1. Introduction
An earthquake is always an unexpected phenomenon. Modern science is not able to predict the time or the place or the earthquake strength. The problem of locating the focus of a starting earthquake has not even been set due to the poor level of understanding the processes preceding its start. At present the main earthquake hypothesis is the “explosive” relaxation of the high elastic stresses accumulated in the lithosphere. A serious objection to the above hypothesis is the stress relaxation caused by the plastic flow whose rate grows exponentially with temperature and stress [1] . In the lithosphere the temperature and the pressure increase with the depth and, therefore, models of the earthquake focus with no elastic stress concentrations, such as the Inertial Earthquake Focus (IEF) model, are more probable [2] - [4] .
Nowadays, geophysical measurements can be performed only on the surface or in the thin subsurface layer of the Earth, so all the earthquake hypotheses are purely theoretical. Although some data can be obtained from seismic waves, their amount is far from sufficient, since the waves are long and provide little information. Therefore, there remains only one way of locating the focus of a starting earthquake―to develop a method using the elastic stress field of a starting earthquake focus. This method is suggested in the present work.
2. Inertial Earthquake Focus
In the lithosphere tectonic plates move and turn relative to each other. Due to the Earth’s rotation each plate possesses the moment of momentum 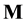 parallel to the axis of rotation of the Earth’s body [5]
parallel to the axis of rotation of the Earth’s body [5]
 .
.
Here 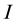 is the moment of inertia,
is the moment of inertia, 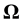 is the vector of the angular velocity of the Earth’s rotation. There can be two types of change of the angular velocity of rotation illustrated in Figure 1 by the example of a rotating cylinder. One is precession, when by the action of the external moment, that is perpendicular to the axis of rotation , the orientation of the axis of rotation in space changes, whereas the angular velocity value does not change in magnitude. The direction of the axis of rotation changes from the vertical orientation in Figure 1(а) into the horizontal one, as is shown in Figure 1(b), its position relative to the material points of the cylinder does not change, and the external moment does not perform work. The other type of change of the angular velocity of rotation is shown in Figure 1(c), where the position of the axis of rotation relative to the material points of the cylinder changes.
is the vector of the angular velocity of the Earth’s rotation. There can be two types of change of the angular velocity of rotation illustrated in Figure 1 by the example of a rotating cylinder. One is precession, when by the action of the external moment, that is perpendicular to the axis of rotation , the orientation of the axis of rotation in space changes, whereas the angular velocity value does not change in magnitude. The direction of the axis of rotation changes from the vertical orientation in Figure 1(а) into the horizontal one, as is shown in Figure 1(b), its position relative to the material points of the cylinder does not change, and the external moment does not perform work. The other type of change of the angular velocity of rotation is shown in Figure 1(c), where the position of the axis of rotation relative to the material points of the cylinder changes.
For a cylinder to change the orientation of the rotation axis relative to the points of the body, it is necessary, first, in the horizontal rotation position of a cylinder (b) to apply the external moment of force directed opposite to the angular velocity vector 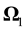 and stop the rotation. Then, it is necessary to apply the external moment of force directed along the axis and make the cylinder rotate around and along the axis (Figure 1(c)).
and stop the rotation. Then, it is necessary to apply the external moment of force directed along the axis and make the cylinder rotate around and along the axis (Figure 1(c)).
For simplicity, let us consider the IEF in the form of a sphere. As a result of tectonic movement, the direction of axis will deviate by an angle 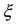 from the Earth’s axis of rotation. If the turn occurred in a vacuum, the direction of the angular velocity would deviate by the angle
from the Earth’s axis of rotation. If the turn occurred in a vacuum, the direction of the angular velocity would deviate by the angle 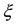 and its value would be
and its value would be 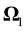 . At the same time, the equality
. At the same time, the equality 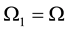 would be satisfied. However, the IEF is located in the solid lithosphere and rotates together with the Earth, so the angular velocity cannot differ in value or direction from the Earth’s angular velocity
would be satisfied. However, the IEF is located in the solid lithosphere and rotates together with the Earth, so the angular velocity cannot differ in value or direction from the Earth’s angular velocity 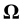 . Here there occurs a change in the position of the axis of rotation relative to the IEF points. Therefore, first we stop the IEF rotation applying elastic stresses with the moment of force
. Here there occurs a change in the position of the axis of rotation relative to the IEF points. Therefore, first we stop the IEF rotation applying elastic stresses with the moment of force 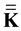 inclined at the angle of
inclined at the angle of 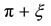 to the Earth’s rotation axis, with the IEF kinetic energy wholly turning into the potential energy of the elastic stresses occurring around it in the lithosphere. Then we make the IEF rotate reaching the angular velocity
to the Earth’s rotation axis, with the IEF kinetic energy wholly turning into the potential energy of the elastic stresses occurring around it in the lithosphere. Then we make the IEF rotate reaching the angular velocity 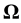 applying to it the elastic stress with the moment of force
applying to it the elastic stress with the moment of force 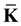 directed along the Earth’s rotation axis. The kinetic energy of rotation completely turns into the potential energy of the elastic stresses and vice versa, which means that the following equality will be satisfied
directed along the Earth’s rotation axis. The kinetic energy of rotation completely turns into the potential energy of the elastic stresses and vice versa, which means that the following equality will be satisfied
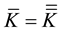 (2.1)
(2.1)
The resulting vector is
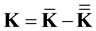 (2.2)
(2.2)
hence
![]() (2.3)
(2.3)
Thus, the IEF gets its own moment of force ![]() . As is known, the condition of equilibrium in the elasticity theory requires that all the concentrated moments be zero [6] . However, the above condition applies only to in-
. As is known, the condition of equilibrium in the elasticity theory requires that all the concentrated moments be zero [6] . However, the above condition applies only to in-
![]() (a) (b) (c)
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 1. The orientation change of the rotating axis is displayed.
ertial systems, whereas the rotating Earth is not such a system. If the Earth did not rotate, there would be no moment of force .
The stress field of the moment of force ![]() cannot be reduced by plastic relaxation without turning the IEF as a whole returning to the initial position. As the angle
cannot be reduced by plastic relaxation without turning the IEF as a whole returning to the initial position. As the angle ![]() increases, the stresses grow and can achieve a critical value, the IEF turns abruptly decreasing the angle
increases, the stresses grow and can achieve a critical value, the IEF turns abruptly decreasing the angle ![]() and the stress field, and an earthquake takes place.
and the stress field, and an earthquake takes place.
3. The Elastic Field of the Moment of Force
The equation of elastic equilibrium for the displacement vector ![]() is [6]
is [6]
![]() (3.1)
(3.1)
The deformation tensor is
![]()
and the stress tensor is
![]() (3.2)
(3.2)
Here ![]() is the shear modulus,
is the shear modulus, ![]() is the Poisson coefficient,
is the Poisson coefficient, ![]() is the Kronekker symbol. For the sphere
is the Kronekker symbol. For the sphere ![]() of the radius
of the radius![]() with the center in the origin of coordinates the force is
with the center in the origin of coordinates the force is
![]() (3.3)
(3.3)
and the moment of force is
![]() (3.4)
(3.4)
Here ![]() is the radius-vector,
is the radius-vector, ![]() is the unitary normal to
is the unitary normal to ![]() . If the moment (3.4) is not zero, the region will be referred to as the Torque Region (TR). Substituting (3.2) into (3.4) we derive
. If the moment (3.4) is not zero, the region will be referred to as the Torque Region (TR). Substituting (3.2) into (3.4) we derive
![]() (3.5)
(3.5)
since for a sphere with the center in the origin of coordinates the vector ![]() and
and ![]() are parallel. Suppose that
are parallel. Suppose that ![]() is a solenoidal vector, that is, there exists the vector
is a solenoidal vector, that is, there exists the vector ![]() such that
such that
![]() (3.6)
(3.6)
Then (3.1) is reduced to the equation
![]() (3.7)
(3.7)
since the first term in (3.1) becomes zero. For the moment of force ![]() in (3.5) to be independent of
in (3.5) to be independent of![]() , it is necessary that
, it is necessary that ![]() . Therefore, let us take the vector
. Therefore, let us take the vector ![]() in the form
in the form
![]() (3.8)
(3.8)
Here ![]() is the arbitrary constant. The vector (3.8) is the solution (3.7), then
is the arbitrary constant. The vector (3.8) is the solution (3.7), then
![]() (3.9)
(3.9)
Here the displacement vector is written first in the Cartesian system of coordinates and then in the spherical one. The sequence of writing the spherical vector components is as follows: radial ![]() zenith
zenith ![]() and asymuthal
and asymuthal ![]() . The Cartesian coordinates are related to the spherical ones in the following way
. The Cartesian coordinates are related to the spherical ones in the following way
![]()
Differentiating (3.9) we obtain that
![]() (3.10)
(3.10)
The potential vector ![]() produces a deformation tensor having two components not equal to zero in the sphe- rical coordinates
produces a deformation tensor having two components not equal to zero in the sphe- rical coordinates
![]() (3.11)
(3.11)
The stress tensor has the same
![]() (3.12)
(3.12)
The values (3.9), (3.11), (3.12) are not zero only outside the IEF. Let us choose a system of coordinates so that the moment of force had only one component along the axis ![]() not equal to zero, then
not equal to zero, then
![]() (3.13)
(3.13)
hence
![]() (3.14)
(3.14)
If a source is produced by inertial effects, that is the IEF, then multiplying (3.14) by ![]() we derive
we derive
![]() (3.15)
(3.15)
Similarly,
![]() (3.16)
(3.16)
![]() (3.17)
(3.17)
![]() (3.18)
(3.18)
The elastic energy density will be written as
![]()
The elastic energy of the stresses of the moment of force (2.3) is
![]() (3.19)
(3.19)
The unknown constant ![]() can be determined from two conditions. The first condition is when the moment of force is specified, and then the value of
can be determined from two conditions. The first condition is when the moment of force is specified, and then the value of ![]() is found according to (3.14). The second condition is when
is found according to (3.14). The second condition is when ![]() is determined according to a specified kinetic energy of rotation. The energy density of the elastic field (3.9) is as follows
is determined according to a specified kinetic energy of rotation. The energy density of the elastic field (3.9) is as follows
![]()
and the energy will be
![]() (3.20)
(3.20)
The constant ![]() is determined from the condition of the complete change of the kinetic energy
is determined from the condition of the complete change of the kinetic energy
![]()
into the potential energy of the elastic stresses (3.12). The inertial moment of a sphere is
![]() (3.21)
(3.21)
As a result, we obtain
![]() (3.22)
(3.22)
Substituting (3.22) into (3.15) we derive the value of the moment of force
![]() (3.23)
(3.23)
The stress field according to (3.18) looks like
![]() .
.
Substituting (3.22)into (3.19) we obtain an expression for the IEF
![]() (3.24)
(3.24)
On the IEF surface the stresses are
![]() (3.25)
(3.25)
As is shown in [7] , in order to derive a general solution for the elasticity problem, a nonpotential solution should be added the potential solution (3.16). However, in the Appendix it is shown that the interaction energy of the potential and nonpotential solutions is zero. Addition of the nonpotential solution to the potential one (3.16) will increase the system energy, and for this reason it is excluded from consideration.
4. Interaction of Focuses. Locating an Earthquake Focus
If there exist two torque regions, there is energy of elastic interaction between them, that can be used to locate the focus of a starting earthquake. For this purpose, it is necessary to create an artificial TR in the lithosphere applying shear stresses to the surface of the artificial cavity. Let us designate the values relating to the artificial TR by one point at the top (further referred to as the first TR), and the IEF by two points (further referred to as the second TR). The centres of these focuses are located on the abscissa at point ![]() for the first TR and
for the first TR and ![]() for the second TR. The plane is vertical and passes through the Earth’s center,
for the second TR. The plane is vertical and passes through the Earth’s center, ![]() -coordinate is normal to it and forms the angle
-coordinate is normal to it and forms the angle ![]() with the Earth’s axis. The direction of
with the Earth’s axis. The direction of ![]() -coordinate is chosen so that the system of coordinates was right. The vector potentials of the moment of force will be
-coordinate is chosen so that the system of coordinates was right. The vector potentials of the moment of force will be
![]() (4.1)
(4.1)
Here
![]() .
.
The zenith angles ![]() and
and ![]() are measured from
are measured from ![]() axis, and the angles
axis, and the angles ![]() and
and ![]() from that of abscissa. The moments
from that of abscissa. The moments ![]() and
and ![]() coincide in direction with
coincide in direction with ![]() and
and ![]() . The laboratory Cartesian system with the origin in the center of the first focus is oriented in the following way (the variables related to it are designated by the sign ^): the axis
. The laboratory Cartesian system with the origin in the center of the first focus is oriented in the following way (the variables related to it are designated by the sign ^): the axis ![]() coincides with the vertical at the given point and is directed upward, the axis
coincides with the vertical at the given point and is directed upward, the axis ![]() is directed along the meridian to the north and the axis
is directed along the meridian to the north and the axis ![]() is directed along the latitude to the west. The plane
is directed along the latitude to the west. The plane ![]() is meridianal, the angle between the normals of the planes
is meridianal, the angle between the normals of the planes ![]() and
and ![]() , that is between the axes
, that is between the axes ![]() and
and ![]() , is
, is ![]() . The change to the laboratory Cartesian system of coordinates is implemented by turning around axis
. The change to the laboratory Cartesian system of coordinates is implemented by turning around axis ![]() by the angle
by the angle ![]() and is described by the matrix
and is described by the matrix
![]()
The displacement vectors in the laboratory system of coordinates can be represented like this
![]() (4.2)
(4.2)
The displacements (4.2) determine the deformation tensors
![]() (4.3)
(4.3)
![]() (4.4)
(4.4)
The total deformation tensor is
![]() (4.5)
(4.5)
The total elastic energy density is written as
![]() (4.6)
(4.6)
Substituting here (4.5) we find that the total density energy is the sum of the following components: the density of the energy of the first focus
![]()
the energy density of the second focus
![]()
and the density of the interaction energy of the focuses
![]()
Integrating ![]() and
and ![]() we obtain the focus energies in the form (3.19). The interaction energy of the focuses is
we obtain the focus energies in the form (3.19). The interaction energy of the focuses is
![]() (4.7)
(4.7)
For integrating turn to the bipolar coordinates in (4.7). The elastic energy density is a scalar, and the change to the bipolar coordinates is performed by replacing the Cartesian coordinates by the bipolar ones (4.7) using the formulas [8] :
![]() (4.8)
(4.8)
The coordinate surface for ![]() is the radius sphere
is the radius sphere
![]() (4.9)
(4.9)
with the center on the abscissa at the point![]() . At
. At ![]() the value of
the value of ![]() is close to unity and the center of the coordinate sphere, in fact, coincides with that of the IEF. For instance, already for
is close to unity and the center of the coordinate sphere, in fact, coincides with that of the IEF. For instance, already for ![]() the value of
the value of ![]() . Therefore, one can expect with sufficiently great accuracy that the centers of the focuses and the centers of the coordinate spheres coincide. For this reason, the limits of integration over
. Therefore, one can expect with sufficiently great accuracy that the centers of the focuses and the centers of the coordinate spheres coincide. For this reason, the limits of integration over ![]() , in accordance with (4.9), are as follows
, in accordance with (4.9), are as follows
![]() .
.
The elastic interaction energy (4.7) in the bipolar coordinates is written as
![]() (4.10)
(4.10)
Here it is designated
![]() (4.11)
(4.11)
Since the first TR is an artificial source of the moment of force, the distance to the focus will always be much larger than its size ![]() , therefore,
, therefore,
![]()
hence
![]()
For the second TR the following relation can be true ![]() , however, in both cases, we deal with the equality
, however, in both cases, we deal with the equality
![]()
As a result, we derive from (4.10)
![]()
The total energy will be written as
![]() (4.12)
(4.12)
Here, instead of ![]() , the value of
, the value of ![]() is used, which is the distance between the centers of the focuses. Differentiating the energy
is used, which is the distance between the centers of the focuses. Differentiating the energy ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]() we obtain a generalized force acting between the focuses in the form
we obtain a generalized force acting between the focuses in the form
![]() (4.13)
(4.13)
If ![]() , then the focuses are attracted to each other, and if
, then the focuses are attracted to each other, and if ![]() , then they repel. The sign depends on the
, then they repel. The sign depends on the
coefficient ![]() from (4.11) The following unknowns are included here:
from (4.11) The following unknowns are included here: ![]() is the IEF size,
is the IEF size, ![]() , the distance
, the distance
between the focuses![]() , and
, and ![]() .The values
.The values ![]() and
and ![]() are known, they are specified during an experiment. After measuring the value
are known, they are specified during an experiment. After measuring the value ![]() for various orientations of the vector
for various orientations of the vector ![]() , we determine the orientation factor
, we determine the orientation factor ![]() , that is the IEF orientation. The above method does not allow defining the value
, that is the IEF orientation. The above method does not allow defining the value ![]() separately from
separately from ![]() . However, we can suppose that the angle
. However, we can suppose that the angle ![]() will not be very small, otherwise the energy of the focus of a starting earthquake will not be very small too, so it may be that
will not be very small, otherwise the energy of the focus of a starting earthquake will not be very small too, so it may be that ![]() will be of the order of
will be of the order of ![]() , then the size of the focus of a starting earthquake
, then the size of the focus of a starting earthquake ![]() and its energy are evaluated according to (3.24) and (4.13). Making measurements for various orientations one can define the unknown parameters
and its energy are evaluated according to (3.24) and (4.13). Making measurements for various orientations one can define the unknown parameters ![]() and
and ![]() and hence the IEF orientation.
and hence the IEF orientation.
The force ![]() acting on the first focus can be considered as the concentrated force. The displacement field of the concentrated force can be found from the following considerations. As the value of the concentrated force does not depend on the radius of the integration sphere in (3.3), so the stress field must decrease with the distance from the point of its application as
acting on the first focus can be considered as the concentrated force. The displacement field of the concentrated force can be found from the following considerations. As the value of the concentrated force does not depend on the radius of the integration sphere in (3.3), so the stress field must decrease with the distance from the point of its application as![]() ,and then the displacement field will decrease as
,and then the displacement field will decrease as ![]() . Consider that the concentrated force is directed along the axis
. Consider that the concentrated force is directed along the axis ![]() , therefore, let us take the displacement vector such as
, therefore, let us take the displacement vector such as
![]()
Here ![]() is the arbitrary constant. The above vector does not satisfy the equation of elastic equilibrium (3.1), whereas a check proves that the following equality is satisfied
is the arbitrary constant. The above vector does not satisfy the equation of elastic equilibrium (3.1), whereas a check proves that the following equality is satisfied
![]()
We have
![]()
The potential ![]() satisfying the equation
satisfying the equation
![]()
is
![]()
The vector
![]()
is the solution of the Equation (3.1). Here the vector ![]() is written in the Cartesian system of coordinates. The force (3.3) caused by the field
is written in the Cartesian system of coordinates. The force (3.3) caused by the field ![]() does not depend on the size of the integration sphere
does not depend on the size of the integration sphere ![]() and is
and is
![]() (4.14)
(4.14)
This force is directed along the line connecting the IEF centers. Equating the forces (4.13) and (4.14) we obtain the value of the arbitrary constant ![]()
![]() .
.
The displacement vector component ![]() is directed along the line connecting the IEF centers and can be written as
is directed along the line connecting the IEF centers and can be written as
![]() .
.
It consists of two terms. The first term is the displacement of the radius sphere r as a whole without deformation. The second term is the deformation component. Substituting the coefficient B with the change of ![]() into the first term, we get the displacement of the first TR in the form
into the first term, we get the displacement of the first TR in the form
![]() .
.
Measuring ![]() for various orientations and at several points we obtain a set of equations to determine the angles
for various orientations and at several points we obtain a set of equations to determine the angles ![]() the distance
the distance ![]() and the size of the focus
and the size of the focus ![]() . In this way we determine the focus location, its orientation and energy. For instance, for the following parameters:
. In this way we determine the focus location, its orientation and energy. For instance, for the following parameters:![]() ,
, ![]() , a = 40000 m,
, a = 40000 m, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() (such a value of
(such a value of ![]() corresponds to the focus energy of the order of
corresponds to the focus energy of the order of![]() ), we obtain
), we obtain ![]() . The direction of the displacement vector
. The direction of the displacement vector ![]() is always oriented to the focus of a starting earthquake. Depending on the sign of the orientation factor
is always oriented to the focus of a starting earthquake. Depending on the sign of the orientation factor ![]() the displacement will be either toward IEF or from it. Measuring
the displacement will be either toward IEF or from it. Measuring ![]() at several points one can define the IEF coordinates and evaluate the energy level by the value
at several points one can define the IEF coordinates and evaluate the energy level by the value ![]() . According to (3.24) and (3.25), even for the most intensive earthquakes of an energy of the order of
. According to (3.24) and (3.25), even for the most intensive earthquakes of an energy of the order of![]() , when
, when![]() , the maximum stress will be
, the maximum stress will be ![]() . In the IEF there is no stress concentration.
. In the IEF there is no stress concentration.
To locate an IEF, it is necessary to determine the displacement of an artificial TR with an accuracy up to a millimeter and better. In order to create the moment of force, one can use precession. Between the moment of force ![]() normal to the moment of momentum
normal to the moment of momentum ![]() and the angular velocity of precession
and the angular velocity of precession ![]() there exists the relation [5]
there exists the relation [5]
![]()
The above method can be the simplest one. It allows achieving an arbitrary orientation of the moment of force, which is necessary to perform measurements.
5. Conclusions
In the present work a method of locating the focus of a starting earthquake is suggested. The existence of the IEF is the effect of the Earth’s rotation. Its analogue is the Coriolis force. Cyclones and anticyclones are caused by the Earth’s rotation. In the lithosphere they are analogous to the IEF. Undoubtedly, the IEF evolution takes much longer than a cyclone, and the rates of gas flows in the atmosphere are by orders of magnitude higher than tectonic rates. However, it should not lead to denying or ignoring inertial effects in the lithosphere.
The existence of tectonic plates with localization of elastic stresses is the main hypothesis of earthquake focuses. The reasons for stress localization can be different as well as their space dependence. If there exist two regions with a similar space distribution of stresses, then between them there is the energy of elastic interaction. Using the above energy it is possible to locate the focus of a starting earthquake creating artificially a region with a specified stress profile. Mathematical calculation of other models of earthquake focuses will be somewhat different from the one discussed here, which is not a problem.
Appendix. Nonpotential Solution
As is known, along with the potential solution there can also be a nonpotential one [7] [9] . A general solution will be their linear combination, whose coefficients are determined from the condition of the total energy minimum.
To derive the nonpotential solution take the vector
![]()
The rotor is
![]() (6.1)
(6.1)
One must find the solenoidal vector ![]() , such that
, such that
![]() ,
,
then the vector
![]() (6.2)
(6.2)
is the solution (3.1). For simplification, let us integrate (6.1) over ![]() :
:
![]() (6.3)
(6.3)
Here it is designated
![]() .
.
Since ![]() is the solenoidal vector, that is
is the solenoidal vector, that is ![]() , the following equality takes place
, the following equality takes place ![]() . Proceeding from (6.3) it is necessary to solve two equations
. Proceeding from (6.3) it is necessary to solve two equations
![]() (6.4)
(6.4)
![]() (6.5)
(6.5)
Integrate (6.4) over and (6.5) over ![]() . As a result, we will derive, practically, the same equation
. As a result, we will derive, practically, the same equation
![]()
Here it is designated
![]()
In the spherical coordinates we have
![]()
Its solution is
![]()
Differentiating we obtain the components of the vector ![]() in the form
in the form
![]() (6.6)
(6.6)
The vector divergence is
![]() .
.
which means that the vector ![]() is solenoidal. Differentiating (6.6) over
is solenoidal. Differentiating (6.6) over ![]() we find
we find
![]() ,
,
hence
![]() .
.
The nonpotential solution (6.2) is written in Cartesian and spherical coordinates as
![]()
In the deformation tensor for the displacement ![]() the component
the component ![]() and in the deformation tensor (3.17) only this component is other than zero. It means that the interaction energy of the potential and nonpotential solutions is zero. Hence, the elastic energy minimum is achieved using the potential solution (3.9).
and in the deformation tensor (3.17) only this component is other than zero. It means that the interaction energy of the potential and nonpotential solutions is zero. Hence, the elastic energy minimum is achieved using the potential solution (3.9).