Development of a Hybrid Best Management Practice System for Control of Agricultural Nonpoint Water Pollution ()
1. Introduction
The measurement, control, and regulation of nonpoint source (NPS) pollution is known to be difficult, because this originates from across wide geographical areas and is discharged into receiving water bodies through various mechanisms [1] . According to a report by the Korea Ministry of Environment (2006), the contribution of NPS pollution to total loading in four major rivers in the country ranged from 42% - 69%, depending on river basin characteristics and on highly variable meteorological conditions [2] . Agricultural activities that lead to NPS pollution include poorly sited or managed animal feeding operations, overgrazing, excessive or badly- timed plowing, as well as improper, excessive, or poorly-timed application of pesticides, irrigation water, and fertilizers [3] . During rainy seasons, drainage waterways (e.g., ditches) play a leading role as transitional zones- contributing nonpoint source loadings (such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and sediment), subsequently causing eu- trophication in receiving water bodies [4] . A study by Lee et al. (2012) reported that in South Korea approxim- ately 20% - 30% of total nutrients measured during field harrowing were drained into a ditch through excessive irrigation [5] .
To prevent soil erosion and sedimentation, both of which contribute to turbid conditions and to poor water quality, check dams of loosely placed erosion stone, riprap, or stone-filled gabions, are commonly constructed. However, suspended clay particles and particulates in runoff water do not settle out easily due to their very small size; this means that these cannot be effectively filtered or removed through such conventional rock check dams. Recent studies by McLaughlin et al. (2009) and Kang et al. (2013) found that alternative check dams made of fiber materials outperformed rock in reducing ditch erosion; the addition of polyacrylamide (PAM) was also found to reduce turbidity significantly. Such alternative check dams have already been installed and evaluated, with particular targeting of construction sites; this is because construction contributes significantly to sediment loading, with erosion rates from construction sites up to 100 times those from cropland [6] [7] . In the case of rural land, the physiochemical impacts of soil erosion and sedimentation on aquatic resources can be magnified when runoff is laden with agricultural contaminants, such as sediment, inorganic fertilizers, herbicides, insecti- cides, organic matter, and irrigation residues [8] . This study therefore constructed a hybrid Best Management Practice (BMP) system for reducing agricultural NPS pollutants discharged through agricultural ditches and furrows, intended to supplement existing BMPs. This differs from previous approaches by McLaughlin et al. (2009) and Kang et al. (2013), in that it features extensive use of agricultural byproducts [6] [7] .
As noted above, one of the drawbacks of conventional check dams is their inability to capture suspended solids from agricultural discharges. For this reason, PAM, a water-soluble synthetic polymer that acts as a highly effective binding agent with fine silts and clays, is used in this study in conjunction with biodegradable check dams (BCDs). The use of this synthetic polymer leads suspended particles to easily bond together to form flocs, which can then settle out of the water, significantly reducing turbidity. The versatility of PAM is one of its strong features; for example, it can be used to control surface sealing and crusting, to increase seedling emergen- ce, to reduce runoff and erosion, and to reduce fertilizer and pesticide losses. Additionally, PAM can be used on soils within different land-use types, including in furrow irrigated and rain-fed agriculture, within construction sites and road-cuts, and on mine spoils and other disturbed soil areas [9] .
The objectives of this study include the following: 1) to optimize the design of a hybrid BMP system, using BCDs and PAM, 2) to evaluate the feasibility of using agricultural byproducts as alternative dam materials to reduce runoff velocity and increase retention time and discharge capacity, 3) to evaluate the performance of synthetic polymers in enhancing flocculation and deposition of suspended particles in runoff, 4) to assess the effectiveness of the hybrid BMP system inmitigating pollution under artificial experimental conditions, and 5) to evaluate its performance through an actual case study.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Biodegradable Check Dam Materials and Synthetic Polymer
This study focused on selecting effective, inexpensive, easily accessible, and environment-friendly materials for construction of BCDs. A tube-shaped BCD design was developed; the dams were filled with various materials including rice straw, sawdust, rice husks, coconut fiber, and a mixture of the latter two (Figure 1). Coconut is not cultivated in South Korea; however, it was included to enable a comparison of its performance with that of other types of agricultural byproducts. All materials were cut into small pieces and wrapped in a completely biodegradable net (e.g., burlap net). The performance of the dams was evaluated based on the rate of turbidity reduction, using an artificial open channel experiment. The diameter of the BCDs was 3 - 3.5 cm, with length of 21 - 23 cm, sufficient to fit an open channel cross-section and to maintain centerline flow.
![]() Coconut fiber Rice straw Rice husks Coconut fiber and rice husks
Coconut fiber Rice straw Rice husks Coconut fiber and rice husks
Figure 1. Four types of BCD materials derived from various agricultural byproducts.
PAM is available as a powder, emulsion, or solid block [10] . It is nontoxic to humans and to other species. Barvenik (1994) and Deskin (1996) provide a summary of safety considerations for use of PAMs in environmentally sensitive applications, also taking into account human safety during material handling [11] [12] . They conclude that the broad class of PAM chemicals exhibits a generally low order of toxicity to mammals. Primary applications of PAM are varied, depending on PAM types; the applications of powder and emulsion include hydroseeding, water truck applications, and hand spreading, while in its solid block form, PAM is used for mine tailings, waste pile ditches, and dredging operations. For the sake of convenience, PAM emulsion has been commercialized, since it is somewhat difficult to dissolve PAM powder unless a solution is lukewarm [10] .
2.2. Experimental Setup and Procedure
A total of 19 PAM products were tested in this study: Magnafloc 336 (Ciba Specialty Chemicals, Korea, now BASF Global), E-Z-PAM, Silt Stop APS#605, 630, 640, 702, 705, 707, 712, 730, 740, 745, Floc Log APS#702b, 703d, 703d#3, 706b, 707a, 708x and 730b (Applied Polymer Systems, USA).
A series of experiments was conducted using jar tests, cylinder tests, and artificial open channel methods, in order to evaluate response time, flocculation rate, and temporal duration of turbidity readings after PAM application. Results were used to select the type of PAM with best performance and to optimize the design of the hybrid BMP system. A brief explanation of each experiment follows below.
For the jar test, turbid water samples were prepared by dissolving kaolin powder (2 g) in distilled water (1 L) (Figure 2). The initial reading of the kaolin solution was 4500 NTU. Each beaker filled with kaolin solution was stirred at 300 rpm. A pre-defined concentration of PAMs was quickly added to each beaker, with these continuing to be rapidly mixed for 1 min. The speed of the stirrer was reduced to 40 rpm and supernatant samples were collected at 30 sec, 90 sec, and 150 sec, to analyze the reduction in turbidity over time.
For the flocculation test, stopped-Plexiglas cylinders were each filled with 1 L of PAM solution mixed with kaolin clay powder (Figure 2). Cylinders were closed and inverted ten times; subsequently, these were set upright and the height of the solid phase was measured at regular time intervals (0.5, 1, 3, 6, 10, 15, and 20 min). The settling rate was calculated by plotting the curve of height against time (the rate of fall of the mud line in suspension within a measuring cylinder). Samples for turbidity measurement were withdrawn after 20 min from the previously inverted cylinder using an automatic pipette from a height halfway below the surface of suspension. The turbidity of samples was measured using a 2100 AN turbidimeter (HACH Co., USA), calibrated using standard solutions. The samples that were withdrawn directly after inverting represent initial turbidity, while samples obtained after 20 min represent residual turbidity. The percentage turbidity decrease was calculated using initial and final turbidity readings.
A rectangular open channel, 10 m long and 0.2 m wide, was constructed; the gradient of the channel could be varied between 2˚ - 10˚ (Figure 3). The channel bed was covered with concrete and the walls of the channel were composed of plexiglass (acrylic). In order to simulate real flow roughness conditions, sand was glued to the bed of the channel. A settling tank was also developed and fitted, to boost effective purification of turbid water (Figure 3). The sediment trap, with dimensions of 132 cm length, 63 cm width, and 43 cm height, consisted of three parts and was placed at the end of the water channel. The various parts of the trap were separated
![]()
![]()
Figure 2. Flocculationtests using jar tester (left) and cylinder (right) [15] .
![]()
Figure 3. Schematic of artificial open channel equipped with a hybrid BCD (a) experimental channel; (b) BCD sprinkled with PAM, and c: flow over BCD) (modified from [15] ).
using partition walls of changeable height. Predefined amounts of granulated, liquefied, and log-type PAMs were sprayed onto the center section and positioned at the rear of each BCD. As turbid inflow passed over each BCD, PAM was slowly released. Sedimentation, followed by coagulation/flocculation, can be expected to occur within the settling tank, removing most of the suspended particles in runoff before the water discharges into streams and/or rivers. Experimental conditions (e.g., channel slope and flow, turbidity level, PAM dosage, number of BCDs installed, and BCD material and shape) were varied to assess their influence on turbidity reduction performance.
A number of BCDs were put in place within the channel, prior to initiating inflow of turbid water. The latter, a mixture of water and clay of average particle size of 130 μm with predefined concentrations (12.7 mg/L, 25.3 mg/L, 50.7 mg/L; total sediment loadings of 75 g, 150 g, and 300 g, respectively) was pumped from an injection tank (110 cm × 110 cm × 77.5 cm, 625 L capacity) to the channel, at controlled discharge rates of 0.0021 m3/s (125 L/min) and 0.0042 m3/s (250 L/min). Except in two experimental cases involving a change of channel slope and inflow rate, experiments were conducted with a channel slope of 2˚ and 125 L/min of inflow rate).
Water samples of approximately 50 mL were obtained manually from points just before and after the settling tank, at time intervals of 50 sec, 90 sec, 120 sec, and 150 sec after turbid water started to flow from the outlet of the channel. All samples brought for laboratory analysis were shaken to re-suspend the sediment and turbidity was measured using a turbidimeter (HACH 2100AN, HACH, Co., USA).
To quantify and compare performance in different experimental cases, the percentage of turbidity reduction (R) was calculated using Equation (1):
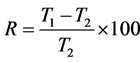 (1)
(1)
where T1 and T2 are average turbidity readings (NTU) in region 1 (before settling tank) and region 2 (after settling tank), respectively.
2.3. Description of Field Study
The study site, which has an area of 1000 m2, is located in Hwaseong city (Gyeonggi province, Republic of Korea). It has a slope of 0.3% - 18% and is comprised of loamy soil. The major crops cultivated within the area are peril a and hot pepper. The site is considered to be vulnerable to soil erosion and nutrient loss due to its relatively steep slope and to lack of soil cover (plastic, vegetation, etc.). Facilities for good drainage and erosion/sedi- ment control are therefore required. The drainage canal within the study site is 1 m wide and 55 m long; for purposes of the experiment, its non-uniform slope was straightened out to 10%.
A total of three BCDs were installed within an agricultural ditch and approximately 100 g of APS 705 were sprinkled on top of each check dam and also up-section of burlap mat. A weighing-type rain gauge and a par shall flume were installed to measure the amounts of rainfall and runoff. Water samples were collected over time following each rainfall event using an automatic sampler (ISCO 2100, Teledyne ISCO, NE, USA), and subsequently analyzed; this enabled assessment of the performance of BCD sin terms of improving water quality (Figure 4). A self-contained and solar-powered weather station was setup to record temperature, humidity, and wind direction/speed; a self-emptying rain gauge was also installed, taking measurements at 30 min intervals.
Time-variant runoff samples were collected before/after each BCD and at the outlet of the agricultural ditch. All water samples were analyzed for their physiochemical properties, such as EC, pH, suspended solids (SS), turbidity, BOD, COD, T-N, T-P, and fecal coliforms. Samples were analyzed using standard methods [13] ; standard methods for the examination of environmental pollution [14] were also referred to for the study. pH and EC readings were taken using an EA 940 ion analyzer (Orion, USA) and a Model 162 conductivity meter (Orion, USA), respectively. Other chemical properties (NH4-N, 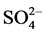 , NO3-N, and Cl) and cations were analyzed using the indophenol method, the nephelometry method, ultraviolet spectrophotometry, and Mercury (II) Thiocyanate and ICP (GBC Intergra XMP, Australia) methods, respectively.
, NO3-N, and Cl) and cations were analyzed using the indophenol method, the nephelometry method, ultraviolet spectrophotometry, and Mercury (II) Thiocyanate and ICP (GBC Intergra XMP, Australia) methods, respectively.
All experiments were repeated three times, with and without PAM, to increase experimental accuracy and to evaluate the effectiveness of PAM clearly. In addition, all values were averaged for plotting purposes.
The residual test is essential for the safe use of PAM; however, the residual PAM concentration is not commonly measured. It requires substantial amount of time and cost; therefore, this study developed a quick and easy way to quantify the PAM concentration in water samples. The100 mL of PAM solutions with the pre-de- fined concentration (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 15, 20 ppm) were mixed with 900 mL of turbid water with a known concentration (50 g Kaolin/900 mL tap water) using a 1-Liter cylinder, and their flocculation rates were measured to construct the standard curve. The runoff samples collected from the agricultural ditches were then mixed with turbid water to obtain the flocculation rates, and then the PAM residual amount in runoff waters were then back calculated using the standard curve.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimal Design of the Hybrid BMP and Its Water Quality Improvement Performance
This study evaluated factors affecting the sediment trapping and flocculating efficiency of biodegradable check dams (BCDs) integrated with different types of synthetic polymers; factors considered included bed slope, turbidity levels, BCD materials, BCD manufacturing design, the number of BCDs installed, BCD installation types, and PAM dosage/type. Material testing was carried out for Magnafloc 336 (powder), dissolved Magnafloc 336 (emulsion), and APS 700 Series Floc Logs®. In addition, the effect of PAM dosage on turbidity reduction was investigated.
Figure 5 shows selected experimental results. Powder-type PAM exhibited approximately 73% better turbidity removal than emulsion- and block-type PAMs. As can be expected, a greater reduction in turbidity was observed with an increase in PAM dosage. However, the effect of PAM on turbidity reduction was finite, and a separate test showed the existence of a logarithmic relation between PAM dosage and turbidity reduction [15] . Having more than three BCDs installed within a channel did not reduce the level of turbidity. Increased channel slope and flow reduced the effect of turbidity control. The best material for BCDs was found to be coconut fiber, followed by rice husks, rice straw, and a combination of rice straw and coconut fiber. Use of an additional burlap mat also enhanced the turbidity reduction performance of BCDs. Overall, the hybrid turbidity reduction system enabled a reduction in the level of turbidity in water of up to 72%.
![]()
![]()
Figure 4. Installation of parshall flume and automatic sampler (left) and hybrid BMP within a ditch (right).
3.2. Field Application of the Hybrid BMP
This study compared the total amount of soil eroded during the years 2012 and 2013, i.e., 19.8 ton and 1.46 ton, respectively. Physical conditions, including climatic and soil properties, were not consistent across the two years, with potential to influence soil erosion; nevertheless, it was evident that the hybrid BMPs developed in this study served to improve water quality, as indicated by the following parameter changes:10.0% to 98.3% for suspended solids, 25.2% to 98.4% for turbidity, 21.1% to 91.1% for BOD, 19.2% to 75.4% for COD, 21% to 73.3% for T-N, 5.9% to 91.2% for T-P, and 35.7% to 97.6% for fecal coliforms (Figure 6). The study also included residual tests of runoff samples to assess the amount of PAM remaining. A simple screening test conducted using a cylinder showed that most samples containing a concentration of 1 - 9 ppm were within the range of about 10% - 15% of the maximum allowance established by the North Carolina Division of Soil and Water Conservation (USA) (data not shown), i.e., within a safe level.
4. Conclusions
A series of laboratory experiments using an artificial open channel were conducted to optimally design the hybrid turbidity reduction system or agricultural NPS control. Use of PAM with the BCD was shown to result in superior performance. From the various PAM products (powder, emulsion and block), powder was shown to work best, followed by emulsion and block. An increase in PAM dosage resulted in high turbidity removal efficiency. Increases in channel slope and flow rate negatively affected turbidity reduction in water.
The number of BCDs that should be installed depends on the level of turbidity and on the amount of inflow; however, a final decision should also take into account economic factors. The best turbidity reduction result was achieved when using three BCDs made of coconut fiber. The main benefits of the developed BCD design included the ease of manufacture, transport, and field handling, the possibility of quick installation without the need for equipment or deep trenching, and convenient post-management. However, the unit price of coconut fiber is expensive due to import duties and it is somewhat difficult for this material to be shaped into a roll. This study therefore ultimately opted for selection of a BCD that uses rice husks. Simultaneous use of both a burlap mat and a settling tank enabled better removal efficiency. Through analysis of six water quality parameters, the field experiment also showed that up to 90% water quality improvement was achieved. Overall, the results ob-
![]()
![]()
![]()
Figure 6. Time-variant water quality and percentage reduction.
tained clearly indicate that BCDs sprinkled with PAM and placed on a burlap mat could play a significant role in supplementing conventional BMPs.
The hybrid turbidity reduction system developed in this study could thus make a significant contribution towards addressing agricultural nonpoint sources of pollution through establishment of areas for pollutant retention and control. However, it should be noted that careful attention should be paid to the design and installation of such measures, in order to ensure lower discharges of sediment from sloping farmland and significantly lower levels of turbidity.
Acknowledgements
This study was carried out with the support of “Research Program for Agricultural Science & Technology Development (Project No. 907097032013),” National Academy of Agricultural Science, Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.