1. Introduction
The Kenyan population only consumes 5% of the tea produced in the country which is mostly aerated (black) Cut Tear and Curl (CTC) tea [1] [2] . According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations (UN), the world market for aerated (black) tea is anticipated to shrink in future whereas that for un-ae- rated (green, purple etc.) tea and other forms of specialty teas is expected to grow [3] - [5] . Kenya has therefore embarked on opportunities to diversify its tea products in order to access this market [6] . To address these issues, the Tea Research Institute (TRI) has taken the challenge to develop technologies for production of these tea products [3] [7] . Product diversification is expected to lead to increased production and utilization of the tea crop through value addition [3] [6] [8] - [10] a practice that has commenced in several areas. Un-aerated purple tea is a relatively new product in the Kenyan market and the world market at large and for this reason it has lower market share compared to black and green tea [2] . In terms of taste un-aerated purple tea is as mild as black tea owing to the anthocyanin content in them [7] [8] . Spices have been used by people from various walks of life to modify flavour of foods and beverages making them more appealing to consumers. Different spices are suitable for different foods while others have a broad range of application. In the Kenyan market, spices are sold for use with a broad range of foods while others are specifically sold for specific foods like tea (tea masala, ginger) and rice (pilau masala). Apart from the flavours and aroma, spices have health benefits which can be championed to sell the tea product [11] - [13] . This study focused on determining the effect of addition of spices to consumer acceptability, anti-oxidant properties and pricing on the developed spiced un-aerated purple tea product from TRFK 306 [14] [15] . The work was carried out in three phases which included developing flavoured teas by blending the processed un-aerated purple tea with selected spices including ginger, lemon grass, nutmeg, cinnamon, tea masala, and rosemary. Different ratios of tea and spices were blended and the resulting products assessed using a sensory panel. Antioxidant capacities of the products and the impact of spice addition to the resulting tea spice mixes were also determined. The results of the assays were statistically analyzed and the interpretation given [14] - [16] .
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
Purple tea (TRFK 306) and TRFK 6/8 was used. TRFK 6/8 is usually used as a standard for quality black or green tea in Kenya [17] , while TRFK 306 is a new tea variety characterized with purple leafs and is rich in anthocyanin [18] [19] . Un-aerated purple tea was processed at TRI, Kericho, Kenya using the method by [20] , Spices including ginger, lemon grass, nutmeg, cinnamon, tea masala, and rosemary were obtained from local retail stores.
2.2. Spiced Tea Development
Selected spices were obtained dried and ground. Blending was done on a weight to weight ratio (w/w) of spice to processed teas and manually mixed by hand in stainless steel holding vessels for about fifteen minutes and left overnight for complete flavouring. Initially the six spices were blended with the processed un-aerated purple tea at high percentages of 25, 50 and 75 and later lowered to 5, 10, 15 and 25 to determine sensory economic threshold levels.
2.3. Extraction and Quantification of Anthocyanins
Extraction and analysis of anthocyanins was done according to the method by [21] . Anthocyanins were only quantified in purple tea (TRFK 306). The standards used were Cyanidin-3-O-galactoside, Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside, Cyanidin chloride, Delphinidin chloride, Petunidin chloride, Pelargonidin chloride and Malvidin chloride purchased fron Sigma Aldrich, UK. Quantification of anthocyanins was performed at 520 nm. The total anthocyanin content was expressed as a concentration by mass on a sample dry matter (Table 1).
2.4. Catechin Analysis
The purple un-aerated teas (TRFK 306) and the green tea from TRFK 306 were assayed for quality through catechin, caffeine and gallic acid profiling [22] ISO14502-2E: 2005) and the profiles compared for quality (Table 1). Extraction of catechins was done according to the procedure by [22] . The standards used were +C, (−)-EGC, (−)-EC, (−)-EGCG and (−)-ECG. Total Catechins were expressed as a percentage by mass on a sample dry matter basis and was given as a summation of individual catechins as; Percentage (%) Total Catechin 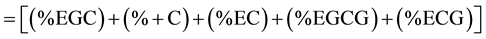 (Table 1).
(Table 1).
![]()
Table 1. Pyto chemical components of un-aerated tea from TRFK 306 and TRFK 6/8.
Values are means ± SD of 3 replicates. Means in the same column with the same letter are not significantly different (P ≤ 0.05). GA = Gallic acid, EGC = Epigallocatechin, C = Catechin, CAF = Caffine, EC = Epicatechin, EGCG = Epigallocatechingallete, ECG = Epicatechingallete, TCA = Total catechin, ANT = Anthocyanins.
2.5. Antioxidant Activity
The antioxidant properties of the all the spices and spiced un-aerated purple tea from TRFK 306 were determined using the method described by (Ochanda et al., 2011). The stable 2, 2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical (DPPH) was used for determination of free radical scavenging of tea and spice. A spectrophotometer (UV-Vis Shimadzu 1800) was used to determine the absorbance at 517 nm. The percentage inhibition of the DPPH radical was calculated [23] (Table 2).
2.6. Sensory Evaluation
Sensory evaluation was done on the 6 developed un-aerated spiced purple tea products from TRFK 306. Two (2) grams of the teas were infused with hot water (2 g of tea/250 ml of water) and sweetened with sugar (2 g of sugar/250 ml of infused tea) before serving to a sensory evaluation panel for assay. Panelists of mixed gender of between 18 - 65 years of age participated in the exercise [14] - [16] [24] . Randomized warm (25˚C - 30˚C) samples, of 20 to 25 mL, were served in clear 170 mL glasses marked with random digit numbers and covered with aluminum foils. Potable clean water was provided for rinsing of the palate during the exercise. Evaluation was conducted at room temperatures of 20˚C - 22˚C under natural light. The samples were evaluated using a 9 point Hedonic scale (IDF, 1987). This scale consisted of the test parameters of taste, smell, texture, general acceptability, and colour accompanied by a scale of nine categories as: 1 = dislike extremely; 2 = dislike much; 3 = dislike moderately; 4 = dislike slightly, 5 = neither dislike nor like, 6 = like slightly; 7 = like moderately; 8 = like much; 9 = like extremely [14] . Prior to evaluation, a session was held to familiarize panelists with the evaluation process. Panelists were asked to read through the questionnaires and the meaning of each attribute (taste, smell, flavour, colour, acceptability) explained [15] [24] . No discussions were allowed during the exercise. The sensory evaluation data was presented as means of five groups of panelist’s scores using SAS 9.1 Statistical package [25] . Significant differences were accepted at P ≤ 0.05 [5] [26] [27] .
2.7. Economic Evaluation
The best rated spiced tea was used to determine economic threshold values for the consumer market. Prices of un-aerated purple tea products and cinnamon spice were averaged and used for the economic evaluation and analysis. Statistical evaluation was used to determine significant differences in prices (P ≤ 0.05) [5] [27] .
3. Results and Discussion
The assay of purple tea in comparison to that of the standard quality TRFK 6/8 revealed that the purple TRFK 306 had less total catechins (9.11%) compared to the green tea from TRFK 6/8 (14.68). However, TRFK 306 had higher levels of anthocyanis (945.30 µg/ml) which were significantly greater (P ≤ 0.5) than that of green tea from TRFK 6/8 (50.0030 µg/ml) Table 1. The purple have high quantities of anthocyanis as well as catechins. This phytochemicals profiling is essential for determination of tea quality.
The antioxidant activities assayed for the spices and teas revealed that tea had the highest contents of antioxi-
![]()
Table 2. Percentage antioxidant activity of selected spices and Purple tea (TRFK 306).
Values are Mean ± SD of 3 replicates. Means in the same row with the same letters are not significantly different.
dants of 92.73% followed by cinnamon at 89.89%, Rosemary at 89.47%, ginger at 69.23% tea masala at 55.70% and nutmeg at 46.99% (Table 2). Spices significantly (P ≤ 0.05) lowered antioxidant activities of the un-aerated tea from TRFK 306 (Table 2). Increasing quantities of the spices decreased the antioxidant activity of the resulting spiced tea even further [22] [23] [28] . This does not mean that spices do not have other intrinsic benefits of their own as shown by an examination of work by other scientists [12] [13] [29] - [31] . Indeed some of the assayed spices have been associated with such health benefits as antimicrobial, anti-cancer and anti-inflammation effects among others [8] [32] - [36] .
The addition of spice in tea at the rage of 0% - 75% had varying results for overall mean rating depending on the spice used (Table 3(a)). Ginger had a mean value of 5.56, 5.75, 5.93, and 6.99 for blending at 0%, 25%, 50%
and 75% respectively indicating an increase with each addition of spice in the tea. Lemongrass mean values were 6.29, 6.67, 5.60 and 5.76 for blending done at 0%, 25%, 50% and 75% respectively indicating a decline in
liking at 50% and above blending. Cinnamon had mean ratings of 6.42, 6.42, 6.76 and 6.74 for blending at 0%, 25%, 50% and 75% respectively showing a decrease in liking at addition above 75%. Nutmeg mean ratings were 6.53, 6.63, 5.92 and 5.17 for blending at 0%, 25%, 50% and 75% respectively indicating a decrease at above
![]() (a). Values are Means ± SD of 21replicates for ginger 27 for lemongrass 34 for cinnamon, 23 for nutmeg, 24 for rosemary and 34 for tea masala. Means in the same row with the same letter(s) are not significantly different (P > 0.05).
(a). Values are Means ± SD of 21replicates for ginger 27 for lemongrass 34 for cinnamon, 23 for nutmeg, 24 for rosemary and 34 for tea masala. Means in the same row with the same letter(s) are not significantly different (P > 0.05). ![]() (b).Values are Mean ± SD of 3 replicates. N of panelist for spices = 23, 11 and 17 for cinnamon, nutmeg and lemongrass respectively. Means in the same row with the same letter(s) are not significantly (P > 0.05) different
(b).Values are Mean ± SD of 3 replicates. N of panelist for spices = 23, 11 and 17 for cinnamon, nutmeg and lemongrass respectively. Means in the same row with the same letter(s) are not significantly (P > 0.05) different
Table 3. (a) Effect of spices on sensory attributes of spiced un-aerated purple tea (TRFK 306); (b) Sensory evaluation of unaerated purple tea (TRFK 306) with cinnamon, lemongrass and nutmeg at less than 25% spice to tea ratio.
50% spice addition. Rosemary had ratings of 5.68, 6.20, 6.27 and 6.21 at blending rates of 0%, 25%, 50% and 75% respectively indicating a decrease in liking at spice addition at above 75%. Tea masala mixed spice had ratings of 5.53, 5.55, 5.56 and 5.05 at blending ratios of 0%, 25%, 50% and 75% respectively showing a decrease in liking at addition of over 75% spice ratio.
Optimization of spice to get critical and economic thresholds for tea blending was then done by spicing of teas at spice ranges below 25%. The results are shown in Table 3(b). The results for the first three best rated spices have been shown including cinnamon, lemongrass and nutmeg. Cinnamon ratings were 4.90, 6.54, 6.88, 5.59 and 6.46 respectively for ratios of 0%, 5%, 10%, 15% and 25% respectively indicating an optimum threshold at 10% blending ratio. Lemongrass on the other had had ratings of 5.48, 5.76, 6.08, 5.95, and 6.24 respectively at 0%, 5%, 15%, 20% and 25% ratios also giving an optimum at 25% addition but this was not significantly different from the rating at 10% spice addition. Nutmeg ratings were 5.06, 6.55, 6.92, 5.95 and 6.29 respectively for 0%, 5%, 15%, 20% and 25% ratios giving an optimum at 15% blending ratio.
Costing
Unit Cost was calculated by dividing the product cost and quantity. Costs of commodities are in Kenya Shillings (Ksh) and that of quantity in grams (g). Values of unit cost of Table 4(a) were used to generate the cost of different tea spice quantities. Table 4(b) shows possible costs of the nutmeg purple tea product at different percentage mixes.
Table 4(b) shows that there was a significant (P ≤ 0.05) increase in the cost of production with an increase in the quantity of spice added. So sensory evaluation data and economic analysis of the spice and tea mixes have to be used in the development of products which are acceptable to the consumer and profitable to the producer [20] [24] [37] .
4. Conclusion
The results reported in this article have shown that preference for un-aerated purple tea palatability is enhanced by spice or flavour addition to the tea. Further, the data have shown that some spices are preferred at higher quantities than others for optimum tastes of the un-aerated purple tea blends. Commercial production of spiced un-aerated purple tea will therefore have to get suitable threshold levels for product development in order to minimize the quantities of spices required for developing the blends, because the addition of spice in tea leads to increase in production costs. The research has also shown that some spices may not be compatible with un-aerated purple tea at high concentrations but at lower concentration the acceptability is increased.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge financial support from the National Commission for Science, Technology and Innova-
![]() (a).Product cost (Ksh) = Kenya shillings. Quantity of the product (g) = grams. Unit cost (Ksh/g) = cost of one gram of the tea or spice (Kenya shillings per gram of product).
(a).Product cost (Ksh) = Kenya shillings. Quantity of the product (g) = grams. Unit cost (Ksh/g) = cost of one gram of the tea or spice (Kenya shillings per gram of product). ![]() (b).Values are Mean ± SD of 3 replicates for spices and 3 replicates of tea Means in the same column with the same letter(s) are not significantly (P > 0.05) different. Pdt = 1 unit of product comprising of spice and tea mixed at a specified ratio. Tea and product prices are in Kenya shillings per 100 g. TCA = Total catechin, ANT = Anthocyanins.
(b).Values are Mean ± SD of 3 replicates for spices and 3 replicates of tea Means in the same column with the same letter(s) are not significantly (P > 0.05) different. Pdt = 1 unit of product comprising of spice and tea mixed at a specified ratio. Tea and product prices are in Kenya shillings per 100 g. TCA = Total catechin, ANT = Anthocyanins.
Table 4. (a) Un-aerated purple tea and nutmeg spice product calculated with unit prices; (b) Summary of the price of un-aerated purple tea at different nutmeg spice ratios.
tion (NACOSTI), Kenya and the Tea Research Institute. The technical support of staff from Tea Processing and Value Addition Programme of the TRI is also acknowledged.