1. Introduction
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is widely used in clinical diagnosis because of benefits such as excellent soft tissue contrast and the use of non-ionizing radiation. Many patients―including patients with metallic implanted medical devices―will undergo MRI during the course of their life. While MRI is considered to be a safe technology, there are possible risks, such as tissue heating caused by the radio frequency (RF) electromagnetic energy used to elicit the MRI signal [1] -[10] . This issue may be exacerbated in patients with metallic implants, because of the RF currents induced along the implant and the related electric field enhancement at the interface between implant and tissue [11] . For this reason, many patients with medical implants cannot undergo MRI. In order to facilitate the development of medical implants that are safe for MRI use, there is a need to design real time and robust methods to test the extent of RF-induced heating of tissue generated during an MRI scan. Currently, heating tests are performed using point temperature measurements made with fluoroptic probes. The measurements only provide the temperature of a small volume (1 mm3) near the probe, and are limited to the total number of probes available. Because of this, these measurements are inherently difficult due to the need for precise probe positioning related to the highly geometry-dependent and spatially inhomogeneous RF-induced heating [12] .
Over the past years, researchers have focused on using MR Thermometry because of the inherent ability of providing a volumetric assessment of temperature that overcomes the limitations of the fluoroptic probes [13] -[21] .
The most commonly used method in MR Thermometry (MRT) is the water proton resonance frequency (PRF) method, which is based on the phase shifts caused by the temperature dependence of the chemical shift of the water proton (1H) resonance [13] -[15] . However, MRT of the water proton is characterized by weak temperature sensitivities (~ 0.01 ppm/˚C), high sensitivity to main magnetic field (Bo) inhomogeneity, and susceptibility effects [16] [17] due to the relatively long echo times used. Therefore, the PRF method is not well suited for imaging around medical implants. Recently, the dependence of the water spin-lattice relaxation time (T1) on temperature has also been used in MR Thermometry [8] . However, because the T1 dependence is weak (i.e., 10 - 35 ms/˚C), this approach is less suited for measuring small temperature changes. Another difficulty in using the water resonance is the need for interleaved off-resonance RF pulses for heating, which is difficult to implement on many scanners due to software constraints.
Recent studies have proposed the NMR spectroscopic use of paramagnetic lanthanide complexes, namely thulium 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetramethyl-1,4,7,10-tetraacetate (Tm-DOTMA) and thulium 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetrakis (methylene phosphonate) (Tm-DOTP) for measuring temperature changes [16] [17] . These compounds are characterized by a high sensitivity of the chemical shift to temperature changes (methyl resonance: 0.57 - 0.7 ppm/˚C of Tm-DOTMA and ~1 ppm/˚C of Tm-DOTP [17] -[22] ). Compared to Tm-DOTP, Tm-DOTMA has lower temperature sensitivity, but much higher (about five-fold) signal, longer T2 and it is less sensitive to other parameters such as pH and concentrations of Ca2+ [18] -[22] . Additionally, these lanthanide complexes have short T1 and spin-spin relaxation time (T2) values (e.g., T1 and T2 values of CH3 proton in Tm-DOTMA at 9.4 T are 5.3 ms and 4.1 ms [21] , respectively), which could allow the use of shorter echo time (TE) and repetition time (TR). In addition, high flip angle and short TR were used in the in vitro experiments to increase the amount of RF heating to be detected with MRT.
Despite some of the positive attributes described above, the utility of Tm-DOTMA for real time MR thermometry imaging has not been previously reported. In this study, we have characterized the behavior of Tm- DOTMA in agarose gel and explored the use of Tm-DOTMA for real time MRT using both chemical shift imaging (CSI) and phase mapping method (PMM) [13] -[15] of PRF shift to map real time temperature changes in a phantom containing a metallic object, namely either a copper wire or a titanium screw. In addition, we have compared the results with those using conventional water PRF methods.
2. Materials and Methods
MR Thermometry experiments using water proton and paramagnetic lanthanide complex, Tm-DOTMA (Macrocyclics, Dallas, TX), were performed on a 4.7 T (200 MHz) Avance system (Bruker Biospin, Billerica, MA, USA) with a shielded high-pass birdcage RF coil.
A. TDCSC measurement and CSI implementation
Temperature dependent chemical shift coefficient (TDCSC) measurements of Tm-DOTMA were performed in agarose gel (Sigma-Aldrich,
St. Louis
,
MO
) and in distilled water. Three agarose gel samples (20 mM, 10 mM, and 4 mM Tm-DOTMA) as well as a 7.15 mM liquid solution were tested. The gel and liquid samples were prepared in a plastic tube that snugly fit inside a glass water jacket, which in turn was placed inside a saddle RF coil (diameter: 18 mm and length: 8 mm) as shown in Figure 1(a). Temperature control was achieved by circulating warm water through the jacket using a conventional hyper-hypothermia system (CSZ medical Inc., Cincinnati, OH, USA). The temperature was monitored using a multichannel thermometer system with two fluoroptic fiber probes (Luxtron 3100, Santa Clara, CA, USA), of which one was located at the center of the sample tube and the second one outside of the sample but inside the jacket to ensure temperature equilibration (Figure 1(a)). The system allowed obtaining a temperature over the whole tube spatially homogenous and constant over time.
Using the above setup, both 1D spectroscopy and 2D-CSI were performed to calibrate the chemical shift changes as a function of temperature and to validate the implementation of the 2D-CSI pulse sequence. 1D spectroscopy for the TDCSC measurements was performed using the following parameters: TR = 220 ms, number of averages (NA) = 32, 1024 data points, flip angle = 90˚ and bandwidth = 5 KHz, FID Acquisition time of 0.2 sec. The acquired data was processed using interactive left shifting, Fourier transform, zero filling, filtering, and phase correction. Analysis of the results was performed in Matlab (The MathWorks, Inc., Natick, MA). The 2D-CSI imaging sequence was implemented with the following parameters: TR = 55 ms, NA = 4, FOV = 25.6 × 25.6 mm, matrix size = 32 × 32, slice gap = 2 mm, and slice thickness = 5 mm. The temperature change (∆T) was calculated using the relationship between measured frequency shift of each voxel and the measured TDCSC of Tm-DOTMA.
B. Setup for real-time thermometry
A rectangular 1.0% agarose gel phantom (length LR = 116 mm, width WR = 55 mm and height = 20 mm, as shown in Figure 1(d)) containing 15 mM Tm-DOTMA was used. MRT was performed with either an copper wire (84 mm long) or a titanium bone screw (35 mm long and with 3 mm diameter), placed inside the gel. The copper wire was insulated, except for one of the two tips where a 1 cm-section of the insulation was removed. The implant (copper wire/titanium screw) was oriented along the z-axis and placed by the edge on one side of the phantom. A fiber optic probe was positioned near the tip of the implant and the second one was positioned on the contra-lateral side of the rectangular phantom (at 45 mm from the tip) to measure a reference temperature. Measurements were performed with a linear transmit/receive birdcage coil (diameter: ~ 72 mm, length: ~110 mm).
The temperature increase was achieved using two strategies. The first consisted of using pre-scans with high RF power (450˚ flip angle) followed by ~7 second imaging; progressively higher temperatures were achieved by
![]()
Figure 1. Experimental setup for measurement of temperature dependent chemical shift coefficient (TDCSC) (a) and fast thermometry (b) using a copper wire (c), a titanium screw ((b) and (d)) and a birdcage coil (e). The temperature increase was induced using flowing water (a) or RF heating (b). Four different solutions, i.e., three agarose gel samples (20 mM, 10 mM, and 4 mM Tm-DOTMA) as well as a 7.15 mM liquid solution, with same dimension of (a) were used in the TDCSC measurement. Two fluoroptic temperature probes were used to record the temperature changes near the implant and at a reference location. Physical dimensions: LP = 70 mm, DP = 10 mm, WR = 55 mm, LR = 116 mm, LC = 84 mm, LT = 10 mm, LS = 35 mm, and DRF = 72 mm.
increasing the number of pre-scans from 0 to 800. The second strategy was based on the heating generated from the RF pulses used for continuous dynamic imaging. With the two heating strategies described above, fast imaging of the methyl peak of Tm-DOTMA was performed using both 2D-CSI and 3D-PMM of PRF shift with the following parameters:
2D-CSI: 2D slice selective pulse (1 ms), TR = 25 ms, flip angle = 90˚, phase encode gradient time = 0.86 ms, FID acquisition time =12 ms, NA=1, variable FOV = (120 to 80) × (80 to 30) mm, matrix size = 16 × 16, variable spatial resolution = (7.5 to 5.0) × (5 to 1.9) mm/pixel, and spectral width = 10 kHz (~49.8 ppm).
3D-PMM: TR/TE = 14/(2.2 to 2.7) ms, a frequency selective pulse with flip angle = 90˚, NA = 2, FOV = 150 × 80 × 30 mm, matrix size = (64 to 128) (Readout) × 32 × 8, spatial resolution = (1.17 to 2.34) × 2.50 × 3.75 mm/pixel, and scanning time = 7.2 sec for each scan. Centric phase encoding was used for both 2D and 3D scans to minimize the effects of phase cancellation during the scan.
Water proton MRT was performed using a conventional 2D GRE sequence with the following parameters: TR/TE = 100/10 ms, flip angle = 30˚, NA = 1, FOV = 120 × 80 mm, matrix size = 120 × 80, spatial resolution = 1 × 1 mm/pixel, slice thickness = 2 mm, and scanning time = 8.0 sec. Because the RF pulse power was not high enough, only the pre-scan heating approach was used with water proton MRT.
MRT phase maps were generated off-line from the phase difference images (∆ϕ) using MATLAB scripts and phase unwrapping. The later was performed using edge detection and region-merging algorithm, based on a method by Mark [23] . The pixel wise ∆T computed with respect to the initial image was calculated as [14] :
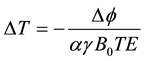 (1)
(1)
where ∆ϕ is the phase difference computed from each image at various temperatures and the initial image acquired before the first heating period, B0 is the static main magnetic field, γ is the gyromagnetic ratio, and α is the TDCSC of each proton (i.e., Tm-DOTMA or water).
C. Numerical electromagnetic field simulations
Numerical simulations were conducted for the evaluation of orientation dependency using the copper wire in 4.7 T (200 MHz). The geometry of the RF coil, RF shield, sample and copper wire with different orientations used in the simulation is shown in Figure 2. The modeled RF coil (ID: 72 mm, Length: 110 mm), RF shield (ID: 120 mm, Length: 110 mm) and sample (Height: 32 mm, Width: 55 mm, Length: 116 mm) geometries closely matched those used in experiment. Four different orientations of the copper wire, i.e., 0, 30, 60 and 90˚, were used in the simulation. A total of 12 radially oriented voltage sources located along the end rings and having 1 V peak-to-peak amplitude were used for ideal HP birdcage coil excitation. A 2 × 2 × 2 mm3 isotropic resolution
![]()
Figure 2. Geometry of the 12-rod birdcage coil, RF shield (yellow), sample (violet) and copper wire. (a) located inside the sample with different orientations of 0, 30, 60 and 90˚; (b) used for numerical simulations.
was used for the numerical simulations. All simulation results were normalized to obtain rotating RF magnetic field (|B1+|) = 4 μT at the center of the coil.
3. Results
The measured frequency shift relative to temperature using 1D spectroscopy and four different Tm-DOTMA samples (20 mM, 10 mM and 4 mM agarose gel and a 7.16 mM aqueous solution) (Figure 1(a)) were found to be 137 ± 3, 140 ± 6, 139 ± 5 and 141 ± 3 Hz/˚C, respectively. These values correspond to a TDCSC value of 0.685 ± 0.015, 0.7 ± 0.03, 0.695 ± 0.025, and 0.705 ± 0.015 ppm/˚C, respectively. In addition, the line widths of the spectra were found to be typically less than 120 Hz.
Figure 3(a) shows CSI color maps for a single slice, for the methyl peak of 20 mM Tm-DOTMA agarose sample at four different temperatures. The peak frequency was converted to a color scale when generating the images. The corresponding spectra for the four temperatures are shown in Figure 3(b). When the temperature measured by fiber optic probes increased from 16.6˚C (A) to 24.7˚C (D), the frequency changed from 273 Hz to 1386 Hz. The corresponding TDCSC value from 2D CSI was 0.685 ± 0.005 ppm/˚C, equals to 137 ± 1 Hz/˚C, in good agreement with the result of the 1D spectroscopy.
Figure 4 shows examples of thermal maps depicting temperature changes (∆T) that were obtained by application of 800 high power (450˚ flip) pre-scans, using the 2D CSI (a) and a PMM (b) of PRF technique, in a 15 mM Tm-DOTMA agarose-gel phantom with the copper wire. The pre-scan caused a temperature increase of approximately 1˚C near the tip as indicated by the fluoroptic probe. Both imaging techniques (2D-CSI and 3D- PMM of PRF shift) clearly revealed the temperature change using the Tm-DOTMA resonance, even though the scan time was 7 to 8 sec. Conversely, the corresponding water 2D-PMM of PRF shift scan (8 sec scan time) revealed in comparison with only minimal changes. In addition, the coronal Tm-DOTMA image showed tip heating at both ends of the wire, with a smaller effect on the side that was fully insulated. This weaker heating effect was not detected with the water PRF scan.
Figure 5 shows the real time temperature changes induced by the RF pulse used for imaging in the rectangular phantom. Sample images obtained using 2D CSI (a) and 3D- PMM of PRF shift (b) are shown. Each thermal map was computed by determining the frequency/phase shifts relative to the first image (reference). The temperatures measured by the fluoroptic probes and by the images acquired with both 2D CSI and 3D-PMM are shown in the lower panel.
Figure 6 shows an example of the thermal maps obtained using the gel phantom (Figure 1(b)) with the titanium screw instead of the copper wire. RF heating was induced by 800 pre-scan RF pulses. Thermal maps were
![]()
Figure 3. (a) Frequency shift map along an axial slice acquired using 2D-CSI with 20 mM agarose gel Tm-DOTMA phantom. The dashed rectangular box in (A) represents the region of interest (ROI) used for the calculation of an average frequency shift. The temperature measured using fiber optic probes located inside the phantom was 16.6 ˚C (A), 20.5 ˚C (B), 22.3˚C (C), and 24.7˚C (D). (b) Corresponding averaged spectra within the ROI. The pulse sequence parameters were: repetition time (TR) = 55 msec, FOV = 25.6 × 25.6 mm, matrix = 32 × 32, number of slice = 1, and scan time = 3 min and 45 sec. The calculated TDCSC was 137 ± 1 Hz/˚C, in line with the previous results of 1D spectroscopy.
![]()
Figure 4. Temperature change maps (∆T) obtained using the 2D CSI (a) and phase mapping method (b) of PRF technique in a 15 mM Tm-DOTMA agarose gel phantom containing the copper wire. The temperature change was induced by application of 800 high-power pre-scans. With the 2D CSI method tip heating can be observed in the transverse slice position near the tip of the wire. The coronal 3D-PRF maps of the methyl resonance of Tm-DOTMA ((b)-top) showed hot spots at both ends of the copper wire. The corresponding water proton 2D-PRF map ((b)-bottom) showed a smaller phase shift consistent with the lower sensitivity. The position of the probe is indicated by the red arrow.
![]()
Figure 5. Real time temperature changes due to heating caused by the RF pulse used for imaging are shown using 2D CSI (a) and 3D PMM of PRF shift (b) with the 15 mM Tm-DOTMA agarose gel phantom and the copper wire. Each ∆T image was calculated using a frequency shift relative to the first image (reference). (c) Temperatures measured by the optic probes (blue rectangles in (c)) and by the acquired images (red asterisk) with the 2D-CSI. (d) Temperatures measured by the optic probes (blue rectangles) and by the acquired images (green asterisk) with the 3D PMM. The position of the probe is indicated by the red arrow.
generated using PRF technique, 3D scan for Tm-DOTMA and 2D scan for water proton. Despite the considerable signal loss seen at both ends of the screw due the magnetic susceptibility effects, the Tm-DOTMA map showed a clearer heating pattern compared to the water image.
2D simulation results of |B1+|, electric field intensity(||E||), local specific absorption rate (SAR) defined as absorbed power divided by mass density [14] and 10 g-avg. SAR were shown in Figure 7 and 1D profile of the ||E|| at the tip of the copper wire is shown in Figure 8. Simulation results in Figure 8 show that the maximum ||E|| in the 1D profile is increased over 3 times (80 vs. 270 V/m) when the angle is decreased from 90˚ to 0˚.
4. Discussion
In this study we have explored the use of Tm-DOTMA to obtain near real time thermal maps in a phantom containing metal objects. Because the methyl resonance of Tm-DOTMA has much higher temperature sensitivity and substantially smaller T1 and T2 values than water proton [16] -[21] , it has the potential to decrease scan
![]()
Figure 6. Thermal maps obtained using a 15 mM Tm-DOTMA agarose-gel phantom containing the titanium screw. The phantom was heated with the pre-scan method (i.e., 800 RF pulses) (see also Figure 4). The top panel shows the 3D-PRF shift image from methyl resonance of Tm-DOTMA. The bottom panel shows the corresponding water PRF shift image. Considerable signal loss is seen at the tips due the magnetic susceptibility effects in both images. The scanning time without a pre-scan was 7.2 sec (Tm-DOTMA) and 8.0 sec (water proton). The MRT performed using Tm-DOTMA showed better sensitivity than that of a water proton. The position of the probe is indicated by the red arrow.
![]()
Figure 7. Numerical simulation results of |B1+| (first row), ||E|| (second row), Local SAR (third row), and 10 g-avg. SAR (fourth row) calculated without (first column) and with the copper wire having different orientations of 0(second column), 30 (third column), 60 (fourth column) and 90˚ (fifth column). All simulation results were normalized to obtain |B1+| = 4 μT at the center of the coil.
times by shortening TR and TE to about 2.2 (Figure 5(b)) or 2.7 ms (Figure 4(c) and Figure 6) compared to the range of 10 - 20 ms with water proton used in previous studies [14] [15] .
Gensler et al. [8] recently proposed a method of fast T1-based thermometry to detect the RF-induced heating of medical devices using off-resonance heating pulses. This method has two key limitations: 1) the quantifications at high temperature levels are not accurate because of the nonlinear and weak temperature dependence of T1; and 2) the method requires interleaved RF pulses for heating. Compared to the T1-based method, the Tm-
![]()
Figure 8. 1D profile of electric field intensity (||E||) without (green line) and with the copper wire having different orientations of 0 (red line), 30 (blue line), 60 (black line) and 90˚ (yellow line). Dashed red lines in the left image indicate the line selected for the graph. Values were normalized to obtain |B1+| = 4 μT at the center of the coil.
DOTMA method is based on the PRF shift and offers several advantages, including linear and sensitive dependence on temperature, potential for short TR/TE, and absence of dependence on tissue type [8] [24] . Additionally, the utility of T1 approach used by Gensler has not been studied for higher fields (>1.5 T) where the T1 is significantly longer.
The experiments used to acquire frequency shift maps of the four different Tm-DOTMA solutions (Figure 3) were performed by varying the temperature using a temperature controlled flow system which allowed excellent temperature control. Additionally, using a small cylindrical tube yielded uniform temperature throughout the sample by equilibration. The calculated TDCSC using the acquired frequency shift map was about 0.7 ± 0.03 ppm/˚C, which was consistent with previous research reporting 0.7 ± 0.1 ppm/˚C at 4.0 T using samples containing 4 mM of the agent, 3 mM of 3-(trimethylsilyl) propionic-2,2,3,3-d4 acid (TSP), and 10% of D2O with different cation (e.g., K+, Na+, Ca2+) concentrations [20] .
The experiments performed with the heating induced by pre-scan (Figure 4 and Figure 6) were limited by the maximum RF power tolerated by the coil, which allowed a 450˚ RF pulse. The use of Tm-DOTMA with either CSI or phase mapping allowed detecting a temperature change of less than 1˚C in near real time (7-8 sec). Additionally, Tm-DOTMA allowed capturing more details than the water PRF, such as the difference in temperature between the two tips―insulated vs. non-insulated―of the copper wire Figure 4(b).
The 2D CSI map (Figure 4(a)) agreed the difference qualitatively, but contained a few artifacts. The negative temperature change pixels may be due to intra-voxel phase cancelation, or due to inhomogeneous broadening from thermal gradients. Further investigation is required to understand the underlying mechanism. One of the drawbacks of the CSI method is that the TR time is limited by the long FID read time (~20 ms) necessary for the spectral resolution to detect small changes in chemical shift. In the 2D CSI scans, water suppression pulse sequences, such as CHESS [25] and VAPOR [26] , were not used in our experiment because of the relatively big frequency difference between water and methyl peak of Tm-DOTMA [20] , i.e., 100 ppm. Instead the water peak was filtered out by using a relatively narrow receive bandwidth. For the Tm-DOTMA PRF scan, the water signal was eliminated by using a frequency selective excitation of the methyl resonance in conjunction with phase encoding in two dimensions. Further temporal improvements could be potentially achieved using a spectral-spatial excitation with 2D imaging, which was not available on our scanner.
The experiment performed by heating the gel with the RF pulse used for imaging (Figure 5)―instead of the prescans―exploited one of the key strengths of Tm-DOTMA, namely the ability of using minimum TR and high flip angle due to the short T1 of the methyl resonance of Tm-DOTMA (~5.3ms at 9.4 T [21] ). The TR/TE used here is MRI scanner limited and can be shortened by a factor of two or three in modern clinical scanners. Shortening the TE further also has the potential to minimize susceptibility effects. The measured temperature changes from these near real time acquired images (red and green asterisk in Figure 5(c) and Figure 5(d)) matches well with that of the optic probes (blue rectangle in Figure 5(c) and Figure 5(d)).
In the experiments performed with the titanium bone screw (Figure 6), signal dropout was seen for both water proton PRF scan and Tm-DOTMA, however, the heating pattern was well visualized for 2D CSI of Tm- DOTMA but not for the water proton PRF.
In the context of testing for RF-induced heating due to the presence of metallic implants, the thermometry scan has to be fast compared to temperature changes due to heating. However, a unique challenge emerges for monitoring real time changes in temperature caused by the RF pulses of the imaging pulse sequence. If the heating is too rapid, or if the imaging scan is too slow, this can cause chemical shift related artifacts. Ideally, the heating from the RF pulses should be fast compared to heat dissipation due to conduction, and imaging scan need to be sensitive and fast enough to minimize artifacts. In addition, the estimates of local SAR depend on the initial slope of temperature increase. Typically, the slopes are under a few degrees/min [27] -[29] . Hence the need for a sub-minute time resolution for real time thermometry.
The source of the heating is the electric field as well as the physical properties (e.g., conductivity, relative permittivity, mass density, heat capacity) of the copper wire and the surrounding phantom [13] -[15] . The electric field is composed of conservative electric field (primarily originating with the scalar electric potential in the coil), and the magnetically-induced electric fields (caused by the time-varying magnetic field) [14] [27] . The two components may affect unevenly to the heating. However, it is difficult to separate these two components in our study because of a significant wavelength effect (200 MHz, 150 cm wavelength in air, ~19 cm wavelength in the phantom, RF coil diameter = 10 cm) [27] .
Our approach using Tm-DOTMA presents some limitations. Tm-DOTMA is not approved for human use, but can be used in phantom or animal testing [5] -[10] . Tests in gel-phantom have been used to evaluate RF-induced heating of metallic implants in high field MRI. In this study, we focused on the possibility of medical device evaluation using a phantom, not a human volunteer.MR images acquired in this study with Tm-DOTMA showed substantially lower SNR compared to those of a water proton images because of the significant difference in concentration (i.e., Molar level concentration for the Tm-DOTMA vs. Molar level for the water proton). However, this limitation can be partially overcome if a higher concentration Tm-DOTMA is used for phantom experiments.
5. Conclusion
We have implemented real-time and sensitive MR Thermometry using CSI and phase mapping of PRF shift with a Tm-DOTMA phantom to image small temperature changes caused by RF-induced heating near two types of implants, namely a copper wire and a titanium bone screw. We have compared the results with those using the conventional water PRF method to show that the Tm-DOTMA based approach is more sensitive and able to image changes that are less than 1˚C.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Howard Bassen and Daniel M. Krainak for technical discussion. This work was supported by the FDA Center of Devices and Radiological Health Critical Path Program.
Disclaimer: The mention of commercial products, their sources, or their use in connection with material reported herein is not to be construed as either an actual or implied endorsement of such products by the US Government Department of Health and Human Services.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.