Deficit in Phonological Working Memory: A Psycholinguistic Marker in Portuguese Speaking Children with Specific Language Impairment? ()

1. Introduction
Among the disorders of language, the disorder known as Specific Language Impairment (SLI) has aroused the interest of many researchers due to its peculiarity. It refers to a severe difficulty in developing language skills in the absence of hearing impairments, motor disorders, mental retardation, brain damage, broad development disorders, acquired brain injuries, restricted social interaction or significant emotional disorder (Leonard, 1998; Bishop & Leonard, 2001). The clinical manifestations in the sphere of language are heterogeneous and mutable, varying with the severity of each case and including one or more subsystems of language and comprehension (Hage & Guerreiro, 2010).
The language alterations in this disorder have been widely discussed and classified into different taxonomies (Allen & Rapin, 1988; Korkman & Häkkinen-Rihu, 1994; Conti-Ramsden, 2000). However, what caught the attention of researchers, much more than the classification of symptoms, is the nature of the linguistic deficit of SLI. In general, two major research groups can be distinguished: one that assigns the linguistic damage in children with SLI to a specific deficit in linguistic knowledge, in particular grammar (Yang, 2004), and another that attaches it to a deficit in processing verbal information. In the latter, there is the possibility that language difficulties may be due to a perceptual deficit (Tallal, 2000) and a deficit in phonological processing, specifically in phonological working memory (PWM). Some research has demonstrated that subjects with SLI have deficits in short-term memory skills and the phonological component of working memory, which leads them to have semantic and syntactic difficulties, both in expression and comprehension (Montgomery, 2003; Dodwell & Bavin, 2008). This study will be focused on this latter hypothesis.
The working memory is a system of processing and short-term storage of information allows thinking, learning and communication. It involves the temporal storage and manipulation of the necessary information required to perform complex cognitive activities (Baddeley, 2006; Baddeley, Andersen, & Eysenck, 2011).
The phonological component of the working memory, in other words—the PWM, has a crucial role in the acquisition of language skills of children, who retain the principal lexical items that formulate the sentence in an active form, until the syntactic rules are applied and the articulatory speech production is planned. Therefore, a deficit in this memory, which affects the temporary maintenance of linguistic information, results in sentences that are less complex syntactically, such as shorter sentences with less lexical diversity (Adams & Gathercole, 1995). There is also evidence that the PWM is related to learning to read (Conti-Ramsden, Botting, Simkin, & Knox, 2001; Archibald & Gathercole, 2006).
Phonological working memory is implicated as a possible clinical hallmark of specific language impairment. This deficit would be one of the factors that affect language acquisition, the morphosyntactic performance and sentence comprehension in this population (Montgomery, Magimairaj, & Finney, 2010; Alt, 2011).
This study has hypothesized that most cases of SLI show deficits relating to PWM, particularly those that negatively affect the expression and understanding of language, resulting in implications for reading and writing for these children. The aim of this study was to compare the performance on a PWM test in children with SLI and normal children and verify whether there is an association between the performance on this test and a test that assesses reading and writing.
2. Methodology
This work was carried out in the Speech Therapy Clinic of the University of São Paulo (USP), SP, Brazil after being approved by the Ethics Committee of the same university (protocol 80/2009). Parents agreed to their children participating in this study, having read and signed the informed consent form.
3. Participants
We selected 44 school children, whose ages ranged between seven and ten years old, of both sexes. Twenty-two of them presented with SLI—Study Group (SG)—and 22 had typical language development (TLD)—Control Group (CG). They were matched according to chronological age and school grade.
The children in the SG were selected from patients diagnosed with SLI in the Speech Therapy Clinic of the University—USP. Inclusion criteria were the diagnosis of SLI, according to the criteria proposed by Leonard (1998), described below:
• Have performance in language tests and analysis of samples of oral language less than that expected for the mental and chronological age, covering expression and/or understanding;
• Have hearing threshold within normal limits;
• Intellectual quotient equal to or above 85, with a discrepancy between verbal and nonverbal cognitive skills;
• Absence of behavioral problems and/or emotional problems;
• Absence of classical neurological symptoms such as cerebral palsy, intellectual impairment, children’s aphasia (acquired).
The children of the CG were selected from two elementary schools. Inclusion criteria for subjects in the CG were:
• No history of aberrations in, or complaint about the development of oral language and hearing, and a school performance compatible with the age and education;
• Performance in a phonology test (Wertzner, 2004) and a reading and writing test (Stein, 1994) compatible with the chronological age.
To meet the inclusion criteria, the teachers were questioned about possible deficits in the oral language, listening and school performance of their students. Those who had a history or complaint of difficulties in one or more of these factors were excluded from the sample.
4. Instruments and Procedures
After verification of the inclusion criteria, all subjects were subjected to the following procedures:
• Test of Phonological Working Memory—TPWM (Hage & Grivol, 2009), which aims to assess the number of items that each child is able to retain and retrieve from memory immediately after oral presentation of a list of words and digits in the forward and reverse form. The scores are calculated as follows: 2 points when the repetition is correct the first time, 1 point when correct the second time, and 0 when not correct in two attempts. To be considered an appropriate response, the repetition should be identical to that said by the evaluator, with the evaluator being allowed to repeat every word only once.
The presence of phonological simplifications in the case of children with SLI has been previously noted in the answer sheet and was not considered errors of repetition. Previously, the subjects with SLI submitted to the phonology test of the ABFW (Wertzner, 2004) to determine possible phonological disorders had these phonological processes considered during analysis of the responses.
• Test Analysis of Reading and Writing (Teste de Análise de Leitura e Escrita—TALE) developed by Toro & Cervera (1990), translated, adapted and standardized for the Brazilian population by Anderle (2005). This instrument can provide data that can identify evolutionary characteristics of reading and writing at different levels of education. For reading, the evaluation included only the subtests of reading text and reading comprehension, and for the evaluation of writing the subtests of dictation and spontaneous writing were used.
Qualitative analysis and statistical analysis was carried out between the groups. For statistical analysis we used the Chi-square test. For analysis and discussion of the results, a level less than or equal to 0.05 was considered significant.
5. Results
Table 1 lists the 22 children with SLI, showing age, gender and the occurrence of familial history.
The study and control groups were compared using the results of the PWM, as determined by the TPWM and reading and writing through the TALE test.
Figure 1 shows the occurrence (in percent) of alteration in both groups as a result of PWM ability and Figure 2 shows the occurrence (in percent) of alteration in both groups in reading and writing (TALE test).
The differences between the subjects with SLI and TLD were statistically significant in the repetition of nonwords (p = 0.00000005), the digits in direct order (p = 0.00046799) and digits in reverse order (p = 0.00176634).
The differences between the subjects with SLI and TLD were statistically significant on the reading test
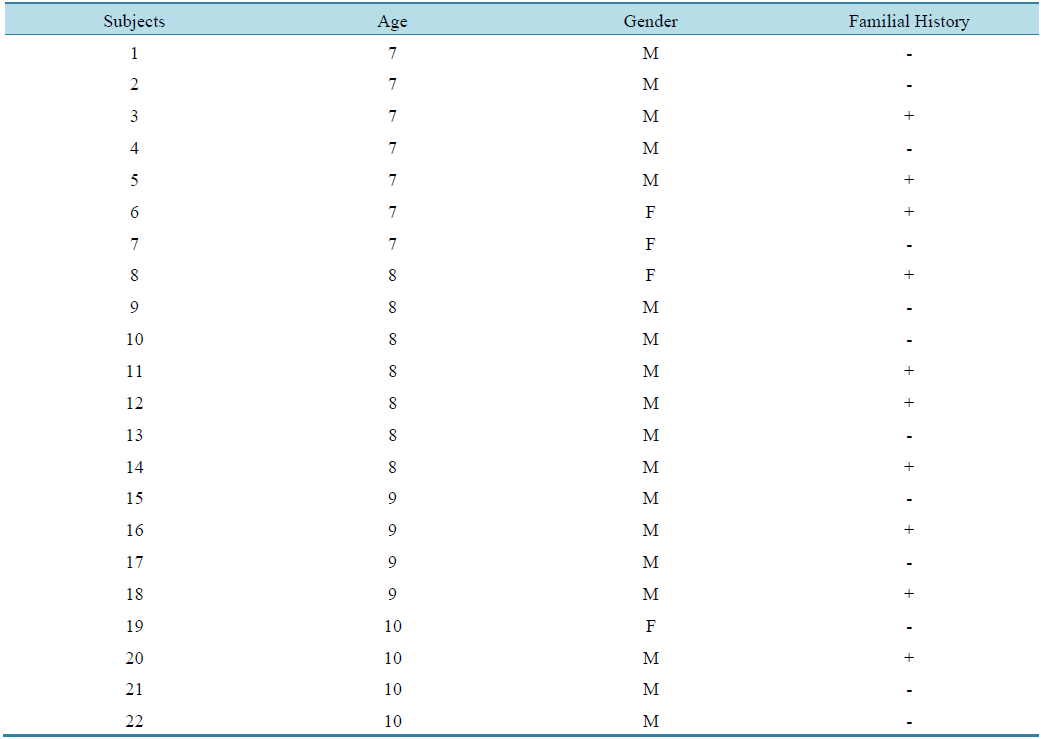
Table 1. Description of the subjects with SLI age, gender and occurrence of family history.
Legend: M = male; F = female; + = presence; - = absence.
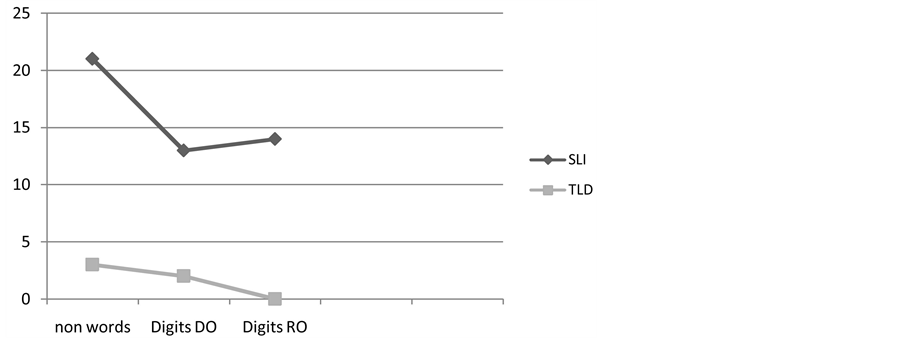
Figure 1. Comparison between the experimental and control groups in PWM test. Legend: DO: direct order; RO: reverse order; SLI: specific language impairment; TLD: typical language development.
(p = 0.00000001), reading comprehension (p = 0.00000014), dictation (p = 0.00000001) and writing (p = 0.00000003).
Statistical associations were determined by using the Chi-square test to verify whether there was a relationship between the performance achieved in the test for PWM and evidence of reading and writing (TALE test) in subjects with SLI.
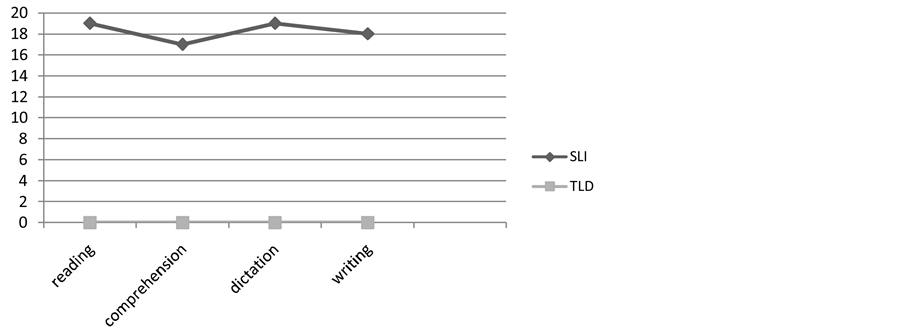
Figure 2. Comparison SG and CG in TALE test.
Table 2 and Table 3 show these statistical associations. p values were statistically significant between the nonword repetition (PWM test) and reading and nonword repetition and dictation/writing of the TALE test.
6. Discussion
Research with subjects with SLI exposed to different languages can contribute significantly to the understanding of the linguistic deficit in these disorders.
The children with SLI that we evaluated were between the ages of seven and 10 years old, as were the CG. Unfortunately, in Brazil, the diagnosis of SLI is delayed; many children come to the clinics after seven years of age, presenting with oral language difficulties, and consequently, in most cases, already showing problems in school performance. The reason for this late diagnosis is almost always a lack of knowledge among health professionals and early childhood teachers about the differences in child development that would result in a specific language disorder, such as SLI.
Of the 22 children with SLI (Table 1), 17 were males and five females, 10 of whom had a family history of language disorders, pointing to evidence of a strong influence of genetic factors in cases of SLI. Stromswold (1998) reviewed 14 studies that investigated the incidence of positive data for family history of language disorders in children with SLI, and the median incidence was 39% (range 24% to 77%). Our study showed that more than 40% of children had a history of language impairment in the family. Although the high incidence of family history in SLI can be explained by other factors, environmental and genetic studies of twins with SLI have shown that genetic factors are probably more important (Bishop, 2002).
The importance of phonological working memory in language development, because it allows the child to analyze the structural properties of language to which he is exposed, is well known. The PWM has a critical role in processing language during the early stages of development of language (Gonçalves, 2002). Many studies proved the existence of a correlation between linguistic knowledge, especially lexical and phonological, and PWM in typically language developing Brazilian Portuguese and English speaking children (Rodrigues & BefiLopes, 2009).
It is also well known that there is a strong relationship between the PWM difficulties and SLI. Language disorders may have a close correlation with memory difficulties, specifically the working memory. Several studies have suggested that the language difficulties in individuals with SLI are related to a deficit in PWM (Montgomery, 2003; Archilbald & Gathercole, 2006; Marton, Schwartz, Farkas, & Katsnelson, 2006; Dodwel & Bavin, 2008; Montgomery, Magimairaj, & Finney, 2010). The limitation in the capacity of working memory results in breaks within and between different linguistic domains, increasing the demand necessary for semantic and syntactic processing, resulting in errors in these and or other areas.
With regard to phonology, a disorder of the PWM would be responsible for impairment in the learning of the phonological form of words, impeding the learning of new words, as this type of memory functions as a mediator for the construction of phonological representations in permanent, long term memory (Archilbald & Gathercole, 2006). According to one study, the PWM deficit is related to the severity of phonological disorders, and the knowledge of this relationship is important to outline the process origins of the changes in speech

Table 2. Statistical associations between the PWM test and reading tests in the subjects of SG.

Table 3 . Statistical association between PWM test and writing test in the subjects of SG.
development (Linassi, Keske-Soares, & Mota, 2005). In this line of investigation, one researcher investigated some aspects of the PWM in preschool children with SLI. The results confirmed the plausibility of the hypothesis that alterations in phonological representations occur due to change in this type of memory in children with SLI (Martinez, Bruna, Guzman, Herrera, Valle, & Vásquez, 2002). Thus, children with SLI may have difficulties in the nature of phonological representations and the ability to manipulate phonological information in the PWM, demonstrating that the phonological representation is not well established.
In this study, data analysis showed that children in the SG showed a worse performance than the CG in all the tests evaluating the PWM (Figure 1), indicating that Portuguese speaking children with SLI have a significant gap in the PWM and that gap can explain the difficulties with oral language. The nonword test registered the largest difference between the performance of children in the SG and CG, and is therefore a good indicator of difference.
Among the procedures that evaluate the PWM, the repetition of nonwords has been the most reliable, as through it one can see how accurately the child repeats forms not part of her natural, everyday repertoire, in the absence of lexical support. The repetition of nonwords may be a valuable clinical tool for identifying language disorders (Dollaghan & Campbell, 1998; Weismer, Tomblin, Zhang, Buckwalter, Chynoweth, & Jones, 2000; Munson, Kurtz, & Windsor, 2005) but should not be seen as an isolated indicator, as difficulties of this kind of repetition are not specific to children with SLI. Children with other language disorders, who had similar patterns in lowered cognitive function, demonstrated a low score in repeated nonwords when compared to their TLD peers, giving proof that nonwords testing should be another tool within a set of diagnostic tests.
The repetition of nonwords has been a neuropsycholinguistic marker of English and Spanish speaking children with SLI (Conti-Ramsden, 2003; Conti-Ramsden & Hesketh, 2003; Aguado, Cuestos-Vega, Domezáin, & Pascual, 2006; Montgomery & Evans, 2009). On the other hand, research that evaluated 14 children with SLI, whose mother tongue was Cantonese (Chinese dialect spoken in Guangzhou, China) and 30 with TLD found no significant difference between the group with SLI and the TLD group in the repeating nonwords test. The results, unlike those in English, did not suggest problems with PWM in Cantonese speaking children with SLI (Stokes, Wong, Flecher, & Leonard, 2006). It is therefore important to investigate the PWM in children with SLI who spoke other languages, to check the relationship of the PWM and language in question.
The relationship between oral language and written language, including that in Portuguese, is pointed out in several works (França, Wolf, Moojen, & Rotta, 2004; Giangiacomo & Navas, 2008). In our study, the differences between the subjects with SLI and TLD were statistically significant on the reading test, reading comprehension, dictation and writing (Figure 2). Only one of 22 children with SLI had satisfactory performance in all TALE tests, indicating that children with SLI often have academic difficulties. The ccurrence of these difficulties in this population has been described in the literature (Conti-Ramsden, Botting, Simkin, & Knox, 2001; Nicolielo, Fernandes, Garcia, & Hage, 2008; Dockrell, Lindsay, & Connelly, 2009; Nicolielo & Hage, 2011).
Children with SLI are at high risk for academic problems, and this risk increases when verbal comprehension is affected (Simkin & Conti-Ramsden, 2006). It is common for children with SLI manifest problems throughout their schooling, since it may be affected both their emotional and social development, as an academic (Conti- Ramsden, St Clair, Pickles, & Darkin, 2012).
Alterations in the written language are somehow expected in the subjects with SLI, due to the presence of persistent alterations in oral language, mainly related to the phonological aspect, which then damage the development of reading and writing skills. It is noteworthy that the vast majority of errors were phonological simplifications. The few who had no simplifications had a high degree of intelligibility in terms of substitutions and omissions of phonemes or syllables. Learning English, because it is an alphabetic system, depends on the relationship between the letter and the sound and therefore depends on the condition of the phonological system at the time of learning. Thus, the presence of alteration in oral language in English speaking children with SLI.
Statistical analysis (Table 2 and Table 3) showed an association between the repetition of nonwords and proofreading text, dictation and spontaneous writing, suggesting that the difficulties encountered in the field of written language in children with SLI may be connected, even in part, to difficulties in PWM. One study stated that a good PWM is an important factor for ensuring reading comprehension (Giangiacomo & Navas, 2008). The memory capacity predicts performance capacity of the reading comprehension of the subject (Seigneuric, Erlich, Oakhill, & Yuill, 2000; Palladino, Cornoldi, De Beni, & Pazzaglia, 2001; Dockrell, Lindsay, & Connelly, 2009).
Thus, when there are changes in acquisition and development of oral language, particularly with regard to the phonological aspect, this will probably change the skills of reading and writing due to the fact that oral and written language share the same skills required for the processing of linguistic information.
7. Conclusion
Data analysis showed that subjects in the SG performed worse than the CG in all the tests that evaluated the PWM, indicating that Portuguese speaking children with SLI have a significant gap in their PWM and that this gap can explain the difficulties they experience with oral language. The nonwords test showed the largest difference between the performance of children in the SG and CG, being a good marker of difference.
Data analysis showed an association between the nonword repetition test and reading text, dictation and spontaneous writing, suggesting that the difficulties encountered in the field of written language in children with SLI may be connected, even in part, to difficulties the PWM.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financing support from State of São Paulo Research Foundation.