Evaluation of the Impact of the Ongoing Water Resource Management Plans on Nitrate Concentration in Gaza Coastal Aquifer Using Modeling Approach ()
1. Introduction
In Gaza strip, Palestine, groundwater is the major source for water supply for domestic and agricultural uses and it has already been not enough. Rainfall, the main water replenishment source, became insufficient to balance the groundwater system. In year 2002, the available yield of groundwater was about 91 MCM/year while the total abstraction for domestic and agricultural purposes was 153 MCM/year [1] . This result is affecting in a negative way the quality and the quantity of the municipal water that is pumped to the consumers. Nitrate is one of the most important and widespread of the numerous potential groundwater contaminants.
The excess 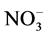 in the groundwater of the Gaza Strip occurred as a result of
in the groundwater of the Gaza Strip occurred as a result of 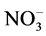 leaching from irrigation, wastewater septic tanks, sewage sludge, animal manure and synthetic fertilizers.
leaching from irrigation, wastewater septic tanks, sewage sludge, animal manure and synthetic fertilizers.
The problem of high nitrate concentrations in drinking water constitutes a major health risk to both humans and stock life. Nitrite reacts directly with hemoglobin in human blood and other warm-blooded animals to produce methaemoglobin. Methaemoglobin destroys the ability of red blood cells to transport oxygen. This condition is especially serious for babies. It causes a condition known as methaemoglobinemia or “blue baby” disease. The WHO assigned the nitrate of 50 mg/l as a health significant value in drinking water [2] .
Therefore the effective management of water resources is essential to the development of health, environmental, social, agricultural and industrial development in all countries, especially the developing ones.
Great efforts have been introduced by PWA in making plans such as IAMP, NWP and recently GETAP, 2011. These plans include very effective projects that help to improve the situation, but they are facing a lot of constrains such as political situation, funding limitations, and others. And by the year of 2011, some of the projects and plans have been implemented, others haven’t, which reflected on the water situation and the aquifer in the strip.
2. Study Area
Gaza strip is a strip of land on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea, located in the Middle East (at latitudes 31˚16'' and 31˚45''N and longitudes 34˚20'' and 34˚25''E) that borders Negev Desert and Egyptian Sinai Peninsula on the southwest (11 km) and Israel on the east and north (51 km).
The Gaza Strip has a characteristically semiarid climate. Annual average rainfall ranges between 400 mm/ year in the north to about 200 mm/year in the south near Rafah. Apparently, there is a general north-south pattern of rainfall. There is a five month period in winter (November-March) with a rainfall surplus. During the rest of the year, evaporation greatly exceeds the rainfall. The annual average relative humidity is about 72%. The average mean daily temperature in Gaza City ranges from 26˚C in summer to 12˚C in winter [1] [3] . The width of the Gaza Coastal Aquifer varies from 15 km in the north to about 20 km in the south. The depth to groundwater in the GCA ranges from 20 m in the south-east to about 180 m in the north-west. The Gaza Coastal Aquifer is composed of sands, calcareous sandstone, and pebbles. Semi permeable and impermeable layers are sandwiched in between, dividing the aquifer system into subaquifers in the western part. Further inland, the subaquifers effectively merge to form one system. Gaza Coastal Aquifer consists of the Pleistocene age Kurkar Group and recent (Holocene age) sand dunes. The Kurkar Group consists of marine sandstone, reddish silty sandstone, silts, clays, unconsolidated sands, and conglomerates. Regionally, the Kurkar Group is distributed in a belt parallel to the coastline. Regional groundwater flow is toward the Mediterranean Sea. However, natural flow patterns have been disturbed by pumping. Within the Gaza Strip, large cones of depression have formed over the past years within the Gaza, Khan Yunis, and Rafah municipalities. All along the coast, there are areas of seawater intrusion due to overpumping of the freshwater aquifer [3] .
3. Research Methodology and Analysis
It is intended to achieve the objectives of the study by the following steps as shown in Figure 1.
![]()
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of study methodology.
4. Build Gaza Coastal Aquifer Model
Develop the conceptual flow and transport model of the study area using “VMODFLOW Pro”. Two-stage finite difference simulation algorithms were used under steady andtransient states for calibrating the flow and transport parameters.
4.1. Model Boundaries
Regarding the eastern boundary it is selected to be far enough from the eastern boundary of Gaza area where the aquifer thickness is negligible. The model domain is about 16 km by 47 km. It consists of vertically to seven layers consistent in with the stratification of the Gaza coastal aquifer system hydrogeology as shown in Figure 2 and a finite difference mesh of 157 rows and 53 columns, discretized horizontally to cells of 300 m × 300 m.
Figure 3 shows the boundary conditions imposed on the developed three dimensional numerical groundwater flow model are defined as constant head boundary along the Mediterranean Sea, and no flow boundary in the north, east and south. The north and south boundaries are defined as no flow boundaries based on the groundwater level contour maps where groundwater flow is perpendicular to the sea shore line. For the eastern boundary its assumed no flow boundary and the flow from the east is assigned as recharge wells along the eastern border.
4.2. Internal Hydrologic Stresses
4.2.1. From Precipitation
A GIS model was built to include Soil type, rainfall, land use layers. Each data set was used as a theme or shape file in Arc View. A grid size of 0.002 × 0.002 decimal degrees (latitude × longitude) was chosen, which is approximately 200 m × 200 m, or 660 feet × 660 feet. Each grid in each layer was assigned a value for the Soil type, Land Use and rainfall.
4.2.2. Pumping Wells
In 2001, according to the Palestinian Water Authority (PWA), there are around 91 municipal wells within the Gaza strip as shown in Figure 4. The estimated municipal abstraction totals about 54 MCM/yr. Agricultural
![]()
Figure 2. Vertical cross section through model, (row 117).
![]()
Figure 3. The model domain with the grid origin, orientation and boundaries.
![]()
Figure 4. Wells distribution Gaza strip within model domain in year 2001 (Pumping wells).
wells have not been metered since 1994. In 2001, MoA reported a total average annual abstraction for the 3680 legal and illegal agricultural wells in Gaza strip was approximately 82 MCM/yr as shown in Figure 4. The collected data contained partial data set of all known wells in the period between 2001 and 2011, including wells location, coordinates, screens depths, abstractions and water quality parameters. Limited information of well construction and pumping readings are available for illegal wells, they are known mostly from a survey conducted by PWA.
4.2.3. Flows
There are three primary sources of return flow in the Gaza strip: leakage from municipal water distribution system, wastewater return flows and irrigation return flow. According to the Palestinian Water authority, the leakage from municipal water distribution system was estimated from 10% - 50% of the total abstraction. This is related with the network system efficiency in each municipality.
Wastewater returns flows from North Gaza WWTP have been estimated to about 100%, from Gaza WWTP estimated about 24% and from Rafah WWTP has been estimated to about 42%. The total quantity of recharge from this wastewater was inserted in the model in the corresponding areas. Irrigation return flow has been estimated to be about 25% of the total agricultural abstraction [1] .
4.3. Steady State Calibration
Calibrated groundwater levels for year 2001 conditions are shown in Figure 5. Average water levels of year 2001 for 114 wells within the model domain were used as calibration targets. The calculated residual mean error and absolute mean error are about −0.65 (m) and 0.871 (m), respectively, with a correlation coefficient for the model domain of 0.923. In general, the residual values range from −3.037 m to −0.013 m, as shown in Figure 6. This year was selected because it represents a year when rainfall records were close to the long-term average which as a result has produced an appreciable recharge and groundwater recovery to the coastal aquifer system.
![]()
Figure 5. Simulated groundwater table for year 2001 calculated by VMODFLOW.
![]()
Figure 6. Calculated versus measured groundwater levels at the end of year 2001.
Though it is not truly steady-state, the quasi-steady state conditions could be assumed as a result of the high recovery of groundwater in this year.
§ Calibrated Parameters
The field measurements of groundwater levels in 2001 were taken as targets of steady state calibration. Observed heads of about 114 observation wells shown in Figure 7 were used as target points for steady state calibration. The model steady-state calibration was also checked for the transient situation extending from 2001 through 2011.
The model was run a number of times for various values of hydraulic conductivity distributed over the domain. Those values were varied according to the stratification in the conceptual model above, the results of pumping well tests mentioned in the literature, and the calculated values in the previous studies. The horizontal hydraulic conductivity was adjusted during many sequential model runs until accepted match between the observed and calculated heads were obtained.
Table 1 summarizes the results and statistics of steady state calibration for many selected hydraulic conduc- tivities within the range values indicated in the literature, the result show no significant changes of convergence between observed and simulated heads.
The calibrated hydraulic conductivity in sandstone layers (sub aquifers) was found to be 34 m/d in all areas, while it was 0.02 m/d for the three aquitards (clay layers). The vertical hydraulic conductivity was 10% of the corresponding horizontal values.
![]()
Figure 7. Distribution of head observation wells within the model area.
![]()
Table 1. Steady state calibration in 2001 based on the different values of hydraulic conductivity.
4.4. Transient Calibration
The simulation period was conducted over 10 years, starting in 2001 and ending in 2011 for transient calibration. The transient calibration aimed to calibrate the specific yield and specific storage of the aquifer. Therefore, transient simulation was set to simulate the groundwater levels for the period from 2001 to 2011. The agricultural abstraction data could be used without any modifications. Moreover, the real data of municipal wells were available, they included measured monthly abstractions for all municipal wells for the entire simulation period. Also, yearly precipitation and recharge data were available and distributed. The initial conditions or heads of the transient period were taken from the steady-state output of the year 2001 to ensure the setting of calibrated hydraulic parameters. Model parameters were adjusted by trial-and-error to reduce the differences between simulated and measured values. Calibration under transient conditions included adjustment of specific yield. Calibrated values are summarized in Table 2. All these calibrated values are within the range of literature values given for Gaza aquifer.
Calibrated groundwater levels versus measured groundwater levels for the years 2001, 2005 and 2011 are done with correlation coefficient above 92% as shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9.
Figure 10 shows calculated heads versus time for the selected observation wells (L47, E45, L57 and H11). From these figures it is very clear that the model can simulate the aquifer system relatively good.
4.5. Transport Model
The model setup was conducted based on the results of the flow model. The parameters values adopted in the solute transport model are chosen based on previous modeling in Gaza strip aquifer such as Alghamri, 2009 and Jaber, 2008 [4] [5] . In these studies the longitudinal dispersivity is about 10 m, horizontal dispersivity ratio 0.1 and vertical transverse dispersivity ratio 0.01. Transport model was checked for both steady state flow and transient flow conditions.
a) Assumptions for the Transport Model
· All the calibrated physical and hydrogeological parameters of the aquifer were kept the same as in the baseline model in the previous (flow model).
· About 150 mg/l nitrate concentration were assigned long the eastern boundary assumed that its coming from the lateral flow.
· Natural precipitation & atmospheric deposition were ignored.
· Transformation of nitrogen forms in the unsaturated zone above water table is not considered in details in this research, because there is a wide variability in the conditions that control the mechanisms of each process, i.e. nitrification, denitrification…etc. Accurate determination of the contribution of each process in the mass of nitrate reaching the water table is very difficult and many parameters are needed, which are not available in Gaza due to the lack of data specially laboratory measurements.
· Initial concentrations of the transport model under transient state groundwater flow conditions (2001-2011) were set as the observed concentrations of nitrate in the model area at the end of year 2001.
![]()
Figure 8. Calculated versus measured groundwater levels at 2001.
![]()
Table 2. Summary of the final calibrated parameters transient calibration for target period (2001-2011).
b) Calibration of Transport Model
The process of calibration requires adjustments of the model input parameters that influence the output in MT3D are specially the recharge concentration value. These values were adjusted and refined throughout the trial and error calibration process until an improved conformity between simulated and observed values was attained. Nitrate concentration values were obtained based on(AlMahallawi, 2005) [6] , the nitrate load was assumed dissolved within the amount of recharge percolating to the groundwater.
The calibration procedure is performed under transient state groundwater flow conditions. Transport calibration for the transient flow was conducted for the target period (2001-2011).
Results of the correlation coefficient between the observed nitrate concentration and the calibrated nitrate concentration within Gaza strip are above 90% as shown in Figure 11 at the end of the year’s 2005 and 2011 as drawn by VMODFLOW, while calculated nitrate concentration versus the measured for the year 2010 and the highest concentration location are shown in Figure 12.
![]()
![]()
Figure 9. Calculated versus measured groundwater levels at 2005, 2011.
![]()
![]()
Figure 11. Calculated versus observed ![]() concentration at 2005 and 2011, respectively.
concentration at 2005 and 2011, respectively.
![]()
Figure 12. Calculated nitrate concentrations versus measured by CMWU for year 2010 in (mg/l) [7] .
5. The Properties of All Scenarios
This section identified the properties for each scenarios depending on the GETAP projects, and their effects on the modeling tasks.
I. Work as usual (zero scenario) (SC.1).
· Annually increasing of pumping from the aquifer according to the growth of population in both domestic and agriculture uses.
· Annually leakage from distribution network in both sewer and draining networks.
· Bad and random using of fertilizers at agricultural areas.
II. Upgrading and maintaining pipe work (SC.2).
· Assumed that all sewer in overall Gaza strip are covered by sewer networks.
· Leakage from water distribution drinking and sewer network are decreased to reach 15% in all governorate.
III. Imported water from Israel (SC.3).
· Reduction pumping from the aquifer.
· The model considered the reduction of abstraction as represented in Table 3.
IV. Construction of Short Term Low volume desalination Plant (STLV) (SC.4).
· Reduction pumping from the aquifer.
· The model considered the reduction of abstraction as represented in Table 4.
V. Construction of Two regional Desalination plant (SC.5).
· Reduction pumping from the aquifer.
· About 55 MCM/year will supplied from the original desalination plant in middle Gaza and 22 MCM/year will supplied from the either southern Gaza of north Egypt Desalination plant.
· The quantity of desalinated water means that about more than 90% of the municipal wells for domestic use will stopped.
VI. Reuse of treated wastewater in addition to decrease N-fertilizer (SC.6).
· Close the infiltration basins.
· About 82 MCM/year from three WWTP on the north, Gaza, Rafah Governorates will be produced which will be used in agriculture need.
![]()
Table 3. Imported water from Israel Scenario.
![]()
Table 4. Short term low volume desalination plant scenario.
· More than 90% of agriculture wells will be stopped.
· It assumed that the N-fertilizer will decreased by 50%.
6. Result and Discussion
In this section we select four various wells two from the northern areas and two from the southern area, while that’s because of the highly concentration on the mentioned areas. The each two wells, one of them is located on built up areas and the other on agriculture areas, Figures 13-16 represent how the four wells affected by applying all scenarios. It is shown that the most effective scenarios is divided in two cases:
a) In domestic areas the better scenarios is the STLV desalination plant and the upgrade and maintaining the pipe work in addition to apply all scenarios together.
b) In Agriculture areas the better scenarios or the scenario which only have significant effect is the reuse of the TWW addition to apply all scenarios together.
Analysis of the previous management scenarios indicated that as percent of reduction in nitrate loadings increase or the percent of abstraction from the aquifer decrease, the average simulated nitrate concentrations of all target points decrease. Table 5 and Figure 17 show the comparison between the results of all management scenarios. Results in Table 5 show that the yearly change in nitrate concentration in all scenarios ranges between −2.44 mg/l to 8.15 mg/l. This means that the deterioration of the Gaza aquifer is fast, while the remedial scenarios lead the aquifer to better, but slowly.
Applying all scenarios together will lead to acceptable nitrate concentration meets the WHO Standards in year 2038 as shown in Figure 18.
7. Conclusions
§ The used finite-difference code MODFLOW to simulate the hydraulic head within the groundwater and the MT3D to simulate the nitrate transport are good tools, meanwhile other modeling tools may introduces only on graphics and outputs better than VMODFLOW.
§ According to the management scenarios explained in chapter 5, the main source of nitrate is the agriculture uses of chemical fertilizers and manure in addition to the leakage from the distribution sewer and drinking water.
§ The abstraction from the aquifer affects the nitrate concentration in groundwater. Whenever the pumping from the aquifer increased the nitrate concentration increased. This relation may be due to change in direction and velocity of the flow of groundwater, especially in the areas of cones of depression. Other factor may enhance this relation is the significant change of aquifer storage.
§ In the event of work as usual, the average nitrate concentration in Gaza strip governorate will increases by more than 8 mg/l annually.
§ The combination of Reused of Treated wastewater and Reduction of usage N-fertilizers by 50% will have the better effect on nitrate concentration where it will reduce the rising of average nitrate concentration to 2.15 mg/l annually.
![]()
Table 5. Average simulated nitrate concentrations versus management scenarios (2011 to 2038).
![]()
Figure 13. Nitrate concentrations versus scenarios (2012-2038) for a domestic well (A.180).
![]()
Figure 14. Nitrate concentrations versus scenarios (2012-2038) for agriculture well (C.25).
![]()
Figure 15. Nitrate concentrations versus scenarios (2012-2038) for a domestic well (P.10).
![]()
Figure 16. Nitrate concentrations versus scenarios (2012-2038) for agriculture well (K.21).
![]()
Figure 17. Average simulated nitrate concentrations versus management sce- narios (20122038).
§ Combination of all management scenarios will lead to acceptable nitrate of concentration below and very close to the WHO Standards in groundwater on 2038.
§ The main effective projects of the GETAP on the nitrate concentration is the upgrading the pipe work, STLV desalination plant and the reused TWW in addition to reduce N-Fertilizers.
§ The imported water from Israel has no significant effect on the nitrate concentration but it pushes up the average annual decrease of nitrate concentration in overall.
§ The regional desalination plants have significant effect but the implementation is too late.
8. Recommendations
§ The GETAP not focused in the reduce of N-Fertilizers, so the reduce of N-Fertilizers must be one of the main tasks in the planning programme for Gaza strip coastal aquifer.
§ Coming Planning should consider an awareness campaign among farmers on the optimum use of fertilizers and cooperation with the Ministry of Agriculture about feeding the market of fertilizers does not contain large amounts of nitrates.
§ The continuous deterioration of Gaza aquifer should be stopped. The discussed management options in this study may help to stop the deterioration.
§ STLV scenario and rehabilitation of sewer and drinking water distribution network should be on the main tasks for the domestic sector.
§ Reuse TWW in addition to reduce N-Fertilizers should be on the main tasks for the agriculture sector.
![]()
Figure 18. ![]() concentrations for (SC.7), (2012, 2018, 2023 and 2038) years, respectively.
concentrations for (SC.7), (2012, 2018, 2023 and 2038) years, respectively.
§ Develop guidelines for groundwater protection zones around major potable water supply areas specifically focusing on nitrate sources.
§ The expected desalinated quantity and imported water have to be disturbed over the whole Gaza strip.