Zoning of CO Emissions in Tehran in the Medium Term by Using Third Quartile as the Exposure Candidate ()
1. Introduction
The air pollution of metropolitan areas is one of the major problems of the world at present. In Tehran, air pollution has been created by population growth and industrial development. Tehran’s air pollution is below the world standards and the government of the Islamic Republic of Iran identified the pollution as a high priority environmental and health challenge. An important cause of air pollution is the exhaust from about 1.4 million motor vehicles, including about 0.5 million motorcycles, operating in an extremely congested road space (average vehicle speeds below 18 Km/h) and 70,000 industrial units. It is known that between 65 to 70 percent of total emissions are related to urban transport operations [1] . Reported average concentrations of pollutants such as carbon monoxide (CO), particulate matter (less than 10 micron diameter (PM-10)) and sulfur dioxide (SO2), in the city center in 2007, were two to three times above average levels recommended by WHO/USEPA. The growth in the number of vehicles over the last two years has made the situation even more severe.
Proper planning, management and monitoring of the pollution status depend on the availability of accurate information. The integration of data generated in the areas of etc. can lead to identification of pollution stress zones having unique combination of characteristics and hence specific suitability in terms of scientific methods to decrease the pollution load without compromising long term action plans for the environmental quality [2] .
Remote sensing as a powerful technology for mapping and modeling of pollution studies is proper tools to monitor the pollution zoning. Interpolation techniques are the main keys of these models. For instance, Lam (1983) and Burrough (1986) describe a variety of quantitative interpolation methods suitable for computer contouring algorithms [3] [4] which are commonly used in the interpolation models.
Tehran as the capital city of Iran has significant air pollution problems. Due to some recent studies it was resulted that the magnitude of the health impact estimated for the city of Tehran underscores the need for urgent action to reduce the health burden of air pollution [5] . One of the main air pollutants is carbon monoxide (CO). It is a colorless, odorless and tasteless gas that is a product of the incomplete combustion of solid, liquid and gaseous carbon-based fuels. These include wood, coal, petrol, diesel, LPG, CNG kerosene and oil.
Sources of carbon monoxide concentrations in ambient air in Tehran are typically motor vehicle emissions and domestic home heating in most urban areas. Concentrations of carbon monoxide in the indoor environment from indoor sources can also pose a major health threat. High concentrations of CO indoors can occur as a result of emissions from non-vented gas cookers and heaters. Other common indoor sources of CO include solid fuel burning and smoking [6] .
In this study the data of 14 air quality control stations located in Tehran in 2009 and 2012 are considered. Each station hourly checked the CO concentration and saved the amounts. For accurate results the third quartile (Q3) of the concentrations is calculated and considered for the mean amount of each station. The third quartile (Q3) is the middle value between the median and the highest value of the data set [7] . Using third quartile is due to being more exposed to the air pollutants during the day.
2. Materials & Methods
2.1. Study Area
The present study assessed the health impact of air quality on the residents of Tehran, the capital city of Iran, the largest urban area of Iran with a population of 8,700,000 in 2011 [8] . The city also is ranked as one of the largest cities in Western Asia and 19th in the whole world. As in other large cities, Tehran is faced with serious air quality problems. In general, 20% of the total energy of the country is consumed in Tehran.
The city has a capacity for 700,000 registered cars yet 3 million roam its streets on a daily basis. Compounding Tehran’s air pollution problem is its geographical location. With the location of 35˚41'N - 51˚25'E and altitude of 1000 - 1800 meters above mean sea level, Tehran is located in valleys and is surrounded on the north, northwest, east and southeast by high to medium high (3800 - 1000 m) mountain ranges. The mountain range tops the flow of the humid wind to the main capital and prevents the polluted air from being carried away from the city. Thus, during winter, the lack of wind and cold air causes the polluted air to be trapped within the city [9] .
2.2. Interpolation Model
In the mathematical field of numerical analysis, interpolation is a method of constructing new data points within the range of a discrete set of known data points [10] . There are several different ways to classify spatial interpolation procedures in the ArcGIS which here due to the available data the Spline method is chosen.
The Spline tool uses an interpolation method that estimates values using a mathematical function that minimizes overall surface curvature, resulting in a smooth surface that passes exactly through the input points.
Conceptually, the sample points are extruded to the height of their magnitude; Spline bends a sheet of rubber that passes through the input points while minimizing the total curvature of the surface. It fits a mathematical function to a specified number of nearest input points while passing through the sample points. This method is best for generating gently varying surfaces such as elevation, water table heights, or pollution concentrations.
The basic form of the minimum curvature Spline interpolation imposes the following two conditions on the interpolant:
· The surface must pass exactly through the data points.
· The surface must have minimum curvature, the cumulative sum of the squares of the second derivative terms of the surface taken over each point on the surface must be a minimum.
The basic minimum curvature technique is also referred to as thin plate interpolation. It ensures a smooth (continuous and differentiable) surface, together with continuous first-derivative surfaces. Rapid changes in gradient or slope (the first derivative) can occur in the vicinity of the data points; hence, this model is not suitable for estimating second derivative (curvature). The basic interpolation technique can be applied by using a value of zero for the Weight argument to the Spline tool.
There are two Spline methods: Regularized and Tension. The Regularized method creates a smooth, gradually changing surface with values that may lie outside the sample data range. The Tension method controls the stiffness of the surface according to the character of the modeled phenomenon. It creates a less smooth surface with values more closely constrained by the sample data range. In this study the regularized method is used.
The minimization criteria can be modified by the REGULARIZED option. However, third-derivative terms are incorporated into the minimization criteria. The weight attached to the third-derivative terms during minimization is specified by the weight parameter while higher values of this term cause smoother surfaces. Moreover, weight parameter values between 0 and 0.5 are suitable to reach the smoothing results as can be concluded, applying the REGULARIZED option ensures a smooth surface together with smooth first-derivative surfaces. Also, this method is useful if the second derivative of the interpolated surface needs to be computed [11] [12] .
Output surface’s control is accomplished by two additional parameters including; weight and number of points. Interestingly, the weight parameter defines the weight of the third derivatives of the surface in the curvature minimization expression. For the regularized Spline method, where the higher the weight, the smoother the output surface would reached. Usually, the weight of the third derivatives values is equal to or greater than zero whereas, due to the recent research the typical values that are recommended are 0, 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, and 0.5 [13] [14] .
The number of points identifies the number of points used in the calculation of each interpolated cell. The more input points you specify, the more each cell is influenced by distant points and the smoother the output surface is which can be concluded that he larger the number of points leads to gain the longer time needed to process the output raster.
The algorithm used for the Spline tool uses the following formula for the surface interpolation [13] [14] :
 (1)
(1)
where:
 and N is the number of points.
and N is the number of points.
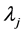 are coefficients found by the solution of a system of linear equations. rj is the distance from the point (x, y) to the jth point and
are coefficients found by the solution of a system of linear equations. rj is the distance from the point (x, y) to the jth point and  and
and 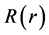 are defined differently, depending on the selected option.
are defined differently, depending on the selected option.
For computational purposes, the entire space of the output raster is divided into blocks or regions equal in size. The number of regions in x and in y directions is the same, and they are rectangular in shape. The number of regions is determined by dividing the total amount of points in the input point dataset by the value specified for the number of points. For data less uniformly distributed, the regions may contain a significantly different number of points, with the value for the number of points being only the rough average. If in any region, the number of points is smaller than eight, the region is expanded until it contains a minimum of eight points.
For the REGULARIZED option
 (2)
(2)
where ai are coefficients found by the solution of a system of linear equations. And,
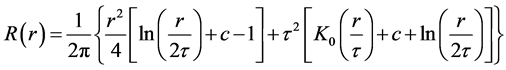 (3)
(3)
where r is the distance between the point and the sample.  is the weight parameter. K0 is the modified Bessel function and the c is a constant equal to 0.577215.
is the weight parameter. K0 is the modified Bessel function and the c is a constant equal to 0.577215.
3. Results & Discussion
The CO concentration in 2009 and 2012 are chosen to evaluate the pattern of CO pollution in the Tehran. Hence, the data of Air Quality Concentration Centers (AQCC) located in Tehran are gathered. 14 AQCC are considered due to their distribution in the urban area. The names of the stations are presented in Table 1.
As can be seen in Figure 1, two typical daily CO exposures are illustrated. The red horizontal axis is the mean value of the hourly CO values whereas the blue one is the third quartile (Q3). In a typical day hours, human mostly expose to the highest pollution values which in the midnight the pollution values are the lowest. Hence, using mean value is not proper and cannot be considered as an accurate exposure candidate which the Q3 shows more realistic pattern and can be considered as the best factor to show the pollution exposure to human.
![]()
Table 1. Data gathered from Tehran’s AQCC.
![]()
Figure 1. Typical daily CO exposure in Tehran.
A significant notice is that Q3 is used in the interpolation instead of the mean value. Usually, human are expose to the air pollutants in the day period while in this period the concentration of the pollutants are more than the similar period at night. Therefore, if the mean value is considered as the exposure indicator it would not consider the reality. So, to cover this problem the Q3 is chosen as a more proper exposure indicator in the calculation. The Q3 amounts for CO concentrations are given in Table 1.
GIS is a suitable tool for managing air quality as we have a high volume of data that depends on time and position. With time-position analyzing and identifying critical pollution position, it is possible for manager in different level to decide on localization of new industrial centers, transfering air pollution producer in the way that they have the least effect on air pollution of Tehran, creating area which requires clean air, identifying region need to creating green space.
Utilizing specialized GIS to control air quality we can have optimum site selecting of station. Considering the effect of distribution of pollution for instance topographic data, land use, climatologic and geographic agents and their influence on distributing of environmental pollutant we should attend to previous factor and modeling to enter this agent in GIS we must assure and accurate of above analyzes.
As can be seen in Figure 2 and Figure 3, the concentration of CO is decreased between 2009 and 2012. However, the center of the city still has problems and the concentration of CO is higher than the standard amount. It should be mentioned that due to the Iran’s environmental agency the standard concentration of CO in the urban area is 5 ppm.
There are two extra AQCC in the Figure 2 and Figure 3 namely; CO1 and CO2. These extra stations are considered for decrease the error of the extrapolation. Before considering these stations the errors are very high and unacceptable, so using these extra stations showed acceptable errors.
The circles show the Q3 value of each station whilst the size represents the level of pollutants concentration. In other words, the bigger circles detected higher level of CO concentration.
Due to comparing Figure 2 and Figure 3, the concentration of the CO in Tehran sharply declined between 2009 and 2012. However, the center of the city still has problems. The South West of the city in 2009 shows a critical condition where as the concentration in this place in 2012 is less than the standard. On the other hand, the CO concentration at the North West of Tehran is increased from 2009 to 2012. A reason of these changes can be increasing the industries and urban expansion at the North West and building an artificial lake at the West of the city.
It should be mentioned that the map based on the interpolation is more accurate that the extrapolation. Hence the critical zones at the edge of the maps have more errors. Hence, the interpolation zones should be considered.
4. Conclusions
By calculating the Q3 amounts of CO concentration of Tehran in 2009 and 2012 the interpolation maps are extracted and illustrated. The main novelty of this research is using the third quartile (Q3) as the pollution indicator which leads to more accurate results based on the exposure pattern in a day. By the concept and pattern of CO exposure in a day period using Q3 shows more proper results rather than the mean values. A significant notice is that Q3 is used in the interpolation instead of the mean value. Usually, human are exposed to the air pollutants in the day period while in this period the concentration of the pollutants is more than the similar period at night. Therefore, if the mean value is considered as the exposure indicator, it would not consider the reality. So, to cover this problem the Q3 is chosen as a more proper exposure indicator in the calculation.
![]()
Figure 2. CO emission interpolation in 2009.
![]()
Figure 3. CO emission interpolation in 2012.
The Spline method is chosen to interpolate the CO concentration according to the considered AQCC. Due to the interpolation maps the condition of the city based on the CO concentration in 2012 is better than 2009. And the most changes are seen in the West of the city. Comparing these maps would lead to clear the authorities’ points of view in monitoring the air pollutants in Tehran.