New Developments in the Mechanism of Drug Action and Toxicity of Conjugated Imines and Iminiums, including Related Alkaloids ()
1. Introduction
Electron transfer (ET) functionalities that received the most attention in earlier years are quinone (and phenolic precursors) and aromatic nitro compounds (and hydroxylamine and nitroso metabolites). In more recent years, primary-aromatic amins (and hydroxylamine and nitroso metabolites) have been added [1] . Other types receiving increased attention are conjugated imine and iminium species. This category is the focus of the present review in relation to drug types and alkaloids, which represent an extension of the prior report [2] . Scheme 1 depicts redox cycling by the ET functional group with formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). The initial superoxide is a precursor of hydrogen peroxide and the hydroxyl radical, as illustrated in Scheme 2.
Iminiums are usually better electron acceptors than imines, due partly to positive charge (Scheme 3). In vivo redox cycling with oxygen can occur, giving rise to oxidative stress (OS) through generation of ROS, such as hydrogen peroxide, hydroperoxides, alkyl peroxides, and diverse radicals (hydroxyl, alkoxyl, hydroperoxyl, and superoxide). In some cases, ET results in involvement with normal electrical effects (e.g., in respiration or neurochemistry). Generally, active entities possessing ET groups display reduction potentials in the physiological responsive range, (i.e., more positive than about −0.5 V). Hence, ET in vivo can occur resulting in production of ROS which can be beneficial in cell signaling at low concentrations, but produce toxic results at high levels. Electron donors consist of phenols, N-heterocycles or disulfides in proteins which produce relatively stable radical cations. ET, ROS, and OS have been increasingly implicated in the mode of action of drugs and toxins, (e.g., antiinfective agents [3] , anticancer drugs [4] , carcinogens [5] , reproductive toxins [6] , nephrotoxins [7] , hepatotoxins [8] , cardiovascular toxins [9] , nerve toxins [10] , mitochondrial toxins [11] , abused drugs [12] , pulmonary toxins [13] , ototoxins [14] , and various other categories [15] .
There is a plethora of experimental evidence supporting the ET-ROS theoretical framework. This evidence includes generation of the common ROS, lipid peroxidation, degeneration products of oxidation, depletion of AOs, effect of exogenous AOs, and DNA oxidation and cleavage products, as well as electrochemical data. This comprehensive, unifying mechanism is consistent with the frequent observations that many ET substances display a variety of activities, e.g., multiple-drug properties, as well as toxic effects. Possible additional modes of action are not discussed since the focus is on ET-ROS-OS.
It is important to recognize that mode of action in the biodomain is often multifaceted. In addition to the ET-ROS-OS approach, other aspects may pertain, such as, enzyme inhibition, allosteric effects, receptor binding, metabolism and physical factors.
The conjugated imines and iminiums in the first section were selected from the Merck Index [16] . It is instructive that an appreciable number of agents in this category can be found as bioactive agents. An important aspect to recognize is that, in many cases, these ET species are generated metabolically. Imines are formed from oxidation of primary and secondary amines, as well as by condensation of carbonyls with primary amines. Iminiums arise from oxidation of tertiary amines and protonation or alkylation of iminies. This category encompasses various imine-iminium types, including iminoquinones and analogs, pyridinium ions, quinolinium ions and higher polynuclear analogs, imines with aromatic conjugation, and others. The aromatic N-heterocycles are iminium-like. There are similar types of conjugated imine-iminiums in the alkaloid class. In both cases, physiological effects are documented.

Scheme 1. ET with formation of ROS.

Scheme 2. ROS formation from superoxide.

Scheme 3. ET by conjugated iminium.
A purpose of this review is to provide a different perspective in analyzing the biological activity of alkaloids that possess certain structural features which may enhance their ability to act as ET agents. Natural products, with their unique structural features and pronounced biological activities, continue to provide lead structures in the search for new drugs from nature. Invertebrates, such as, sponges, tunicates, and mollusks, have so far provided the largest number of marine –derived secondary products, including some of the most interesting drug candidates. These substances provide a broad and structurally diverse array of pharmacologically active compounds that have proved to be indispensible for the cure of many diseases or as lead structures for novel pharmaceuticals.
There is paucity of information for these compounds in relation to ET-ROS-OS, plus data on reduction potentials and electron affinity. Our aim is for this review to stimulate future research on these missing aspects.
2. Bioactivity of Conjugated Imines and Iminiums
These compounds, mostly drugs, are taken from the Merck Index [16] with listing in alphabetical order along with physiological activity. In some cases, the imine moiety could be converted to the electrophilic iminium by intramolecular protonation by carboxyl substituents. Some of the compounds incorporate other potential ET groups. Figures are often abbreviated in order to focus on the conjugated imine or iminium portion. There is a common mechanistic theme applicable to the compounds which can be found in the Introduction.

Adrenochrome (1), psychotomimetic agent; Alstonine (2), antipsychotic [17] ; Amiloride (3), diuretic.

Aminopterin (4), rodenticide; Chlelerythrine (5), anthelmintic [18] .

Cinnabarine (6), antiviral, toxicity and antitumor [19] ; Dactinomycin (7), antineoplastic.
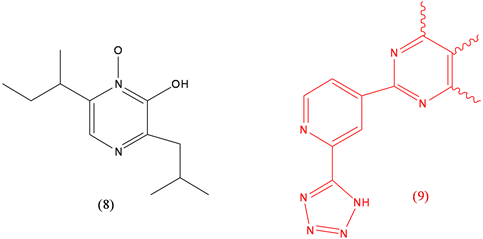
Aspergillic acid (8), proposed as hypotensive, toxin; Clazosentan (9), treatment of cerebral vasospasm.

Clofentezine (10), toxic, bioactive; Coptisine (11), antifungal [20] , and antidepressant (monoamine oxidase A inhibitor) [21] .

Denopterin (12), antineoplastic; Difenzoquat (13), herbicide, fungicide; Dihydralazine (14), antihypertensive.

Diniconazole (15), fungicide; 5-Diazouracil (16), antibacterial, mutagen, DNA cleavage [22] ; Diflufenzopyr (17), herbicide.

Edatrexate (18), antineoplastic; Endralazine (19), antihypertensive; Fast Green FCF (20), clastogenic [23] .

Diquat (21), herbicide; Drometrizole (22), UV screen; Echinomycin (23), antibacterial [24] .

Endralazine (24), antihypertensive; Fazadinium Bromide (25), pharmacology and toxicity; Fenpyroxrimate (26), acaricide.

Fipronil (27), parasiticide; Flavopereirine (28), anticancer [25] .

Fluoxastrobin (29), fungicide; Furonazide (30), antibacterial.

Imazamox (31), herbicide; Isradipine (32), antihypertensive; Loxzpine (33), anxiolytic.

Methyl Blue (34), antiseptic; Mitoguazone (35), antineoplastic; Mofezolac (36), analgesic; Oxantel (37), anthelmintic.
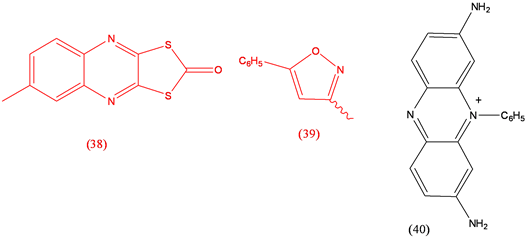
Oxythioquinox (38), fungicide; Perisoxal (39), analgesic; Phenosafranine (40), electron transfer agent [26] .

Pyronaridine (41), antimalarial; Ridogrel (42), antithrombotic.

Sanguinarine (43), antimicrobial; Sulfaquinoxaline (44), coccidiostat.
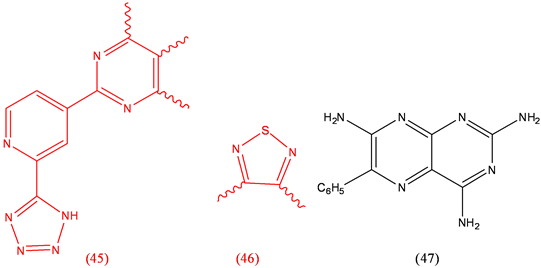
Tezosentan (45), heart disease; Timolol (46), antihypertensive, antiarrhythmic; Triamterene (47), diuretic.
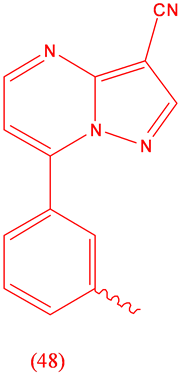
Zalepion (48), sedative, hypnotic.
3. Imine and Iminium Alkaloids
Most of the ET agents described above are laboratory synthesized molecules and in addition to these a number of naturally occurring alkaloids also fall into the imine and iminium category. Most are isolated from fungi, micro and marine organisms with varied bioactivity.
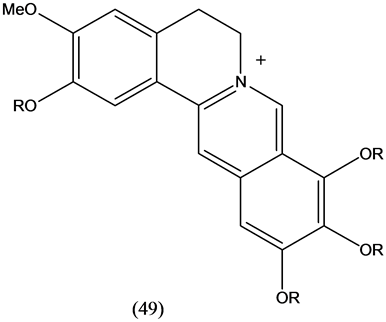
Iminium alkaloids (49) with berberine skeletal framework were isolated from Annona glabra. All of them showed acetylchoilnesterase inhibitory properties [27] . A review from 2000 to 2010 [28] deals with anti-inflammatory activity of berberine and other alkaoids.
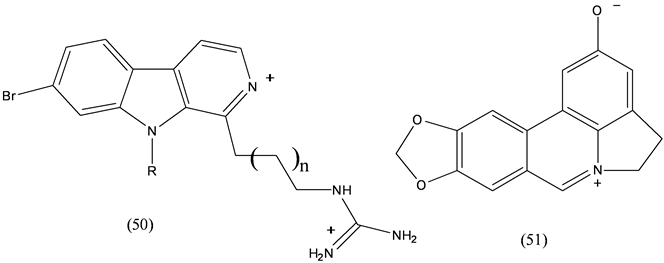
Carboline alkaloids (50) [29] containing an iminium functionality isolated from New Zealand ascidian Pseudodistoma opacum showed antimalarial activity toward a chloroquine-resistant strain of Plasmodium falciparum. Ungermine (51) an Amaryllidaceae alkaloid showed activity against apoptosis-resistant cancer cells [30] .

Clathridimine (51), isolated from calcareous sponge Clathrina clathrus exhibits broad antimicrobial activity [31] .

Synthetic pyrroloquinolines (52) showed a wide range of biological activity, such as DNA intercalation and antileukemic properties [32] . Pyrroloquinolines (53) isolated from gliding bacterium Ohtaekwangia kribbensis showed antibacterial, antifungal and moderate cytotoxicity against growing mammalian cell lines [33] . Ammosamide alkaloids (54), isolated from the marine Strepmyces strain CNR-698, were found to inhibit quinone reductase 2 [34] .

Pyrrolocarbazoles (55) and synthetic analogues were found to inhibit topoisomerase I and diverse kinases [35] . Nitrosubstituted maleilides, such as aqabamycin (56) isolated from coral-associated Vibrio sp., showed varying antibacterial activity [36] .

The red pigment and antibiotic prodigison (57) and its cyclized analogue (58) isolated from marine Vibrinaceae have a broad range of biological activities, including antimicrobial, antimalarial, immunosuppressive, and anticancer. Prodiginines have clinical potential in anticancer therapy and prodigison (57) is currently in preclinical trials (Aida Pharmaceutical) for pancreatic cancer [36] . Violacein (59), a violet pigment isolated from bacteria of the genus Chromobacterium, has a variety of biological activities, including antiviral, antibacterial, antiulcerogenic, antileishmanial, and anticancer [37] .
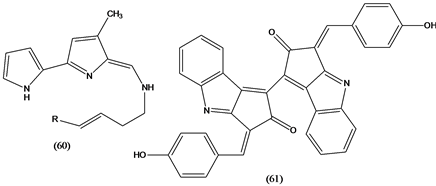
Tambjamines (60) are alkaloids isolated from various marine organisms, such as bryozoans, nudibranches and ascidians, displayed cytotoxic activity against several tumor cells and have a range of antifouling activities [37] . Scytonemin (61), a yellow pigment isolated from aquatic cyanobacteria, forms when the bacteria are exposed to sunlight. The pigment has anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative activities by inhibiting protein kinase Cβ (PKCβ), a well known mediator of the inflammatory process. In addition, the molecule inhibits phorbol-induced mouse ear edema and the proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells [37] .

More than 6000 phenazine derivatives (62, 63) have been identified and described during the last two centuries. Many show antibiotic activities against bacteria, fungi or plant/animal tissues [37] . Phenazines (63) inhibit TNF-α-induced NF kB activity and LPS-induced nitric oxide production in mammalian cell culture studies [38] . A review deals with bioactive pigments from marine bacteria and their applications and physiological roles [37] .

Tyrindoleninone (64), isolated from Dicathais orbita, selectively induce apoptosis in female reproductive cancer cells [39] .

Veranamine (65), with structural similarities to indoles and cannabinoids was isolated from Verongida rigida, and showed promising antidepressant activity in the forced swim test [40] . Lophocladines B (66), isolated from red alga, possessed moderate cytotoxic activity breast cancer cell lines [41] .

Various reports deal with bioactivity of iminoquinones. About 100 phenazine derivatives have been isolated from microorganisms belonging to a wide range of genera. Phenazines (67,68) display a broad range of activities and act as antioxidant, neuroprotectant, broad spectrum antimicrobial, antiparasitic, antiviral, antitumor, and antimalarial agents, affecting a wide range of target organisms [42] .

New pyridoacridine alkaloids (69,70) were isolated from the sponge Xestosponia carbonaria along with the known amphimedine (71) and neoamphimedine (72). Amphimedine (71) was the only compound that caused a phenotype in zebrafish embryos [43] . Another study showed that amphimedine (72) acts as anticancer agent by inhibiting. TopoII α-dependent DNA decantation in the presence of metnase [44] .

Lakshminine (73), belonging to a family of oxoisoaporphine alkaloids, including (74) showed marginal antiproliferative activity against human normal fibroblasts and human solid tumor cell lines [45] .

Ascididemin (75), a marine-derived pyridoacridine alkaloid, is known to exert cytotoxicity via inhibition of DNA topoisomerase II, leading to cleavage of DNA and cell death. These cytotoxic effects clearly limit the potential antibiotic utility of the natural product. Two synthetic analogues (76) were found to inhibit growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, with negligible cytotoxicity [46] .

Several new pyridoacridine alkaloids (77, 78) isolated from different Ascidian species showed antimicrobial properties [47] . A review deals with alkaloids from marine Ascidians, highlighting their potential as therapeutic agents for the treatment of cancer or viral infections [48] .

Synthetic pyrroloiminoquinone (79) BA-TPQ, based on natural alkaloid makaluvamine scaffold, showed promise as an anti-breast cancer agent [49] [50] .

Marine invertebrate-derived polycyclic heteroaromatic alkaloids with 16-18 π electron containing cores are relevant for therapeutic development, as they interfere with many biological disease targets [51] . Pyrroloacridine alkaloid (80), isolated from Plakortis quasiamphiaster, exhibited cytotoxicity against human colon H-116 cells, but showed no effects against yeast diploid homozygous delection strain of topoisomerase. By contrast, alkaloid (81) was inactive against H-116 cells, but was potent in the yeast halo screen [51] .

Two phenoxazinone alkaloids, chandrananimycin and pitucamycin (82), isolated from Streptomyces grieus, exhibited antimicrobial, antproliferative and cytotoxic activities against a number of tumor cell lines [52] .
Acknowledgements
Editorial assistance by Thelma Chavez is acknowledged.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.