Interactions in Aqueous Solution of a Zwitterionic Surfactant with a Water Treatment Protein from Moringa oleifera Seeds Studied by Surface Tension and Ultrasonic Velocity Measurements* ()
1. Introduction
It is well-known that solution environment such as pH, salt and surfactant can significantly alter the behaviour and overall performance of biomolecules. In our earlier research of the protein from Moringa oleifera (MO) seeds, we have used a number of techniques to study their effects on the properties of the protein in order to understand the nature and mechanism of this protein in water treatment [1-7]. Most of these studies have used anionic surfactants particularly sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS) although some of them used also cationic and nonanionic surfactants but not with zwitterionic surfactant. Generally, zwitterionic surfactants have been much less studied than other classes of surfactants. Their behavior is often described in relation to ionic and nonionic surfactants but the electrically neutral nature of zwitterionic surfactants clearly distinguishes them from ionic surfactants. Studies of the MO protein-surfactant interactions have been performed in our labs aiming to understand how the surfactant binding may affect the protein structure and function and hence its efficient use for water treatment.
Zwitterionic surfactants, which contain both positively and negatively charged head groups, are interesting molecules because of their many unique properties. In general, they are mild to the skin and eyes, exhibit low toxicity, display excellent water solubility, broad isoelectric ranges, high foam stability, and resistance to hard water and to degradation by oxidizing agents [8]. Also, changes in temperature, pH, and added electrolyte have been found to have minimal effect on zwitterionic surfactants. In order to obtain better insight into their interactions with aqueous MO protein systems, we report here the results of an investigation of the interactions of a zwitterionic surfactant with a water treatment protein extracted from MO seeds, studied by surface tension and ultrasonic velocity techniques.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
A zwitterionic surfactant N-dodecyl-N,N-dimethyl-3-ammonio-1-propanesulfonate (DDAPS) (also named n-dodecyl sulfobetaine) was supplied by Sigma Aldrich (≥98% assay, critical micelle concentration of 2 - 4 mM in the range 20 - 25˚C, Mol. Wt. = 335.55 g·mol−1) and was used without any further purification. The structure formula of DDAPS is shown in Figure 1. Sodium chloride (99% purity) was supplied by Rochelle Chemicals. Distilled water was used for all experiments.
2.2. Extraction and Purification of Protein
The extraction and purification of protein powder was done using the method of Ndabigengesere and Narasiah [9], and the experimental details are as described previously by Kwaambwa and Maikokera [1]. To minimize the number of components, no buffer was used. This is with the view that the protein investigated is used for water treatment and buffer conditions would not reflect the environment is it intended. Furthermore, previous studies have shown that the protein is insensitive up to as high as pH 9 [2,4,7] and the isoelectric has been reported to be between pH 10 and 11 [9], suggesting that it is very stable and to a large extent considered self-buffering.
2.3. Surface Tension Measurements
Surface tension of a series of differing concentrations of surfactant (DDAPS) in the absence and presence of the freeze dried protein, were measured with a Krüss K9 tensiometer using the Du Nouy platinum ring detachment method which was calibrated using distilled water. Readings were taken in triplicates. The platinum ring was cleaned before each measurement by heating on a Bunsen burner flame to remove any residual deposits.
A series of different concentrations of surfactant were prepared from the stock solution by dilution using distilled water and varying protein concentrations in distilled water as required. The surface tension measurements were measured at room temperature immediately after sample preparation. Surfactant solutions in the presence of the protein were used to study the protein-surfactant interactions.
The surface tension data was analysed using the simplest form of the Gibbs equation written as
 (1)
(1)
where γ is the surface tension, R is the universal gas constant, and T is the temperature in kelvins (K), whereas Γi and ai are the surface excesses and activities of all the independent components. For measurements on a non-

Figure 1. Schematic structure of N-Dodecyl-N,N-dimethyl- 3-ammonio-1-propane sulphonate, showing the location of positive and negative charges.
ionic surfactant solution, this generally reduces to
 (2)
(2)
There are some considerations concerning the definition of Γ but these are generally unimportant in the context of surfactant systems. For nonionic surfactants, the usual practice is to use the approximation of concentrations (c) rather than activities except at or above the CMC. The slope of the plot of γ against ln c gives the corresponding surface excess Γ at that point using Equation (2).
2.4. Density Measurements
For a macromolecule such as a polyelectrolyte, a detailed understanding of the solution requires information on a variety of physical properties such as partial specific volume. The partial specific volume of a protein (or other macromolecule) is needed for a number of physicochemical techniques such as analytical ultracentrifugation, sedimentation equilibrium, and small-angle scattering. Specific volumes may be obtained from density measurements. However, partial specific volumes are not always accurately determined because experimental precision may be limited by the preparation of solutions of different concentrations. In this study, density data of the solutions were needed in the ultrasonic velocity measurements.
The measurements were performed at a constant temperature of 298.15 K using an Anton Parr DMA 4500 vibrating-tube precision density meter. The measurements were taken in triplicates to get an average value. The density meter was calibrated using distilled water as its density is accurately known from literature.
2.5. Ultrasonic Velocity Measurements
All measurements were performed at 298.15 K. The speed of sound was measured with uncertainty of ±0.3% using a multi frequency ultrasonic interferometer (Mittal Enterprises, New Delhi, India), operating at 1 MHz, which was calibrated with water. Since the speed of sound of our samples spans an interval ranging approximately from 1500 to 1525 ms−1, the apparatus was calibrated with pure water for which there was reliable speed of sound values in the literature. The temperature stability was maintained within ±0.2 K by circulating thermostated water around the cell with a circulating pump.
Ultrasonic waves of known frequency are produced by a quartz crystal fixed at the bottom of the ultrasonic cell. These waves are reflected by a movable metallic plate kept parallel to the quartz crystal and standing waves are formed in the medium. This acoustic resonance gives rise to an electrical reaction on the generator driving the quartz crystal.
If the distance between crystal and plate is now increased or decreased and the variation is exactly one half wavelength, λ/2, or multiple of it, anode current becomes maximum or minimum. In order to minimize the uncertainty of the measurement, their number n is counted. Each maximum is recorded with the highest swing of the needle on the micrometer scale. The total distance, d, moved by the reflector is given by
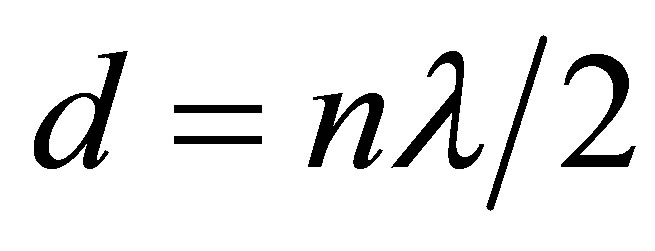 (3)
(3)
where λ is the wavelength. A linear plot of d versus n gives a slope of λ/2. The frequency of the cell crystal ν being accurately known (1 MHz), the speed of sound, u, is calculated by using the relation:
 (4)
(4)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Tension Measurements
Figure 2 shows the plot of γ as a function of ln[DDAPS] with and without the protein based on Gibbs equation. This method is widely used to determine the critical micelle concentration (CMC) on a wide variety of surfactants [10]. The CMC of DDAPS was found to be 2.6 ± 0.3 mM, which fall within the range given by the chemical supplier (i.e. 2 - 4 mM) and also reported in literature [8,11]. The shapes of the plots around the CMC show that the surfactant is impure. A pure surfactant will have a net break at the CMC but the plots do not show a net break but rather it reduces and then increases steadily, that is, it has a minimum which results from the impurity.
The effect of the protein extracted from protein on the

Figure 2. Variation of the surface tension a zwitterionic surfactant, DDAPS, in the presence (circles) and absence (triangles) of 0.02% MO protein.
zwitterionic surfactant, DDAPS, surface tension was also studied and is shown in the same figure. The results show that the protein interacts mildly with the surfactant in the concentration range studied. In other words, the protein does not interact significantly with the zwitterionic surfactant to affect its surface activity. In fact, the behaviour observed for the protein/zwitterion system is similar to what Kwaambwa and Maikokera observed for the protein and nonionic surfactant triton X-100 (TX-100) [3]. This is not surprising because zwitterionic surfactants, although have ionic groups, are overall neutral and hence behave like nonionic surfactants.
Although an analysis of the surface tension curves can, in principle, provide quantitative information on surfactant-protein interactions, practically speaking, complete interpretation of the data becomes more difficult when the protein itself is appreciably surface active as it is the case for the protein from MO seeds. The surface tension profiles were obtained both for the surfactant systems and in the presence of protein, showing the characteristic break points in mixed protein/surfactant systems. For ease of interpretation of the analysis, the experiments were done in distilled water rather than in a buffer.
In addition to the typical CMC observed for DDAPS solutions, the profiles of the protein/surfactant mixtures show inflection points commonly known as the critical micelle concentration in the presence of protein (CMC*). The values are determined in a similar way as CMC, i.e. the surfactant concentration at which the surface tension reaches a minimum value. The CMC* values for different protein concentrations are normally higher than in pure water, which can be explained by considering the amount of surfactant that is bound to the protein. In our study, surface tension at CMC*, i.e. when the protein is saturated by surfactant and free micelles start to form, reached value close to that obtained for the surfactant solution alone as shown in Figure 2. It should be noted that this value is not influenced by the protein concentration as it is envisaged that protein molecules are totally displaced from the interface when the surfactant concentration reaches the CMC*.
Addition of NaCl seems to lower the surface tension but not the CMC as shown in Figure 3. The addition of salt reduced the surface tension more in the low DDAPS concentration region of the plot implying that more protein molecules were adsorbed onto the air/water interface to cause a reduction in surface tension (i.e. the salt makes the protein more surface active). The protein is known to be cationic (implying that the positive charges are more than the negative charges or the positive charges of the protein are more exposed) and so addition of salt results in neutralisation of the positive ions and hence making the protein more surface active.

Figure 3. Variation of the surface tension of a zwitterionic surfactant, DDAPS, in 0.02% protein (circles) and in a mixture of 0.02% protein and 0.01 M NaCl (triangles).
3.2. Density Measurements
Figure 4 shows the linear variation of density of DDAPS as its function of concentration in the presence and absence of the protein. The partial specific volume of DDAPS was estimated from density measurements. Density values, ρ, increase with the concentration of the polyelectrolyte. If the partial specific volume ν is independent of the concentration, the following equation is obeyed