Migration Rate and Its Effect on the Economy of the Country: A Case of Madagascar ()
1. Introduction
Geography of Madagascar
The Republic of Madagascar is a country located in Eastern Africa, consisting of the world’s fourth largest island and some smaller islands in the Indian Ocean. Madagascar has a coastal plain, high plateau and mountains. Major rivers include the Betsiboka, Onilahy, Mangoky and Tsiribihina. The east coast of Madagascar has lowlands leading to steep bluffs and central highlands. The Tsaratanana Massif in the north has volcanic mountains. The west coast has many protected harbors and broad plains, while the southwest is a plateau and desert region. The largest city and capital is Antananarivo. Other important cities are Antsirabe, Mahajanga and Toamasina. Highest peak is the Maromokotro reaching 2876 meters above sea level (Figure 1).
The dynamics of world has been characterized not just by the international flow of capital, commodities, goods, services and information but more so of labor. The global labor market, mainly for the highly skilled is increasing. The migration of the highly skilled from developing countries is rising. Developing countries needs a critical mass of highly skilled scientists, engineers and other specialists to accomplish socioeconomic improvement. High quality experts are compulsory not only for industrial growth and competitiveness but also for provision of social services such as health, sanitation, energy infrastructure, education and agriculture. Migration of highly skilled scientists, engineers and medical professionals is generally known to bear a negative effect on a country’s economic and social growth. Source countries lose out not only on the investment they have made on training of highly skilled people but are often forced to hire foreign consultants to meet specific development needs at a high cost to tax payers. It is estimated that 30 to 50 per cent of the developing world’s population trained in science and technology live in the developed world [1] .
As per there is not a high rate of migration from Madagascar but only small amount of highly skilled people migrate from Madagascar. Push factors can be unemployment, underemployment, security issues, underde-
veloped education system and weak institutions of innovation and scientific research. Further factors can be include noncompetitive employment and career advancement, lack of research funding, insufficient intellectual stimulation, inefficient management of resources, low social capital and low salary structures. Pull factors can be better learning chances as members of international networks, access to high quality scientific structure and frontier technologies, higher salaries, competitive job environment, access to better education and health facilities for family and accessibility of funds for research and innovation. At the other hand advanced and developed countries always attract people from developing and developing countries like Madagascar. Developed countries with advanced knowledge-based economies would continue to attract human capital from the developing world as there will be more opportunities for the highly skilled.
Due to high rate of migration from some countries especially a case of India a recent study by the Federation of the American Immigration Reform (FAIR) on Brain Drain showed that India is experiencing a shortage of 145,000 engineers although it trains an estimated 178,000 software engineers each year. The shortage of software engineering in India is increasing; the one reason may be the migration rate of India. International migration is a mighty force globally. Over 175 m people, accounting for 3% of world is population, live permanently outside their countries of birth [2] . The stock of international migrants in the world doubled in the quarter century to the year 2000 and almost ten percent of the persons residing in the developed regions of the world are now international migrants [3] . From these migrants stock of 175 million of international migrants in the world, nearly one third was in Europe, another 29 percent in Asia and 23 percent in North America in 2000. During the third decades, the Asian and Pacific region has witnessed a substantial increase in the scale, diversity and complexity of population movements. More than 60% of the world population lives in this region and there are major migration flows from this continent to Europe and North America [4] . The majority of these migrants cross borders are in search of better economic and social opportunities. These economic migrants are the world's fastest rising group of migrants. Globalization has enlarged the flexibility of labour, and a decline in fertility and working-age populations in many developed countries is leading to a rising demand for workers from abroad to sustain national economies. There are different types of migration, some people moved permanently to other countries with their whole families but most of the Migration is temporary or circular bases and these types of families remain in contact with their home countries. Migrants make important contributions to the economic prosperity of their host countries, the flow of financial, technological, social and human capital back to their countries of origin also is having a significant impact on poverty reduction and economic development. Remittances from migrants are a major source of capital for developing countries. High fertility and rapid population growth in some developing countries created pressures to emigrate by taxing infrastructures, education, health and social service systems and the environment. At the same time, migration has become an important component of population growth in countries where fertility has declined. In some parts of Europe, Asia and Africa migration is mitigating population decline resulting from below-replacement fertility and population ageing. Net migration has already either prevented population decline or contributed to population growth in a number of countries. Many people move from poorer to richer countries, for example from many parts of Sub-Saharan Africa to South Africa and from many parts of Southeast Asia to Singapore and Malaysia. Migration also has some significant benefits for global economic welfare. When migrant workers move between differently endowed countries (e. g. from a country where there are large labour surpluses in one sector to another where there are labour shortages in that sector), that movement can enhance economic conditions in both sending and receiving countries. Indeed, one estimate suggests that if developed countries were to increase the proportion of migrant workers in the labour force equivalent to 3 per cent, world welfare would increase by over 150 billion dollars per annum [5] . Where these flows lead to a drain of highly skilled people from developing countries, the ability of those countries to develop may be compromised. The absence of these key workers hampers the ability (‘brain strain’) of these countries to come up with homegrown solutions to their problems. Where those migrants move and contribute to economic dynamism in destination countries, there is a risk that migration can widen the gap between richer and poorer countries. These impacts are often worst in the poorest countries. For some poor countries that have high rates of permanent emigration, especially of highly skilled people, migration can be a significant threat. Where these countries have poor economic and financial infrastructure, the potential for emigrants to contribute to development through remittances, investment, and return/circulation migration is also hampered. Yet, migration can also have positive economic impacts on countries of origin. The money that migrants send home (remittances) can contribute significantly to the recipients’ welfare as well the receiving country’s economic well-being. Where migrants return home, either permanently or for short periods, with new skills that they put to good use, they and their communities can benefit. Even when they don’t return in person, members of a Diaspora can contribute to the development of their erstwhile homes through trade, investment, networking, and skills transfer.
Migration has effect on economics widely, sometime may be it leaves effect in short term, but in long term it has very positive impact on the economy of the country. Immigration have economics effects for both sending and receiving countries, sometime also depend that who is moving especially with the respect of migrate workers’ skills levels. For sending countries, the short-term economic benefits of emigration are found in remittances. Remittances are funds that emigrants earn abroad and send back to their home country for to support their family in back home. International migration has substantial consequences for development. There are more than 215 international migrants and over 700 million internal migrants worldwide. According to official estimates, migrants from developing countries sent over USD 325 billion in officially recorded remittances to their origin countries in 2010—three times the size of official development assistance. Remittances flows to developing countries remained resilient during the recent global financial crisis compared to significant declines in private capital flows. Unlike commonly believed, around half of the official international migration from the South is to other developing countries rather than to wealthier countries in the North [6] .
2. Most Important Impact of Migration on Madagascar
The Republic of Madagascar, the fourth largest island in the world, is in the western Indian Ocean, about 500km east of Mozambique and southern Africa. Accordingly International labor Organization (2012) the GDP growth rate is 3.1. Madagascar is facing a lot challenges this types which can be in the shape of poverty, unemployment, lack of houses, etc. More than 80% of its population lives in poverty, with most of them working in low productivity jobs, primarily in the agricultural sector. In Madagascar, it is not unemployment which is the problem, per se, but rather, underemployment, that is, employment that does not earn workers a living wage. Many Malagasy citizens are trapped in low-wage activities, often in the informal sector and usually in the agricultural sector [7] . Madagascar population is steadily increasing throughout the twentieth century. This rate has made Madagascar one of the most rapidly growing countries in the Africa. With a large youthful population in 1992 nearly 55 percent population was under twenty years old.
Brain drains can also comprise industrialists and students (i.e. future professionals). The former’s departure denies the home country of some of the people who create businesses and employment. As for students, most developing countries send some of them abroad for tertiary-level studies, as a means of expanding and improving the human capital stock of the home country. However, this often becomes a route to brain drain. The greater the gap between the conditions in the study country and those in the home country, the higher the probability of graduates staying abroad [8] , which shrinks the human capital base of the home country. Migrations always have some effect on both sending and receiving countries. It is may be difficult to collect the data how much a countries is getting money from migrants people, Because the people send money by different sources, some are official and some people also used unofficial ways for to send money to their countries and some sort of things and gifts are on the other hand. International remittances are of the greatest importance for the economy since internal remittances have no effect on the money growth within the country. It is sure migrants have positive and negative effect on the countries, as per a country like Madagascar which is the top hundred countries from where people moved to other countries for the income purposes. So these migrants have some positive and some negative effect on the country (Table 1).
Migrant’s rate from Asia is high, while migrant’s rate from the African country is not so high, but still these migrants have some effective impact on the economy and on the education system of the country. In Table 2, we can see the total number of migrants every year by region from the 1960 to 2010 (Table 2).
In Figure 2, we can see the percentage of skilled migrant’s people from LDCs countries. Emigrants from the Madagascar are not so high but still some people move from Madagascar to other countries for the better future. High-skilled people migrate [12] [13] . Given the fundamental role played by human capital in long-term growth and development, brain drain could have the impact of slowing down the origin country’s economic growth rate [14] -[16] . The adverse impact of shrinking human capital on development is especially acute as the world economy becomes increasingly knowledge based.
Reason of Migration from Madagascar to Others Countries
Net migration rate in Madagascar is 0 migrant(s)/1,000 populations (2013 est.) (Figure 3). This entry includes the

Table 1 . Summary of migration effect on country.
Source: Adapted by authors from UN/DESA (2004) [9] .

Table 2. Total numbers of migrants.
Source: United Nations (UN/DESA), International Migrants stock. The 2008 Revision (http://esa.un.org/migration) [10] .
figure for the difference between the number of persons entering and leaving a country during the year per 1,000 persons (based on midyear population). An excess of persons entering the country is referred to as net immigration (e.g., 3.56 migrants/1000 population); an excess of persons leaving the country as net emigration (e.g., −9.26 migrants/1000 population). The net migration rate indicates the contribution of migration to the overall level of population change. High levels of migration can cause problems such as increasing unemployment and potential ethnic strife (if people are coming in) or a reduction in the labor force, perhaps in certain key sectors (if people are leaving) [17] .
People move across countries due to many reasons. Economic theory most prominently highlights the international labor mobility that descends from wage differences across countries. Likewise, many students from developing economies migrate to advanced countries, for either short or long durations, to study in the schools and universities of advanced countries [18] , in some countries these students also work in the some allowed hours and send money to the home country for their family which is also a positive sign for the receiving country. A lot student moved every year from Madagascar to other countries for the study purpose. Sadly, many migrations are also the result of hardships or oppressions, as the growth of refugees in Northern Europe attests. The nature of the migration will impact education levels, ages, and tenures of immigrants, and consequently their probable assimilation. When migrants have the power to choose, the nature of the migration will also impact the host country selected.
3. Conclusions
It is impossible to simplify about the effects of migration on sending countries because the effects of migration on their economies depend very much on their position within the migration cycle. Most emigration countries will pass through some version of the stages of this cycle. Emigrations have an affective role on growth and poverty reduction through three channels: changes in the labor supply, changes in productivity, and through migrants’ remittances. The net benefit (that is, benefits minus costs) of emigration is the sum of these three effectsNumber of skilled emigrants from LDCs, 1990 and 2000
(Thousand persons)
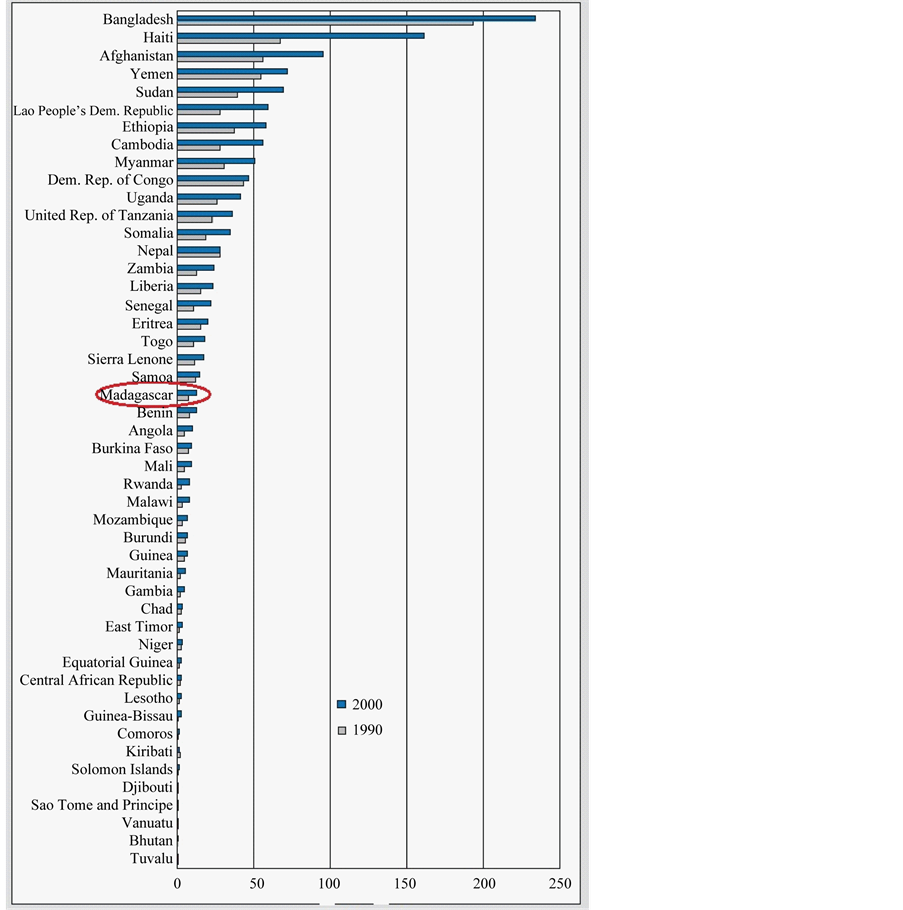
Figure 2. Source: UNCTAD secretariat calculations, based on data from Docquier et al. (2011). [11] .
and the relative importance of each channel varies over the life of the migration cycle. The five stages of the migration cycle are exit, adjustment, consolidation, networking and return. Some stages may be skipped or accelerated and return may coincide with immigration from other countries. By this study, I can say that migration has different types of effect on you, your family, education, effect on people and on the host and home country. Migration is a powerful vehicle for the development of both sending and receiving countries. Targeted migration policies are needed to enhance the quality of labor mobility and leverage remittances for development especially for the country Madagascar.
The Migration also have some effect on the other areas of life, just like one person he can get better education from advanced and developed country then after he come back he can work better for the country in the education sector and some other sector of science and technology. In the medical prospective a person from developing can gain better knowledge from the developed country. The relationship between migration and development is at once extremely significant but also marginal in many ways. It is important for all the reasons outlined MADAGASCAR

Figure 3. Source: International organization for migration IOM (2013).
above. Development is marginal to migration: when we consider all the various aspects of managing migration, the development impacts on countries of origin is rarely going to be as projecting a research or policy issue as matters such as immigrant integration, migrant rights and the economic influences of immigration. Similarly, migration is marginal to development: of all the factors that form the development possible of an economy, migration is almost always going to be comparatively insignificant. Country like Madagascar need influence policies for this sector.
Due to lake of data, we could not give the full picture of people who are abroad from Madagascar now and how much revenue country is getting from these types of people, but as per the current situation of Madagascar we can suggest these types of some recommendations.
1) Government of Madagascar should take computerized data-bank of all migrants within very short time and government should try to make availability the data online.
2) Policy maker should make some polices for the poor people to go outside for the betterment of these types of families, government can introduced some sort of vocational courses for them because the skilled person demand is high before to go abroad. NGO and some other social organizations are can also do the same job for poor people.
To provide security to the whole country is the duty of government so the families which are living in Madagascar and their relatives are abroad, government should provide them security so that they can lead their life peacefully and do not think to leave country permanently.