Determining the Optimal Algorithm to Locate the Best Place for Earthquake Refugee Camps: A Case Study for Tehran, Iran ()
1. Introduction
Earthquake is a natural disaster, which based on its magnitude can create great tragedies in a short time [1] . A fundamental truth about this disaster is that in the face of such disasters, much work cannot be done at the moment of occurrence, while their impacts can be neutralized or minimized by previous planning [2] .
Iran is located on the way of Hymalya-Alpineorogenic belt and has a variable climate, as well as temporary and transient instabilities [3] .
Tehran with a population of 13.6 million during the day is in the list of the first 10 cities with the highest risk of earthquake which in the base of potentially affected population locates in sixth rank after Tokyo, Jakarta, Manila, Los Angeles and Osaka cities [4] .
Throughout history, many natural disasters, particularly earthquakes have occurred in Tehran that their number reaches 12. The recent earthquakes occurred related to the region of Buin Zahra in 1962 with the magnitude of 2.7 on the Richter scale, in 1973 at Varamin and Eyvanki regions with magnitude of 5 [1] .
Given the history of these types of natural disasters in the region, the necessity of planning (crisis management) is left after an disaster that in addition to creating the proper location in terms of physical, security, social,…, would be a place where human dignity is preserved in them and provide a rapid return to normal life for the people affected. It can be stated certainly that the prerequisite to achieve this goal is planning before crisis and disaster occurrence in the urban prone areas.
In relation to temporary resettling of earthquake victims, studies having been done that can be pointed to a study was conducted by Esmail Zebardast and Asal Mohammadi (2005) with the title of locating the relief centers, which has been facing the multi criteria evaluation of AHP in earthquake using GIS software. In this research, using AHP method has been studied locating of relief center for rescue operations in earthquake occurrence conditions in district 11 of Tehran Municipality and its vulnerability rate against the possible earthquake [2] .
In another study by Samad Zadeh et al. (2005), entitled “Locating Temporary Resettling for Disaster Management Based on the Application of Intelligent Spatial Information System”, Fuzzy logic system is used that their ability is proved in solving various problems of spatial information based on GIS, in order to decide for locating [5] .
Islami et al. (2001) also have presented a research entitled “Locating Relief and Resettling Center” in district 1 of Tehran Municipality in order to determine proper locations to establish relief centers after the crisis, especially earthquakes [4] .
The purpose of article ahead is to investigate differences and determine the advantages and disadvantages of various methods of locating and selecting the optimal method for temporary resettling of victims after earthquake in Tehran utilizing GIS.
Considering the importance and abundance of available criteria, such that each of these criteria could lead to a peaceful and secure environment and far from hazardous environments, the criteria considered which finally criteria for evaluation is combined and proper locations will be determined. It is notable that in this writing method of OWA, TOPSIS, AHP and Fuzzy will be investigated.
2. Geographical Location of the Study Area
Tehran city geographically located in the southern foothills of the Alborz Mountains, between 51 degrees 2 minutes east longitude to 51 degrees 36 minutes east. Tehran has a length of approximately 50 km, and longitude 35 degrees 34 minutes north and 35 degrees 50 minutes north latitude and approximately 30 km wide and is located in the northern half of the country. Its elevation is 1800 m in the northern most point and 1050 meters above the sea level in the southern most point. Tehran has led to the mountains area from the north and desert areas from the south [6] .
There are three main faults in this city in the North, East and also Ray fault in the south. North Tehran fault has started from Lashkarak and Suhanak to Farahzad and Hessarak regions and then extending toward west. This fault covers in its path regions of Niavaran, Tajrish, Zafaranieh, Elahieh and Farmanieh. Ray fault in the south of Tehran, which is the most high loss fault of the country and perhaps the world, has started from Khavaran road and with passage from Dowlatabad and move on the ring road of Tehran, ends at the quorum of ChaharDangeh brick kilns.
The east fault that also has ability of the strongest earthquake, Imported from the East to Tehran and with passing from the Sorkhehessar areas and move on ShahidBabaei Highway extending to Majidieh and Seyed Khandan. It is interesting that most of the power transmission lines are located on these earthquake faults. In the meantime the single fault Mulla Sadra, which transferred from Shariati St to ShahrakeGharb has made unsafe Vanak, Mirdamad, Sa’adat Abad and Shahrakegharb neighborhoods. Milad tower is also constructed just adjacent to this fault [7] .
In historical records of the city of Tehran, great earthquakes have been recorded such as Damavand 7.1 magnitude earthquake in 2001, 7.2 magnitude in 1711 AD in Karaj, 7.7 magnitude in Taleghan in 958 AD, Ray earthquake 7.1 magnitude in 855, and many other earthquakes over 7 magnitude in Richter. Return period of earthquake in Tehran is about 150 to 200 years; since it has passed more than 170 years from the last strong earthquake, the risk of earthquake is very high in Tehran [7] .
Figure 1 shows regions of earthquake in Tehran.
Areas marked in yellow on this map are the boundary of the faults rupture. In this area no buildings remain intact with any safety factor. The next area is shown in blue, because it is located near the rupture zone, the destruction would have a very severe.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Collecting the Criteria
In this study using previous research as well as interviews with experts in crisis management, the criteria used are collected [9] .
These criteria are extracted ultimately from Tehran topographic maps with a scale of 1:25000.
Table 1 shows the selected criteria for localization.
3.2. Models Evaluated
3.2.1. Hierarchical Model (AHP)
In hierarchical analysis, there is the possibility of reformulating the problem and consider various quantitative and qualitative criteria. In this process, various options can be incorporated in decision-making and there is the
![]()
Table 1. Criteria and Policy for each criterion.
possibility of sensitivity analysis on the parameters. AHP is based on pair comparison that make easy the judgment and raises the accuracy. Also one of the main advantages of this method is calculation of inconsistent rate which by its determination appeal the judgment occurs [10] .
AHP input is paired comparison matrix which its elements determine the relative importance of criteria. In this method, comparison is done to obtain the criteria weights and the priority of different classes of criteria. Decision maker should first evaluate and compare all the relevant criteria, then convert the results to qualitative values by a standard scale [6] .
First a hierarchy of paired comparison matrix is created and then the weight is calculated and finally the inconsistency rate can be determined.
Inconsistency rate consists of three parts:
A) Eigenvectors
B) inconsistency rate:
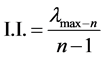 (1)
(1)
n: dimension/size of matrix
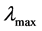 : Largest eigenvalue that is always greater than or equal to n.
: Largest eigenvalue that is always greater than or equal to n.
I.I: Inconsistence criterion
RI: inconsistence criterion from average matrix
C) Inconsistence rate:
 (2)
(2)
This value is acceptable when less than 0.1 is.
Each of selected criteria have sub-criterion that these sub-criterion specified based on expert opinions, field studies and a review of previous research. Range of vulnerabilities: Vulnerable categories of low, medium and high vulnerability.
Each of the criteria and sub-criteria of the study, have a different impact on the range of vulnerability. Thus each of the criteria and sub-criteria have a different importance factor on vulnerability function of earthquake. So for vulnerability analysis of range taking into all the proposed criteria and sub-criteria, importance factor of all of them should be specified and also three option of high, medium and low vulnerability in association with sub-criteria should be weighted, and ultimately the final score of each options specified [9] .
Table 2 is a table of weighting our selecting criteria.
Weighting are obtained by overlapping models and arithmetic mean for the whole region according to all criteria, and the final weight of regions are obtained from sum of the multiplying weight of criteria to the weight of related option of that criterion. The final map of this method is shown in Figure 2.
Legendre numbers shown on the left, show the suitability of each area as shown in the picture with a specific color for each numerical range. The red color represents the highest probability of occurrence and the green color indicates the least probability.
3.2.2. Fuzzy Logic Model
Fuzzy logic is a new technology that was developed for processing non definite events and does logically and mathematically what we connect in the nature and daily life. Fuzzy logic is versus logic of binary or Boolean logic and is used for design of Expert Systems. Fuzzy set theory is a mathematical theory designed to model the uncertainty associated with the process of human knowledge (Journal of Operational Research). Decision maker can freely choose the desired ranges. Uncertain expert judgment can be described by Fuzzy numbers [10] .
Unlike others who believe that we should take a closer approximation to productivity increases, Fuzzy logic is a generalization of the classical theory of sets in mathematics. The theory of Fuzzy sets suggests membership and grading. This means that an element can to some degree but not completely be part of a set. Therefore, there is uncertainty in Fuzzy logic and always an ambiguous space is governed on each set of logic.
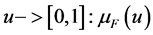 (3)
(3)
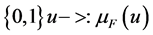 (4)
(4)
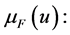 Fuzzy sets
Fuzzy sets
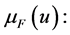 Absolute set
Absolute set
Zimmermann (1985) has been defined operators of Fuzzy algebraic product, Fuzzy algebraic sum and gamma operator as follows.
![]()
Table 2. Criteria and weights were obtained by the method of hierarchical.
![]()
Figure 2. The final output of the hierarchical approach.
Maps based on this model are combined in a variety of Fuzzy operators such as algebraic multiplication and sum. It is notable that sum accuracy unlike Fuzzy multiplying is very low at locating and a wide field is selected as proper locations. Due to the nature of the formulation of the operator and the nature of numbers between 0 and 1, the operator has a high sensitivity in the locating. Of course, high sensitivity of this Fuzzy multiplying in locating is not a reason to suitability of the model, because there may be other suitable areas that is not in the proper areas.
1) Application of Fuzzy GIS for Locating
One of the important applications of GIS in urban planning is locating of users and urban functions that due to the complexity of urban problems and impact of nonphysical factors on the changes of urban complications, results of GIS analysis and decision-makings don’t have certainty and in this case Fuzzy GIS systems are required.
Environmental systems are more consistent with Fuzzy logic. Boundaries in the urban environment are not inseparable from each other with precision and behavior of a system cannot be evaluated with a logic 0 and 1. Thus the use of the binary logic would be inefficient. For example, when defining the radius of influence of an urban park in the GIS system by Buffer analysis, range cannot be specified with a specified border (Crisp), because the radius of users access to a park is not a border wall barrier like.
2) Fuzzification processes in GIS
Figure 3 shows the fuzzification process in GIS.
Membership in Fuzzy logic method is expressed on a categorized scale from 1 (full membership) to zero (no full membership).
The final map will be as Figure 4.
Legendre numbers shown on the left of the figure display suitability percentage of each area that shown with a specific color for each interval numbers in the figure. The red color represents the highest probability of occurrence and the green color indicates the probability is minimal.
![]()
Figure 3. Fuzzification processes in GIS.
![]()
Figure 4. The final output of the Fuzzy method.
3.2.3. OWA Method (Ordered Weight Analysis)
Method of sorted weighted average using the degree weights gives this power to decision-maker to put more important factors that in his view influence locating problem further with the same important in issues. Due to this superiority, results of the locating by OWA method have the better resolution.
This method is a method of decision which capable to consider the subjective priorities and assessments of decision-maker that is investigated at risk management and has the ability to consider the risk appetite and risk aversion of decision-maker in decision process and can the final decision based on risk appetite/risk aversion. Using the OWA method, the final response and decision will be selected by more accuracy.
In a decision problem, risky people emphasis on good properties and risk-averse on bad properties of an option and put it their selection criteria. Ordered weight analysis (OWA) method enable to calculate risk appetite and risk aversion of people and enter it into the final selection. Some of properties of this method are: shift, uniformity, same power and bounded.
The degree weights are applied in the OWA weight analysis and represent importance degree of criteria that has the most impact [11] . Extraction of degree weights of evaluated criteria can be derived from expert opinions.
The problem that usually occurs in locational decision-makings is how to combine the criterion maps with a set of descriptive values (weights) and also priorities of decision-makers. Locational decision-makings leads to selection of one (or more) locational option. Each of these options 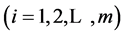 are described by a set of standardized values.
are described by a set of standardized values.
 (5)
(5)
The problem of multi-criteria evaluation is also included a set of priority as criteria weights, 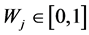 for
for![]() . By having the map layers and criterion weights. OWA combined operator assign a set of ordered weights
. By having the map layers and criterion weights. OWA combined operator assign a set of ordered weights ![]() to location of the cell I, so that for each
to location of the cell I, so that for each ![]() we have:
we have:
![]() (6)
(6)
OWA combined operator is defined as follows: (Yager, 1998, Malczewski, et al., 2003).
Figure 5 shows the output of OWA method.
Legendre numbers shown on the left of the figure display suitability percentage of each area that shown with a specific color for each interval numbers in the figure. The red color represents the highest probability of occurrence and the green color indicates the probability is minimal.
3.2.4. Multi Criteria Decision-Making Methods (TOPSIS)
In this way, M factors or option by a person or group of people who are decision makers evaluated. This technique is based on the concept that each of selective factor should have the minimum distance to the positive ideal (most important) and the maximum distance from the negative ideal (least important factor) [12] .
TOPSIS method is a risk-averse method that this should be considered in decision making and risk management. A prominent feature of TOPSIS is its superiority compared to other decision methods, especially OWA method, in the reflection of subjective properties of decision maker in taking the final decision of method.
![]()
Figure 5. The final output of OWA method.
This type of models is selector and uses to select the most suitable option among M available options. Criteria here are in the two forms of quantitative and qualitative and interfere simultaneously and should be converted into quantitative. In this model a subjective option is the best option which supply the most preferred value or desirability of each criterion [13] .
These methods are set of methods that analyze the complex decision making problems which evaluating of decision making options in them is based on conflicting and inconsistent criteria [13] . This method is applied easily and fast. Prioritization in this method is done by similarity logic to the ideal solution. Accordingly, the selective option has the shortest distance from the ideal solution and the farthest distance from the worst answer. Decision making matrix is evaluated in this method which has M option and N criterion.
Implementation steps of TOPSIS algorithm
First stage: We provide qualitative and quantitative matrix. In this step if we have numerical constraint, number is used itself or the criterion has qualitative criterion. In this step should first be converted quality to quantity, then draw the same direction and standard matrix [14] .
Second stage: Here, decision matrix is normalized by weighting and importance factor of criteria and sub criteria is explained and determined. Set of weights that their sum is equal 1 is considered for criteria by Dm.
At this step, quantity table is used where 1 points is referred to equal importance, 3 points to little more importance, 5 to more importance, 7 to much more, and 9 points to absolute importance; numbers 2, 4, 6, 8 is referred to intermediate stages.
Based on these criteria, pairwise comparison of criteria is done. Criteria is then obtained from geometric average method, and by dividing of each criterion on the obtained summation, importance factor of that criterion is calculated.
Third stage: the entropy technique
First step: normalizing decision making matrix
The presented scales in the matrix, makes decision without scale. Each of the values divided by the size of the vector corresponding to the same criterion [15] .
![]() (7)
(7)
![]() Binary weighted matrix elements
Binary weighted matrix elements
m: Number of criteria
Second step:
![]() (8)
(8)
![]() Normalizing the values of the matrix
Normalizing the values of the matrix
![]() (9)
(9)
![]() (10)
(10)
![]()
![]() (11)
(11)
Third step:
![]() Using of entropy technique for calculation of matrix elements.
Using of entropy technique for calculation of matrix elements.
Forth step: obtaining the uncertainly or the degree of deviation.
![]() Degree of deviation.
Degree of deviation.
Fifth step: determining the weights.
Forth stage: Algorithm of Decision making matrix.
W: weight.
The final output of this method is shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6 displays the output of the TOPSIS method.
![]()
Figure 6. The final output of TOPSIS method.
4. Discussion and Results
To use all the data, criterion overlap or Fuzzy overlap methods can be applied. No data is not removed in the Fuzzy manner and in the final maps are ranked according to their importance. In the Fuzzy model, especially in multiplication that all informative layers are multiplied, and due to the nature of numbers between 0 and 1, which is the membership degree in the Fuzzy set, As a result the less number of pixels are placed in a very well classes and so this operator would have a high sensitivity [16] .
Using both qualitative and quantitative criteria simultaneously and compatibility in judgment, which is a method for determining the importance factor of parameters used in the research to determine the level of vulnerability of the area from earthquake accordance, is one of the advantages of AHP method. AHP method reduces the conceptual complexity of the decision-making significantly, because only two elements (binary comparison) will be discussed at a time.
Despite the qualitative variables using AHP method, this method is not able to model the uncertainty about the judge’s decision-makers. Experts are faced with uncertainty in assigning evaluation weights of the AHP method.
Fuzzy logic helped to formulate the ambiguity of the judgments and put into mathematical language. Because of lower uncertainty in Fuzzy, thus this points has more reliability than the area result of AHP method. AHP method takes into consideration more in weighting and high accuracy for modeling of real phenomena, simplicity of algorithm and requirements to little information. So this simplicity leads to perform this operation faster at the right time.
AHP and Fuzzy are methods that have ability of modeling qualitative and linguist variables, but AHP method is a process with hierarchical organization and represent more logical resultant. TOPSIS had the capability to support locational decision-making and with the availability of numerous options and answers in the form of GIS and helps managers in decision-making and identify priorities. This model only has the ability to identify areas with high and very high sensitivity.
From benefit of OWA method is that the investigator can produce a wide domain of maps, various solutions and forecast scenarios by re-arranging and change criterion parameters. AHP method is used to extract features of weights, while OWA operator function shows a wide domain of decision making options to demonstrate uncertainty associated with the interaction of several criteria and indicates the results in a scale between zero and one.
AHP and TOPSIS methods operate faster than OWA method and OWA is faster than Fuzzy method.
5. Conclusion and Suggestion
Locating of resettling spaces and urban potential study for the establishment of a preventive plan against losses resulting from earthquakes, require a scientific and systematic perspective and detailed planning. One of these plannings is proper locating for resettling earthquake victims.
Geographic information systems with spatial data management and their analysis have the high ability in proper locating to resettle the victims after the earthquake. There are several ways for locating. In order to select the best model for locating, in addition to model properties, properties of the area, the scale of study, the number of informative layers and the software used also should be considered to obtain the best result. Integrating of informative layer without considering the importance of each layer in locating cannot interfere the actual value of informative layers and units with different values are placed in a class.
In this study Fuzzy, AHP, OWA and TOPPIS methods were investigated to locate establishment place of victims by several criteria and their results studied in terms of speed, simplicity and how to use criteria. According to the features of each method, combined methods of Fuzzy and AHP can create high ability in locating for resettling of victims.
AHP capability can be improved by combining with the OWA operator. Simultaneous existence of AHP and OWA in a model can result in preparing of more powerful decision-making tool for structuring and solving various problems.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.