The Cytokinesis-Block Micronucleus Assay on Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes as a Prospective Biological Test-System to Estimate the Influence of Radon on the Human Organism: Recent Progress and Future Prospects ()
1. Radon: Genesis and Genotoxicity
Radon (222Rn) is a naturally radioactive noble gas. It is generated from uranium, a chemical element that is widespread in the earth’s crust. Despite the fact that radon is chemically inert, it seeps into the atmosphere from rocks and soil along with trace amount of uranium. The rate of radon seepage is variable and depends upon the amount of uranium present in the soil [1] . The concentration of radon in outside air is usually lower than indoors [2] . In addition, the concentration of radon in indoor air depends on the permeability of the ground, climatic factors, and the construction and ventilation of the house [3] .
Although radon is a physical agent that is present in the everyday environment of living organisms, it also plays a role in DNA damage. Radon, being electrically neutral, is not itself a potential health threat, but its decay daughter products, 218Po, 214Po, 214Pb, and 214Bi, are electrically charged and can affix themselves to tiny dust or smoke particles in indoor air. These particles can be inhaled into the lung where they may penetrate the epithetlial cells that cover the bronchi and alveoli. These short-lived, unstable decay daughter products (especially 218Po and 214Po) emit alpha particles that can interact with biological tissues in the lungs and induce DNA damage [2] [4] . Radon-induced DNA damage may be carcinogenic [5] .
In addition to its mutagenic potential, radon exposure significantly increases the risk of lung cancer in humans [6] . Comprehensive studies on radon as a mutagenic and carcinogenic agent have been performed in cases of increased concentration in buildings, spas, caves, and underground mines. By measuring radon levels and performing medical examinations, reduced exposure doses of radiation and an important decrease of cytogenetic mutations were shown. Radon induces long-lasting changes in the genomes of living cells. As the most sensitive target of genotoxic agents, DNA may be affected directly or indirectly [4] .
It has been reported that more than 50% of natural radiation sources to which a person is exposed every year consists of radon and its decay daughter products [7] . Therefore, maintaining radon safety is one of the most critical challenges in ecological and genetic toxicology. In addition to using dosimetry methods to evaluate the risk of harmful radiation, the severity of such a risk should be evaluated by biological test-systems, which can evaluate the quality of the environment and its suitability for humans.
2. Micronucleus Assay: Prospective Test-System for the Estimation of Radon Influence
2.1. The Micronucleus Assay Technique
The cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay (CBMN) in peripheral blood lymphocytes is one of the most established in vivo cytogenetic assays in the field of genetic toxicology. Micronuclei (MN) are found in dividing cells that either contain acentric chromosome fragments and/or whole chromosomes that are unable to travel to the spindle poles during mitosis (Figures 1(a) and (b)). By telophase, a nuclear envelope is formed around the lagging chromosomes and fragments, which then uncoil and gradually assume the morphology of an interphase nucleus with the exception that they are smaller than the main nucleus in the cell; hence, they are called “micronuclei” (Figure 2). MN therefore provides a convenient and reliable index of both chromosome breakage and chromosome loss [8] . Occasionally, nucleoplasmic bridges (NPBs) (Figure 1(c)) are observed between the nuclei of a binucleated cell. These are most likely dicentric chromosomes that have been pulled to opposite poles of the cell, with the DNA in the resulting bridge being covered by nuclear membrane. Thus, NPBs in binucleated cells provide an additional and complementary measure of chromosome rearrangement, which can be scored together with the MN count [9] . In addition to MN and NPBs, the CBMN assay detects nuclear buds (NBUDs) (Figures 1(d) and (e)), which represent a mechanism by which cells remove amplified DNA; nuclear buds are therefore considered markers of gene amplification. Finally, information regarding other cellular events, such as the mitotic rate (Figures 3(a)-(c)) and cell death by apoptosis (Figures 3(d) and (e)), can be simultaneously obtained from the same slides [10] .
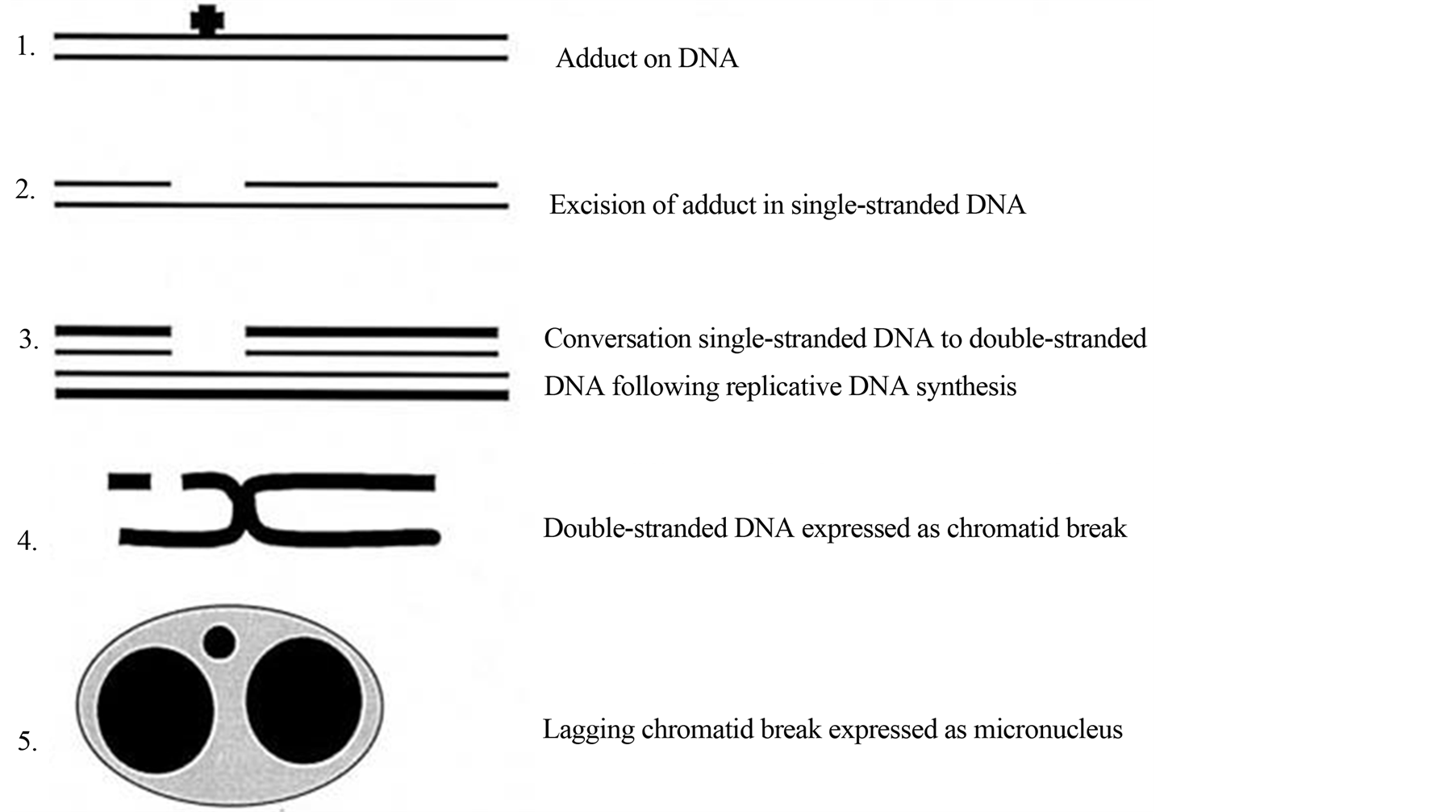
Figure 2. A schematic diagram explaining the mechanism for an excision-repairable DNA lesion to a micronucleus within one division cycle [9] .
For each slide, the following information should be obtained:
1) The number of MN in at least 1000 binucleate (BN) cells should be scored, and the frequency of MN per 1000 BN cells should be calculated;
2) The distribution of BN cells with zero, one, or more MN. The number of MN in a single binucleated cell normally ranges from zero to three in the lymphocytes of healthy individuals but can be greater than three depending on genotoxic exposure and age;
3) The frequency of micronucleated BN cells in at least 1000 BN cells;
4) The frequency of nucleoplasmic bridges in 1000 BN cells;
5) The proportion of mononucleated, binucleated, tri-nucleated and tetra-nucleated cells per 500 cells scored. From this information, the Nuclear Division Index can be derived;
6) The proportion of dead cells due to apoptosis per 500 cells may also be scored on the same slide while scoring the frequency of viable mono-, biand multi-nucleated cells. It is important to note that it is best to skip scoring a cell if one is uncertain on how to classify it [9] .
2.2. Genetic Instability in Uranium Miners
In 1993, a group of Canadian scientists carried out a study showing that lung cancer mortality was increasing more rapidly among Ontario uranium miners than in the surrounding male population. The increase of mortality was clearly related to exposure to radon and its decay daughter products.
The uranium miners in this study were defined as men who had worked for at least two weeks in a uranium mine or who were reported by a uranium mining company to have been exposed to short lived radon progeny underground. In total, 26,674 uranium miners including 1344 uranium mill workers were identified. There were 1359 uranium miners who also worked in uranium mines outside Ontario. These miners were excluded from the study because their exposure data were not available to us. Another 558 uranium miners who also mined asbestos were excluded to remove the confounding factor of asbestos-exposure. Another 1613 men who either worked in jobs on the surface where there was no exposure or who did not have their exposure recorded were also excluded from the analysis. Fifty-eight women were excluded from the analysis and another 1740 men were excluded because their dates of birth were either missing or were erroneous. Thus, 21,346 male uranium miners remained in the study. Deaths were registered by linking the list of miners from the Canadian Mortality Database of deaths that occurred between 1955 and 1986.
We showed that exposure to short-lived radon progeny contributed to increased mortality from lung cancer in Ontario uranium miners. An association between lung cancer mortality and exposure to short-lived radon progeny was revealed as well. The excess relative risk of lung cancer resulting from exposure to short-lived radon progeny was greatest in miners under the age of 55 and least in miners over the age of 65. The relative risk was greater five to 14 years after exposure than in subsequent years [11] .
Mészáros et al. [12] reported increased chromosomal damage, such as dicentric chromosomes and acentric fragments, in Hungarian uranium miners many years after they finished underground work. In the group of miners who finished their work 14 - 23 years ago, the frequency of dicentrics was still above 50% of the original value (no statistically significant difference), whereas the frequency of acentrics was approximately 25% of the original value (a highly significant reduction but still more than would be expected assuming a half-life of 1 - 3 years). In a study on German uranium miners, Kryscio et al. [13] did not find enhanced frequency of MN-containing lymphocytes 7 - 30 years after the miners finished underground work, but they did discover a higher percentage of micronuclei originating from acentric fragments. Additionally, no correlation between frequency of MN-containing cells and radon exposure (given in working level month) was found in former German uranium miners [14] . MN can be recognised after FISH with a centromere-specific DNA probe [15] [16] .
In a recent study, a group of Czech scientists analysed samples of 60 uranium miners with an average age of 50 years using CBMN and FISH. There were no significant differences in the number of centromere-positive MN compared to the control group, but the number of centromere-negative MN (containing acentric fragments) significantly differed (p ˃ 0.05, 34% ± 38% versus 12% ± 21%). In addition, another study found a correlation between the frequency of MN-containing cells and the time since last exposure in the mines, i.e., since finishing work underground (p ˃ 0.05) [17] .
2.3. The Risk of Radon Radiation in Coal Mines
Coal is one of the most widespread minerals used for energy generation. However, its extraction and use are an important pollution factor that represents a major threat for human health. During coal extraction, large quantities of coal dust particles are emitted, contributing to environmental pollution [18] . In addition, coal extraction is associated with the destruction of rocks that cause radon to seep into the air of mines. The presence of this coaldust increases the harmful influence of radon. Radionuclides accumulate on the fine-dispersed particles of dust and in the lungs of miners, creating a continuous source of internal radiation.
Coal miners are constantly exposed to potentially hazardous environmental compounds. Therefore, characterising and estimating the risks of exposure is central to the safety of individuals working in a coal-mining environment [19] .
In Poland, measurements of natural radioactivity in coal mines have been made since the 1970s, but until the end of 1980s there were no specific regulations concerning this problem. Finally, in 1988, a Polish standard was established in which dose limits, methods of monitoring and general requirements of monitoring range and frequency were set. The following types of natural radioactivity assessment were established: 1) concentration of potential alpha energy of short-lived radon daughters in air; 2) gamma radiation dose rate; and 3) concentration of radium isotopes in water and deposits. In 1997 in Polish coal mines, approximately 5500 measurements of the concentration of alpha energy of short-lived radon daughters were performed. The mean value of potential alpha energy concentration of short-lived radon daughters was 0.12 μJ∙m−3, maximum value –6.89 μJ∙m−3. In addition, they showed an increase of other indicators [20] . Similar studies were performed in British coal mines [21] .
Previous studies performed using different organisms in coal mining areas have shown increased DNA damage [22] . A study of workers in open coal mines as well as those working in excavations, showed an increase in the rate of chromosomal aberrations, sister chromatid exchange, and MN [23] [24] .
León-Mejía et al. conducted a study with comet assays and CBMN in a group of coal miners. The mean values of both biomarkers in the exposed group showed significant differences when compared to the values of the non-exposed control group (p < 0.001). The results obtained in CBMN showed that the values in the exposed to coal group (8.6 ± 4.8) were higher compared to the non-exposed control group (2.9 ± 4.0). The differences were significant as evaluated by the Mann Whitney U-test (p < 0.001). The Spearman correlation coefficients for MN frequency with age and DNA damage (tail length, % of tail DNA, DI) for non-exposed control and exposed groups were not significant. Correlations between the MN frequency with time of service were not significant either. They also analysed the effect of alcohol consumption on MN frequencies and DNA damage in all groups using the Mann Whitney U-test and found no difference in any group [18] .
A study by Turkish researchers investigated a group of CWP (coal workers’ pneumoconiosis) patients and found that MN frequencies (8.76 ± 0.54) were significantly higher than those of coal worker or control groups (p < 0.01) (4.75 ± 0.24). There were positive correlations between SCE (sister chromatid exchange) and MN frequencies with different cytogenetic markers in the CWP miner group (R = 0.793, p < 0.01). Some factors, such as age, smoking habits, and the duration of exposure were analysed using multiple linear regression models, but no effect was found on MN frequencies in the study population [25] .
A recent study involved 128 men, 71 of whom reported working in jobs with exposure to coal and 57 of whom reported working at different jobs (unexposed group). The mean exposure time for the exposed group was 12.63 ± 7.87 years. All individuals included in this study were non-smokers to eliminate confounding factors. Significant differences were observed between the exposed and unexposed groups based on the MN and NPB frequencies (7.46 ± 4.64 vs. 3.12 ± 2.93 and 12.33 ± 7.48 vs. 5.59 ± 4.06) (p < 0.001, Mann-Whitney U-test). No correlation was found between age and exposure [19] .
2.4. Genotoxity Risk in Conditions of Life
It is important to note that current models estimating the risk of radiation-related hazards are based upon analysis of data collected from irradiated miners. Currently, it is not clear how transferrable this risk model is to studies involving inhabitants of areas with high-radiation conditions. Therefore, assessing the effects of radon in areas that have a developed mining industry is of particular interest [26] [27] . The health risk related to indoor radon exposure is still a subject of discussion. It has been shown that residential radon exposure may contribute to increased cancer incidence. The average radon exposure of 50 Bq/m3 has been estimated to be responsible for 13% - 25% of myeloid leukemia cases at all ages [28] [29] . Indoor exposure at an annual dose of 7 - 11 mSv from radon has been associated with a significantly increased frequency of chromosome aberrations and micronuclei in children [30] . To decrease radon levels in the working and living environment, some countries have established programmes for remediation work in buildings, primarily schools and homes [28] .
Previously, we have shown that the DNA of people living in areas with high radon concentrations may be affected by substantial genotoxicity. This was reflected in our study by an increased frequency of cells with MN, particularly in binucleated peripheral blood lymphocytes (0.6% of cells with MN in the exposed group vs. 0.3% in the control, p < 0.001) [31] . The same findings were discovered by another group [26] .
The frequency of MN-containing binucleate cells was determined from 42 blood samples from radon spa personnel in the Czech Republic. The results were between zero and two cells with MN per 100 binucleate cells, with an average of 0.95 ± 0.83 for the radon spa personnel and 0.50 ± 0.42 for the controls. The difference between spa personnel and controls was significant (MW test p = 0.017 and KS test p = 0.009). This is similar to the results of parallel studies in which the same method was used for the investigation of uranium miners [17] . If the micronuclei observed in the spa personnel were radiation induced, we should expect their dispersion index to be higher than that of the controls. The average dispersion index was the same for spa personnel (1.13 ± 0.25) as for controls (1.12 ± 0.27). This lack of a significant difference was probably because only some of the micronuclei in the spa personnel were radiation induced. It would of course be interesting to see whether the MN frequency or content was in any way related to radiation exposure. Unfortunately, no individual radiation monitoring was carried out for this group [32] .
3. Future Prospects
The problem of assessment of exposure to natural sources of ionising radiation, including radon, on the human organism is one of the most important in radiobiology and genetic toxicology. CBMN is a promising and sensitive method for this type of assessment. However, analysis of the literature showed that there are not many studies in this field. The most studied group is uranium miners, but there are not many studies on cytogenetic effects in cohorts of coal miners and the radon-exposed populations in residential installations. Therefore, we created the following future prospects:
1) Creation of a biological test-system for the assessment of genotoxic effects of low doses of ionising radiation on coal mining industry employees based on CBMN;
2) Creation of a biological test-system for the assessment of genotoxic effects of low doses of ionising radiation on humans who live or work under the influence of radon for a long time, based on CBMN;
3) In addition to MN, evaluation of NPBs and NBUDs as additional markers of genotoxic effects in the above cohorts;
4) Using the expanded protocol of CBMN, with not only binucleated lymphocytes but also multinucleated ones, which have undergone more than one mitotic division since the beginning of the culturing and quantification of damage in such cells;
5) Evaluation of individual genosensitivity by analysing the frequency of MN, NPBs, and NBUDs in people with different allelic variants of repair genes and biotransformation genes;
6) Standardisation and automatisation of the CBMN technique.