A New Approach for Database Fragmentation and Allocation to Improve the Distributed Database Management System Performance ()
1. Introduction
Many researches have been done in the last few years in order to improve the performance of distributed data- base management systems (DDBMS). DDBMS is a collection of logically interrelated data that are physically allocated at different locations over a computer network [1] . Most of recent researches are concerned about keeping the performance of DDBMS high so that they focused on how to design the database such that the over- all cost is kept minimal. Keeping the cost minimal is not an easy task as there are huge amount of transactions processing that increase the complexity of distributed databases. Several techniques have been proposed in order to improve database performance which can be achieved by improving at least one of the following database management issues: database fragmentation, data allocation and replication, and the network sites clustering.
The fragmentation process divides the database into portions each of which is called a fragment. Fragmenta- tion can be horizontal, vertical or mixed. The main advantage of fragmentation is to improve the performance of distributed database design by increasing the efficiency since data is stored only where it is needed. Fragments can be allocated at different network sites in a process called data allocation.
The fragments allocation is an NP-complete problem so that the complexity is high. In order to reduce the complexity, some heuristic algorithms have been proposed to solve the problem. In the allocation process, each fragment is assigned to a network node and sometimes to more than one node to achieve the data availability, system reliability and performance.
The clustering technique is used for grouping distributed database network sites into logical clusters. In order to reduce the communication time for data allocation, there are many algorithms that are use to find the optimal solution for grouping distributed database network sites into a disjoint clusters and making a better data distribu- tion among them. The clustering technique aims at eliminating the extra communication costs between the net- work sites and then enhancing the DDBMS performance.
Many existing algorithms of data fragmentation and allocation in DDBMS assume some restrictions on the number of network sites so that the results of such algorithms are impractical, and reflected on the efficiency and validity of their outcomes. Moreover, some constraints on network connectivity and transactions processing time will limit the applicability of the proposed solutions to a small number of DDBMS cases [1] .
One of the drawbacks of fragmentation and allocation solutions is the high computational complexity of their associated algorithms. In fact, when distributing a database over a network with a big number of sites and then finding an efficient, reliable and optimal solution for fragmentation and allocation are considered difficult tasks.
This paper proposed a new technique that splits the database relations into disjoint fragments. In addition, it introduces a high speed clustering technique that groups the distributed network sites into a set of clusters ac- cording to their communication cost. Also, it proposes a new intelligent technique for data allocation and redi- stribution based on transactions processing cost functions. Moreover, it implements a user-friendly simulation tool that performs fragmentation, clustering, allocation and replication of a database, in addition to assisting da- tabase administrators in measuring DDBMS performance.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 summarizes related work. A method for partitioning the database is presented in Section 3. A description of network site clustering is covered in Section 4. In Sec- tion 5, fragments allocation to the clusters and then to their sites is discussed. Performance evaluation is pre- sented in Section 6. Finally, the conclusions and the future work are presented in Section 7.
2. Related Work
Many studies have been published on attempts of improving the performance of DDBMS. These researches have mostly investigated fragmentation, allocation and sometimes clustering problems. In this section, we pre- sent the main contributions related to these problems, discuss them and highlight novelties of our proposed solu- tions with respect to fragmentation, allocation and clustering.
There are many types of fragmentation [2] vertical, horizontal and mixed. In vertical fragmentation each schema is divided into small fragments and all fragments must contain a common candidate key. A new algo- rithm; as proposed by [3] ; has employed vertical fragmentation for object relational database system; this frag- mentation method depends on user input at different sites.
In [4] , the authors provide a solution for initial fragmentation problem of relational database for DDBMS. It partitioned the relational database properly at the initial stage when no data statistics and query execution fre- quencies are available.
In order to minimize communication time required for data allocation and query processing, many researches have been done to group large number of network sites into a small number of logical clusters which improve the performance of a DDBMS by increasing transactions response time [5] .
The authors of [6] present a new formulation for the problem of fragmentation and allocating those fragments with minimum cost for both structured and unstructured data, by grouping sites which are nearer to each other into one cluster, hence they have low cost. Also, a dynamic clustering method is adopted for both structured and unstructured database to reduce the movement of data between sites.
In a DDBMS, the cost of communication is high so that many researches tried to minimize the cost and load sharing by making load balancing which can be achieved by making analysis of sharing resources, allocation of fragments and transaction in DDBMS [7] .
The complexity of a distributed database algorithm depends on the allocation method used. Some enhance- ments have been done in reallocation algorithms. The authors of [8] proposed an algorithm that reallocates fragments based on calculating the cost for each fragment individually. The reallocation depends on finding the maximum update cost value for each fragment. This technique takes into account the network topology and set of queries frequency values employed over the network.
Data allocation of a DDBMS can be done by means of mobile agents and many algorithms implemented to make optimization and solve allocation problems [9] .
The authors of [10] present a biogeography-based optimization technique for no-replicated static allocation of data fragments during database design that minimize total data transmission cost during the execution of a set of queries.
3. Database Partitioning
Various methods already exist describe data fragmentation in distributed DDBMS. Naturally, there are benefits and drawbacks to all schemes. Some methods need to incorporate performance evaluation ways, may not mi- nimize the transactions response time and cannot guarantee the ability to process a given portion of a given transaction in all sites [2] [3] and [4] .
In our proposed approach, the database will be partitioned into pair-wise disjoint fragments by using a hori- zontal partitioning technique, in which the records of a relation split into disjoint fragments; this strategy guar- antees the ability to processing all portions of a given transaction and distributes it precisely over the DDBMS sites.
Generating data fragments accomplished by performing the following processes respectively: defining trans- actions, creating segments and extracting disjoint fragments. Figure 1 below describes the architecture of the fragmentation method that supports the use of knowledge extraction and helps to achieve the effective use of small data packets.
As shown in Figure 1, the data request is initiated from the DDBMS sites (Site1, Site2, and Site3) and defines transactions as queries (Query1, Query2, and Query3) and then these transactions (queries) are processed into disjoint fragments (Fragment1, Fragment2, and Fragment3). The database transaction could be associated with
![]()
Figure 1. Generating disjoint fragments.
more than one relation, in this case, the transaction should be divided into a number of sub-transactions equal to the number of relations used that transaction. The process of generating fragments is described as follows:
1) Database fragmentation starts with any two fragments having intersection records between them. If there is an intersection, then three disjoint fragments will be generated as follows:
· The common records in the two intersected fragments,
· The records in the first fragment but not in the second segment, and
· The records in the second fragment but not in the first segment.
2) The intersecting fragments are then removed from the fragments list. This process continues until removing all the intersecting fragments.
3) The new derived fragments and the non-overlapped ones that do not intersect with any other fragments from the new list of totally disjoint fragments.
We developed the fragmentation algorithm described in Listing 1 to generate database disjoint fragments.
In the partitioning method, all transactions are processed, redundant transactions are eliminated, and the ap- plication speed and efficiency are improved by getting the minimum number of fragments to be accessed.
4. Network Sites Clustering
The benefit of generating database disjoint fragments can’t be completed unless it enhances the performance of the distributed database system. As the number of database sites becomes too large, a problem of supporting high system performance with consistency and availability constraints becomes crucial. Different techniques could be developed for this purpose; one of them consists of clustering distributed networking sites. Clustering database sites is a technique in which the sites that have similar physical property (e.g., having comparable communication costs) are logically grouped together in order to increase the performance of the distributed da- tabase system. However, grouping sites into clusters is still an open problem and it is proven that the optimal solution to this problem is NP-Complete since it is transformed to a cheapest path problem. Therefore, near-op- timal solution for grouping database sites into clusters helps to eliminate the extra communication costs between the sites during the process of data allocation and improves the system performance. Performing sites grouping after database fragmentation, will speed up the process of data allocation by distributing the fragments over clusters of sites rather than site by site. Thus, the communication costs are minimized and the distributed data- base system performance is improved.
A high speed clustering technique based on the least average communication cost between sites will be intro- duced. This is suitable for distributed databases where the communication costs between two sites are equal or near-equal, and similar computers on the network are used. The clustering parameters that will be used to con- trol the input/output computations for generating clusters and determining the set of site(s) in each cluster are described and computed as follows:
· The Clustering Decision Value (cdv) that determines whether or not a site can be grouped in a specific clus- ter.
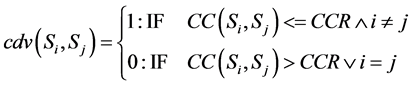 (1)
(1)
Accordingly, if cdv(Si, Sj) is equal to 1, then the sites Si and Sj are assigned to one cluster, otherwise they are assigned to different clusters. Each site should be included in only one cluster, and the final distribution of the network sites will be represented by the cluster that satisfies the least average communication cost between the sites.
· The Communication Cost between the sites CC(Si, Sj). This is the cost of loading and processing database fragment(s) in ms/byte between any two sites in the distributed database system. CC(Si, Sj) = cost of creation the data packet + cost of transmitting the data packet between Si, Sj
· The Communication Cost Range CCR (ms/byte) that the site should match to be grouped in a specific cluster. This value is determined by the network administrators and depends on how much time is allowed for the sites to transmit or receive their data to be considered in the same cluster.
Based on the parameters, assumptions, and computations described above, we developed the following clus- tering algorithm illustrated in Listing 2 to classify the networks clusters and their respective sites.
Listing 1. Fragmentation algorithm.
Listing 2. Clustering algorithm.
Clustering Example
To demonstrate the applicability of clustering, a simulation of the clustering algorithm on the given communica- tion cost between 12 sites will take place at clustering range CR equals to 5 (CR could be any communication cost as multiples of 0.125 ms/byte). The cluster set matrix resulted as shown in Table 1.
From the cluster set matrix, it is clear that only S1 can be grouped in the first cluster because the other sites can’t match the cluster range along with S1. The sites S2, S5, S6, S7, and S8 are also grouped in the second cluster because their communication costs match the cluster range between them. Since the cluster range match the communication costs between S3, S9, S10 and the other sites are far from them, then these three sites can be only grouped in the third cluster. In the same way, the fourth cluster is constructed only from sites S4, S11, and S12. Table 2 displays the generated clusters and their respective sites.
The communication costs within and between clusters have to be taken into consideration in the computation of the fragment allocation. The optimal way to find the communication cost between clusters and between sites within each cluster is to find the shortest path between the clusters/sites and compute the communication cost between them. However, this way is considered to be NP complete, therefore, the cluster average communica- tion cost with symmetric communication cost between clusters is suitable for the computations of fragments al- location in many distributed database environments where similar computers with similar communication costs between sites are used.
![]()
Table 2. The generated clusters and their sites.
5. Fragments Allocation
Data allocation and replication technique places and distributes the database fragments on the clusters and their respective sites. Initially fragments are allocated to the clusters that have transactions using that fragments. Al- locating fragments to a small number of clusters instead of large number of sites will reduce the number of communications and therefore enhance the system performance. Figure 2 illustrates the structure of data alloca- tion and replication technique.
A heuristic fragment allocation and replication technique will be introduced to perform the processes of frag- ments allocation in the distributed database system. Initially, all fragments are subject for allocating to all clus- ters having transactions using these fragments at their sites. If the fragment shows positive allocation decision value (i.e. allocation benefit greater than or equal to zero) for a specific cluster, then the fragment is subject for allocating at each site in this cluster, otherwise the fragment is not allocated (cancelled) from this cluster. This step is repeated for each cluster in the distributed database system.
As a result of the previous step, the fragment that shows positive allocation decision value at any cluster is a candidate for allocating at all sites of this cluster. If the fragment shows positive allocation decision value at a site of cluster that already shows positive allocation decision value, then the fragment is allocated at this site, otherwise, the fragment is not allocated to this site. This step is repeated for each site at this cluster.
To ensure data availability in the distributed database system, each fragment should be allocated to at least one cluster and one site. In case a fragment shows negative allocation decision value at all clusters, the fragment is allocated to the cluster that holds the least average communication cost and then to the site that has the least communication cost in this cluster.
5.1. Allocation Cost Functions
The allocation cost functions identifies the allocation status which is computed as a logical value for the com- parison between the cost of remote access the fragment to the cluster/site and the cost of allocating the fragment to the cluster/site. If the cost of remote access the fragment to the cluster/site is greater than or equals to the cost of allocating the fragment to the cluster/site, then the allocation status is positive and the fragment is allocated to the cluster/site. On the other hand, if the cost of remote access is less than the cost of allocating, then the alloca- tion status is negative and the fragment is cancelled from the cluster/site.
5.1.1. Cost of Allocating Fragments
The cost of allocating the fragment Fi issued by the transaction Tk to the cluster Cj, identified as CA(Tk, Fi, Cj), is defined in terms of the following costs:
· Cost of Local Retrievals issued by the transaction Tk to the fragment Fi at cluster Cj. It is computed as the multiplication of the average cost of local retrievals for all sites (m) at cluster Cj times the average number of frequency of local retrievals issued by the transaction Tk to the fragment Fi for all sites at cluster Cj.
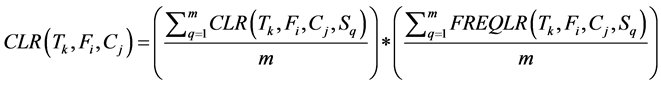 (2)
(2)
· Cost of Local Updates issued by the transaction Tk to the fragment Fi at cluster Cj. This cost is computed as the result of the product of the average cost of local updates for all sites (m) at cluster Cj times the average frequency of local updates.
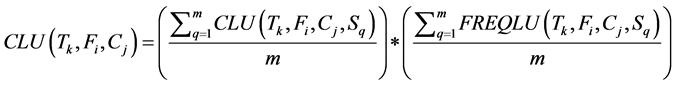 (3)
(3)
![]()
Figure 2. Data allocation and replication technique.
· Cost of Space occupied by the fragment Fi in the cluster Cj. The space is computed as a result of multiplica- tion of the average space cost for all sites (m) at cluster Cj occupied by the fragment Fi times the fragment size.
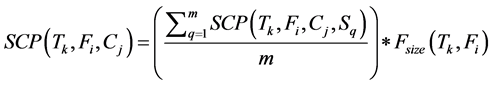 (4)
(4)
· Cost of Remote Updates issued by the transaction Tk to the fragment Fi sent from all clusters (n) in the dis- tributed database system except the current cluster Cj. This remote cost is computed as the result of the product of cost of local updates (Equation (3)) times the average frequency of remote update.
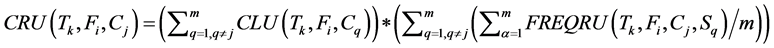 (5)
(5)
· Update ratio which determines the percentage of update transactions.
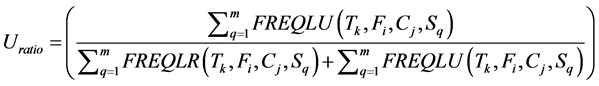 (6)
(6)
· Cost of Remote Communications issued for the transaction Tk to the fragment Fi sent from all clusters (n) in the distributed database system except the current cluster Cj. This cost is computed as the result of multipli- cation of the average cost of remote communication times the average frequency of local update times up- date ratio.
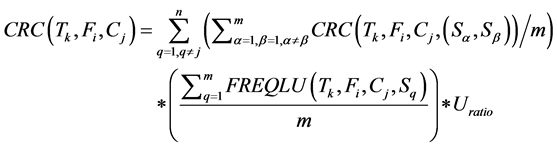 (7)
(7)
· According to the computations in the previous cost Equations (2)-(7), the Cost of Allocating a fragment to a cluster is computed as the sum of costs of local retrievals, local updates, space, remote update, and remote communication.
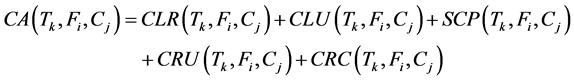 (8)
(8)
5.1.2. Cost of Not Allocating Fragments
The cost of not allocating the fragment Fi issued by the transaction Tk to the cluster Cj, identified as CN(Tk, Fi, Cj), is defined in terms of the following costs:
· Cost of local retrievals issued by the transaction Tk to the fragment Fi at cluster Cj as computed in Equation (2).
· Retrieval ratio which determines the percentage of retrieval transactions.
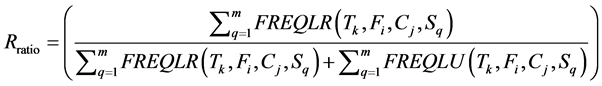 (9)
(9)
· Cost of Remote Retrievals issued by the transaction Tk to the fragment Fi sent from all clusters (n) in the dis- tributed database system except the current cluster Cj. This cost is computed as the product of the cost of communications between all clusters times the frequency of remote retrieval times the retrieval ratio
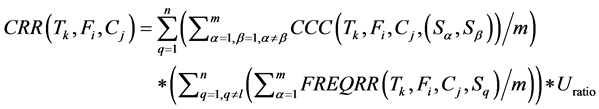 (10)
(10)
· According to the computations in the previous cost equations (2,9,10), the Cost of Not allocating a fragment to a cluster is computed as follows:
![]() (11)
(11)
5.1.3. Cost of Allocation Decision Value
The Allocation Decision Value ADV determines the allocation status of the fragment at the cluster and its re- spective sites. ADV is computed as a logical value resulted from the comparison between the cost of not allo- cating the fragment to the cluster CN(Tk, Fi, Cj) and the cost of allocating the fragment to the cluster CA(Tk, Fi, Cj).
![]() (12)
(12)
Accordingly, if CN(Tk, Fi, Cj) is greater than or equal to CA(Tk, Fi, Cj), then the allocation status ADV(Tk, Fi, Cj) shows positive allocation benefit and the fragment is allocated to the cluster. On the other hand, if CN(Tk, Fi, Cj) is less than CA(Tk, Fi, Cj), then the allocation status ADV(Tk, Fi, Cj) shows negative allocation benefit and the fragment is cancelled (not allocated) from the cluster.
Based on the fragment allocation procedures and the generated equations described above, we developed the fragment allocation algorithm described in Listing 3 to allocate database fragments in the network clusters and their respective sites.
Once the fragments are allocated and replicated at the clusters of distributed database systems, then studying the benefit of allocating the fragments at all sites of each cluster becomes crucial. To get better system perfor- mance, fragments should be distributed over the sites of clusters where a clear allocation benefit is accomplished. The same allocation and replication algorithm will be applied in this case, taking to consideration the costs for/ between sites in each cluster.
6. Performance Evaluation
We believe that the performance of allocation and network load are the major performance issues; hence, we will focused our performance evaluation on these two issues as they will maximize the overall system through- put at each network site in the distributed database environment, and minimize the cost of data that has been transferred and processed.
6.1. Fragment Allocation Performance Evaluation
The technique of fragment allocation and replication at clusters is evaluated according to the performance gen- erated by reducing the size of fragments that allocated finally at the clusters. The closest methods in the litera- ture to the proposed technique of fragment allocation and replication are those proposed in [7] -[10] . The main differences between these two methods are described as follows.
Compared to the allocation techniques in the literature, our allocation and replication technique considers dif- ferent communication costs, namely, the cost of the real network communication between cluster sites, the up- date and retrieval costs (i.e., it mostly represents the cost of writing operation that takes place during the execu- tion time). Moreover, with our clustering technique, database sites are grouped according to a clustering range and not only to a specific communication cost. Our clusters can communicate with each other instead of prefer- ring to have all fragments in their sites. This communication is cheaper than allocating fragments in all sites. In addition to the gain in term of communication cost, the independency of our clusters makes our DDBMS more reliable and more functional.
Figure 3 illustrates the effectiveness of the proposed fragment allocation and replication technique in terms of average computation time over the other two fragment allocation methods.
This figure shows that the proposed fragment allocation and replication technique results in the least average computation time required for fragment allocation. This is because the clustering technique produces groups (clusters) of small number of sites, and then the fragments will be reduced to the related fragments at each clus- ter. From Figure 3, it can be inferred that the average computation time for fragment allocation increases as the
Listing 3. Allocation algorithm.
![]()
Figure 3. Fragments allocation after clustering.
number of sites in the cluster increases and vice versa. Besides, this figure depicts the fact that our fragment allocation and replication technique outperform the other two methods.
6.2. Network Performance Evaluation
The DDBMS network workload involves the queries from a number of database users who access the same data- base simultaneously. The amount of data needed per second and the time in which the queries should be processed depend on performance of the database applications running under DDBMS network. The DDBMS network system performance evaluation will be simulated by using the OPNET IT Guru Academic Edition 9.1 software [11] .
Figure 4 shows the distribution of disjoint fragments over 4 clusters: C1 (node_12), C2 (node_5), C3 (node_7) and C4 (node_17). The first cluster (C1), combines node_18 and represents Site 1. The second cluster (C2) combines node_0, node_1, node_2, node_3 and node_4 and represents Sites 2, 5, 6, 7 and 8 respectively. The third cluster (C3) combines node_8, node_9 and node_10 and represents Sites 3, 9 and 10 respectively. The fourth cluster (C4) combines node_13, node_14 and node 15 and represents Sites 4, 11 and 12 respectively.
Figure 4 depicts the network topology for the proposed DDBMS should be evaluated. The figure depicts a simulation of building DDBMS and consists of 12 sites which are represented by nodes (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 9, 10, 11, 16, 17, 18, and 20).
6.2.1. Server Load
The server load determines how much the speed of the server in terms of bits per seconds. The following figures depict the network server loads in the proposed DDBMS. The loads (bits/sec) on the DDBMS servers (C1, C2, C3, C4) are compared and illustrated in Figure 5.
This figure shows that at its peak, the load on server 2 (node 6) is well below 1300 bits/second, on server 3 (node 13) the load is well below 750 bits/second. The load on server 4 (node 14) is also well below 750 bits/ second, and the load on server 1 (node 22) is well below 500 bits/second. The results of comparison states that the network is almost balanced throughout processing sites clustering.
6.2.2. Network Delay
The network delay is the delay caused by the transactions traffic on the server of the distributed database system. The maximum time required for the network system to reach the steady state is defined as network delay, it’s measured in millisecond. Figure 6 shows the network delay caused by each server (C1, C2, C3, C4).
The distributed database system reaches the steady state after 0.065 milliseconds and less network delay time
is consumed in case of distributing the sites over 4 servers compares to the delay time consumed in case of hav- ing all sites connected to 1 or 2 servers.
7. Conclusion and Future Work
In this work we proposed a new approach to improve DDBMS performance. This approach is integrating three enhanced techniques namely; database fragmentation, network sites clustering and fragments allocation. These techniques are developed to avoid drawbacks of database fragmentation and data allocation like data redundancy and complexity of data redistribution problem. In addition, a novelty of our approach is to satisfy a certain level of data availability and consistency. The results obtained in our evaluation showed that our approach signifi- cantly improved performance requirement satisfaction in distributed systems. This conclusion requires more in- vestigation and experiments. Therefore, as future work we plan to investigate our approach on larger scale net- works involving great number of database sites. Also, we will apply different types of clustering and use strong database sites grouping criteria. Finally, we plan to introduce search based technique to perform more intelligent data redistribution.