Experimental Design and Its Posterior Efficiency for the Calibration of Wearable Sensors ()
1. Introduction
Wearable health monitoring system is one of the most promising technologies to provide effective solutions to health monitoring for aging populations. Various wearable sensors equipped with artificial intelligence, e.g., neural networks, fuzzy logical, genetic algorithm, particle swarm optimization, and clustering, have already been utilized for specific health monitoring tasks [1] . However, in general, the accuracy of the wearable sensors needs to be substantially enhanced in order to improve the reliability of wearable systems to meet medical device standards.
With the rapid development of Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) technology, chip-based wearable sensors are becoming small, inexpensive, lightweight, and low energy-consuming, which stimulate their applications in the development of wearable systems in health monitoring [2] , e.g., gait analysis and fall detection/ prediction [3] . However, due to their fabrication process, similar to most wearable sensors, MEMS sensors have large bias instability and output noise. Regular calibrations are therefore necessary to improve the accuracy of sensors’ measurements. However, due to the inaccessible of laboratory equipments, users of wearable health monitoring systems are normally unable to implement designed experiment sufficiently.
Several recent papers [4] - [6] report that a new calibration method for MEMS triaxial accelerometer, recognized as autocalibration, can be implemented in non-experimental condition. However, the quality, especially the assessment of each individual calibration, has not received the attention it deserves. To authors’ best knowledge, unlike traditional calibration method, there is no paper systemically discussing the issues of Experimental Design (DoE) yet. Most studies concentrate on the parameter estimation algorithms and its feasibility investigations. Few papers [7] [8] qualitatively described the selections of experimental observations.
This paper aims to provide a systematic investigation of Experimental Design (DoE) for autocalibration method. A major focus of DoE is to optimally design suitable input signals to stimulate the system significantly so that the information about the system can be extracted from the experiments. For the identification of a static model of an inertial sensor, a well selected/designed set of experimental observations with desired properties, in terms of DoE, can significantly improve the accuracy of parameter estimation [9] .
Classical accelerometer calibration, normally carried out in a well-controlled laboratory environment, can be formulated as a static linear parameter identification problem, for which DoE theory has been well established [9] - [13] . However, the models associated with the autocalibration are often nonlinear. This makes the linear DoE approaches, which are effective and theoretically rigorous in traditional accelerometer calibration, invalid for autocalibration.
In this study, a new linearization method for autocalibration [4] is developed in order to utilize linear DoE for this new calibration method. A 12-observation Icosahedron design has been proposed for a linearized 9-para- meter model [6] to improve the accuracy of autocalibration. Two performance indices of optimal experimental design, D-optimality and G-optimality, are investigated based on the analysis of the information matrix of this Icosahedron design. Furthermore, a posterior type D-efficiency [11] is introduced to evaluate a specific experiment when compared with the D-optimal value under ideal experimental conditions.
The paper is structured as follows. The next section introduces the proposed linearization method for the 9- parameter model for autocalibration. In Section 3, an experimental design is proposed and the details of its indices will be analysed. Section 4 shows experimental validation of the designed experiment and Section 5 concludes the paper.
2. New Linearization Method for Auto-Calibration Model
A classical static linear second-order model for an accelerometer can be written as follows:
 (1)
(1)
where 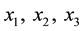 are the associated control or input variables (i.e., the input acceleration for each axis),
are the associated control or input variables (i.e., the input acceleration for each axis), 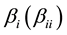 are the unknown constant coefficients (also referred to as parameters), and
are the unknown constant coefficients (also referred to as parameters), and 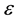 represent the random errors in experimental measurements.
represent the random errors in experimental measurements.
Assume a set of 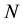 experimental observations have been performed. Then, the matrix form of the experiment can be expressed as follows [9] :
experimental observations have been performed. Then, the matrix form of the experiment can be expressed as follows [9] :
 (2)
(2)
where 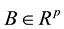 is the vector of the unknown parameters,
is the vector of the unknown parameters, 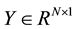 is the vector of measurements, matrix
is the vector of measurements, matrix 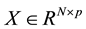 is generated by the input signals, and
is generated by the input signals, and 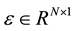 is the vector of random errors.
is the vector of random errors.
Assume that the random errors 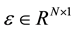 are zero mean, then the information matrix for
are zero mean, then the information matrix for  in Equation (2) can be defined as
in Equation (2) can be defined as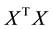 :
:
 (3)
(3)
where  is the i-th row of matrix X [14] . For a specific N trials design
is the i-th row of matrix X [14] . For a specific N trials design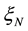 , Equation (3) can be normalized as:
, Equation (3) can be normalized as:
![]() (4)
(4)
which is also known as moment matrix. If ![]() is full rank, the variance-covariance matrix of the least square (LS) estimator
is full rank, the variance-covariance matrix of the least square (LS) estimator ![]() is:
is:
![]() (5)
(5)
The variance of ![]() is of the form:
is of the form:
![]() (6)
(6)
In order to compare within different experimental designs, the scaled prediction variance is often defined as follows [14] :
![]() (7)
(7)
To apply DoE theory for the calibration of MEMS accelerometer, we define uncalibrated acceleration gener-
ated from accelerometer output as![]() , which is generated from the measurement of accelerometers. We also define
, which is generated from the measurement of accelerometers. We also define ![]() as the offset of the accelerometer. The vector
as the offset of the accelerometer. The vector ![]()
is the real acceleration component on each axis.
A model describing the accelerometer can then be expressed in matrix form as below:
![]() (8)
(8)
where ![]() is the scale factor matrix. The diagonal elements
is the scale factor matrix. The diagonal elements ![]() represent sensitivity of each direction and off- diagonal elements
represent sensitivity of each direction and off- diagonal elements ![]() represent cross-axis sensitivity. Considering the symmetry constraint for the scale factor matrix
represent cross-axis sensitivity. Considering the symmetry constraint for the scale factor matrix ![]() (i.e.,
(i.e., ![]() [6] ). Therefore, the model in Equation (8) can be expressed in 9 independent parameters.
[6] ). Therefore, the model in Equation (8) can be expressed in 9 independent parameters.
The autocalibration method is based on the fact that the overall acceleration which is measured by triaxial accelerometer should equal to the local gravity acceleration “1g” in static condition. The principle of autocalibration is:
![]() (9)
(9)
By applying the method of autocalibration (see Equation (9)) for the 9-parameter model from Equation (8), we have:
![]() (10)
(10)
where ![]() is squared difference between accelerometer output and local gravity acceleration “1g”. Equation (10) can be further expressed as:
is squared difference between accelerometer output and local gravity acceleration “1g”. Equation (10) can be further expressed as:
![]() (11)
(11)
where![]() .
.
Equation (11) cannot be written in the form of Equation (1) because of its nonlinearity with the parameters. To estimate the parameters, most existing studies use either nonlinear least square method [4] [11] or nonlinear recursive algorithms [7] . However, the key of these approaches is to locally linearize the nonlinear Equation (11) and recursively identify the unknown parameters.
Inspired by these studies, this paper proposes a new linearization scheme to directly linearize Equation (11) and transform it in the form of Equation (1). From this, mature linear DoE theory can be directly applied to handle experimental design and parameter estimation for the autocalibration scheme. In contrast with local linearization (e.g., Taylor expansion around the observation point), the main strategy of the proposed linearization method is based on re-combination of parameters.
Firstly, this approach disregards the items in Equation (11) which have little impact on parameter estimation. Table 1 indicates that zero-g offset for each axis could be quite large in the worst case. If necessary, a pre-cali- bration is recommended to reduce initial zero-g offsets. After this procedure, the residual ![]() in Equation (12) will be much smaller when comparing to local gravity acceleration “1g”. Let us compute and simplify
in Equation (12) will be much smaller when comparing to local gravity acceleration “1g”. Let us compute and simplify![]() :
:
![]() (12)
(12)
From Table 1, we can see the cross-axis sensitivity ![]() is only 1%. Therefore, the terms in Equation (12) contain
is only 1%. Therefore, the terms in Equation (12) contain ![]() and
and ![]() which
which ![]() can be disregarded. We also disregard the items contained
can be disregarded. We also disregard the items contained ![]() and
and ![]() as these items can be reduced significantly after pre-calibration. The remains of
as these items can be reduced significantly after pre-calibration. The remains of ![]() is:
is:
![]() (13)
(13)
We can apply the same simplification method for ![]() and
and ![]() to simplify Equation (11) as follows:
to simplify Equation (11) as follows:
![]() (14)
(14)
where![]() ,
, ![]() is zero mean Gaussian noise and
is zero mean Gaussian noise and ![]() is non-zero random error representing the mean of the summation of the disregarded items.
is non-zero random error representing the mean of the summation of the disregarded items.
From Equation (14), let us define new parameters for the re-combined parameters as follows:
![]() (15)
(15)
Let us use ![]() to represent
to represent![]() , Equation (14) can be expressed as:
, Equation (14) can be expressed as:
![]() (16)
(16)
This can be simplified as:
![]() (17)
(17)
Since ![]() is input signal, the equation is now a linear equation about unknown parameters
is input signal, the equation is now a linear equation about unknown parameters![]() . If we tentatively disregard
. If we tentatively disregard ![]() (in Section 4, we will show this unknown number can be recursively estimated), Equation (17) becomes a special case of Equation (1).
(in Section 4, we will show this unknown number can be recursively estimated), Equation (17) becomes a special case of Equation (1).
![]()
Table 1. Some significant specifications of ADXL345.
Applying linear least square estimation (LSE) method for the simplified linear model, we have
![]() (18)
(18)
where
![]()
and
![]()
Based on linear least square method, all new unknown parameters from Equation (16) can be estimated. According to the definition of Equation (15), the original 9 independent parameters![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() can therefore be computed. However, as the nonzero random error
can therefore be computed. However, as the nonzero random error ![]() is disregarded, to obtain desired estimation accuracy, the LSE method should be recursively performed (see Section 4 for details). It should be noticed that
is disregarded, to obtain desired estimation accuracy, the LSE method should be recursively performed (see Section 4 for details). It should be noticed that ![]() and
and ![]() are not independent. For example, both
are not independent. For example, both ![]() and
and ![]() include common term
include common term ![]() from the definition above.
from the definition above.
3. Proposed Experimental Plan and Optimality Indices
3.1. Icosahedron Design
In order to estimate 9 unknown parameters, a minimum number of 9 observations are necessary. To balance the cost and accuracy, we propose a 12-observation Icosahedron design, which is a space filling design aiming for the uniformly distribution of experimental observations on experimental domain. This experimental design is for the linearized 9-parameter model derived in Section 2. The idea of Icosahedron design is that all 12 observations uniformly distribute on the surface of sphere.
Due to the constraint of the gravity based calibration, all the experimental observations will be situated uniformly on the surface of a sphere whose radius equals to local gravity “1g”. In another word, these 12 experimental observations will construct an Icosahedron whose circumcircle has radius of “1g”.
For Icosahedron design, if the radius of its circumcircle is “1g”, then all 12 observations can be pinpointed on rectangular coordinate system (see Table 2 for details). In Table 2, ![]() ,
,![]() .
.
For each individual observation, the relationship of Table 2 can be well described by the following equations:
・ ![]() ,
, ![]() is tilt angle between
is tilt angle between ![]() and gravity;
and gravity;
・ ![]() ,
, ![]() is tilt angle between
is tilt angle between ![]() and gravity;
and gravity;
・ ![]() ,
, ![]() is tilt angle between
is tilt angle between ![]() and gravity.
and gravity.
3.2. G-Optimality
G-optimal design is seeking to minimize the maximum value of the scaled prediction variance in Equation (7) over the experimental region [14] :
![]() (19)
(19)
![]()
Table 2. Three factors icosahedron design for triaxial accelerometer model and the tilt angle in three dimensional coordinate.
G-optimal is an important measurement of performance which indicates satisfactory prediction of output throughout the design region.
We propose the following theorem to show the proposed Icosahedron design is G-optimal.
Theorem 1. The proposed Icosahedron design for the linearized 9-parameter accelerometer model
![]() (20)
(20)
is G-optimal.
Proof. The variance equation of predicted ![]() is:
is:
![]() (21)
(21)
Recall scaled prediction variance from Equation (7):
![]()
A G-optimal design ![]() is one which can min-max
is one which can min-max![]() , i.e.,
, i.e.,
![]() (22)
(22)
Regarding Equation (21), G-optimal is equivalent to
![]() (23)
(23)
where ![]() is the moment matrix
is the moment matrix![]() .
.
According to [9]
![]() (24)
(24)
where ![]() is the number of parameters.
is the number of parameters.
That is, for a specific experimental design, if
![]() (25)
(25)
then this experimental design is G-optimal design [9] .
Consider the Icosahedron design proposed above for 9-parameter model:
![]()
Recall Icosahedron design, matrix ![]() in Equation (21) is:
in Equation (21) is:
![]()
Substituting the value of ![]() and
and ![]() into Icosahedron design, as a result, we can compute the inverse of the moment matrix
into Icosahedron design, as a result, we can compute the inverse of the moment matrix![]() :
:
![]()
Considering that
![]()
we have
![]() (26)
(26)
Under the constrain![]() , it is easy to see:
, it is easy to see:
![]()
According to the theorem of G-optimal in [4] , this 12-observation Icosahedron design for the linearized 9- parameter model is G-optimal. □
3.3. D-Optimality
Another desired design characteristic of experimental design is D-optimality. The criterion of D-optimality is maximizing the determinant of the information matrix for continuous design or moment matrix for exact design [14] :
![]() (27)
(27)
which leads to minimize the size of the confidence ellipsoid for the estimator ![]() in Equation (5).
in Equation (5).
Kiefer and Wolfowitz [15] [16] developed the well-known Equivalence Theorem (KWT theorem), which provides a practical way to check if a design is D-optimal. This theorem shows that for continuous designs, D- and G-optimal designs are equivalent under some standard assumptions [15] [16] .
Based on KWT theorem, we show the proposed Icosahedron design is also D-optimal.
Theorem 2. The proposed Icosahedron design is D-optimal for the linearized 9-parameter model
![]()
Proof. Let us consider a continuous experimental design ![]() with finite observation N. From Equation (21), if
with finite observation N. From Equation (21), if ![]() , then this experiment is continuous G-optimal design. For our Icosahedron design, we proved that
, then this experiment is continuous G-optimal design. For our Icosahedron design, we proved that ![]() in Theorem 1.
in Theorem 1.
To convert exact design ![]() to continuous design
to continuous design![]() , let us consider that each observation in the experimental design shares the same weight. In this case, the value of
, let us consider that each observation in the experimental design shares the same weight. In this case, the value of ![]() for our Icosahedron design will also be 9 which means Icosahedron design is continuous G-optimal design for the linearized 9-parameter model.
for our Icosahedron design will also be 9 which means Icosahedron design is continuous G-optimal design for the linearized 9-parameter model.
Based on KWT Equivalence Theorem [14] - [16] , since the Icosahedron design can be considered as continuous G-optimal design, it is also continuous D-optimal design. □
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
The ![]() -IMU that we use to test the Icosahedron design contains a triaxial accelerometer ADXL345 manufactured by Analog Device. The main characteristics of ADXL345 are listed in Table 1.
-IMU that we use to test the Icosahedron design contains a triaxial accelerometer ADXL345 manufactured by Analog Device. The main characteristics of ADXL345 are listed in Table 1.
Based on the described experimental design in Section 3, we tried to implement the Icosahedron design. It is not supervising that the proposed plan cannot be fully implemented by using the “non-professional” calibration devices. To access the quality of a specific experiment, we adopt the following index, D-efficiency [10] , to evaluate the quality of a particular experiment
![]() (28)
(28)
where ![]() and
and ![]() stand for the designed optimal experiment and a specific experiment respectively.
stand for the designed optimal experiment and a specific experiment respectively.
To evaluate the efficiency of a specific experiment, ideally, we need the exact input value of each observation for a specific design![]() . In a traditional accelerometer calibration experiment, the input (acceleration) to the accelerometer can be accurately measured and its value are adjustable. Therefore, for traditional accelerometer calibration, the D-efficiency can be determined even before the experiments.
. In a traditional accelerometer calibration experiment, the input (acceleration) to the accelerometer can be accurately measured and its value are adjustable. Therefore, for traditional accelerometer calibration, the D-efficiency can be determined even before the experiments.
However, for auto-calibration, the input value on each axis of a particular observation, denoted by a vector A, cannot be directly measured from the calibration device. We therefore have to use the output of the accelerometer, which is under calibration, to estimate the real input acceleration A. Equation (8) describes the relationship between the uncalibrated acceleration output V and the real acceleration input A if assuming the scale factor and offset are accurate. Let us recall Equation (8) and simplify it as:
![]() (29)
(29)
In order to obtain real acceleration A, we need to compute scale factor S and offset O first. Towards the end of Section 2, we mentioned the scale factor ![]() and offset
and offset ![]() can be recursively estimated by LSE. Based on Equation (17), the linearized 9-parameter triaxial accelerometer model can be rewrited as:
can be recursively estimated by LSE. Based on Equation (17), the linearized 9-parameter triaxial accelerometer model can be rewrited as:
![]() (30)
(30)
where Y is local gravity “1 g”, V1 represents uncalibrated acceleration from accelerometer, B1 is vector of re- combined parameters defined in Equation (15), ![]() is zero mean error and
is zero mean error and ![]() is non zero error representing the mean of disregarded items. To apply LSE for Equation (30), let us disregard
is non zero error representing the mean of disregarded items. To apply LSE for Equation (30), let us disregard![]() :
:
![]() (31)
(31)
where Y is local gravity “1 g”, V1 is the known quantity from accelerometer and B1 is re-combined parameter by scale factor S and offset O. S1 and O1 can then be solved by using LSE as shown in Equation (18).
From Equation (29), we have
![]() (32)
(32)
Due to the fact that we neglected some little impact items during LSE, A1 will not be exactly the same as real acceleration A, but A1 is closer to real acceleration A comparing to V1. In this case, when A1 is closer to A, the value of offset O will be reduced. Recall from Section 2 that all disregarded items contain offset O, it means the mean of the summation of all disregarded items ![]() will reduce. We replace V1 with A1 (A1 is marked as
will reduce. We replace V1 with A1 (A1 is marked as ![]() in Equation (33) and apply LSE again for the equation below with less impact from
in Equation (33) and apply LSE again for the equation below with less impact from![]() :
:
![]() (33)
(33)
From Equation (15) and Equation (18), the new scale factor S2 and offset O2 can then be solved. Recall Equation (29):
![]() (34)
(34)
In this case, ![]() will be even closer to real acceleration
will be even closer to real acceleration ![]() comparing to
comparing to![]() .
.
Let us repeat this procedure, Ai is approaching to real acceleration A while offset O is reducing to 0. The accuracy of LSE will increase because all disregarded items contain offset O will drop to 0. Eventually, offset O and cross-axis factors ![]() will be 0, sensitivity factor of each direction
will be 0, sensitivity factor of each direction ![]() will be 1. Then this acceleration
will be 1. Then this acceleration ![]() will be optimal estimation of real acceleration A.
will be optimal estimation of real acceleration A.
The overall equation of Equation (29) is:
![]() (35)
(35)
Now, as ![]() can be applied for experiment evaluation, this recursive procedure can guarantee the accuracy of the evaluation for posterior type D-efficiency.
can be applied for experiment evaluation, this recursive procedure can guarantee the accuracy of the evaluation for posterior type D-efficiency.
We performed the calibration experiment in the Center of Health Technologies (CHT), University of Technology, Sydney (UTS), without using a turntable. In contrast with the ideal setting, the posterior type D-effi- ciency for our experiment is around 99.7% which is slighter smaller than 100%. It indicates our experiment achieved desired results.
Experimental results also showed the Mean Square Error (MSE) has been reduced from 0.00344 g2 to 0.000255 g2 by the proposed experimental design/calibration method.
5. Conclusion
This study investigates the DoE for autocalibration of triaxial accelerometer in a wearable micro Inertial Measurement Unit (μ-IMU), and our contribution is two-fold. Firstly, a new model linearization strategy is proposed to linearize the nonlinear model associated with the autocalibration of triaxial accelerometer. The major technique of the proposed linearization strategy is based on recombination of parameters rather than local linearization around observation point (e.g. Taylor expansion). With such a linearized model, the classical linear model identification and DoE approaches can be applied to calibrate the triaxial accelerometer in a non-experimental environment. The second contribution is that this paper introduces a new experimental scheme, Icosahedron design. We have proved that this scheme is both G-optimal and D-optimal for the linearized 9-parameter triaxial accelerometer model. Experimental results also demonstrate that the proposed DoE scheme can significantly decrease the MSE of triaxial accelerometer after calibration. This indicates that the proposed linearization method is reliable and efficient. We believe that the proposed experimental design approach can provide an efficient tool for the users of wearable sensors to efficiently calibrate the sensors in free living condition.