B-Spline Collocation Method for Solving Singularly Perturbed Boundary Value Problems ()
1. Introduction
Consider following singularly perturbed boundary value problem
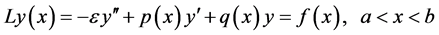 (1)
(1)
with boundary conditions
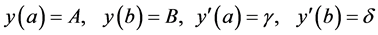 (2)
(2)
B-spline functions are useful wavelet basis functions; the stiffness matrix is sparse when it is used as trial functions. B-splines were introduced by Schoenberg in 1946 [5] . Up to now, B-spline approximation method for numerical solutions has been researched by various researchers [6] - [8] .
2. Description of the B-Spline Collocation Method
The expression of fifth order B-spline function is as follows:
 (3)
(3)
The fifth order B-spline function 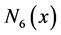 is used to calculate in this work and possesses the following characters: piecewise smooth, compact support, Symmetry, rapidly decaying, differentiability, linear combination.
is used to calculate in this work and possesses the following characters: piecewise smooth, compact support, Symmetry, rapidly decaying, differentiability, linear combination.
The region [a,b] is partitioned into uniformly sized finite elements of length h by the knots 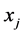 such that
such that 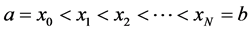 with
with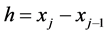 ,
, 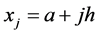 ,
, . Let
. Let 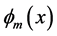 be fifth order B-spline function with knots at the points
be fifth order B-spline function with knots at the points ,
,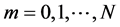 . The set of splines
. The set of splines 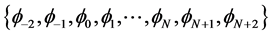 forms a basis for functions defined over [a,b].
forms a basis for functions defined over [a,b].
In the proposed algorithm, The fifth order B-spline function 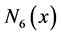 is used as a single mother wavelet, i.e.
is used as a single mother wavelet, i.e. 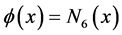 and dilation and translation of mother wavelet functions can construct any function of
and dilation and translation of mother wavelet functions can construct any function of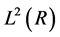 .
.
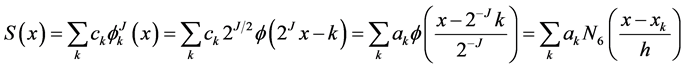 (4)
(4)
where 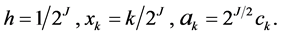
So the global approximation ![]() to the function
to the function ![]() can be written in terms of the B-spline as follows
can be written in terms of the B-spline as follows
![]() , (5)
, (5)
where![]() ,
, ![]() are unknown real coefficients.
are unknown real coefficients.
Using the fifth order B-spline function and the approximate solution Equation (5), the nodal values![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() at the node
at the node ![]() are given in terms of element parameters by
are given in terms of element parameters by
![]() (6)
(6)
![]() (7)
(7)
![]() (8)
(8)
where the symbols ![]() and
and ![]() denote first and second differentiation with respect to x, respectively.
denote first and second differentiation with respect to x, respectively.
Substituting Equations (6)-(8) into Equation (1) and Equation (2), we can obtain following linear equations
![]() (9)
(9)
where
![]()
![]() ,
, ![]()
Note ![]()
![]()
where
![]()
It is easily seen that the matrix B is strictly diagonally dominant and hence nonsingular. Since B is nonsingular, we can solve the system ![]() for
for ![]() . Hence the method of collocation using the fifth order B-spline function
. Hence the method of collocation using the fifth order B-spline function ![]() as a basis function applied to the singularly perturbed boundary value problem has a unique solution
as a basis function applied to the singularly perturbed boundary value problem has a unique solution ![]() given by Equation (5).
given by Equation (5).
3. Numerical Results
In the section, we illustrate the numerical techniques discussed in the previous section by the following problems.
Example 1. Consider the convention-dominated equation:
![]() (10)
(10)
with boundary conditions:![]() ,
,
![]() ,
,
![]() .
.
The exact solution is given by
![]() (11)
(11)
where ![]()
Comparison of the numerical results and point-wise errors is given in Table 1.
It observed that
1) when h decreases (i.e. collocation number increases) for fixed ![]() the point-wise errors decrease;
the point-wise errors decrease;
2) when ![]() decreases for fixed h the point-wise errors increase;
decreases for fixed h the point-wise errors increase;
3) when![]() ,
, ![]() the errors are very large.
the errors are very large.
Example 2. Solve the following non-homogeneous equation:
![]() (12)
(12)
with boundary conditions
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,![]() .
.
The analytical solution is given by
![]() (13)
(13)
where
![]() ,
,![]() .
.
And ![]() and
and ![]() are the real solutions of the characteristic equation
are the real solutions of the characteristic equation![]() .
.
Approximation solutions for different values of ![]() and for fixed p are given in Figure 1. It observed that
and for fixed p are given in Figure 1. It observed that
![]()
Table 1. Example 1. Comparison of results and point-wise errors.
![]()
Figure 1. Approximation solutions of example 2 for different values of epsilon g and for fixed p.
1) when ![]() and
and![]() , the approximation solutions are in good agreement with exact solution; 2) when
, the approximation solutions are in good agreement with exact solution; 2) when ![]() and
and![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() the errors are very large; 3) when
the errors are very large; 3) when ![]() decreases for fixed p the width of boundary layer becomes small and wave shape change more and more stiff at
decreases for fixed p the width of boundary layer becomes small and wave shape change more and more stiff at ![]() and
and![]() .
.
4. Conclusion
The numerical results show clearly the effect of ![]() on the boundary layer and the B-spline collocation method solving singular boundary value problems is relatively simple to collocate the solution at the mesh points. It is applicable technique and approximates the exact solution very well.
on the boundary layer and the B-spline collocation method solving singular boundary value problems is relatively simple to collocate the solution at the mesh points. It is applicable technique and approximates the exact solution very well.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the editor and the reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions to improve the results of this paper. This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong (No. 2015A030313827).