Game Analysis of Reputation Model on Cooperation of Employees in Probation Period and Formal Work Stage ()
1. Introduction
In reality, most companies use probation to choose appropriate employees for the job positions. The employee probation period starts from the first day the new employee comes to work, including pre-job training and job familiarity until they are competent for the job [1] . In the probation period, the employees tend to work hard, supply real work reports positively and other cooperative behaviors for the job they expect because they have the motive for becoming a regular worker. While in formal work stage, employees may tend to slacken and slow down as they have settled down, they even try to fabricate impressions that they are working hard, provide fake work reports and other uncooperative behaviors.
The cooperation between employees and companies could bring win-win situation, but employees’ opportunism tendency is the main obstacle to their cooperation. Nevertheless, when a company operates stably, the employee’s opportunism behavior will just bring him the short-term interests and bad reputation, furthermore, they can’t stay long in the company to obtain long-term interests. As is shown above, the employees are faced with a tradeoff between short-term interests and long-term interests. As a man who pursues his maximal interest in a company, the employee has to take his long-term interest into consideration. Therefore, the employees need to consider establishing a good reputation for themselves. Based on this, we put forward the assumption of this paper: reputation effect is an important incentive mechanism of the corporation between employees and companies when the companies operate stably, have good culture atmosphere, possess standard management systems or sufficient information. Under the reputation effect, the cooperation between employees and companies will be efficient for the operation of the whole company.
Since a company has no direct administration authority to its employees, it can’t implement administrative commands directly to them. Obviously, reputation incentive effect is connected with the nature of a company, which can be explained that an employee establishes good reputation in a company for purpose of obtaining long-term interests or he is just waiting for a better opportunity to realize his own maximal interest by using up all the established and accumulated good reputation at once, which means that at the same time he loses his faith in cooperation with the company. In this paper, we will use reputation theory of Kreps and Willson (1982) [2] , Kreps, Willson, Milgrom and Roberts (1982) [3] to discuss the incentive effect of reputation mechanism on interaction and cooperation between employees and companies.
2. A Dynamic Game Model of Reputation with One-Side Incomplete Information
As is known, the employee in a company is limited rational and liable to opportunism, which means the cooperative contract between employee and company is incomplete, and one side or both the two sides of the contract have the motive to encroach on other’s interest to gain more interests for himself under this condition. But under some certain conditions, the transaction cost between employee and company is low and the cooperation effect between employee and company is large, the cooperation will bring both of them more opportunities to gain more interests than noncooperation between them. To some extent, the cooperative relationship between employee and company itself is an incentive mechanism to both sides. Furthermore, in order to keep a stable cooperative relationship between employee and cooperation and make it run effectively, an incentive mechanism needs to be established. Nevertheless, a good reputation is such an effective incentive. So we will prove the above assumption by discussing in two parts, that is probation period and formal work stage, and we will establish a reputation model on employees and companies.
2.1. Hypothesis of the Model
We design a dynamic game model of reputation with incomplete information in this paper. First, we assume a company and its employee are the two sides in the game. Second, the company is cooperative while the employee is uncertain, which means he could be either cooperative or uncooperative. In other words, the company aims at maximizing the whole interests of itself and it won’t encroach on the employee’s interests by opportunism behaviors, while the employee aims at maximizing his own interests and he may encroach on the interests of the company by opportunism behaviors. Besides, the employee knows what type the company is while the com- pany doesn’t know what type the employee is. That means the employee has an advantage to decide whether to keep cooperating with the company. For the company, the type of employee is private information, but it doesn’t mean that the company is completely passive. The company could observe its interactive cooperation with employee in the practical working process to speculate what type the employee is, and correct its judgment constantly in the process of observing the employee’s behaviors. Third, the company will terminate the cooperative contract relationship with the employee once he takes the advantage of opportunism to encroach on its interests and result in the decline in performance of the whole company, and it will never cooperate with him. Otherwise the company will keep on cooperating with the employee. Since we assume the company is cooperative, the employee’s behaviors will be focused on in the following part.
2.2. One-Stage Game in Probation Period
The rate that the employee actually encroaches on the interests of the company is denoted as E, which could be interpreted as the potential maximal occupancy of the company interests that the employee exceeds the returns in the contract. It also can be considered as the inefficient transaction behaviors of the employee in the company, such as slackening and slowing down, trying to fabricate impressions that they are working hard, providing fake work reports in his working process. 0 ≤ E ≤ 1, and we will take it as the interest encroachment by these uncooperative behaviors of the employee in the next analysis. The employee’s interest encroachment rate that the company expects is denoted as Ee, 0 ≤ Ee ≤ 1. α = 0 denotes the employee is cooperative, which means that he won’t encroach on the interests of the company, α = 1 denotes the employee is uncooperative, which means that he may encroach on the interests of the company. We establish a utility function of the employee in probation period [4] :
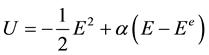 (1)
(1)
When α = 0, that is the employee is cooperative, and he will not encroach the interests of the company because only when E = 0 can he get his maximal utility, it is the best choice for him in this condition. When α = 1,
that is the employee is uncooperative, and the utility function becomes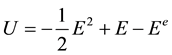 , 0 ≤ E ≤ 1, so if we
, 0 ≤ E ≤ 1, so if we
want to keep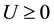 , we only need Ee to be sufficiently small. That means the company has the lowest expectation that the employee will encroach on its interests.
, we only need Ee to be sufficiently small. That means the company has the lowest expectation that the employee will encroach on its interests.
Now we take the derivative of formula (1) with respect to E, here is: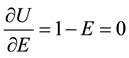 , E = 1. That is to say, if
, E = 1. That is to say, if
the uncooperative employee wants to maximize his utility in the probation period, his best choice is encroaching on the interests of the company and the optimal interests encroachment rate is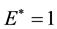 ,
, 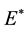 denotes the optimal encroachment rate. This can be interpreted as the poor probation period management of the company, which makes the employee believe that his working time in the company is only probation period. So as a rational uncooperative employee, he has no reason to keep on collaborating with the company.
denotes the optimal encroachment rate. This can be interpreted as the poor probation period management of the company, which makes the employee believe that his working time in the company is only probation period. So as a rational uncooperative employee, he has no reason to keep on collaborating with the company.
2.3. Repeated Dynamic Game in Formal Work Stage
When the employee passes the performance appraisal in probation period, he could become a regular worker and start his formal work stage in the company. Compared to probation period, the employee has no pressure to pass the appraisal to get into the company formally, he may slacken and slow down, try to fabricate hard-working im- pression and provide fake work reports in his working process. In this stage, the company is still not sure about the type of the employee, but there is a prior probability which could be revised by observing the behavior of the employee. The employee can choose to cooperate or not, and he is the only one who knows what type he is. Since a cooperative employee will definitely choose to cooperate with the company to maximize his interests, we will focus on discussing the behavior of an uncooperative employee in the game in the next analysis, which is in a condition when α = 1.
The prior probability that the company takes the employee as cooperative is denoted as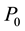 , then the prior probability that the company take the employee as uncooperative is
, then the prior probability that the company take the employee as uncooperative is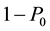 . We suppose that the game in formal work stage will repeat M times, which means the game period will be divided into M stages. We denote the probability that the company takes the employee as cooperative in stage M as
. We suppose that the game in formal work stage will repeat M times, which means the game period will be divided into M stages. We denote the probability that the company takes the employee as cooperative in stage M as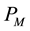 , then the probability that the company takes the employee as uncooperative in stage M is
, then the probability that the company takes the employee as uncooperative in stage M is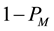 . Now we make
. Now we make 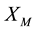 denotes the probability that the company thinks the employee will choose to cooperate in stage M,
denotes the probability that the company thinks the employee will choose to cooperate in stage M, 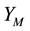 denotes the probability that the employee will choose to cooperate in stage M. When
denotes the probability that the employee will choose to cooperate in stage M. When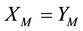 , the game will reach the equilibrium.
, the game will reach the equilibrium.
We make A denote the event that the company considers the employee to be cooperative, B denote the event that the company will not observe the encroachment behavior of the employee in stage M, namely the employee chooses to cooperate. If the company does not observe the encroachment behavior, then according to Bayes Law:
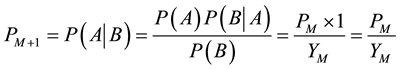 (2)
(2)
It could be predicted that 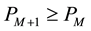 in formula (2) just because
in formula (2) just because . That means that the posterior probability that the company takes the employee as cooperative in stage M + 1 is not less than the probability that the company takes the employee as cooperative in stage M. In other words, if the employee chooses to cooperate in current stage, then the probability that company takes the employee as cooperative in next stage will increase. Similarly, if the employee chooses not to cooperate in current stage, then the value of
. That means that the posterior probability that the company takes the employee as cooperative in stage M + 1 is not less than the probability that the company takes the employee as cooperative in stage M. In other words, if the employee chooses to cooperate in current stage, then the probability that company takes the employee as cooperative in next stage will increase. Similarly, if the employee chooses not to cooperate in current stage, then the value of ![]() in formula (2) is 0, namely in next stage the probability that the company takes the employee as cooperative is 0.So if the employee chooses not to cooperate in current stage, the company will deduce that he is uncooperative, then he may lose the cooperative opportunity with the company in next stage. Therefore, the employee will not choose to be uncooperative until the last stage arrives. The last two stages are denoted as stage M − 1 and stage M, here:
in formula (2) is 0, namely in next stage the probability that the company takes the employee as cooperative is 0.So if the employee chooses not to cooperate in current stage, the company will deduce that he is uncooperative, then he may lose the cooperative opportunity with the company in next stage. Therefore, the employee will not choose to be uncooperative until the last stage arrives. The last two stages are denoted as stage M − 1 and stage M, here:
In stage M, the uncooperative employee has no necessary to establish a reputation that he is cooperative, his best choice is![]() , and the employee’s interest encroachment rate that the company expects is
, and the employee’s interest encroachment rate that the company expects is
![]() (3)
(3)
We can see that the employee’s interest encroachment rate that the company expects is the product of the probability that the company takes the employee as uncooperative, the probability the company thinks the uncooperative employee chooses not to cooperate and the employee’s optimal interest encroachment rate in practical. Then the employee’s utility in this stage is:
![]()
So the utility of the uncooperative employee in last stage is an increasing function of![]() . The larger the probability that the company takes the employee as cooperative in last stage is, the higher the utility that the uncooperative employee gets. Since formula (2) has proved if the employee takes cooperative behaviors in current stage, the probability that the company takes him as cooperative in next stage will increase, we can deduce that the utility of the uncooperative employee in last stage is an increasing function of reputation. And if there is no relevant constraint mechanism in the last stage, the employee will maximize his own interests by extravagantly encroaching on the interests of the company. This can be confirmed in real life, For example, some managers make off with money.
. The larger the probability that the company takes the employee as cooperative in last stage is, the higher the utility that the uncooperative employee gets. Since formula (2) has proved if the employee takes cooperative behaviors in current stage, the probability that the company takes him as cooperative in next stage will increase, we can deduce that the utility of the uncooperative employee in last stage is an increasing function of reputation. And if there is no relevant constraint mechanism in the last stage, the employee will maximize his own interests by extravagantly encroaching on the interests of the company. This can be confirmed in real life, For example, some managers make off with money.
In stage M ? 1, we suppose that the uncooperative employee choose to strengthen cooperation with the company before this stage, then the employee’s interest encroachment rate that the company expects is
![]()
![]() denotes the optimal interest encroachment rate of the employee in stage T ? 1, and its value is 1.
denotes the optimal interest encroachment rate of the employee in stage T ? 1, and its value is 1.
Now we assume parameter γ to be a discount factor, it denotes the discount relationship of the employee’s utility between current stage and next stage, or the patience degree that the uncooperative employee pretend to be cooperative. If the company operates more stably, has better culture atmosphere, possesses more standard management system or more sufficient information, the patience degree that the uncooperative employee pretend to be cooperative will be higher, and the discount factor will be larger. We will only take the pure strategy into consideration next, that is to say the value of ![]() will be 0 or 1, and we will compare and analyze the utility of the employee’s two different strategies in stage M ? 1.
will be 0 or 1, and we will compare and analyze the utility of the employee’s two different strategies in stage M ? 1.
On the one hand, if the uncooperative employee chooses to encroach on the interests of the company in stage M ? 1, namely![]() , since the value of
, since the value of ![]() is 1, then the probability that the company takes the employee as cooperative is 0, namely
is 1, then the probability that the company takes the employee as cooperative is 0, namely![]() , so
, so![]() , meanwhile
, meanwhile![]() , so the employee’s total utility in the last two stages is
, so the employee’s total utility in the last two stages is
![]() (4)
(4)
On the other hand, if the uncooperative employee choose not to encroach on the interests of the company in stage M ? 1, namely![]() , since the value of
, since the value of ![]() is 0, then the employee’s total utility in the last two stages is
is 0, then the employee’s total utility in the last two stages is
![]() (5)
(5)
If the value of formula (4) is less than formula (5), then the cooperative behaviors will win the employee more
interests than uncooperative behaviors in stage M ? 1. Make calculation (5) ≥ (4), we can get![]() . Besides,
. Besides,
the game reach the equilibrium when![]() , since
, since![]() , so
, so![]() . By formula (2), we
. By formula (2), we
get![]() , so
, so![]() . In conclusion, if the probability the company takes the employee as cooperative in stage M ? 1 is less than
. In conclusion, if the probability the company takes the employee as cooperative in stage M ? 1 is less than![]() , then cooperation will be a better choice for the uncooperative employee because he can maximize his long-term utility. On the contrary, when
, then cooperation will be a better choice for the uncooperative employee because he can maximize his long-term utility. On the contrary, when![]() , the uncooperative be-
, the uncooperative be-
haviors will bring the employee more benefits than cooperative behaviors, then he will choose not to cooperate with the company. It indicates another Nash equilibrium in this game, that is the uncooperative employee will never choose to cooperate when the value of γ is small enough.
3. Conclusions
We establish a reputation model in this paper to prove this assumption: when the whole company operates stably, has good culture atmosphere, possesses standard management systems or sufficient information, the reputation effect will be the important incentive mechanism for the cooperation between the employees and the companies. Under the reputation effect, the cooperation will be effective for the whole company. If the cooperation is only one time, which means the employee believes that his working time in the company is only probation period, then an uncooperative employee will not choose to cooperate; if the cooperation is repeated many times, even the uncooperative employee will choose to keep cooperating before the ending of the cooperation period to maximize his own utility, and build a good reputation when the whole company operates stably, has good culture atmosphere, possesses standard management systems or sufficient information. When the labor contract is terminated or the employee loses his confidence in the development of the company, the game will be over. And in this situation, the employee will use up the reputation he has established before and encroach on the interests of the company extravagantly. However, once the uncooperative employee has no confidence in the operation and development of the company at the very start, he will suspect the long-term cooperation, and the reputation model will have no any incentive effects on him.
Based on the research above, managers of a company can improve the situation from the following two aspects:
Firstly, strengthen the probation period management. In probation period, the employee is not familiar with anything in the company, but in the meantime it is the best time for them to learn and be influenced by the culture and environment of the company. Probation period is the golden time for the company to pass values, behavioral norms, knowledge system and business experience onto the employees [5] . In order to incorporate themselves into the new work team, the employees in probation period will accept and comply with the new “game rules” up to the hilt, whether they have years of experience or are just beginning their careers. And they will show their modesty and open mind which is far better than the older employees. If the companies miss this opportunity, it will cost them considerable efforts to shape them into the ideal “company men” [6] . Therefore, companies should not only give the necessary care to the new employees in probation period, but also pay attention to train them and eliminate their anxieties as soon as possible [7] , help them incorporate themselves into the culture and environment of the company. Only in this way can the employees have a sense of belonging, and then promote the cooperation between employees and companies. Moreover, it can lay the emotional and cultural foundation for the cooperation in formal work stage.
Secondly, use reputation effect to motivate employees to cooperate with companies in their formal work stage. This requires the effective management of the company itself, such as ensuring the stable operation of the company, creating comfortable work environment, building harmonious culture, establishing standard management system, implementing humanistic management and making the employees feel real care. By creating these superior conditions, the employees will be full of confidence in the development of the company and willing to cooperate all the time to establish good reputations, and then keep long-term cooperation so they can get more opportunities of promotion and development in the company. As a consequence, the win-win situation is realized.