
1. Introduction
A projective plane PG(2,q) over Galois field GF(p), where q is a prime number, consists of
points and
, every line contains
point and every point is on
lines [3]. Any point of the plane has the form of a triple, where
are elements in PG(q) with the exception of a triple consisting of three zero elements. Two triples
and
represent the same point if there exists j in GF(P)/{0}, s.t.
.
The points in PG(2,q) have unique forms which are (1,0,0), (X,1,0), (X,Y,1) for all X,Y in GF(q). There exist one point of the from (1,0,0), q points of the from (X,1,0) and q2 points of the from (X,Y,1) similarly any line in PG(2,q) has the form
,
are elements in GF(q) with the exception of a triple consisting of three zero elements. Two triples represent the same line if thereexist J GF(q)\{0}, s.t
. A point
is incident with the line
iff
[4].
Finally, the points of PG(2,q) can be numerated as follows: the number of the point
is 1, the point is
numerated as X + 2, the point
is numerated as
[5].
Definition 1: A(K,n)-a in PG(2,q) is asset of K points such that NO n + 1 points them are collinear A(K,2)-arc which is called K-arc is a set of K points such that NO three of them are collinear [6].
Definition 2: A(k,n)-arc is a complete if it is not contained in a (k + 1,n)-arc [6].
Definition 3: The maximum number of points that a (K,2)-arc can have is m(2,q) and a (K,2)-arc with this number of points is an Oval. In the even case Ovals are complete [7].
Theorem 1:
[7].
Theorem 2: In PG(2,q), with q odd, every oval is conic [8].
Definition 4: The i-secant of a (K,n)-arc K is a line intersects the arc in exactly i points, a 0-secant is called an external line K, a 1-secant is called a uni secant line, 2-secant is called a bisecant line and 3-secant is called a trisecant line [9].
Corollary 1: A (k,n)-arc K is a maximal if and only if every line PG(2,q) is a 0-secant, or an N-secant [10] [11].
Theorem 3: Let m be a point of a (K,2)-arc K and let t(m) be the number of unisecants through m in PG(2,q) then
[12].
Proof: In PG(2,q), there exist exactly q + 1 lines through q. since M is on k then each line passing through M is either unisecant or bisecant of k. There exists exactly k-1 lines joining M with the remaining k-1 points of k which are bisecant of k. then the number of unisecant through M is
.
(i.e.).
.
Corollary 2: If k is an oval then t(m) = 1 [13].
Theorom 4: Let k be a k-arc in PG(2,q) and let Ti be the number of i-secant of k in the plane, that is, T2 is the number of bisecant, T1 the number of unisecants, and T0 the number of external line, then [13] :
1)
;
2)
;
3)
.
Proof: 1) We have K points in arc K; we take two points from these k point to find the bisecant of k so.
2) There exist exactly K points on arc K. Each point of K has exactly
line of K. The number of unisecants of K is exactly
.
3) Each line of the plane PG(2,q) is either bisecant, unisecant or external line. The number of lines is
.
Corollary: For a (q + 1)-arcs, t = 1,
,
,
[13].
Definition 5: Let Q be a point of PG(2,q) not on the K-arc. Let Si(Q) be the number of i-secants through Q. The number of bisecants S2(Q) is called the index of Q with respect to K and the number of unisecant S1(Q) is called the grade of Q with respect to K [14].
Lemma 1: For any point Q in PG(2,q)\K, then
[14].
Proof: Since each unisecant of K. passes through one point of the arc and each bisecant passing through two points of the arc, the number of the points of the arc is K, then
.
Lemma 2: Let Ci be the number of points Q of index i. Then
1)
;
2)
;
where
is smallest i for Which
, and
is the largest i for Which
.
Proof: 1)
represents all the points of the plane not in K. Since the number of point in the plane is
, then
2)
{(Q,l)/Q ?l\k, l is a bisecant of K} each bisecant contains q − 1 points not in K.
There are 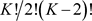 Bisecant of K. Then there exist
Bisecant of K. Then there exist 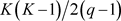 OF points satisfying the equation
OF points satisfying the equation
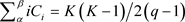
Remark: The (k,n)-arc K is complete if and only if,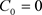 . Thus, K is complete if every point of PG(2,q) lines on some n-secant of K [15] [16].
. Thus, K is complete if every point of PG(2,q) lines on some n-secant of K [15] [16].
2. The Additions and Multiplications Operations of GF(9)
To find the addition and multiplication tables, in GF(9), We have the order pier 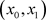 such that
such that  in GF(3), as follows:
in GF(3), as follows:
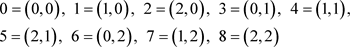
Put these points in one orbit (1,0) at the first point and by the principle of (0,1) Ai, 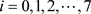 and
and
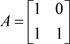
(1,0) 
(0,1) (1,1) (1,2) (2,0) (0,2)(1,2) (2,2)
Now, in the left of the following Table 1 is the operation of multiplication, and in the right n is the operation of addition; in multiplication side, it writes the numeration of points as last, and the addition side take the normal sequence [15] [16].
Mod (8): In addition (Table 2), We have the following relation: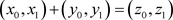 .
.
In multiplication (Table 3), we have the following relations 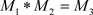
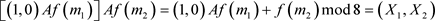 . For Example:
. For Example: 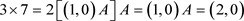 where (2,0) is equal to 2 in multiplication side. Now we have the multiplication (Table 3).
where (2,0) is equal to 2 in multiplication side. Now we have the multiplication (Table 3).
![]()
Table 1. Operation of multiplication.
2.1. The Construction Complete (ki,i)-Arc, Where 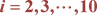 in PG(2,9) over GF(9)
in PG(2,9) over GF(9)
The projective plane PG(2,q) contains (91) points and (91) lines, every line contains (10) points and every point is on (10) lines. Any line in PG(2,q) can be constructed by means of variety V. let Pi and ![]() be the points and lines of PG(2,9), respectively. Let i stands for the point Pi[i] stands for the Li whose coordinates are the same coordinates of the point Pi, and all the points and the lines of PG(2,9) are given in Table 4.
be the points and lines of PG(2,9), respectively. Let i stands for the point Pi[i] stands for the Li whose coordinates are the same coordinates of the point Pi, and all the points and the lines of PG(2,9) are given in Table 4.
2.2. The Construction of (k10,10)-Arc
If i = 10, the M(10,9) = 91 which is the maximal arc, since every line in PG(2,9) is a 10-secan of the (K,10)-arc. This arc contains The construction of (k9,9)-arc, from the (k10,10)-arc: all the points of the plane PG(2,9), So it is a complete arc. Now, we shall construct the (K,m)-arcs as given in Table 4.
2.3. The Construction of (k9,9)-Arc, from the (k10,10)-Arc
We eliminate one line from the (k10,10)-arc, say the line L11 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]. On ather hand, in projective plane any two distinct lines are intersected in a unique point, the eliminating line intersects any line of PG(2,9) in exactly one point consequently, we eliminate one point from any line in the plane PG(2,9) The eliminated line is a 0-secant of K9 and the remaining (90) lines are the 9 secants of the arc. We find:
1) K9 is a maximal (81,9)-arc in PG(2,9), since every line in PG(2,9) is either 0-secant or a 9-secant of K9, as given in Table 5.
2) K9 is a complete (81,9)-arc since there are no point 0f index zero for K9 i.e.![]() .
.
2.4. The Construction of (k8,8)-Arc k from k9
In this section, we construct (K8,8)-arc K8 from K9 by eliminating the line L2 = [11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19] and following points [20, 29, 38, 47, 56, 65, 74, 83] then find:
1) K8 is not a maximal (64,8)-arc in PG(2,9) since every line in PG(2,9) is either 0-secant or a 8-secant of K, as given in Table 6.
2) K8 is acomplete (64,8)-arc since there are no point of index zero for K8 i.e.,![]() .
.
2.5. The Construction of (k7,7)-Arc K from K8
We construct a (K7,7)-arc K from K8 by eliminating one line, the line L29: [20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28] and the following points [30, 39, 48, 57, 66, 75, 84], then we find:
1) K7 is not a maximal (49,7)-arc in PG(2,9) since every line in PG(2,9) is either 0-secant or a 7-secant of K7, as geven in Table 7.
2) K7 is a complete (49,7)-arc since there are no points of index zero for K7, i.e.![]() .
.
![]()
![]()
![]()
Table 4. Point and Line of pG(2,9).
![]()
![]()
![]()
Table 5. Point and Line of pG(2,9).
![]()
![]()
![]()
Table 6. Point and Line of pG(2,9).
![]()
![]()
![]()
Table 7. Point and Line of pG(2,9).
2.6. The Construction of (K6,6)-Arc k6 from k7
WE construct a (K6,6)-arc K6 from K7 by eliminating one line, the line L20 = [29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37] and the following points [40, 49, 58, 67, 76, 85], then we find:
1) K6 is not a maximal (36,6)-arc in PG(2,9) since every line in PG(2,9) is either 0-secant or a 6-secant of K6 as given in Table 8.
2) K6 is a complete (36,6)-arc since there are no points of index zero for K6, i.e.,![]() .
.
![]()
![]()
![]()
Table 8. Point and Line of pG(2,9).
2.7. The Construction of (k5,5)-Arc k5 from k6
We construct a (k5,5)-arc K5 from K6 by eliminating one line, the line L74 = [38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46] and following points [50, 59, 68, 77, 86], then we find:
1) K5 is not a maximal (25,5)-arc in PG(2,9), since every line in PG(2,9) is either 0-secant or a 5-secant of K5 as given in Table 9.
2) K5 is a complete (25,5)-arc since there are no point of index zero for K5, i.e.
![]() .
.
2.8. The Construction of (k4,4)-Arc k4 from k5
We construct a (k4,4)-arc from k5 by eliminating one line, the line L47 = [47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55] and following points [60, 69, 78, 87], then we find:
1) K4 is not a maximal (16,4)-arc inPG(2,9), since every line in PG(2,9) is either 0-secant or a 4-secant of K4 as given in Table 10.
2) K4 is a complete (16,4)-arc since there are no points index zero for K4, i.e.
![]() .
.
2.9. The Constrcution of (k3,3)-Arc k3 from k4
We construct (K3,3)-arc K3 from K4 by eliminting one line, the line L65 = [56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64] and following points [70, 79, 88], we find:
1) K3 is not a maximal (9,3)-arc in PG(2,9), since every line in PG(2,9) is either 0-secant or a 3-secant of K3, as given in Table 11.
2) K3 is a complete (9,3)-arc since there are no points of index zero for K3, i.e.
![]() .
.
2.10. The Construction of (k2,2)-Arc k2 from k3
We construct a (k2,2)-arc K2 from K3 by eliminating one lines the line L56 = [65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73] and following points [80, 89], then we find:
1) K2 is not a maximal (4,2)-arc in PG(2,9), since some line in PG(2,9) which are 0-secant, 1-secants and 2-secant of K2, as given in Table 12.
![]()
![]()
![]()
Table 9. Point and Line of pG(2,9).
2) Since there are no points of index zero for K2, i.e.![]() , (4,2)-arc is a complete arc and it is oval.
, (4,2)-arc is a complete arc and it is oval.