Received 31 May 2016; accepted 8 August 2016; published 11 August 2016

1. Introduction
The Burgers equation was first presented by Bateman [1] and treated later by J. M. Burgers (1895-1981) then it is widely named as Burgers’ equation [2] . Burgers’ equation is nonlinear partial differential equation of second order which is used in various fields of physical phenomena such as boundary layer behaviour, shock weave formation, turbulence, the weather problem, mass transport, traffic flow and acoustic transmission [3] [4] . In addition, the two dimentional Burgers’ equations have played an important role in many physical applications such as investigating the shallow water waves and modeling of gas dynamics [5] [6] . In order to a great applications for burgers’ equations many researchers have been interested in solving it by various techniques. Analytic solution of one dimensional Burgers’ equation are get by many standard methods such as Backland transformation method, differential transformation method and tanh-coth method [6] , while an analytical solution of two dimensional Burgers’ equations was first presented by Fletcher using the Hopf-Cole transfor- mation [7] . The finite difference, finite element, spectral methods, Adomian decomposition method, the varia- tional iteration method, homotopy perturbation method HPM and Eulerian-Lagrangian method gave an nu- merical solution of Burgers’ equations [3] [8] - [15] .
Recently, the OHAM was proposed by Marinca and Herisaun [16] - [19] . OHAM is independent of the existence of a embedding parameter in the problem then overcome the limitations of perturbation technique. However, OHAM is the most generalized form of HPM as it uses a general auxiliary function H(p). This method has been studied by a number of researchers for solving linear and nonlinear partial differential equations [20] - [23] . In [24] - [27] proved OHAM is more efficient to solve Burgers’ equations. In 2006, a new method by Daftardar-Gejji and Jafari for solving nonlinear functional appeared [28] . Convergence of it has been proved in [29] . This method is named later as Daftardar-Jafari method DJM in [30] . J. Ali et al. used DJM in the OHAM for solving non-linear differential equations and they named this method as OHAM with DJ polynomials OHAM-DJ [30] [31] . In 2016, OHAM-DJ has been used to solve linear and nonlinear Klein-Gordon equations [32] . The motive of this paper is to show the efficiency of OHAM-DJ for solving the system of Burger’s equations. We consider the system of Burger’s equations as the following [11] :
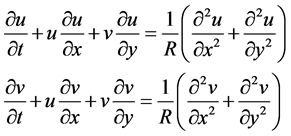 (1.1)
(1.1)
with the initial conditions:
 (1.2)
(1.2)
and the boundary conditions:
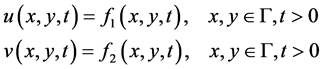 (1.3)
(1.3)
where  and
and 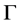 is its boundary,
is its boundary,  and
and 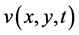 are the velocity components to be determined,
are the velocity components to be determined, 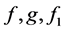 and
and  are known functions and R is the Reynolds number.
are known functions and R is the Reynolds number.
This paper is organized into three sections. In Section 2 methodology of OHAM-DJ is presented. In Section 3 application of this method is solved and absolute error of approximate solutions of proposed method is com- pared with exact solutions. In all cases the proposed method yields better results.
2. Methodology of OHAM-DJ
Consider (1.1) and let
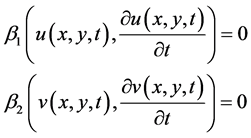 (2.1)
(2.1)
where 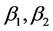 are boundary operators.
are boundary operators.
According to the basic idea of OHAM [16] , we can construct the optimal homotopy:
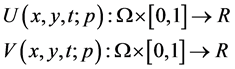 (2.2)
(2.2)
which satisfies
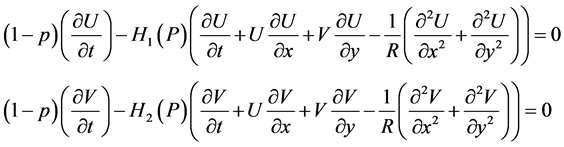 (2.3)
(2.3)
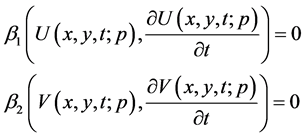 (2.4)
(2.4)
where 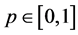 is an embedding parameter while
is an embedding parameter while ![]() and
and ![]() is initial approximation of Equation (1.1) which satisfies the boundary condition,
is initial approximation of Equation (1.1) which satisfies the boundary condition, ![]() and
and ![]() are nonzero auxiliary functions for
are nonzero auxiliary functions for![]() ,
,![]() and
and![]() . Clearly, When
. Clearly, When ![]() and
and![]() , it holds that
, it holds that![]() ,
, ![]() and
and![]() ,
, ![]() respectively. Therefore, as p change from 0 to 1, the solution
respectively. Therefore, as p change from 0 to 1, the solution ![]() and
and ![]() varies from
varies from ![]() to
to ![]() and
and ![]() to
to ![]() respectively, where the initial approximations
respectively, where the initial approximations ![]() and
and ![]() are obtained from (2.3) and (2.4). Now, choosing The auxiliary functions
are obtained from (2.3) and (2.4). Now, choosing The auxiliary functions ![]() and
and ![]() as the form
as the form
![]() (2.5)
(2.5)
where, ![]() are constants to be determined later. Assume that the solutions of (1.1) has the form:
are constants to be determined later. Assume that the solutions of (1.1) has the form:
![]() (2.6)
(2.6)
The nonlinear terms
![]() (2.7)
(2.7)
are decomposed as
![]() (2.8)
(2.8)
where ![]() are (DJ) polynomials,
are (DJ) polynomials,
![]() . For simplicity these polynomials are expressed as:
. For simplicity these polynomials are expressed as:
![]()
Then,
![]() (2.9)
(2.9)
Substiting, (2.5),(2.6), (2.7) and (2.9) into (2.3), and comparing the coefficients of like powers of p, we get
![]() (2.10)
(2.10)
The convergence of (2.6) depend upon the auxiliary constants ![]() and
and![]() , which known convergence control parameters or optimal convergence control parameters [16] , if it is convergent at
, which known convergence control parameters or optimal convergence control parameters [16] , if it is convergent at ![]() we have
we have
![]() (2.11)
(2.11)
Substituting (2.11) into (1.1) we get the residuals ![]() and
and![]() ,
, ![]() these parameters can be optimal identified by various methods [16] [20] [33] . Optimization method is one of theses methods to find out the optimal convergence control parameters by means of the minimum of the squared residuals.
these parameters can be optimal identified by various methods [16] [20] [33] . Optimization method is one of theses methods to find out the optimal convergence control parameters by means of the minimum of the squared residuals.
3. Numerical Examples
In this section, two numerical examples are used to prove the efficiency and the accuracy of the method which we proposed for the system of Burgers’ equations.
3.1. Example 1
Consider the system of two dimensional of Burgers’ equations with the initial conditions as following [34]
![]() (3.1)
(3.1)
with the initial conditions:
![]() (3.2)
(3.2)
The exact solutions are
![]() (3.3)
(3.3)
Accordance to the methodology of OHAM-DJ, ![]()
![]() (3.4)
(3.4)
Their solutions are
![]() (3.5)
(3.5)
Then,
![]() (3.6)
(3.6)
By substituting (3.6) into (3.1) we get the residuals and using the optimization method we have computed that ![]() and
and![]() . Finally, putting the values of
. Finally, putting the values of ![]() and
and ![]() into (3.6), to get the approximate solutions (Tables 1-3, Figure 1 and Figure 2).
into (3.6), to get the approximate solutions (Tables 1-3, Figure 1 and Figure 2).
![]()
Figure 1. Approximation solutions by OHAM-DJ of example 1, t = 0.01,![]() .
.
![]()
Figure 2. Exact solutions of example 1, t = 0.01,![]() .
.
![]()
Table 1. Comparison of OHAM-DJ solutions with exact solutions at mesh point x = 2, y = 1 (example 1).
3.2. Example 2
We consider the following two-dimensional Burgers’ equations [34]
![]() (3.7)
(3.7)
On square domain![]() , with the initial condition:
, with the initial condition:
![]() (3.8)
(3.8)
for which the exact solution is![]() . Where the
. Where the ![]() and
and ![]()
in (1.1) are symmetry in this example, ![]() and the initial condition are symmetry also.
and the initial condition are symmetry also.
![]()
Table 2. Comparison of OHAM-DJ solutions with exact solutions at mesh point x = 1, y = 2 (example 1).
![]()
Table 3. Comparison of OHAM-DJ solutions with exact solutions at mesh point x = 1.5, y = 2 (example 1).
![]() (3.9)
(3.9)
Their solutions are
![]() (3.10)
(3.10)
![]() (3.11)
(3.11)
Substituting (3.11) into (3.7) we get the residuals and using the optimization method we have computed that![]() . Finally, putting the values of
. Finally, putting the values of ![]() into (3.11) to get the approximate solutions (Table 4 and Table 5, Figure 3 and Figure 4).
into (3.11) to get the approximate solutions (Table 4 and Table 5, Figure 3 and Figure 4).
4. Conclusion
In this work, the OHAM-DJ is applied to obtain numerical solutions of the system of Burgers’ equations. The method is efficient and easy to implement where the first or second order solutions rapidly converges to the exact solutions. Furthermore, OHAM-DJ does not need any discretization in time or in space. Thus the solutions of system of Burgers’ equations are not influenced by computer round off errors. The method can be easily
![]()
Table 4. Comparison of OHAM-DJ solutions with exact solutions at mesh point x = 1, y = 1, ![]() (example 2).
(example 2).
![]()
Table 5. Comparison of OHAM-DJ solutions with exact solutions at mesh point x = 1, y = 1.5, ![]() (example 2).
(example 2).
![]()
Figure 3. Approximation solutions by OHAM-DJ of example 2, t = 0.01,![]() .
.
![]()
Figure 4. Exact solutions of example 2, t = 0.01,![]() .
.
extended to other nonlinear equations. Nutshell, OHAM-DJ is a better numerical method for solving nonlinear equations.
Acknowledgements
This paper was funded by King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology (KACST) in Saudi Arabia. The authors therefore, thank them for their full collaboration.