Valuation of Game Option Bonds under the Generalized Ho-Lee Model: A Stochastic Game Approach ()
1. Introduction
Callable and putable bonds are one of the major interest rate derivatives due to its ability to respond the needs of various markets participants. Callable bonds give an issuer the right which can call a bond before the maturity date. The issuer is allowed to exercise the right at the several prescribed exercise times. If the issuer exercises the option, she buys back the bond at a call price from a holder. Then, the issuer is a buyer of the call option and a holder has an obligation to respond to the demand of the issuer. Thereby, a holder of a callable bond generally receives a higher yield than a usual coupon bond in exchange for taking prepayment risk. On the other hand, putable bonds give a holder the right which can sell back the bond before the maturity date. If a holder exercises the option, the issuer must buy back the bond for a put price. Then, the holder is a buyer of the put option, while the issuer is a seller. Thus, the putable bond has a lower yield than a straight bond because of the put option. In this paper, we consider the bond that the issuer and the holder are simultaneously granted the right to call and put a bond, respectively. We call this bond a game option bond.
To represent an interest rate dynamics in markets, we make use of the Generalized Ho-Lee model [1] . It is a discrete-time and an arbitrage-free term structure model of interest rate. The volatilities in each node are dependent on time and states, and hence it generalizes the Ho-Lee model [2] . For this reason, it is more flexible to model interest rate dynamics. Moreover, it is a strong point that the model has the term structure of interest rate at all nodes on the binominal lattice. We assume that the issuer and the holder decide whether to exercise the option only by taking account of the states of interest rates.
The theory of stochastic games was originated by the seminal paper of Shapley [3] . Players in stochastic games play a series of stage games that depends on a state. Using the Generalized Ho-Lee model which is a discrete-time term structure model of interest rate, we apply the stochastic game approach for pricing the game option bond as a finite time horizon problem on a binomial lattice under the risk-neutral probability. The non-arbitrage price of the game option bond is evaluated as the value of the whole game by using a dynamic programming approach [4] -[6] . We derive both the early exercise strategies and the exercise regions for players in terms of the saddle-point equilibrium strategy.
Furthermore, we report key rate duration which measures the price sensitivity of the bond to the key rate shift in a yield curve [7] [8] . Key rate durations are useful to analyze a bond with a contingent claim. We provide the intuitive numerical results for key rate durations.
The organization of this paper is as follows. In section 2, we illustrate the Generalized Ho-Lee model. In section 3, we formulate the game option bond as the stochastic game and derive the optimality equation to evaluate the non-arbitrage values of the game option bonds. In section 4, we show numerical examples for the initial values of bonds and the exercise strategies for the players, and report the key rate durations. Finally, in section 5, we conclude.
2. The Generalized Ho-Lee Model
The Generalized Ho-Lee model is an arbitrage-free term structure model of interest rates [1] . We use recombining binomial lattice structure to describe uncertainties of interest rates. A node on the lattice is denoted by  where n is the time and i the state for
where n is the time and i the state for 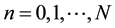 and
and , respectively, and N is the time horizon of the model. Let
, respectively, and N is the time horizon of the model. Let  represent the zero?coupon bond price at node
represent the zero?coupon bond price at node  with remaining maturity of T periods. We call
with remaining maturity of T periods. We call 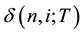 the binomial volatility at node
the binomial volatility at node 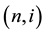 with remaining maturity T, which stands for the uncertainty of interest rate on the binomial lattice. For
with remaining maturity T, which stands for the uncertainty of interest rate on the binomial lattice. For , we define it as
, we define it as
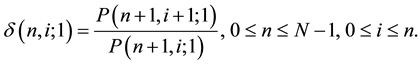
The Ho-Lee model, which is the first arbitrage-free term structure model of interest rates, assumes that the binomial volatilities are independent of the time and state [2] [8] . In contrast, the Generalized Ho-Lee model allows us to use the time and state dependent binomial volatilities at each node. The one-period binomial volatilities at node 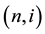 are given by
are given by
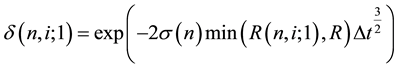 (1)
(1)
where  is the term structure of interest rate volatilities,
is the term structure of interest rate volatilities, 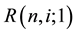 is the one-period yield, R is a thereshold rate, and
is the one-period yield, R is a thereshold rate, and 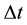 is a time interval of one period. Equation (1) signifies that the interest rate movement is lognormal when
is a time interval of one period. Equation (1) signifies that the interest rate movement is lognormal when 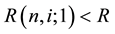 and normal when
and normal when![]() .
. ![]() is given by the following specification:
is given by the following specification:
![]() (2)
(2)
where the parameters ![]() are estimated such that the model prices fit the swaption prices in a market. The binomial volatilities at node
are estimated such that the model prices fit the swaption prices in a market. The binomial volatilities at node ![]() with the remaining maturities T are defined by
with the remaining maturities T are defined by
![]() (3)
(3)
for![]() . Then, the one?period zero?coupon bond prices at node
. Then, the one?period zero?coupon bond prices at node ![]() are
are
![]() (4)
(4)
Similarly, the T-period zero-coupon bond prices are as follows:
![]() (5)
(5)
We use an equal risk?neutral probability of 0.5 for the up-state and down-state. To be an arbitrage-free term structure model of interest rates, the bond prices have to satisfy the following arbitrage-free conditions:
![]() (6)
(6)
for each![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and![]() . When the model for bond prices is given by Equations (3)-(5), we can directly verify Equation (6) by using Equations (3)-(5).
. When the model for bond prices is given by Equations (3)-(5), we can directly verify Equation (6) by using Equations (3)-(5).
Solving recursively Equations (1)-(5), we derive the arbitrage?free term structure model of interest rates on every node.
3. A Stochastic Game Approach
3.1. Callable and Putable Bonds
Callable bonds give an issuer the right to purchase back the bond for a pre-specified price (a call price) before the maturity time. If the issuer exercises the right, she pays the call price to a holder and calls back the bond. In contrast, putable bonds give a holder the right to sell back the bond at a pre-specified price (a put price) before the maturity time. If the holder exercises the right, the issuer must buy back the bond for the put price from the holder. In this paper, we consider the bond that both the issuer and the holder have the right to exercise the call and the put options, respectively. We call its bond a game option bond.
Let ![]() be the time sequences on the bond, where
be the time sequences on the bond, where ![]() is the initial time,
is the initial time, ![]() are the coupon times and
are the coupon times and ![]() is the maturity time. We assume that each of the issuer and the holder can decide whether or
is the maturity time. We assume that each of the issuer and the holder can decide whether or
not to exercise the options at the coupon times ![]()
![]() , where
, where ![]() is the first admissible exercise time. In general, we call
is the first admissible exercise time. In general, we call ![]() the protection period. If each of the issuer and the holder (or both)
the protection period. If each of the issuer and the holder (or both)
exercise at an exercisable time![]() , the holder then receives the corresponding payoffs from the issuer at the next coupon time
, the holder then receives the corresponding payoffs from the issuer at the next coupon time![]() . For simplicity, we use a time index n to represent the time instead of
. For simplicity, we use a time index n to represent the time instead of![]() .
.
Let ![]() and
and ![]() denote the call and the put prices at node
denote the call and the put prices at node ![]() for
for ![]() and
and![]() , respectively. We usually have
, respectively. We usually have ![]() for every exercisable node, otherwise trivial situations arise. If both the issuer and the holder simultaneously exercise the option, we assume that the holder receives
for every exercisable node, otherwise trivial situations arise. If both the issuer and the holder simultaneously exercise the option, we assume that the holder receives ![]() from the issuer and that
from the issuer and that ![]() for every exercisable node. In addition, if we set
for every exercisable node. In addition, if we set![]() , then the game option bond results in a callable bond. In contrast, if we set
, then the game option bond results in a callable bond. In contrast, if we set![]() , then it reduces to a putable bond.
, then it reduces to a putable bond.
3.2. A Stochastic Game Approach
We now apply a stochastic game or a Markov game approach to the valuation of the game option bond. Let the issuer and the holder be the players of the game. Each player has two pure strategies, Exercise or Not Exercise. The holder chooses a strategy x and the issuer chooses a strategy y from the strategy set ![]() at the exercisable nodes
at the exercisable nodes ![]() for
for![]() .The holder gains the payoff
.The holder gains the payoff ![]() from the issuer whenever the pure strategy pair x, y is chosen at a node
from the issuer whenever the pure strategy pair x, y is chosen at a node![]() . If either player exercises the option at the exercisable time , for
. If either player exercises the option at the exercisable time , for![]() , the holder receives the payoff:
, the holder receives the payoff:
![]()
at the next coupon time![]() , where c is the fixed coupon of the bond. Although the coupon could be dependent on node
, where c is the fixed coupon of the bond. Although the coupon could be dependent on node![]() , we set it as a constant for simplicity. Meanwhile, if both players don’t exercise the options, the game changes from a current node
, we set it as a constant for simplicity. Meanwhile, if both players don’t exercise the options, the game changes from a current node ![]() to the following node
to the following node
![]()
where ![]() denotes a random state of interest rates at time
denotes a random state of interest rates at time![]() . Therefore, the issuer and the holder face a two-person and zero-sum stage game at every exercisable node where the payoff and the state transitions are dependent on both the state of interest rate and the strategy (action) of the two players. Then, the holder will always want to maximize her payoff, while the issuer wants to minimize the payoff, so that the rule of the strategy choice composes the exercise strategy for each player.
. Therefore, the issuer and the holder face a two-person and zero-sum stage game at every exercisable node where the payoff and the state transitions are dependent on both the state of interest rate and the strategy (action) of the two players. Then, the holder will always want to maximize her payoff, while the issuer wants to minimize the payoff, so that the rule of the strategy choice composes the exercise strategy for each player.
Given a two-person zero sum game (a matrix game) defined by a payoff matrix![]() , where
, where ![]() stands for the set of real numbers, we define the value of the game as follows:
stands for the set of real numbers, we define the value of the game as follows:
![]() (7)
(7)
where ![]() is an m-dimensional vector representing a mixed strategies for row player,
is an m-dimensional vector representing a mixed strategies for row player, ![]() an n-dimensional vector for column player and, for a positive integer
an n-dimensional vector for column player and, for a positive integer![]() ,
, ![]() denote the k-dimensional unit simplex defined by
denote the k-dimensional unit simplex defined by
![]()
In Equation (7), the second equality is due to the von Neumann minimax theorem.
Let ![]() be the value of the game option bond at node
be the value of the game option bond at node![]() . Then, we will find the solution of the stochastic game by solving backwardly the following Optimality Equation from the maturity time
. Then, we will find the solution of the stochastic game by solving backwardly the following Optimality Equation from the maturity time ![]() to the initial time
to the initial time![]() .
.
Optimality Equation:
![]() (8)
(8)
![]()
![]() (9)
(9)
![]()
![]() (10)
(10)
![]()
where F denotes the principal of the bond, ![]() the one-period discount factor at node
the one-period discount factor at node ![]() which is the one-period zero-coupon bond price based on the Generalized Ho-Lee model, Q the risk-neutral probability measure, and
which is the one-period zero-coupon bond price based on the Generalized Ho-Lee model, Q the risk-neutral probability measure, and ![]() the expectation operator conditional on node
the expectation operator conditional on node ![]() under Q. In the exercisable node, we need to solve the two-person zero sum game defined by the following payoff matrix
under Q. In the exercisable node, we need to solve the two-person zero sum game defined by the following payoff matrix
![]() (11)
(11)
in order to find the exercise strategies for the players, where the holder is the row player because of a maximizer, and the issuer is the column player because of a minimizer. In the Matrix (11), for example, if the holder chooses to exercise and the issuer chooses not to exercise, then the value of the payoff matrix is![]() . Thus, if it is possible to solve efficiently the matrix stage-game (11) for every exercisable node, we can derive simultaneously both the non-arbitrage price of the game option bond and the exercise strategies of the two players.
. Thus, if it is possible to solve efficiently the matrix stage-game (11) for every exercisable node, we can derive simultaneously both the non-arbitrage price of the game option bond and the exercise strategies of the two players.
Next, we show the equilibrium strategies in the stage-game at each exercisable node. In general, it is well known that a two-person zero sum game has a saddle point in mixed strategies including pure strategies. However, the next result shows that a saddle point of our stochastic game exists in pure strategies.
Theorem 1. Suppose ![]() for every exercisable node. Then, the matrix stage-games played in an exercisable node always has a saddle point in pure strategies:
for every exercisable node. Then, the matrix stage-games played in an exercisable node always has a saddle point in pure strategies:
![]()
Furthermore, the equilibrium strategy profiles are
![]()
where E denotes the pure strategy “Exercise” and N “Not Exercise”.
Proof. We suppose ![]() If
If![]() , the issuer chooses a pure strategy N because it is a dominant strategy for her (a minimizer). Then the best response strategy for the
, the issuer chooses a pure strategy N because it is a dominant strategy for her (a minimizer). Then the best response strategy for the
holder is a pure strategy E, and hence![]() . If
. If![]() , a pure strategy N is a dominant strategy for both players, and
, a pure strategy N is a dominant strategy for both players, and![]() . Finally, if
. Finally, if![]() ,
,
the holder chooses a pure strategy N which is the dominant strategy for her(a maximizer). Then, the best response strategy for the issuer is choosing a pure strategy E, and hence![]() .
.
Note that if ![]() for an exercisable node, then there is a possibility that the equilibrium strategy profile is
for an exercisable node, then there is a possibility that the equilibrium strategy profile is![]() because choosing to exercise is optimal for both players. However, in any case, this theorem suggests that we have only to consider a pure strategy in our stochastic game.
because choosing to exercise is optimal for both players. However, in any case, this theorem suggests that we have only to consider a pure strategy in our stochastic game.
4. Numerical Examples
This section proposes the value of the game option bond using the Generalized Ho-Lee model. We consider the bond with a 10-year maturity, the protection period of 5 years, ![]() ,
, ![]() and ∆t = 0.25. We assume that the coupon is paid every three months and players can exercise the option at a coupon time after the protection period. For simplicity, we set
and ∆t = 0.25. We assume that the coupon is paid every three months and players can exercise the option at a coupon time after the protection period. For simplicity, we set ![]() and
and ![]() for all n, and
for all n, and ![]() and
and ![]() for every exercisable node.
for every exercisable node.
We first show the performance surfaces of the bond to a parallel shift in the yield curve and a change in the volatility. The yield curve is shifted in parallel from 4.5% to 5.5% every a 10 bp, and the volatility from 0% to 20% every a 2% increment. Figure 1 presents the straight coupon bond, the callable, the putable, and the game option bonds, respectively. It shows that the bond prices drop with the upward-shift in the yield curve for all bond type, because the discount factor increases. In contrast, a volatility change has different effects for each bond. The coupon bond is not influenced by a volatility change. On the other hand, as the volatility increases, the callable bond value drops, while the putable bond value rises. Besides, we see that the game option bond drops slightly with the increase of volatilities.
We next consider the effect on the exercise regions of the issuer and the holder to the parallel shift in the parameters of interest rate. Figures 2-4 present the exercise regions of the game option bond in yield curve 4%, 5%, and 6%, respectively. In Figures 2-4, the leftmost node represents the initial time, the rightmost nodes the maturity time, the upper nodes the higher state of the interest rate, and a number in each node the game option bond value. In addition, the upper gray-areas are the holder’s exercise region, while the lower enclosed areas are the issuer’s one. Figures 2-4 show that the exercise region of the issuer expands with the downward shift of interest rates. Generally, if an interest rate declines after debt issues, an issuer is likely to want to refinance the loan at a lower interest rate, and hence she will exercise the call option early. In contrast, the exercise region of the holder expands with the upward shift of interest rates. This is because that the holder then can obtain higher yields by switching to other bonds, and the holder of put option will finally sell back for the issuer.
![]()
Figure 2. Exercise region of game option bond in yield curve 4%.
![]()
Figure 3. Exercise region of game option bond in yield curve 5%.
![]()
Figure 4. Exercise region of game option bond in yield curve 6%.
Figure 5 and Figure 6 represent the effect on the exercise region of the game option bond to the volatility of interest rates for 5% and 10%, respectively. From Figure 5 and Figure 6, we see that the exercise regions of the holder expand with the increase of volatility, whereas that of the issuer is not affected by the increase of volatility. We infer that the different effect is attributable to a characteristic of the Generalized Ho-Lee model, where the interest rate process is lognormal when the simulated interest rates are low and normal when the simulated interest rates are high. Thus, when the volatilities increase, the interest rate process tends to rise on the upper nodes where the interest rates are high, while the interest rate process almost never decline in the lower nodes where the interest rates are low. Finally, an increase of the interest rate volatility causes only the holder to exercise early, as shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6. In addition, it is generally known that an increase in volatilities
![]()
Figure 5. Exercise regions of game option bond in the interest rate volatility 5%.
![]()
Figure 6. Optimal exercise regions of game option bond for the interest rate volatility 10%.
rise a value of an option on a contingent claim. As seen from the previous Figure 1, the putable bond price rises with the increase of the volatility, and hence this is consistent with the known property of an option value.
Key rate duration is a measure of the interest rate risk of a bond. We follow Ho [7] and report key rate duration for a variety of bonds. Key rate durations define the risk to the small change of each key rate in a yield curve. We consider a yield curve ranging from zero to ten years. To define key rate durations, we choose a set of seven key rates of three months, one, two, three, five, seven, and ten years. Key rate durations are defined as the price sensitivity to each key rate shift. The sum of key rate durations is identical to the effective duration. It can capture the risk to a yield curve change not only with parallel shift but also with steepness or curvature. We assume that the level of the key rate shift is 10 bp and the other parameters are the same as the previous given values.
Table 1 and Figure 7 compare the key rate duration profiles of the straight coupon bond, the callable, the putable, and the game option bonds. The profile shows that the callable and the game option bonds have high risk exposure to the key rate change on five years, which is the first possible exercise time. On the other hand,
![]()
Table 1. Key rate durations in ![]() and
and![]() .
.
![]()
Figure 7. Key rate duration profiles in ![]() and
and![]() .
.
the coupon and the putable bonds are sensitive to the key rate shift in ten years and are alike in the key rate duration profiles. In comparing the effective durations, Table 1 shows that the option embedded in bonds have lower effective duration. It suggests that the option has an effect of reducing an impact on the interest rate risk due to the key rate change. In particular, the callable bond and the game option bond have lower price sensitivity than the straight coupon bond and the putable bond.
To consider the effect on game option bond value of the call option, we finally propose the key rate duration to different call price. Table 2 and Figure 8 show the key rate duration profile of the game option bond for C(n, i) = 1.01, 1.02, 1.03, and 1.04, where 1.01 is the call price forbidding the issuer to exercise at final exercisable nodes with probability 1. In general, there is a low possibility that an issuer exercises call option as the call price is higher, because the call price is considered to be the penalty for prepayment by the issuer. Table 2 and Figure 8 shows that as the call price becomes higher, the 5-year key rate duration decreases gradually, while the 10-year key rate duration increases. So the key rate duration profile of the game option bond is eventually close to that of the coupon bond with the rising call price. Accordingly, the effective duration in Table 2 increases gradually.
5. Conclusion
In this paper, we propose a valuation of the game option bond under the Generalized Ho-Lee model. We for-
![]()
Table 2. Key rate durations of game option bond for![]() .
.
![]()
Figure 8. Key rate duration profiles of game option bond for![]() .
.
mulate its valuation as a stochastic game on the binomial lattice. We show that our stochastic games always possess saddle points in pure strategies at exercisable nodes. Thereby, we can efficiently solve the optimality equation to value the game option bond. Moreover, then we can obtain simultaneously both the non-arbitrage price of the game option bond and the optimal exercise strategies for the players. We provide the numerical results for the values of the bonds with a variety of contingent claims and the exercise regions for the players of the game option bond. In addition, we report the price sensitivity of the bond to a small parallel shift in some key rates by using key rate duration. The results in key rate duration show that the option embedded in a bond, particularly the call option, has the effect of reducing the exposure with respect to the interest rate change. These numerical results are useful to intuitively understand the interest rate risk in the bonds with an embedded option. However, further studies will be needed in order to value the non-arbitrage price for various interest rate derivatives related to both the credit risk and the interest rate risk [9] .