Measurement of Radon Exhalation Rate in Some Building Materials Using Nuclear Track Detectors ()
1. Introduction
Radon is a natural noble gas has three main natural isotopes namely, radon (222Rn) decay product of 238U series, thoron (220Rn) produced from decay of 232Th series and 219Rn a decay product from the chain originating with 235U [1] . 222Rn isotope has a half-life of 3.82 days while 220Rn isotope has a half-life of 55 seconds and 219Rn isotope has a half-life of about 3.9 seconds. Radon and its daughter products may pose a significant health hazard especially when concentrated in some enclosed areas such as underground mines, caves, cellars or poorly ventilated and badly designed houses. Thus radon concentration in dwellings is important due to the health risk and to determine the design of control strategies [2] .
The valuation of radiological risk related to inhalation of radon and radon progeny is based mainly on the integrated measurements of radon. Therefore, it is desirable not only to measure the radon but also to find out the sources of radon especially in the houses [3] . Radiation exposure due to natural radionuclides in building materials like radon concentration in closed space was recognized as a significant cancer risk for the general population [4] .
Ionizing radiation levels in buildings related to radionuclide content in building material samples is clearly of fundamental importance in the assessment of population exposure as most of the residents spend about 80% of their time indoors [5] .
The present study aimed to determine the radon concentrations and radon exhalation rate in some building materials from local market of Dakahlia Governorate, Egypt, in order to detect any harmful radiation effects on the human and establish a data base for building materials which, is used in a local market.
2. Materials and Methods
Solid state nuclear track detectors have become an important tool in every investigation of the radon levels in the surrounding environment. Can technique with LR-115 detector was used to determine radon concentration and radon exhalation rate of the most commonly used building materials in Dakahlia Governorate. All samples were crushed to a grain size 1 mm and placed into samples containers. All samples were dried in oven at 110˚C for 3 hr, minced, sieved, weighted and carefully sealed for 61 days in cylindrical containers of plastic with dimensions of 9 cm in diameter and 16 cm in depth. The plastic container was capped tightly by an inverted cylindrical plastic cover.
A piece of LR-1115 (manufactured by Kodak Pathe, France) detector of area (1.5 × 1.5) cm2 fixed at the bottom center of the inverted plastic cover. During the exposure time of α-particles from the decay of radon and their daughters bombard the LR-115 detector in the air volume of the cylindrical containers. The detectors were collected after the irradiation period and etched in NaOH solution 2.5 N at 60˚C for one hour [6] . After etching the LR-115 detectors were washed in distilled water and wash time make a final rinse in distilled water and ethyl alcohol solution (1:1) during 2 minutes at 20˚C and dried in air. The track density was determined using optical microscope at 640× magnification which was calibrated before usages. The background of LR-115 track detector was counted by optical microscope and subtracted from the count of all detectors. Radon concentration in the samples was calculated using the following formula [7] :
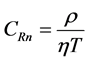 (1)
(1)
where, CRn is radon concentration (Bqm−3), ρ is the track density (track cm−2), T is the exposure time (day) and η is the calibration coefficient of LR-115 detector obtained from the experimental calibration 0.056 tracks cm−2∙day−1/Bqm−3of radon [6] . The surface exhalation rate (Bqm−2∙h−1) in the building material samples was calculated using the following formula:
 (2)
(2)
where, EA is the surface exhalation rate in (Bqm−2∙h−1), C is the integrated radon exposure in (Bqm−3∙h), λ is the decay constant of radon (h−1), V is the effective volume of the cup (m3), A is the cross section area of the can (m2) and Teff is the effective exposure time [8] . The mass exhalation rate (Bqkg−1∙h−1) in the building material samples is calculated using the following formula:
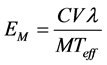 (3)
(3)
where, EM is the mass exhalation rate in (Bqkg−1∙h−1) and M is the mass of sample (kg) [8] . The following equation was used to calculate the annual effective dose:
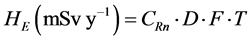 (4)
(4)
where, CRn in Bqm−3 is the measured mean radon activity concentration in air, F is the indoor equilibrium factor between radon and its progeny (0.4), T is time (8760 hy−1) and D is the dose conversion factor 9 nSv/h per Bq/m3 [9] [10] .
3. Results and Discussion
Radon concentration, area exhalation rate, mass exhalation rate and annual effective dose for the building materials were given by Table 1 and Table 2 [11] - [18] . The values of radon concentration for black cement ranged from 148.09 - 281.52 Bqm−3, area exhalation rate ranged from 190.99 - 362.88 mBqm−2∙h−1, mass exhalation rate ranged from 2.81 - 4.48 mBqkg−1∙h−1 and the annual effective dose varied from 4.67 - 8.87 mSvy−1. Cement (Al-Amserya) has a high values but cement (Al-askeria) has a low values. The values of radon concentration for white cement varied from 60.11 - 74.78 Bqm−3, area exhalation rate ranged from 77.44 - 96.43 mBqm−2∙h−1, mass exhalation rate ranged from 1.16 - 1.36 mBqkg−1∙h−1 and the annual effective dose varied from 1.89 - 2.35 mSvy−1. White cement (Sinai) has a low values but white cement (Helwan) has a high values. The values of radon concentration for gypsum varied from 72 - 93.18 Bqm−3, area exhalation rate ranged from 92.76 - 120.05 mBqm−2∙h−1, mass exhalation rate ranged from 1.90 - 2.25 mBqkg−1∙h−1 and the annual effective dose varied from 2.27 - 2.93 mSvy−1. Gypsum (Al-Medena) has a high values but Al-Bulah has a low values. The values of
![]()
Table 1. Radon concentration (CRn), area exhalation rate (EA), mass exhalation rate (EM) and annual effective dose rate (H) for building materials.
![]()
Table 2. Radon concentration (CRn), area exhalation rate (EA), mass exhalation rate (EM) and annual effective dose rate (H) for building materials.
radon concentration for sand varied from 175.77 - 336.65 Bqm−3, area exhalation rate ranged from 226.46 - 433.22 mBqm−2∙h−1, mass exhalation rate ranged from 2.28 - 4.10 mBqkg−1∙h−1 and the annual effective dose varied from 5.54 - 10.61 mSvy−1. Yellow sand (Al-Sharqia) has a high values but white sand (Al-Sharqia) has a low values.
The values of radon concentration of ceramic ranged from 61.41 - 114.35 Bqm−3, area exhalation rate ranged from 79.12 - 147.32 mBqm−2∙h−1, mass exhalation rate ranged from 0.87 - 2.03 mBqkg−1∙h−1 and the annual effective dose varied from 1.93 - 3.60 mSvy−1. Kilopatra ceramic has a high values but alpha has a low values. The values of radon concentration for marble varied from 160.70 - 281.52 Bqm−3, area exhalation rate ranged from 207.35 - 362.88 mBqm−2∙h−1, mass exhalation rate ranged from 2.66 - 3.87 mBqkg−1∙h−1 and the annual effective dose varied from 5.06 - 8.87 mSvy−1. White marble (Turkish) has a high values but green marble (Indian) has a low values.
Radon concentration for bricks varied from 97.36 - 163.06 Bqm−3, area exhalation rate ranged from 125.50 - 210.08 mBqm−2∙h−1, mass exhalation rate ranged from 1.46 - 2.68 mBqkg−1∙h−1 and the annual effective dose varied from 3.07 - 5.14 mSvy−1. Red brick has a high values but jerry brick has a low values.
Radon concentration for stone ranged from 307.07 - 334.60 Bqm−3, area exhalation rate ranged from 395.62 - 431.09 mBqm−2∙h−1, mass exhalation rate ranged from 4.20 - 5.49 mBqkg−1∙h−1 and the annual effective dose varied from 9.68 - 10.55 mSvy−1. Hash (Egyptian) has a high values but mica (Egyptian) has a low values. The values of radon concentration for gravel varied from 74.12 - 146.04 Bqm−3, area exhalation rate ranged from 95.49 - 188.25 mBqm−2∙h−1, mass exhalation rate ranged from 1.07 - 1.84 mBqkg−1∙h−1 and the annual effective dose varied from 2.33 - 4.60 mSvy−1. Ataka gravel has a high values but Salehia gravel has a low values. Radon concentration for granite varied from 590.61 - 1319.06 Bqm−3, area exhalation rate ranged from 761.24 - 1699.46 mBqm−2∙h−1, mass exhalation rate from 7.72 - 19.38 mBqkg−1∙h−1 and the annual effective dose varied from 18.62 - 41.59 mSvy−1. Granite (Jandola) has a high values but granite (rose) has a low values.
The average values of radon concentration, area exhalation rate, mass exhalation rate and annual effective dose for building materials were given by Table 3. The average values of radon concentration for building materials ranged from 68.42 - 845.43 Bqm−3, surface exhalation rate from 88.15 - 1089.25 mBqm−2∙h−1, mass exhalation rate varied from 1.22 - 11.55 mBqkg−1∙h−1 and the average value of annual effective dose varied from 2.05 - 25.58 mSvy−1 as shown in Table 3. From the obtained results the values of granite samples higher than the other building materials but the white cement has a low values. Figure 1, shows the comparison between the values of radon concentration for different building materials. Also the comparison between the values of area exhalation rate for the samples was given by Figure 2. The correlation relation between radon concentration and area exhalation rate is a good linearity relation and the correlation coefficient R2 = 1 as shown in Figure 3. The
![]()
Figure 1. The relation between the sample name and radon concentration (CRn) of the building materials.
![]()
Figure 2. The relation between the sample name and area exhalation rate (EA) of the building materials.
![]()
Figure 3. The correlation between radon concentration (CRn) and area exhalation rate (EA) of the building materials.
comparison between the average values of annual effective dose for the measured samples as shown Figure 4. From the obtained figure we find that the average annual effective dose rate of granite samples have a high values and white cement samples have a low values.
4. Conclusions
This study can be used to assess any changes in the radioactive background level in our houses in order to detect any harmful radiation effects on human and establish a data base for building materials which, is used in a local market.
The average values of radon concentration varied from 68.42 - 845.43 Bqm−3 and exhalation rate varied from 88.15 - 1089.25 Bqm−2∙h−1. From the obtained experimental results, we found that granite samples have a high values, while the lowest average values is white cement. The values of radon concentration and exhalation rate were varied from sample to another due to the variation in the chemical composition of the sample.
The obtained results show that the values of radon concentrations of the most samples are below the allowed limit from ICRP while granite samples higher are than the recommended limit. The International Commission on Radiological Protection recommended that a radon concentration from 200 to 600 Bqm−3 for dwelling [19] . Comparison the present work with results obtained in other parts of the world given by Table 4. The ventilation
![]()
Figure 4. The comparison between annual effective dose and samples of building materials.
![]()
Table 3. The average values of radon concentration (CRn), area exhalation rate (EA), mass exhalation rate (EM) and annual effective dose (HE) for building materials.
![]()
Table 4. The comparison between the obtained experimental results and the published data for building materials in different countries.
rate in the houses is very important role in controlling and protection from indoor radon.