Optimization of Ceric Ammonium Nitrate Initiated Graft Copolymerization of Acrylonitrile onto Chitosan ()
1. Introduction
Chitosan is a unique basic polysaccharide and partially deacetylated polymer of glucosamine obtained after alkaline deacetylation of the chitin [1]. It consists of mainly of β-[1-4]-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucose units and is the second most abundant biopolymer on earth after cellulose, widely distributed in crustacean shells and cell walls of fungus [2,3]. Chitosan is soluble in dilute acids. The solubility occurs by the protonation of the – NH2 function on the C-2 position of the D-glucosamine repeat unit, where by the polysaccharide is converted to a polyelectrolyte in acidic media. Chitosan is the only pseudonatural cationic polymer and thus it finds applications in the wastewater treatment. A few review articles on the potential applications of chitosan for pharmaceutical, veterinary medicine, and biomedicine. Chitin and chitosan are widely used for wastewater treatments of polymers experimentally proven that decrease the chemical oxygen demand, total nitrogen and destroy the microbial population [4,5]. However, due to its low mechanical strength and flexible behaviour, chitosan has limited application of water treatment, while addition of synthetic polymers increased its properties tremendously. Besides these applications chitosan has few drawbacks such as acidic solubility, low thermal and mechanical stability. To improve these drawbacks, chitosan can be modified physically and also chemically. Now days, a lot of attention has been paid on chemical modification of chitosan. One such important modification is graft copolymerization [6-9]. Of all possible modifications, graft copolymerisation of vinyl monomers onto natural polysaccharides is quite promising [10,11].
Grafting onto chitosan and its derivatives has been the thrust of researchers. In chitosan, both hydroxyl and amino groups are possible sites for the reaction to incorporate new and desired functional groups. Graft copolymerization of synthetic polymers onto chitosan can introduce desired properties and enlarge the field of the applications by choosing various types of side chains.
In recent years, a number of initiator systems such as APS (ammonium per sulphate), PPS (potassium per sulphate), CAN (ceric ammonium nitrate), FAS (ferrous ammonium sulphate) have been developed to initiate graft copolymerization [6,12-14]. Many investigations have been carried out on the grafted copolymerization of chitosan and it is considered to be a promising approach for designing a wide variety of molecular matrices. Graft copolymerization of acrylamide on chitosan using ammonium persulfate as an initiator, was prepared [15]. The effect of temperature, pH of the medium and concentrations of initiator, chitosan and acrylamide on grafting kinetics and efficiency were established. Graft copolymerization of mixtures of acrylic acid and acrylamide onto chitosan using potassium per sulphate as initiator and methylenebisacrylamide as a cross-linker was carried [16]. Semi-interpenetrating polymer network hydrogel was pre-pared to recognize hemoglobin, by molecularly imprinted method, in mild aqueous media of chitosan and acylami-de in the presence of N, N’-methylenebisacrylamide as the cross linking agent [17].
In the present study chitosan has been graft copolymerized with acrylonitrile with an aim to develop a product, which could be used for wastewater treatment. The effect of reaction conditions such as monomer concentration, initiator concentration and time of reaction have been optimized at constant temperature of 70˚C.
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Materials
Chitosan was received from India seafoods, Cochin. Ceric ammonium nitrate, concentrated nitric acid and acrylonitrile were of analytical grade and used as received. The copolymer was characterized using FTIR, TGA, DSC, SEM and XRD. Chitosan-g-polyacrylonitrile was prepared in the presence of UV light assisted oxidative polymerisation using CAN as an initiator.
2.2. Preparation of Copolymer
A 2% w/v solution of chitosan was prepared in 2% aqueous acetic acid. A solution of 0.1 M CAN in 10 ml of 1 N nitric acid was added followed by a known amount of acrylonitrile drop by drop with continuous stirring. After a specified time, the reaction was stopped and the product was precipitated using sodium hydroxide solution with vigorous stirring. The precipitate was washed with distilled water for several times and filtered. The percent grafting yield (GY%) and percent grafting efficiency (GE%) were calculated as follows:
Grafting efficiency (GE%) = 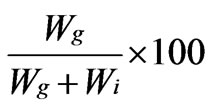
Grafting yield (GY%) =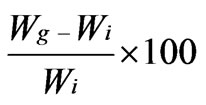
whereWg = weight of grafted copolymer;
Wi = weight of homopolymer (polyacrylonitrile), respectively.
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. FTIR Spectral Studies
Fourier Transform infrared (FTIR) spectral analyses of the copolymer samples were performed with Thermo Nicolet AVATAR 330 spectrophotometer in 4000 - 400 cm–1 wave length range, using KBr pellet method.
2.3.2. Thermo Gravimetric Analysis
Thermogravimetric analysis was conducted to measure the thermal weight loss of the copolymers on a SDT Q600 V8.0 Build 95 instrument at a heating rate of 100˚C per minute in nitrogen atmosphere. The weight losses at different stages were analysed.
2.3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
The differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) was used to examine the thermal property of the copolymers. The measurements were performed with NETZSCH DSC 200 PC in a pan Al, pierced lid in the N2 atmosphere at a heating rate of 100 K/min. The results were recorded and analysed.
2.3.4. X – Ray Diffraction Studies
X–ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of the Chitosan-gacrylonitrile copolymer was studied using X-ray powder diffractometer (XRD–SHIMADZU XD–D1) using a Ni–filtered Cu Ka X–ray radiation source. The relative intensities were recorded within the range of 100 -900 (2q) at a scanning rate of 50 min–1.
2.3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
The surface morphology and cross sectional morphology of the copolymer was observed with scanning electron microscopy to verify the compatibility. For the analysis, the samples were cut into pieces of various sizes and wiped with a thin gold-palladium layer by a sputter coater unit (VG-microtech, UCK field, UK) and the cross section topography was analysed with a Cambridge stereoscan 440 scanning electron microscope (SEM, Leica, Cambridge, UK).
3. Results and Discussion
The grafting of zwitterionic monomer, N, N-dimethyl-Nmethacryloxy-N-(3-sulfopropyl) ammonium onto chitosan using CAN as redox initiator in acetic acid solution under nitrogen atmosphere was investigated [18]. The effect of reaction condition on the rate of poly (acrylonitrile) grafting onto chitosan under inert atmosphere using CAN as initiator was studied [19]. CAN is also reported as a suitable initiator for grafting poly (acryloamide), acrylic acid, poly (4-vinylpyridine) onto chitosan [6].
3.1. Mechanism
Graft copolymerization of vinyl monomers onto chitosan is also carried out using redox initiator system such as CAN. This system is used to produce free radical sites which may improve the properties of chitosan material and hence the graft polymerization of acrylonitrile onto chitosan at 60˚C by using CAN as a initiator is reported. The mechanism as per Don et al. [12]
Step I: Initiation
1) Direct oxidation
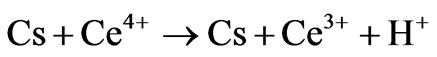
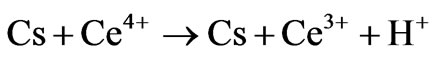
2) Formation of complex
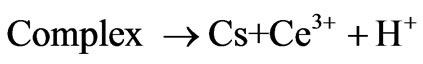

where Cs is chitosan chain, Ce4+ and Ce3+ are ceric and cerous ions, respectively. Cs is chitosan chain radical and M is monomer acrylonitrile.
Step II: Propagation
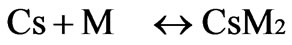
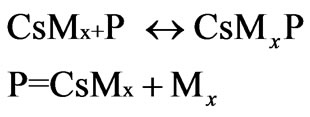
where CsMX is a polyacrylonitrile chain grafted onto with chitosan.
Step 3: Termination
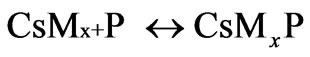
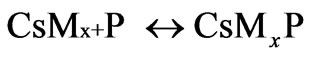
where P is the propagating polymer chains
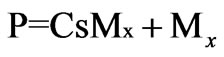
Step 4: Chain transfer
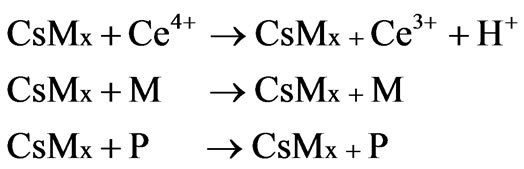
The monomer conversion was found to be between 70 and 80% after 2h of reaction at 60˚C. The grafting efficiency increased with the increase in the amount of chitosan.
3.2. Effect of Reaction Time
The effect of reaction time on copolymer formation was studied by keeping the initiator concentration, monomer (fixed weight of chitosan and polyacrylonitrile, 0.5 g) amount and temperature (70˚C), constant. The yield of copolymer, grafting efficiency and grafting yield have been represented in Figure 1. There is no significant change in graft efficiency with increase in reaction time, whereas, grafting yield is significantly changed with reaction time. As a result, the maximum yield has been found at 55 min. Hence 55 min was found to be rate of grafting [20, 21].
3.3. Effect of Initiator (CAN) Concentration
Figure 2 shows the effect of concentration of CAN on the graft copolymerization of polyacrylonitrile onto chitosan by keeping other reaction conditions constant. Both graft yield and grafting efficiency showed an increase with increase in initiator concentration at first, followed by a decrease with further increase of the initiator concentration. The increase of grafting percentage may be ascribed to the increase of macro radicals generated by the attack of more CAN for the saccharide unit of chitosan and therefore, the more active sites of chitosan reacting with polyacrylonitrile. The maximum yield was found at initiator concentration 1.0 g/10 ml of HNO3, hence 1.0 g was found to be the optimum initiator concentration in this grafting reaction at 70˚C. It was found at lower level of CAN concentration grafting yield is very low, comparatively grafting
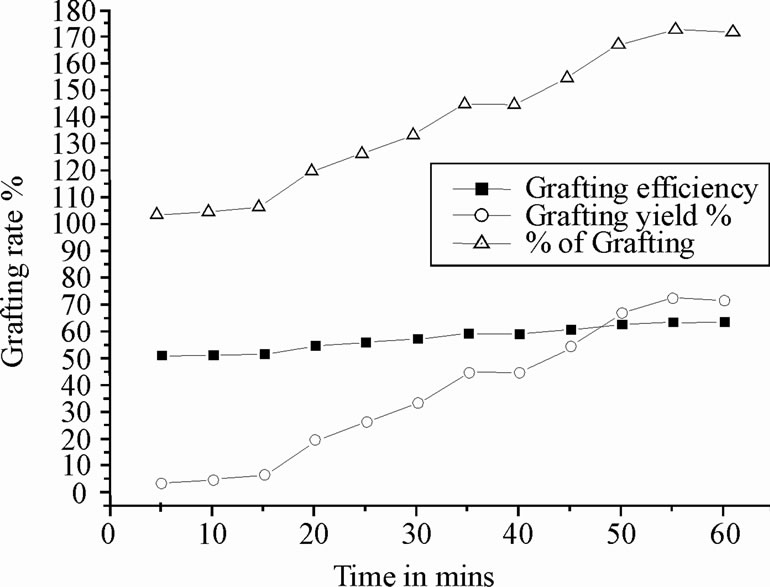
Figure 1. Determination of grafting rate with time
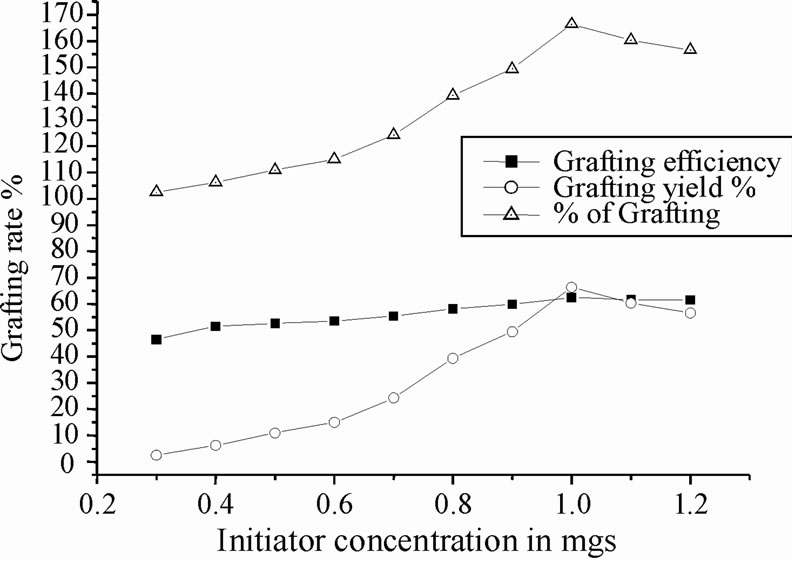
Figure 2. Effect of initiator concentration on copolymerization.
efficiently is moderate. Further increase of initiator concentration resulted in a decrease of grafting efficiency and grafting yield. It might be due to increase in the number of chitosan free radicals terminated prior to polyacrylonitrile addition [20,22].
3.4. Effect of Polyacrylonitrile Concentration
Figure 3 represents the effect of concentration of polyacrylonitrile on copolymerization reaction (grafting parameters). The grafting efficiency and grafting yield were found to increase with increasing polyacrylonitrile concentration. The maximum grafting yield has been found at 0.75 mol/L, and then decreased. This decreasing behavior might be because increasing the polyacrylonitrile concentration causes reduction in the active site of chitosan polymer. Additionally, higher the polyacrylonitrile concentration, the primary radicals attack the monomer instead of reacting with the backbone polymer. The excess polyacrylonitrile concentration will shield the graft copolymer which might be inhibiting the rate of copolymerization. Hence, 0.7 g of polyacrylonitrile was found to be the optimum concentration in this grafting reaction at standard 70˚C [20].