Design and Optimization of the Geometric Properties of a Crane Hook ()
Received 9 June 2016; accepted 31 July 2016; published 3 August 2016

1. Introduction
The stress and deflection in the crane hooks for this study are determined both using theoretical calculations as well as finite element analysis simulation in SOLIDWORKS. The theoretical calculations are based on Figure 1 shown below. It is possible to calculate the eccentricity (e) and normal stress (σ) in a curved hook based on Equation (1) and Equation (2), respectively. The neutral radius (rn) and eccentricity are determined based on the different cross sections shown in Figure 2. Square, trapezoidal, and circular cross sections are considered in this study [1] .
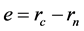 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
![]()
Figure 1. Parameters of a curved hook for stress calculations.
![]()
Figure 2. Diagrams and equations for determining the neutral axis and central radius for various cross sections.
2. Results
2.1. Cross Section Selection
The concept of loading a curved beam is used to determine the maximum stress and displacement in multiple cross section shapes including square, circular, and trapezoidal. A common cross sectional area and hook radius are used for all geometric selections and each cross sections centroid lies on the radius of curvature. The cross sections along with the parameters used for testing are shown in Figure 3.
These three cross sections are used to create solid models of a hook that has a radius of curvature of 4 in. The resulting solid models are used to perform finite element analysis in SOLIDWORKS. In this finite element analysis, a load of 8000 lbs is considered and the resulting normal stress and deflection are analyzed. The finite element models shown in Figures 4-6 indicate the location of maximum stress, and Figures 7-9 show the de-
![]()
Figure 3. Square, circular and trapezoid cross sections and parameters used.
![]()
Figure 4. Square cross section normal stress plot.
![]()
Figure 5. Circular cross section normal stress plot.
flection. These results are summarized in Table 1. These results show that the trapezoid cross section has the most desirable performance due to the lower levels of stress and deflection in comparison to the square and circular cross sections [2] .
![]()
Figure 6. Trapezoid cross section normal stress plot.
![]()
Figure 7. Square cross section y deflection plot.
![]()
Figure 8. Circular cross section y deflection plot.
![]()
Figure 9. Trapezoid cross section y deflection plot.
![]()
Table 1. Summary of cross section testing.
2.2. Cross Section Optimization
It is possible to determine the optimal geometric properties with the trapezoidal cross section selected. The parameters of the trapezoidal cross section detail in Figure 3 are varied to determine the values that provide the optimal performance. In order to achieve this, the value of the neutral radius (rn) is held constant at 3.5 in, while the values of h, bi, and bo are varied simultaneously. The materials being considered in this optimization are A-36 steel, 6061-T6 Aluminum, and Ti-6AL-4V Titanium and their properties are shown in Table 2 [3] - [5] . By selecting 7 values of the parameter ℎ, it is possible to determine values of bi, and bo such that the weight is minimized and the maximum normal stress is constrained to one half of the materials yield strength (σy). The results of this optimization are shown in Figure 10. Exact parameter values are shown in Tables A1-A3 in Appendix A [6] [7] .
3. Conclusions
The results of this research show that for a given cross sectional area, a trapezoid cross section of a hook will have better performance in terms of maximum stress than a circular or square cross section. It is also shown that as the h value of a trapezoidal hook increases, the minimum weight of the hook decreases at a decreasing rate. While the highest value for h will give the lowest weight overall, it is important to keep the proportions of the hook in mind when making the parameter selection. A very large value of h will increase the overall extents of the hook profile and create inefficiencies in packaging and will require a much larger opening on the load that is being moved.
Another observation that is made is in the difference in weight between the three materials while achieving the same goal of maintaining stress levels of one half of the materials yield strength. The percent decrease in weight between steel vs. aluminum or titanium can be as large as 80%. This indicates that in terms of performance, aluminum or titanium will be a clear choice over steel. The difference between aluminum and titanium
![]()
Figure 10. Weight optimization results for three different materials.
however is much smaller. This is where the cost of raw materials and the machinability of the material will factor heavily into the material selection decision.
Appendix A
Optimized Cross Section Values
![]()
Table A1. Ti-6AL-4V titanium optimization.
![]()
Table A3. 6061-T6 aluminum optimization.