1. Introduction
In his world renowned thesis, in 1819 J.G. Cloquet called attention to the frequency (20%) with which the processus vaginalis was found to persist after birth, with diverse types of opening and depth of this peritoneal diverticulum [1] . Additional support is provided by autopsy findings that 15% - 30% of adult males have patent processi vaginales without clinically apparent inguinal hernias during their life [2] [3] . Despite diagnostic laparoscopy which reveals a high incidence of patency on the contralateral side, it is well established that some of these patencies would never present as clinical hernias [4] -[6] .
According to N. Kukudjanov, in 1821 K.J.M. Langenbeck noted that when the abdominal muscles-internal oblique and transverse-contract, they get closer to the inguinal ligament protecting the inguinal canal [7] . In 1924 A. Keith identified the distal movement of the internal oblique in the same canal as the inguinal shutter [8] . Later, in 1935 H. Ogilvie promoted the idea of the protective spermatic cord lifting within the cremaster muscle [9] . At the same time W. Lytle described the U-shaped Hesselbach ligament sling which moves cranio-laterally after contraction of the transversus abdominis [10] . The above mentioned authors as well as others laid the foundations for the study of groin physiology [4] [11] -[13] .
It is noteworthy that in the course of computerized tomography while performing a Valsalva manoeuvre, J. Hahn-Petersen et al. found that the veins of the pampiniform plexus have a protective function [14] .
The high accuracy of ultrasonography in detecting groin hernias has been reported by many authors [15] -[17] . Yet this noninvasive method has not been applied to study the function of the groin from a physiological perspective. In 1995 the author reported blind sonography estimation analysis of seven different methods of inguinal hernia repair [18] . The analysis was done on the basis of three static and four dynamic criteria, the latter being physiological in nature. The aim of this article is to elaborate on my earlier studies [19] [20] , and to add some new findings to the existing knowledge of the physiology of the groin.
2. Material and Methods
Twenty consenting adults—ten women and ten men—who have not suffered groin diseases and had no groin surgeries participated in the prospective study. For the purposes of comparison, we included also five women and five men all with abdominal (but not groin) wall hernias, as well as five men with inguinal hernias. Examination was performed with the subject in the supine position, at rest, during a Valsalva manoeuvre and recording the changes in longitudinal and transverse projections (in the geometrical meaning) with a commercially available linear scanner (Picker LS 2400, Hitachi Medical, Tokyo, Japan) and video printer (Model P5OE, Mitsubishi Electronics, Tokyo, Japan) using 5-MHz transducer. Student’s t test was used to determine statistically significant differences between the groups.
3. Results
3.1. The Internal Oblique and Transversus Abdominis Muscles
The internal oblique muscle is presented as a homogenous muscular layer which allowed measuring its transverse dimensions. The muscle is identified as a body situated between two laminar structures: the external oblique aponeurosis, anteriorly, and the transversus abdominis muscle, behind (Figure 1). When the intra-abdominal pressure rises (Valsalva’s manoeuvre), the distance between both laminar structures (EOA & TA) decreases (Figure 2), the internal oblique muscle descends distally, and the zone of hypo-echogenic spermatic cord is reduced in size or sometimes disappears completely (Figure 3). This curtain-like mechanism observed at the distal end of the internal oblique, could be seen throughout the inguinal canal.
The measurements of the width of the internal oblique muscle are shown in Diagram 1. While in women, both at rest and while straining, there is a lack of dynamics, in men there are pronounced amplitudes during straining (p < 0.05; Diagram 1). The distal descent during the Valsalva’s manoeuvre is of the order of 0.8 cm ± 0.1 in men and in women 0.3 cm ± 0.1 (p < 0.001; Diagram 2). The mobility of the internal oblique muscle in men influences the size of the spermatic cord’s diameter while in women, the barely noticeable round ligament does not allow a similar observation.
While at rest the transversus abdominis muscle delineates the abdominal wall behind as a thin and variable muscular-aponeurotic plate (Figure 4), during the Valsalva manoeuvre the plate changes its initial configurations and takes on the characteristics of an aponeurosis (Figure 5).
3.2. The Rectus Abdominis Muscle
Earlier in our studies, while investigating the groin with ultrasonography, we detected movement of the rectus abdominis muscle in a latero-caudal direction. The present study demonstrates how during the Valsalva manoeuvre the rectus abdominis muscle overlays the medial inguinal fossa in the Hesselbach’s triangle from within the abdominal cavity. This is measured by the latero-caudal shift of its lateral margin (Figure 6).
The data obtained from the rectus abdominis transversal dimensions, at rest and strain, are documented in

Figure 1. Ultrasonographic appearance of the inguinal canal area. Male, left side, longitudinal scan of the canal; AEOM, external oblique aponeurosis; AIP, internal inguinal ring; SC, spermatic cord at external inguinal ring; FT, transversalis fascia plane; White arrows, posterior border of the transversus adominis muscle.

Figure 3. Ultrasonography of the right inguinal area. Male, transversal scan at the mid level of the inguinal canal; FT, transversalis fascia plane; IAP, Valsalva’s manoeuvre; White arrows, the anterior and posterior boundaries of the inguinal abdominal wall.

Figure 4. Sonography of the left inguinal area at rest in a male. Black arrows, delineate the anterior and posterior wall of the transversus abdominis muscle.

Figure 5. The same sonographic appearance as on Figure 4, but during a Valsalva’s maneuvre. FT, the plane the transversus abdominis muscle; Black arrows, external oblique aponerosis.

Figure 6. Right, inguinal canal, male, transversal scan. Left, at rest. Small arrows, lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle; Large arrows, the zone of femoral artery; Right, the same scan during a Valsalva manoeuvre; White arrows, anterior margin of the rectus abdominis muscle.
Diagram 3. They were assessed as significant (p < 0.001). Occasional variations were non-significant for the final results (range analysis with 0.99 confidence interval). The lateral rectus abdominis muscle expansion in men was considerable compared to that in women (Diagram 4). We found that in individuals with failed mechanics of the abdominal wall (i.e. the members of the group with abdominal wall hernias) that the rectus abdominus muscle does not realize the protective function described above. However, this break of the latero-caudal expansion of the rectus abdominis was not registered in the male subjects with inguinal hernias.
4. Discussion
There are no unified descriptions of the protective mechanisms in the groin area. Recently, Skandalakis and co-authors acknowledged two factors important for the integrity of a sound inguinal canal. The first is the
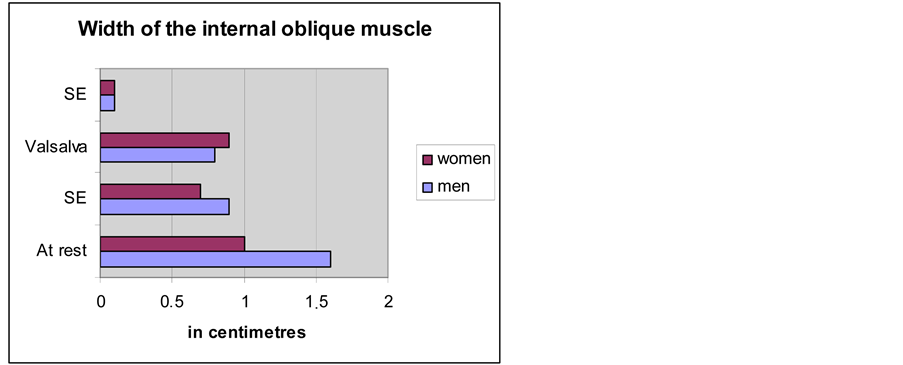
Diagram 1. Comparison of the average width of the internal oblique muscle between men and women.
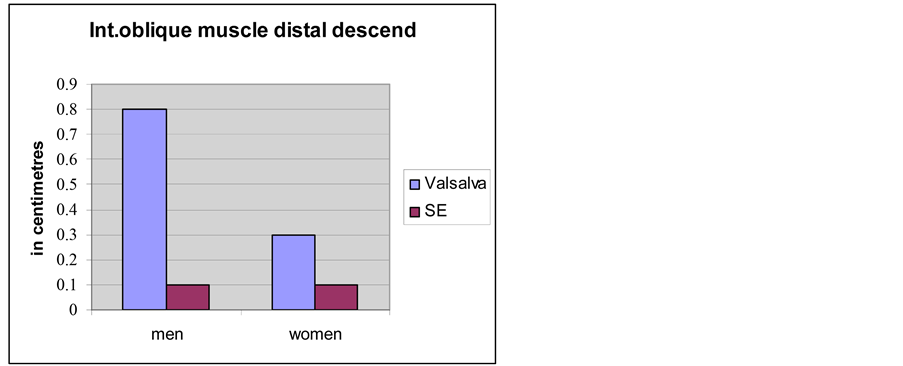
Diagram 2. Comparison of the distal descent of the internal oblique muscle during the Valsalva’s manoeuvre between men and women.
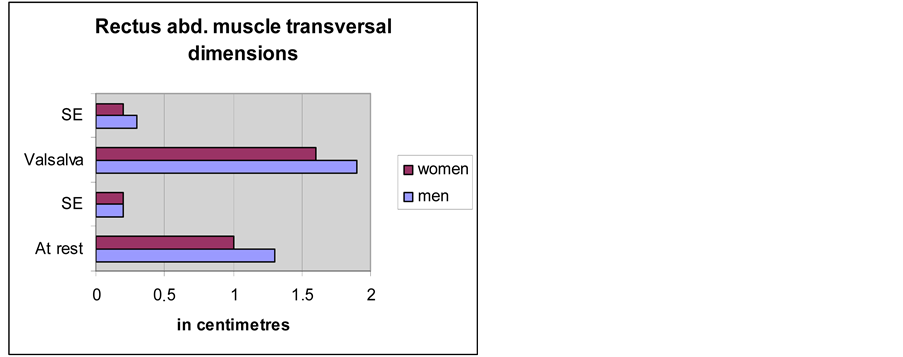
Diagram 3. Comparison of the rectus abdominis muscle transversal dimensions in men and women.

Diagram 4. Comparison of the lateral rectus abdominis muscle expansion between men and women.
sphincteric action of the internal oblique and transversus abdominis muscles in the zone of the internal inguinal ring; it closes the inguinal ring under the muscular edge of the internal oblique muscle by contracting the transversus abdominis. The second is the curtain-like action of the aponeurosis of the transversus abdominis: as the transversus abdominis, the internal oblique muscles contract concurrently; the arch formed by the aponeurosis moves laterally towards the iliopubic tract and the inguinal ligament [4] . The inguinal shutter action has been recognized by others as movement of the transversus abdominis arch in the direction of or in opposition to the iliopubic tract [11] . L.M. Zimmerman describes the sphincteric protective mechanism in the inguinal canal in the following way: “In the relaxed state, this muscle arches over the internal ring, partly covering it. When the abdominal muscles contract during effort or straining, the internal oblique shortens, and descends over the ring as a shutter. Furthermore, in so doing, it approximates itself towards the inguinal ligament, narrowing the interval between these structures in which the cord lies [12] .” P. Donahue has accepted that the shutter mechanism consists of structures that move simultaneously in different planes resembling the shutter of a camera—relying on W. Lytle, he suggested that the planes of motion occur within the internal oblique and transversus layers of the abdominal wall [13] .
At the same time as man became bipedal, and his testicles descended, his problems began [21] . The space where the spermatic cord passes is logically most vulnerable. Since there are no accidental occurrences in nature, it is more than likely that at least two mechanisms would exist to: 1) protect the inguinal canal against herniation; and 2) protect the spermatic cord from trauma [19] [20] .
The workings of the mobile anatomic structures in the groin are oriented in three frontal planes (Figure 7). The first is presented proximally by the layer of the transversus abdominis muscle and distally by the iliopubic tract. The elements that bind them are the transversus abdominis aponeurosis and the transversalis fascia. The internal oblique and the cremaster muscle occupy the second plane—they have a common origin. The third is represented by the external oblique muscle’s aponeurosis. When the abdominal pressure has been raised, the anatomic structures in the first and the third planes function like a muscular sheath in relation to the distal shift of the internal oblique muscle. What is more important—the plug-like action of this muscle is reinforced by the counter-oriented motion of the structures of the first and third layers when they contract [19] [20] . Sonographic studies have demonstrated that in men during the Valsalva manoeuvre, the width of the internal oblique muscle is markedly decreased (Diagram 1). This mechanism is the same for every contractile anatomic entity, including the muscular structure.
As was made clear, here must include the lateral expansion of the rectus abdominis muscle, but we should note that the width of its connection with the pubic bone is especially important [7] [22] . The lack of rectus sheath dorsally (below the semicircular line of Douglas), as well as of the tendinous insertions frontally allow the muscle to slide freely [23] . This contributes to the free movement of the distal rectus abdominis muscle in the protection of the myopectineal orifice of Fruchaud [19] [20] . C. Peiper et al. proposed that the active contraction of the lateral abdominal muscles (obliquus externus abdominis, obliquus internus abdominis, and transversus abdominis) is at best able to lateralize the rectus sheath due to the pull of the muscular and aponeurotic fibers on the anterior lamina of the rectus sheath (caudal arcuate line) which runs nearly parallel to the inguinal ligament [24] . This reinforces the aponeurotic structures in the medial part of Fruchaud’s myopectineal orifice but not the mechanics of the groin’s lateral layers.
The descriptions of the direct connections of the transversalis fascia to the marginal muscles in Hesselbach’s triangle are not uniform. Skandalakis et al. described a fusion of the aponeurosis of the transversus abdominis muscle with the transversalis fascia at the region of the posterior wall of the inguinal canal [25] . Pierpont et al. found muscular fibers of the transversus abdominis muscle which are fixed at the transversalis fascia and nearly inseparable [26] . In other anatomical studies connections between the muscles and the transversalis fascia were not revealed [24] . Regarding the bio-mechanics of the groin area the discussions about the fixation of the transversalis fascia do not change its protective function as an anatomic entity.
But what happens at the two poles of the inguinal canal? In the zone of the internal inguinal ring the Lytle’s mechanism is at work. The external inguinal ring is built from fascial-aponeurotic fibres that narrow it during contraction [7] . This is reinforced by the Ogilvie’s cremaster action. The inguinal canal can thus be understood as a tube which by the simultaneous closure of its two ends protects itself from intra-abdominal pressure (Figure 8). It is important to note here that in this case, the tube is closely occupied or it is chock-full with anatomic structures [19] [20] .
How are the various composite parts of the spermatic cord protected from mechanic trauma? By using contrast imaging during the Valsalva manoeuvre, Hahn-Pedersen et al. discovered that distally within the inguinal canal, the pampiniform plexus distends to two and half times its cross section [14] . Because of the rich venous collateral network this occurrence cannot be associated with passive venous congestion, even though the in-

Figure 7. 1, Transversus abdominis muscle plane; 2, Internal oblique muscle plane; 3, External oblique aponeurosis.

Figure 8. Schematic presentation of the hermetic-like effect on the inguinal canal.
crease of the intra-abdominal pressure leads to an increase in the pressure within the inferior vena cava. The phenomenon could be associated with the contraction of the cremaster muscle and the descent of the internal oblique muscle as an indirect sign of the pseudo-cavernous protection of the spermatic cord within the canal. This additionally is favoured by the abundance of veins in the distal two thirds of the cord. The Danish authors discovered another interesting fact. They observed the above mentioned filling of the pampiniform plexus only in individuals with direct hernias [14] . This confirms the proposed idea about the hermetic function of the plexus inside the inguinal canal and about the elimination of this “plug” effect and “de-hermetization” of the canal due to the indirect hernia content [19] [20] . The indirect hernia disturbs the protective function of the inguinal canal. In cases of direct hernia this is valid only for the canal’s distal part. Here Hahn-Pedersen et al. record a marked asymmetry of the two rectus abdominis muscles, supporting the view of their medial protective effect [14] (Figure 9).
Inguinal hernias appear most frequently in the region of the myopectineal orifice [21] , which is divided by the inguinal ligament into superior and inferior area. It is within the supra-inguinal space of the orifice that the already discussed synchronous protective mechanism operates. In the lower infra-inguinal space, where femoral hernias could appear, the integrity is realized by means of the complex fusion of fascio-ligamentous structures, where the iliopubic tract, the medial condensations of the transversalis fascia and the lacunar ligament are most important [27] [28] . When the abdominal muscles contract, these rigid structures stretch resisting in this way the herniogenic forces in the area.
In subjects with hernias of the abdominal wall, the protective muscular function is ineffective due to its compromised integrity. Consequently, the intra-abdominal pressure depends on the function of these muscles.
The etiology of inguinal hernias in adults is multifactorial, with altered collagen metabolism and changes of the anatomic structural characteristics of the inguinal region being the main causes. The combination of both factors may distort the physiological mechanisms of contention of the abdominal viscera [29] . In other words— structure precedes function.
In the course of the second half of the twentieth century scientists have realized the importance of the posterior wall of the inguinal canal in the surgical repair of these hernias. This tendency is represented today by the wide application (or implementation) of various prosthetic materials through conventionally open techniques or laparoscopically. The study of the physiology of the groin seems to have receded backstage since it has no dis-

Figure 9. The synchronous protective mechanism of the inguinal canal. 1, Transversus abdominis muscle; 2, Internal oblique muscle plane; 3, External oblique aponeurosis; 4, Rectus abdominis muscle; 5, Posterior rectus sheath.
tinct influence on the prosthetic surgical repairs of hernias. Yet, the advancement in understanding of the groin physiology deserves special attention for it could prove especially useful in certain situations.