Performance of Nth Worst Full-Duplex Relay Selection over Nakagami-M Fading Channels ()
1. Introduction
A large number of existing works on cooperative communications assume half- duplex (HD) relaying, where relays transmit and receive the signal in orthogonal channels [1]. In order to overcome the associated bandwidth loss and improve spectral efficiency, full-duplex (FD) transmission has been investigated in the literature [2]-[8]. In FD mode, the relay transmits and receives the signal at the same time and at the same frequency band. FD operation mode has been considered impractical in the past due to its loop interference problems. However, after many works on interference mitigation have been reported, the theoretical analysis for FD relaying networks can be possible [2].
For the multiple relay systems, designing an appropriate relay selection scheme is an efficient approach to achieve space diversity and hardware simplicity. Relay selection problem in AF cooperative system has been studied in [4], the authors considered dynamically switches between FD and HD relaying based on the instantaneous quality of the loop interference, and they showed that the diversity gain can be significantly improved by employing multiple FD relays. In [5], the opportunistic decode-and-forward (DF) relay selection with FD scheme has been studied. Optimal DF relay selection for FD mode in underlay cognitive radio networks has been studied in [7], in which an optimum relay-selection solution for treating the tradeoff between the improved outage probability and the performance degradation can always be achievable within the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) range of (10 dB, 15 dB).
However, in practice, due to some scheduling or load balancing conditions, the best relay may not always be selected. Thus, the study of the 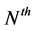 best or worst relay selection will be very necessary. In [9], adaptive DF and AF cooperative diversity systems with the Nth-best relay over Rayleigh fading channels are studied. The main objective of this literature is its diversity order increases linearly with the number of relays and decreases linearly with the order of the relay. The authors in [10] analyzed the asymptotic symbol error rate of AF cooperative communications with the
best or worst relay selection will be very necessary. In [9], adaptive DF and AF cooperative diversity systems with the Nth-best relay over Rayleigh fading channels are studied. The main objective of this literature is its diversity order increases linearly with the number of relays and decreases linearly with the order of the relay. The authors in [10] analyzed the asymptotic symbol error rate of AF cooperative communications with the 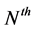 best-relay scheme over independent and non-identical Nakagami-m fading channels. In [11], performance analysis for underlay cognitive DF relay networks with the
best-relay scheme over independent and non-identical Nakagami-m fading channels. In [11], performance analysis for underlay cognitive DF relay networks with the  best relay selection scheme over Rayleigh fading channels is studied; the results show that both the relay selection scheme and the number of relays have great impact on the outage performance of cognitive relay networks. In [12], the outage probability of hybrid Decode-Amplify-Forward protocol with the
best relay selection scheme over Rayleigh fading channels is studied; the results show that both the relay selection scheme and the number of relays have great impact on the outage performance of cognitive relay networks. In [12], the outage probability of hybrid Decode-Amplify-Forward protocol with the 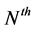 -best relay selection is analyzed, and results show that with the system diversity order is equal to
-best relay selection is analyzed, and results show that with the system diversity order is equal to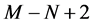 , where
, where 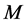 is the number of relays. The accurate approximate outage probability and bit-error rate expressions of two-way relaying networks with the
is the number of relays. The accurate approximate outage probability and bit-error rate expressions of two-way relaying networks with the 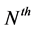 worst relay selection over various fading channels is investigated in [13].
worst relay selection over various fading channels is investigated in [13].
In this letter, we take a step further to investigate the performance of 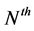 worst relay over independent and non-identical Nakagami-m fading channels. Furthermore, we allow each relay to perform full-duplex operation. We focus on the outage probability as the performance metric, for which we present an accurate approximation in closed-form by deriving statistical expressions of the effective end-to-end SNR. To provide further insight, we analyze the system asymptotic behavior, as well as the effect of several important network parameters, i.e., the number of relays, the order of selected relay and the channel parameter.
worst relay over independent and non-identical Nakagami-m fading channels. Furthermore, we allow each relay to perform full-duplex operation. We focus on the outage probability as the performance metric, for which we present an accurate approximation in closed-form by deriving statistical expressions of the effective end-to-end SNR. To provide further insight, we analyze the system asymptotic behavior, as well as the effect of several important network parameters, i.e., the number of relays, the order of selected relay and the channel parameter.
2. System Model
We assume multiple relay system which consists of one source node (S), one destination node (D) and 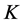 AF relay nodes (Rk,
AF relay nodes (Rk,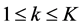 ). The direct link between S and D is assumed strongly attenuated and communication can be established only via the cooperative relays. This typical assumption corresponds to coverage extension scenarios where the distance between S and D is long and relays are used in order to maintain connectivity or scenarios where the direct link is in deep shadowing due to surrounding physical obstacles.
). The direct link between S and D is assumed strongly attenuated and communication can be established only via the cooperative relays. This typical assumption corresponds to coverage extension scenarios where the distance between S and D is long and relays are used in order to maintain connectivity or scenarios where the direct link is in deep shadowing due to surrounding physical obstacles.
Each relay employs an AF protocol and is equipped with two antennas (one receive antenna and one transmit antenna) that enable a full-duplex operation. Meanwhile, we consider an imperfect interference cancellation scheme at each relay by following the analysis, which presented in [2]. Time is considered to be slotted and in each time slot, only one relay Rk is selected to assist the source trans- mission. We denote the channel between node  and node
and node 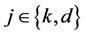 by
by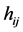 , and assume that all channels are independent and non-necessarily identically Nakagami-m distributed. Specifically,
, and assume that all channels are independent and non-necessarily identically Nakagami-m distributed. Specifically, 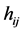 remains constant over one channel block, and varies independently from one block to another with shape parameter
remains constant over one channel block, and varies independently from one block to another with shape parameter  and average power
and average power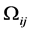 . Without loss of generality, we assume the noise terms are complex additive white Gaussian RVs with zero mean and unit variance.
. Without loss of generality, we assume the noise terms are complex additive white Gaussian RVs with zero mean and unit variance.
At time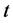 , S transmits the signal to the selected relay node Rk, the received signal at Rk is given by
, S transmits the signal to the selected relay node Rk, the received signal at Rk is given by
![]() (1)
(1)
where ![]() and
and ![]() are the transmit signal of S and Rk with a transmit power
are the transmit signal of S and Rk with a transmit power![]() .
. ![]() is the channel gain between the source and the selected relay Rk, and
is the channel gain between the source and the selected relay Rk, and ![]() is the loop interference channel between the transmit antenna and the receive antenna of the relay Rk.
is the loop interference channel between the transmit antenna and the receive antenna of the relay Rk. ![]() is the additive white Gaussian noise.
is the additive white Gaussian noise.
Due to FD operation, the signal transmitted by Rk at time ![]() is given by
is given by
![]() (2)
(2)
where ![]() is the power amplification factor and
is the power amplification factor and ![]() is the processing delay. Due to the power constraint, the amplification factor
is the processing delay. Due to the power constraint, the amplification factor ![]() can be expressed as
can be expressed as
![]() (3)
(3)
Meanwhile, at time![]() , the received signal at D can be written as
, the received signal at D can be written as
![]() (4)
(4)
where ![]() is the channel gain between the selected relay Rk and D, and
is the channel gain between the selected relay Rk and D, and ![]() is the additive white Gaussian noise.
is the additive white Gaussian noise.
After some manipulation, the instantaneous end-to-end SNR is written as
![]() (5)
(5)
where![]() ,
, ![]() and
and![]() . In order to simplify notation, we define
. In order to simplify notation, we define![]() .
.
In order to use the output SNR in the performance calculations, Equation (5) should be expressed in a more mathematically tractable form [4], which can be rewritten as
![]() (6)
(6)
We consider the relay with the ![]() highest value of
highest value of![]() ,
, ![]() , is selected for retransmitting the source signal to the destination. Hence, the proposed
, is selected for retransmitting the source signal to the destination. Hence, the proposed ![]() worst relay selection scheme can be represented as:
worst relay selection scheme can be represented as:
![]() (7)
(7)
where ![]() denotes to select the
denotes to select the ![]() maximum value from the set
maximum value from the set![]() .
.
3. Performance Analysis
In this section, we investigate the outage performance of the proposed FD-based relay selection policies. We derive exact as well as simple high SNR outage expressions.
3.1. Outage Probability
To evaluate the system outage performance, we should first evaluate the cumulative density function (CDF) of![]() . By arranging the random variables
. By arranging the random variables ![]() in an increasing order of magnitude, we have
in an increasing order of magnitude, we have![]() . Hence,
. Hence, ![]() and
and ![]() corresponds to the worst and the best relay selection cases, respectively. Then, the CDF of the
corresponds to the worst and the best relay selection cases, respectively. Then, the CDF of the ![]() order statistic
order statistic ![]() is given by [14]
is given by [14]
![]() (8)
(8)
where ![]() is the CDF of
is the CDF of![]() .
.
For the case of independent and identically (i.i.d) fading channel, the CDF of the ![]() order statistic
order statistic ![]() can be rewritten as
can be rewritten as
![]() (9)
(9)
where ![]() is the CDF of
is the CDF of![]() .
.
In order to find![]() , we need to find the CDF of
, we need to find the CDF of![]() . Let
. Let ![]() , the CDF for
, the CDF for ![]() can be derived as
can be derived as
![]() (10)
(10)
Since ![]() is a Gamma-distributed random variable, its probability density function (PDF) and CDF are respectively given by
is a Gamma-distributed random variable, its probability density function (PDF) and CDF are respectively given by
![]() (11)
(11)
![]() (12)
(12)
where ![]() is the lower incomplete gamma function, and
is the lower incomplete gamma function, and ![]() is the Gamma function [15].
is the Gamma function [15].
Applying the concepts of probability theory and after some algebraic manipulations, the CDF of ![]() can be expressed as
can be expressed as
![]() (13)
(13)
where ![]() denotes the confluent hypergeometric function of the second kind.
denotes the confluent hypergeometric function of the second kind.
Substituting (13) and the CDF of ![]() into (10), we have
into (10), we have
![]() (14)
(14)
Now substituting (14) into (8) and (9), the outage probability for AF relay system with the ![]() worst relay selection can be readily expressed as
worst relay selection can be readily expressed as
![]() (15)
(15)
where ![]() is a required SNR threshold and
is a required SNR threshold and ![]() is the target rate.
is the target rate.
3.2. Asymptotic Outage Analysis for High SNR
Although the expressions for the outage probability derived in the previous subsection enable numerical evaluation and may not be computationally intensive, the expression do not offer insight into the effect of the different parameters on the system performance (e.g., the order of selected relay![]() ). In this section, we aim to investigate the outage probability at high SNR regime. Moreover, we only investigate the special case of i.i.d fading channel.
). In this section, we aim to investigate the outage probability at high SNR regime. Moreover, we only investigate the special case of i.i.d fading channel.
Applying the series expansion, we can obtain the asymptotic behavior of Equation (14)
![]() (16)
(16)
where
![]() (17)
(17)
Since we only need to consider the dominant term in Equation (9) for the high SNR, the outage probability can be approximated by
![]() (18)
(18)
From (18), since ![]() remains constant in terms of
remains constant in terms of![]() , the outage performance of the system asymptotically converges to an error floor and exhibits a zero diversity gain when
, the outage performance of the system asymptotically converges to an error floor and exhibits a zero diversity gain when![]() . Hence, the
. Hence, the ![]() worst FD relay selection schemes provide zero diversity when
worst FD relay selection schemes provide zero diversity when![]() , and
, and ![]() when
when![]() . Moreover, we can see the effect of
. Moreover, we can see the effect of ![]() is not distinguished, but
is not distinguished, but ![]() has effect on the outage probability coding gains.
has effect on the outage probability coding gains.
4. Numerical Results
In this section, some numerical results are provided to verify our analysis. The following parameters will be used in the numerical results:![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() bits/s/Hz. We plot the outage performance curves versus the SNR of the transmitted signal (
bits/s/Hz. We plot the outage performance curves versus the SNR of the transmitted signal (![]() dB).
dB).
Figure 1 shows the outage performance of the ![]() worst relay selection scheme for different values of
worst relay selection scheme for different values of ![]() and
and![]() . Monte Carlo simulations are also presented to validate the analytical derivations. For the plots, we consider
. Monte Carlo simulations are also presented to validate the analytical derivations. For the plots, we consider ![]() and
and![]() . It is shown that the analytical results are very close to the simulated ones in the whole SNR region. It also can be observed that the outage performance increases linearly with the number of relays (
. It is shown that the analytical results are very close to the simulated ones in the whole SNR region. It also can be observed that the outage performance increases linearly with the number of relays (![]() ) although we use only one relay. The outage performance becomes decreases with the increase of the order of selected relay
) although we use only one relay. The outage performance becomes decreases with the increase of the order of selected relay![]() . From Figure 1, it can be seen that the outage performance improves as we move from the worst relay to the best relay. Moreover, since
. From Figure 1, it can be seen that the outage performance improves as we move from the worst relay to the best relay. Moreover, since![]() , the error floors obviously emerge, which show the accuracy of our analysis.
, the error floors obviously emerge, which show the accuracy of our analysis.
Figure 2 shows the outage performance versus SNR for different fading para-
![]()
Figure 1. Outage probability versus SNR for different values of ![]() and
and![]() .
.
meter of![]() ,
, ![]() and
and![]() . It can be seen that the simulation results closely match with the analytical ones. As expected, improved fading parameter in two links can lower the outage probability. From the results, we can see that the channel gain of link has an important role in the outage performance. When
. It can be seen that the simulation results closely match with the analytical ones. As expected, improved fading parameter in two links can lower the outage probability. From the results, we can see that the channel gain of link has an important role in the outage performance. When![]() , outage performance converge to an error floor and thus provide a zero diversity gain. Moreover, we found that the effect of increasing
, outage performance converge to an error floor and thus provide a zero diversity gain. Moreover, we found that the effect of increasing ![]() for the same fading parameter
for the same fading parameter ![]() in Figure 2 could not be distinguished.
in Figure 2 could not be distinguished.
5. Conclusion
The ![]() worst relay scheme was studied for the full-duplex relay channel over Nakagami-m fading channels. We derived closed-form expressions and approximate performance for the outage probability, and showed their well- matching behavior with the results obtained via simulation. From the analysis, we can conclude that the outage performance can be improved by increasing the number of relays. Moreover, the diversity order is zero when
worst relay scheme was studied for the full-duplex relay channel over Nakagami-m fading channels. We derived closed-form expressions and approximate performance for the outage probability, and showed their well- matching behavior with the results obtained via simulation. From the analysis, we can conclude that the outage performance can be improved by increasing the number of relays. Moreover, the diversity order is zero when ![]() and
and ![]() when
when![]() , and the impact of
, and the impact of ![]() can be negligible.
can be negligible.