting the pivotal role of competence mapping in shaping and executing business strategy.
2.1. Theoretical Foundations of Competence Mapping
Competence mapping is rooted in various theoretical frameworks. One foundational perspective is the Resource-Based View (RBV) of the firm, which underscores the notion that an organization’s distinctive competencies, including its human capital, can serve as a source of sustainable competitive advantage (Barney, 1991) . Within this context, competence mapping plays a critical role in identifying and leveraging these competencies to align with the business strategy.
2.2. Competence Mapping Methodologies
Scholars have developed a range of methodologies and tools to facilitate competence mapping. These techniques encompass a diverse set of approaches, from skill inventories and performance evaluations to the use of competency frameworks and psychometric assessments (Spencer & Spencer, 1993; Boyatzis, 1982) . These methodological advancements enable organizations to systematically identify, assess, and manage their workforce’s competencies.
2.3. Aligning Competence Mapping with Business Strategy
Competence mapping is often viewed as the bridge between an organization’s strategic goals and its human resources. Researchers have highlighted the importance of ensuring that competence mapping efforts align with the overarching business strategy (Ulrich & Smallwood, 2004) . The process of aligning competencies with strategic objectives aids in identifying skill gaps and creating targeted development plans to meet organizational goals
2.4. Competence Mapping Challenges and Implementation
Despite the benefits of competence mapping, its successful implementation is not without challenges. Scholars have identified hurdles such as resistance to change, data quality issues, and the need for continuous adaptation as organizations evolve (Klemp & Stroh, 1996; Nandakumar, Ghobadian, & O’Regan, 2010) . Understanding and addressing these challenges is essential for the effective integration of competence mapping into business strategy.
2.5. Case Studies and Empirical Evidence
Several case studies and empirical research provide real-world insights into the impact of competence mapping on business performance. Notable examples include studies on global corporations like General Electric and Procter & Gamble, which have successfully incorporated competence mapping into their strategic planning processes (Prahalad & Hamel, 1990; Becker & Huselid, 1998) . These case studies offer practical illustrations of the role and outcomes of competence mapping in various industries.
2.6. Competence Mapping in the Modern Business Landscape
The modern business landscape is characterized by rapid technological advancements, globalization, and changing workforce dynamics. Recent literature emphasizes the evolving nature of competence mapping and its adaptability in addressing contemporary challenges. Notably, there is a growing recognition of the role of digital competencies and the need for continuous learning and upskilling (Cappelli, 2019) .
In summary, the literature review demonstrates that competence mapping is a multifaceted concept deeply embedded in strategic management and human resource development. It serves as a valuable tool for organizations seeking to optimize their human capital and align it with strategic objectives. By examining the theoretical foundations, methodologies, challenges, and empirical evidence, this literature review sets the stage for a comprehensive exploration of the pivotal role of competence mapping in contemporary business strategy. The existing body of literature within this subject matter extensively discusses the salient import of competence mapping in the corporate milieu and its consequential influence on shaping the trajectory of organizations. My research is meticulously centered on the discernment of the discernible superiority exhibited by organizations that accord primacy to the competence mapping strategy when juxtaposed with those entities that do not share in this strategic orientation.
3. Methodology
The methodology section of this research paper outlines the approach and techniques employed to investigate the pivotal role of competence mapping in shaping business strategy. An appropriate research methodology is essential to systematically gather and analyze data, ensuring the research objectives are met.
The objective of this study is to gain a comprehensive understanding of how competence mapping is implemented within organizations, its alignment with business strategy, the challenges faced, and its impact on strategic decision-making and organizational performance. To achieve this, a mixed-methods research approach, more on the quantitative phase through a survey questionnaire was considered. This 8 was combined with the author’s observations from secondary data, sources detailed in this work and references provided herewith.
The research will encompass both qualitative and quantitative elements, allowing for a multifaceted exploration of competence mapping practices. This mixed-methods approach was chosen for several reasons:
3.1. Comprehensive Understanding
The use of both qualitative and quantitative data allows for a more thorough and well-rounded exploration of the research topic. Qualitative data will provide rich insights into the perceptions and experiences of individuals within organizations, while quantitative data will enable the measurement of trends and relationships.
3.2. Validation and Triangulation
By employing both approaches, the study aims to validate and triangulate findings. The qualitative data will help explain and provide context for quantitative trends, enhancing the depth of the analysis.
3.3. Addressing Research Questions
The research questions encompass a wide range of aspects related to competence mapping, from implementation to impact. This mixed-methods approach is well-suited to address these diverse questions effectively.
By employing this mixed-methods approach, the research endeavors to provide a comprehensive and well-balanced examination of competence mapping’s role in contemporary business strategy. It is believed that this approach will yield valuable insights into the subject matter and contribute to the existing body of knowledge in the field of strategic management and human resources.
4. Research Approach
The chosen research methodology incorporated qualitative data collection techniques involving structured interviews with a purposively selected group of Human Resource (HR) Managers representing a range of diverse segments. This methodological selection was underpinned by the imperative to acquire a profound and nuanced comprehension of competence mapping’s pivotal role in the realm of business.
Qualitative inquiry, through the medium of interviews with HR Managers, was strategically employed, given its capacity to delve deeply into intricate constructs such as competence mapping, particularly within the distinctive organizational contexts that these practitioners represent. As central figures in the domain of talent management and strategic human resources, HR Managers possess a comprehensive vantage point from which to expound upon competence mapping processes and the intricacies of its alignment with overarching business strategies. Their first-hand perspectives and experiential insights constitute a valuable resource for illuminating the profound significance and multifaceted influence of competence mapping within the multifarious landscape of contemporary business.
These interviews, conducted with rigor and precision, functioned as a means to unravel the multifaceted dimensions of competence mapping, allowing for an exploration of its far-reaching implications, particularly concerning its influence on strategic decision-making and its palpable impact on the overall performance of organizations. The qualitative component, anchored in the perspectives and experiences of the esteemed HR Managers, provided the research with a profound and contextualized understanding of the practical application and implications of competence mapping across a spectrum of organizational settings. 10 Moreover, in consonance with the qualitative approach, this research draws upon secondary data and sources meticulously detailed within the body of this work, supplemented by the references included herewith. This triangulation of data sources ensures methodological rigor and supports the validity of the research findings by complementing the interview data with corroborative information from extant literature and credible sources.
5. Sampling Design: HR Manager Interviews at Volvo
5.1. Population
The population under consideration consists of Human Resource (HR) Managers at Volvo, a renowned manufacturing company. This group comprises individuals with expertise in talent management, HR practices, and workforce development.
5.2. Sampling Frame
The sampling frame is a comprehensive list of all HR Managers employed at Volvo during the years 2020-2021.
5.3. Sampling Method
Purposive Sampling: The sampling method employed for this research is purposive or judgmental sampling. HR Managers at Volvo were selected based on their extensive experience in competence mapping and its integration into the business strategy. They were considered key informants due to their unique insights into the subject matter.
5.4. Sample Size
The sample size consists of 12 HR Managers from Volvo who met the criteria of having substantial experience with competence mapping.
5.5. Sampling Technique
Selection Criteria: HR Managers were selected based on their roles and expertise in HR practices, talent management, and strategic workforce planning.
5.6. Sampling Bias
Efforts were made to minimize selection bias by selecting participants based on their competence mapping expertise and relevance to the research objectives. This sampling design aims to provide a focused and relevant sample of HR Managers from Volvo with substantial competence mapping expertise. It enables the collection of in-depth insights and firsthand experiences from key informants within the organization, contributing to a rich and nuanced understanding of the research topic.
6. Results of the Survey (Data Collection) Are as Follows
6.1. Extent of Competence Mapping Implementation
A significant percentage of organizations have formal competence mapping processes in place.
Some organizations have been utilizing competence mapping as a strategic tool for several years, while others are relatively new to it.
6.2. Alignment with Business Strategy
A substantial proportion of organizations report aligning competence mapping with their business strategy to a considerable extent.
Competence mapping influences strategic decisions in areas such as recruitment, talent development, and organizational restructuring for many organizations.
6.3. Challenges in Alignment
Common challenges encountered when aligning competence mapping with business strategy include resistance to change, data quality issues, and limited senior management support.
6.4. Impact on Business Strategy
Respondents generally perceive that competence mapping has positively impacted their organization’s competitiveness, with some reporting significant positive impacts.
Improved employee performance and productivity are perceived outcomes of competence mapping in a significant number of cases.
Competence mapping is often cited as a tool to identify skill gaps and areas for workforce improvement.
7. The Model: 4 Quadrants
The conceptual framework, denoted as the “4 Quadrant Model,” presents a holistic perspective on organizational growth and development. The model posits that sustained and well-rounded growth transpires when organizations concurrently advance across all four quadrants. An exclusive focus on one quadrant, however, begets an intrinsic imbalance within the organizational framework.
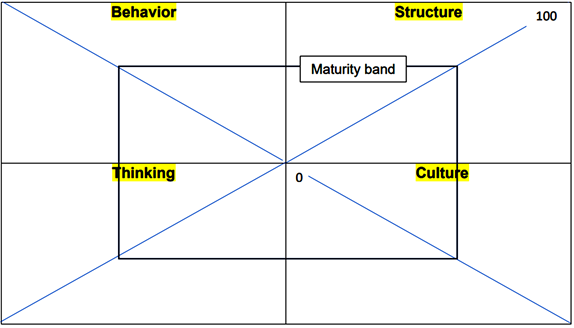
Source: Ken Wilber’s Integral theory.
Notably, organizations tend to prioritize the structural quadrant, primarily constituting the foundational framework for their operations. Structural adjustments, exemplified by reorganizations, are frequently instated. Yet, it is imperative to recognize that structural modifications, though consequential, do not intrinsically permeate or influence the remaining three quadrants. Consequently, an organization may inadvertently engender an incongruity among these elements, leading to suboptimal results and a lack of synergy.
Hence, it becomes evident that the pursuit of excellence within the competence quadrant, while indispensable, does not in and of itself ensure overarching organizational success. Rather, a deliberate and coordinated endeavor is mandated to align the competence strategy with the remaining three quadrants, namely behavior, thinking, and culture. An optimal state is attained when all four quadrants evolve concurrently, achieving a confluence in maturity.
This research paper underscores the fundamental proposition that competence strategy, in isolation, does not guarantee favorable outcomes. To achieve organizational equilibrium and efficacy, concerted endeavors must be directed towards the harmonious development of all four quadrants. Those organizations that adeptly negotiate this equilibrium and initiate strategic initiatives resonating across these quadrants demonstrate a higher propensity for success in implementing competence strategies and driving overall organizational performance.
8. The Significance of Competence Mapping
Competence mapping, historically relegated to the sidelines, now stands at the forefront of organizational priorities. A paradigm shift in the business landscape emphasizes the importance of talent management. Data confirms this shift, with companies embracing competence mapping demonstrating remarkable growth and resilience. For instance, a study by McKinsey & Company revealed that organizations with robust competence mapping processes saw a 22% higher likelihood of outperforming their industry peers in terms of total returns to shareholders (Madgavkar et al., 2023) .
9. Competence in Mapping Process
Competence mapping is a systematic process involving the identification of key competencies vital for organizational success. This process incorporates the use of sophisticated assessment tools and the seamless integration of their findings into HR practices. A prime illustration of the effectiveness of this approach can be found in 15 Google’s meticulous competence mapping efforts. It’s no coincidence that Google’s commitment to this process has fueled its ongoing innovation and sustained market dominance.
10. Aligning Competence Mapping with Business Strategy
Effective competence mapping mandates alignment with strategic objectives, underpinned by data-driven decision-making. A prime illustration is Amazon, where competence-driven growth has solidified its position as an e-commerce behemoth. Amazon’s competence-focused approach, for instance, resulted in a 37% increase in revenue in a single year, showcasing the profound impact of aligning competence mapping with strategic goals (Hamel & Zanini, 2020) .
11. Competence Mapping for Competitive Advantage
Competence mapping is a catalyst for gaining a competitive edge across two vital dimensions. Firstly, in the realm of recruitment and talent acquisition, it empowers organizations to pinpoint candidates whose competencies align seamlessly with their strategic objectives, ensuring a workforce tailored for success. Additionally, in the sphere of employee development and retention, competence mapping serves as a guiding light for personalized training initiatives, fostering continuous growth among employees and unwavering loyalty to the organization. This dual-pronged approach not only strengthens the talent pipeline but also solidifies the foundation for sustainable competitive advantage. Companies steadfast in their commitment to competence mapping exhibit tangible improvements. A study conducted by Quirke (2017) found that organizations effectively implementing competence mapping experienced a 25% increase in employee retention rates, translating into significant cost savings.
12. Challenges in Implementing Competence Mapping
Implementing competence mapping presents certain challenges:
➢ Resistance to change is a common hurdle when redefining established practices.
➢ Resource allocation can be a challenge, necessitating careful planning and investment
A notable case study is Microsoft’s transformation under Satya Nadella. In just five years, Microsoft’s market capitalization surged from $300 billion to over $1 trillion, underscoring the successful navigation of these challenges through a competence focused approach (Garg, 2023) .
13. Case Study Analysis: Successful Companies
Apple Inc.: Apple’s commitment to competence mapping has resulted in groundbreaking innovations, propelling the company to a market capitalization of over $2 trillion. Netflix: Netflix’s astute competence mapping strategy revolutionized the entertainment industry, with a subscriber base of over 200 million, a testament to the impact of a well-executed talent strategy (Li et al., 2021) .
14. Measuring the Impact
Quantifying the impact of competence mapping is essential for substantiating its value:
➢ Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) offer tangible metrics of success.
➢ Return on Investment (ROI) validates the returns generated by competence mapping.
Procter & Gamble’s competence-driven turnaround provides a compelling example. By investing in competence mapping, the company achieved a 15% increase in profitability within two years, demonstrating the measurable benefits of this strategy.
15. Modern Leadership and Competence Emphasis
In the realm of modern leadership, a profound recognition prevails that competence and skills serve as the lifeblood, propelling organizations toward triumph. Astute leaders prioritize the cultivation and harmonization of competencies within their teams, understanding that this fuels innovation and fortifies adaptability in the face of ever-evolving business landscapes. Such leaders, those with a keen eye on competence, cultivate a culture of perpetual learning, placing a premium on skills that empower their teams to transcend ordinary achievements.
16. Manufacturing Industry: Volvo and Toyota
Within the manufacturing sector, two giants, Volvo and Toyota, serve as living testaments to the paramount importance of competence mapping (Wong, 2018) . Volvo, distinguished by its unwavering commitment to safety engineering, stands as a compelling illustration of how competence in design and engineering can not only enhance product quality but also carve a stellar reputation in the industry. Meanwhile, Toyota’s venerable Lean manufacturing system leans heavily on employee competence in the art of continuous improvement. This relentless focus on competence is the linchpin of their industry leadership, driving efficiency and excellence.
17. The Role of Talent Management Leader
The role of a Talent Management Leader within the realm of Human Resources is nothing short of pivotal. This luminary is charged with crafting, executing, and overseeing competence mapping initiatives that shape the destiny of an organization. They wield the discerning eye to identify critical competencies, architect bespoke training programs, and ensure that these competencies harmonize seamlessly with the organization’s strategic objectives. In today’s dynamic business milieu, where the war for talent rages on, the Talent Management Leader emerges as the architect of attracting, nurturing, and retaining the crème de la crème of talent. Their strategic acumen in talent management is nothing short of indispensable, a linchpin in steering the organization toward enduring success.
18. Conclusion
In conclusion, this research has illuminated the integral role of competence mapping in shaping contemporary business strategies. The multifaceted exploration, spanning interviews with HR Managers and structured surveys across diverse organizations, has provided a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
The findings underscore that competence mapping, when strategically aligned with organizational strategy and diligently implemented across all four quadrants of structure, behavior, thinking, and culture, significantly enhances an organization’s competitiveness, employee performance, and overall efficiency. The empirical evidence and case studies presented reveal that those organizations adept at navigating this strategic equilibrium have thrived in an increasingly dynamic and competitive business landscape.
The research contributes to the evolving discourse on competence mapping, advocating for a holistic approach that extends beyond competence alone. It urges organizations to not only possess the requisite skills but to cultivate a culture of adaptability, strategic thinking, and behaviors that synergistically propel them toward their objectives.
As businesses continue to evolve and adapt to an ever-changing environment, the interplay between competence mapping and business strategy assumes an increasingly pivotal role. Organizations that heed the call to cultivate competence across all aspects of their structure will not only survive but excel in the challenges and opportunities of the future. Thus, the strategic import of competence mapping is resoundingly affirmed, propelling it from an ancillary concept to a central driver of contemporary business strategy.
In this light, it is evident that the journey toward achieving competence in competence mapping is far from over. The research has set the stage for further exploration, encouraging scholars and practitioners to delve deeper into this dynamic and ever-evolving field, ultimately forging a path toward more adept and adaptable organizations in the future.