Histopathological, Immunohistochemical and Exfoliative Cytological Studies of Oral Verruciform Xanthoma ()
1. Introduction
Verruciform xanthoma is a rare tumor-like lesion that predominantly affects the oral mucosa and anogenital regions [1] [2] . Characteristic histological features are exophitic proliferation of stratified squamous epithelium and accumulation of foamy macrophages between epithelial processes. As the gross appearance is similar to malignant tumors, it is important to distinguish from verrucous carcinoma, papillary carcinoma and squamous cell carcinomas, which also show marked exophitic growth. Therefore, it is necessary to clarify the differences in characteristics between benign and malignant proliferating epithelial cells. Although immunohistochemical expression of proliferative cell activity and cytokeratins is useful for histopathological diagnosis [3] [4] , expression of these factors in hyperplastic epithelium of verruciform xanthoma has not been fully clarified to date.
On the other hand, exfoliative cytology is an also useful method for tentative diagnosis of various lesions in diagnostic pathology [5] . Although cytology has several advantages, such as simplicity, noninvasiveness and rapid diagnosis, histological construction on smeared cell specimens is unclear when compared to histopathological examination. Thus, contrasting cytological and histopathological findings is important to ensure the correct diagnosis. As the opportunity for the both cytological and histopathological examinations is scarce for verruciform xanthomas, to our knowledge, a comparative analysis of cytological and histological features has not yet been reported.
The purpose of the present study is to perform immunohistochemical analysis using markers of proliferative cell activity and cytokeratins, and to conduct comparative analysis between cytological and histological features in order to clarify the detailed characteristic features of verruciform xanthomas.
2. Materials and Methods
Materials comprised a total of seven cases of rare verruciform xanthomas diagnosed at the Department of Oral Pathology, Nihon University School of Dentistry at Matsudo (Table 1). The diagnostic criteria of the verruciform xanthoma were based on Shaffer’s description [1] . Only 5 cases underwent smear cytology among these cases, because both cytological and histopathological examinations for diagnosing and evaluating verruciform xanthoma have been rare during oral examinations at the time of their first visit to Nihon University Hospital at Matsudo. Consideration was given to patient privacy, diagnosis, and management and prognosis of the lesions.
After surgical excision was performed under local anesthesia, specimens were fixed in 10% formalin. Specimens were dehydrated in increasing concentrations of ethyl alcohol, clarified in xylene and embedded in paraffin. Paraffin-embedded specimens (paraffin blocks) were cut into 4-μm sections, and were subjected to hematoxylin and eosin (HE), and immunohistochemical staining.
The envision polymer + kit (DakoCytomation, Glostrup, Denmark) was used for immunohistochemical staining. Sections were deparaffinized, and after thorough washing, were incubated with target retrieving solution (DakoCytomation, Grostrup, Denmark) at 95˚C for 40 minutes for antigen retrieval. After cooling at room temperature for 20 minutes, sections were incubated with the primary polyclonal antibody, followed by pan-cytokeratin (panCK) and monolyclonal antibodies, and anti-cytokeratin 13 (CK13), anti-CD68 (CD68) and anti-Ki- 67 (Ki-67) (all antibodies purchased by DakoCytomation). Finally, immunohistochemical sections were counterstained with Mayer’s hematoxylin.
For analysis of cell proliferation activity, images were obtained using an optical microscope (original magnification ×600) in 3 arbitrary areas of the epithleium. Positive cell rate (Ki-67 labeling index) was determined using the following formula:
Ki-67 labeling index (%) = (number of positive epithelial cells/number of whole epithelial cells) × 100

Table 1 . Summary of the materials used in the present study.
For exfoliative cytological study, sample cells were obtained using cytobrush, smeared on slide glasses, immediately fixed in 95% ethyl alcohol, and subsequently stained using the standard Papanicolaou staining method for cytological evaluation. The template is used to format your paper and style the text. All margins, column widths, line spaces, and text fonts are prescribed; please do not alter them. You may note peculiarities. For example, the head margin in this template measures proportionately more than is customary. This measurement and others are deliberate, using specifications that anticipate your paper as one part of the entire journals, and not as an independent document. Please do not revise any of the current designations.
3. Results
3.1. Histopathological Findings
The tumor-like lesion consisted of stratified squamous epithelium with hyperkeratosis, acanthosis and relatively uniform elongated rete pegs. Numerous foamy cells had accumulated in the subjacent connective tissues between the rete pegs (Figure 1). The overlying epithelium did not show any cellular and nuclear atypism, but picnosis and hyperchromatism were observed predominantly in the superficial layer.
3.2. Immunohistochemical Findings
Accumulated foamy cells showed positive immunoreactivity for CD68 (Figure 2(A)). CD68-positive cells were also observed in the overlying epithelium. Positive reactivity for Ki-67 was observed in the nuclei of epithelial cells, but negative reactivity was seen in foamy cells (Figure 2(B)). Positive reactivity was mostly distributed in the basal and/or parabasal cell layers and Ki-67 labeling index was 17.7%. Positive reactivity for panCK was widely distributed in most layers of the epithelium, except for basal cell layers (Figure 2(C)), whereas positive reactivity for CK13 was detected in prickle cell layers (Figure 2(D)).
3.3. Findings of Exfoliative Cytology
With regard to cytological findings, various degrees of keratinization in epithelial cells and/or clusters were scattered with inflammatory or bacterial infection background. Some epithelial cells were hyperkeratinized, showing dark yellow cytoplasm, and showing picnosis and hyperchromatism in the nucleus (Figure 3(A)). These features corresponded to histopathological findings of the superficial epithelial cells (Figure 3(B)). There were no foamy cells on cytological examination.
4. Discussion
The materials used in the present study are summarized in Table1 The age range of the patients at the time of surgery was 28 - 87 years (average, 61 years), and the male to female ratio was 4:3. The most commonly affected site was gingiva (5 cases) followed by buccal mucosa (1 case) and tongue (1 case). The clinical features usually show papillary and hyperkeratotic. These clinical findings were in accordance with previous studies [1] [2] [6] [7] . Since the findings resemble papilloma and other papillary lesion, pathological and exfoliative cytological examinations and the comparative analysis are important.
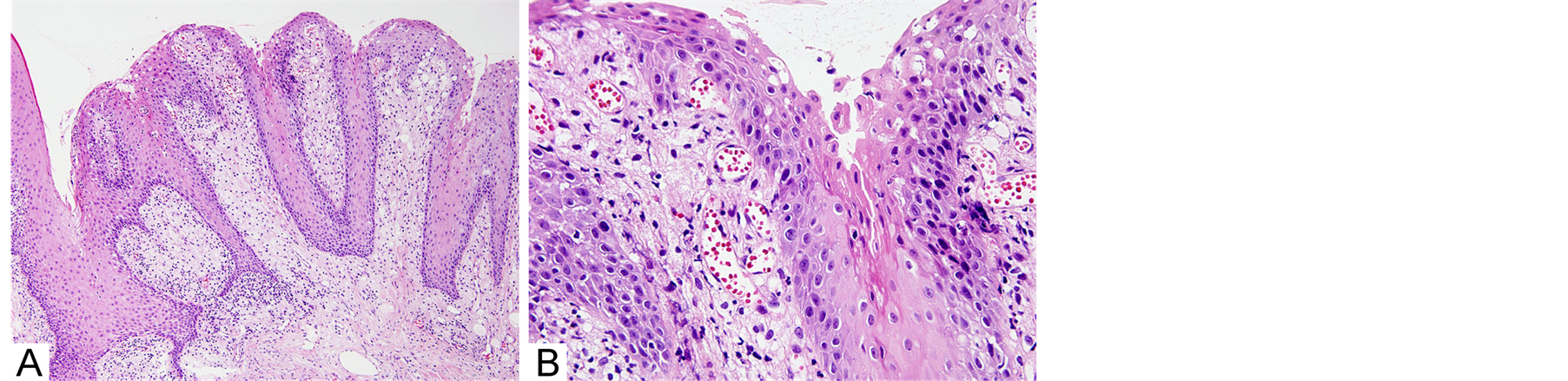
Figure 1. Histopathological features showing papillary exophitic growth of epithelium and accumulation of numerous foamy cells between elongated rete pegs: (A) Low-power magnification 100´; (B) High-power magnification 600´.
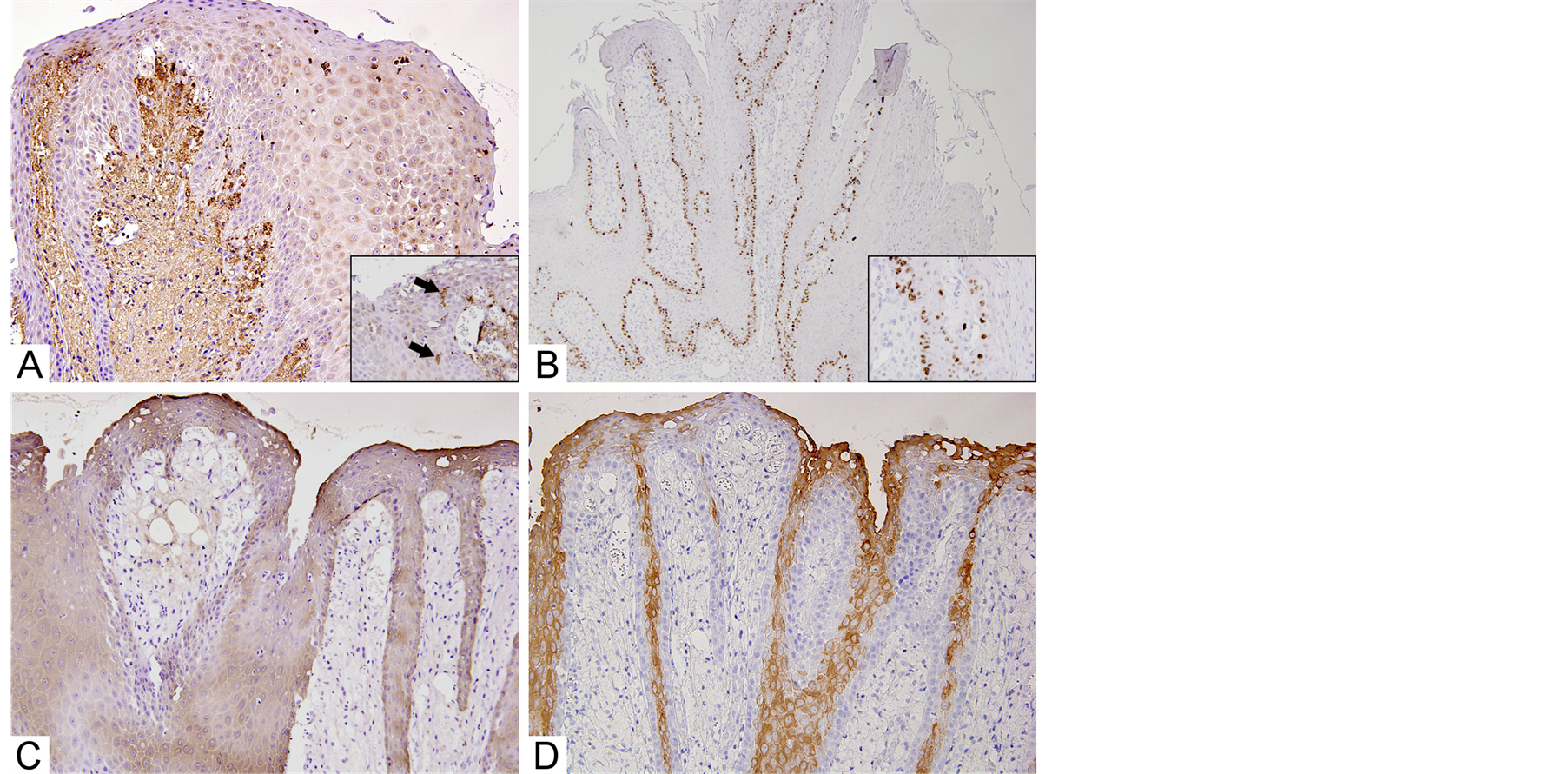
Figure 2. Immunohistochemical features: (A) Foamy cells showing positive immunoreactivity for CD68 (magnification 200´) (in-set; CD68-positive cells also appeared in the epithelium (arrows), magnification 600´); (B) Positive reactivity for Ki-67 innucleus and distributed in basal and/or parabasal layers (in-set; high-power magnification 600´); (C) Positive reactivity for pan-cytokeratin in almost layers of the epithelium (magnification 100´); (D) Positive reactivity for cytokeratin 13 predominantly in prickle cell layers of the epithelium (magnification 600´).
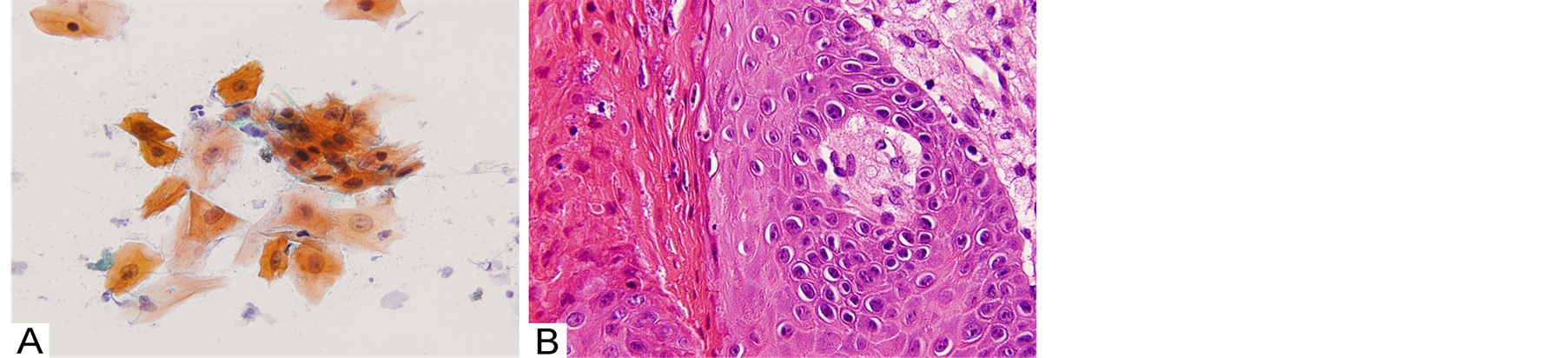
Figure 3. Comparative features between histopathology and exfoliative cytology: (A) Exfoliative cytological features indicating hyperkeratosis strongly stained with orange-G and picnotic nuclear stained with hematoxylin (Papanicolaou staining 600´); (B) Histopathological feature showing hyperkeratotic cells with picnosis in superficial layer of the epithelium. The histopathological features almost correspond to the cytological features of Figure 3(A). (arrows) (hematoxylin-eosin staining 600´).
Histopathologically, verruciform xanthoma is characterized by exophitic epithelial proliferation and accumulation of numerous foamy cells, as well as findings in the present cases. Several researchers have suggested that accumulation of foamy cells is related to inflammatory changes and immune response. Matsuura et al. [8] investigated immunohistochemical distribution of inflammatory infiltrates, and suggested that T cell-mediated local immune response was predominantly associated with the accumulation of antigen-representing foamy cells in local regions. Ide et al. [8] reported immunohistochemical and ultrastructural analyses with a review of the literature. These studies suggested that phagocytosis and accumulation of T cell-mediated macrophages against epithelial lipids and necrosis or degeneration of macrophages are associated with pathogenesis of the lesion, and are related to several critical cytokines and/or immunochemical factors [8] [9] . In the immunohistochemical results of Ki-67, no positive immunoreactivity was observed in foamy cells. These findings suggest that foamy cells are not neoplastic. We also observed CD68-positive foamy cells in both connective tissues papillae and intraepithelium, thus suggesting that verruciform xanthoma is a local immune response associated with macrophages.
Verrucous and/or papillary exophitic epithelial proliferation is also a characteristic feature of verruciform xanthoma. Histopathologically, the proliferating epithelial cells showed no atypical features, and exhibited positive immunoreactivity for CK13, whereas Ki-67-positive cells were distributed predominantly in basal or parabasal layers, and Ki-67 labeling index was 17.7% in the present study. Several studies have suggested that reduction or loss of CK13 may be related to malignancy in the oral mucosa. Yanagawa et al. [10] demonstrated an immunohistochemical analysis of CK13, and suggested that loss of CK13 expression indicates a high potential for recurrence; thus, CK13 immunohistochemistry could be useful for determining the best course of treatment for oral mucosal lesions. Yamashina et al. [11] examined the expression of CK13 and CK17 using cytological specimens, and suggested that loss of CK13 expression and expression of CK17 is related to higher-grade cellular atypia, and analysis using a cytological method is useful for determining cytological diagnosis and evaluation. Immunohistochemical expression of Ki-67 is a standard method for evaluating cell proliferation in neoplastic lesions [3] . Higher cell rates suggest the malignant potential of neoplastic lesions. Nasser et al. [12] demonstrated an immunohistochemical study for oral leukoplakia, which is a precancerous lesion of the oral mucosa, and concluded that higher expression of Ki-67 is also associated with changes in p53 and that p16INK4A is a valuable marker for evaluating malignant potential. Based on these literature reviews, the results of the present study correspond to the benign characteristics of verruciform xanthoma, and suggest that malignant tumors and verrucous and papillary growth can be distinguished by CK expression and Ki-67 labeling index.
The present study also performed an exfoliative cytological analysis. There were no foamy cells in the cytological specimens, although CD68-positive cells were observed in the epithelium. This is thought to be because the number of cells extracted by the exfoliative cytological technique is insufficient to obtain foamy cells. In addition, oral exfoliate cytology is sometimes less useful for diagnosis because the exfoliated cells are predominantly obtained from only surface areas of the mucosal epithelium. The present study obtained findings related to superficial epithelial cells, such as keratinized squamous epithelial cells with picnosis and hyperchromatism.
Dolens et al. [13] performed a systematic literature review of oral cytology, and suggested that cytology has good sensitivity and specificity for diagnosis of oral lesions and allows the use of other associated techniques, such as DNA analysis, which may improve accuracy. Fifita et al. [5] performed a comparative study between cytological and histopathological findings with special reference to flow cytometric analysis, and concluded that combination analysis with exfoliative cytology and flow cytometry is useful in the evaluation of pitfall cases of oral mucosal lesions, while cytological findings alone do not always yield the correct diagnosis. This conclusion also suggests that comparative analysis between cytological and histopathological findings is needed for definitive diagnosis. In addition, despite the difficulty for definitive diagnosis of the oral mucosal lesions using only exfoliative cytology, numerous oral epithelial lesions have thick keratinized cell layers that prevent detection of malignant atypical cells from deeper epithelial layers. As mentioned above, Yamashina et al. [10] performed an immunocytochemical study, and indicated that exfoliative cells obtained from the superficial layer of the oral mucosal lesions provides good information for the definitive diagnosis of oral malignant epithelial lesions, as reduction or loss of CK13 expression and expression of CK17 were also seen in the cytology specimens. Thus, a retrospective analysis is necessary to compare cytology and histopathology. When compared with the histopathological findings in the present studies, if the extracted cells are obtained from the surface of the epithelium, cytological findings are thought to reflect hyperplastic epithelial changes as a characteristic of verruciform xanthoma.
In order to increase the accuracy of oral exfoliative cytology, it is necessary to accumulate comparative analyses between cytological and histopathological findings for oral verruciform xanthoma. Based on cytological findings, the present study suggests that although foamy cells, which are characteristic of this lesion were not detected, the findings provide good information for verruciform xanthoma to be added the differential diagnosis of exophitic tumorous lesion, although further comparative analyses of cytology and histopathology are needed since experience of both oral exfoliative cytology and histopathological examination for diagnosing verruciform xanthoma has been limited.