Availability Equivalence Factors of a General Repairable Parallel-Series System ()
1. Introduction
In reliability analysis, there are two main methods to improve non-repairable system design. These methods are the reduction and redundancy methods [1] . In the reduction method, it is assumed that the system design can be improved by reducing the failure rate(s) of a set of system components by a factor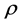 ,
,  , [1] -[4] . The redundancy method assumes that the system can be improved by increasing its components [5] .
, [1] -[4] . The redundancy method assumes that the system can be improved by increasing its components [5] .
There are more than one redundancy methods such as hot, warm, cold and cold with imperfect switch redundancy, named respectively as hot, warm, cold and cold with imperfect switch duplication methods [6] . The redundancy methods can be applied on repairable systems as well. In addition to the reduction method, the repairable system can be improved by increasing the repair rate of some of the system component(s) by a factors,  , [7] [8] .
, [7] [8] .
Using the redundancy method may not be a practical solution for a system in which the minimum size and weight are overriding considerations: for example, in satellites or other space applications, in well-logging equipment, and in pacemakers and similar biomedical applications [9] . In such applications space or weight limitations may indicate an increase in component performance rather than redundancy. Then more emphasis must be placed on better design, manufacturing quality control and on controlling the operating environment. Therefore, the concept of reliability/availability equivalence takes place. In such concept, the design of the system that is improved according to reduction or increasing method should be equivalent to the design of the system improved according to one of redundancy methods. That is, in this concept, one may say that the performance of a system can be improved through an alternative design [10] . In this case, different system designs should be comparable based on a performance characteristic such as 1) the reliability function or mean time to failure in the case of no repairs or 2) the availability in the case of repairable systems.
The concept of comparing different designs is applied in the literature in order to: 1) improve the reliability of a non-repairable system [11] ; 2) determine a representative service provider and create equivalent elements [12] ; 3) derive the reliability equivalence factors of some non-repairable systems [2] and the references therein; and 4) derive the availability equivalence factors of a repairable system [7] [8] .
The reliability equivalence concept applied on various non-repairable systems, [1] [2] [4] [13] -[17] .
In this work, the reliability function and mean time to failure are used as characteristic measures to compare different system designs to derive reliability/mean time equivalence factors.
Repairable system indicates a system that can be repaired to operate normally in the event of any failure, such as automobiles, airplanes, computer network, manufacturing system, sewage systems, power plant or fire prevention system. Availability comprises “reliability” and “recovery part of unreliability after repair”, indicating the probability that repairable systems, machines or components maintain the function at a specific moment [18] . It is generally expressed as the operable time over total time. Parallel-series system indicates sub-systems in which several components are connected in series, and then in parallel, or sub-systems that several components are connected in parallel, and then in series [19] . The reliability/availability of a parallel-series system has drawn continuous attention in both problem characteristics and solution methodologies [2] , [19] and [20] . Recently, [7] [8] discussed the availability equivalence factors of a repairable series-parallel system with independent and identical (non-identical) components.
Our goal in this paper is to derive the availability equivalence factors of a repairable parallel-series system with independent and non-identical components. The availability function of the system will be used as a performance measure to compare different system designs of the original system and other improved systems in order to derive these factors.
The structure of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 introduces the illustration of the parallel-series system and the system availability. Section 3 presents the availabilities of the systems improved according to five different methods that can be applied to improve the performance of the original system. In Section 4, two types of availability equivalence factors of the system are discussed. A numerical example is introduced in Section 5 to illustrate how the idea of this work can be applied. Finally, Section 6 is devoted to the conclusions, which handle the main results derived throughout this work.
2. A General Repairable Parallel-Series System
The system considered here consists of n subsystems connected in parallel, and with subsystem i consisting of mi independent, repairable and nonidentical components connected in series for 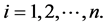 We refer to such system as a general repairable parallel-series system. Figure 1 shows the diagram of that system.
We refer to such system as a general repairable parallel-series system. Figure 1 shows the diagram of that system.
Let  and
and  be the lifetime and repair time, respectively, of component j in subsystem i,
be the lifetime and repair time, respectively, of component j in subsystem i, 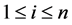 ,
,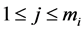 . It is assumed that the life and repair times of component j in subsystem i,
. It is assumed that the life and repair times of component j in subsystem i,  ,
,  , follow exponential distributions with failure rate λij and repair rate μij. Let N be the total number of the system components, that is
, follow exponential distributions with failure rate λij and repair rate μij. Let N be the total number of the system components, that is 
Special Cases: This system generalizes the following cases:
1) Repairable parallel-series system with identical components, when ,
,  ,
,  and
and 
2) Repairable parallel system with non-identical components, when  and
and 
3) Repairable series system with non-identical components, when  and
and 
Let Aij, be the availability of the component j in subsystem i and Ai be the availability of the subsystem i,
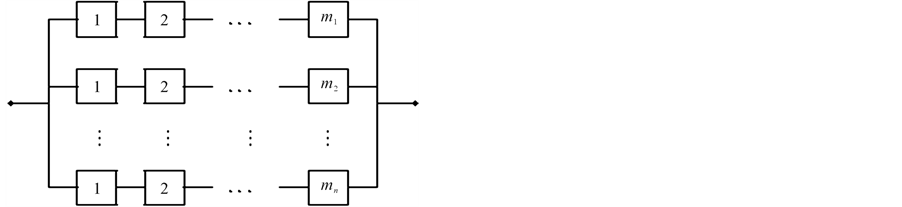
Figure 1. Parallel-series system structure.
 ,
, . One can easily derive Aij and Ai, respectively, as, see [8]
. One can easily derive Aij and Ai, respectively, as, see [8]
 (1)
(1)
and
 (2)
(2)
Therefore, the system availability, denoted  can be derived as
can be derived as
 (3)
(3)
3. Different Designs of Improved System
The system can be improved according to one of the following three different methods:
1) Reduction method. In this method it is assumed that the component can be improved by reducing its failure rate by a factor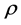 ,
, .
.
2) Increasing method. It is assumed in this method that the component can be improved by increasing its repair rate by a factor ,
, .
.
3) Standby redundancy method:
a) Hot duplication method: in this method we assume that the component is duplicated by an identical hot standby component.
b) Warm duplication method: in this method we assume that the component is duplicated by an identical warm standby component.
c) Cold duplication method: in this method we assume that the component is duplicated by an identical cold standby component.
In the following sections, we derive the availability of the system improved according to the methods mentioned above.
3.1. The Reduction Method
It is assumed in the reduction method that the system can be improved by reducing the failure rates of a set R components by a factor ,
, . We assume that
. We assume that , where Ri is a set of the subsystem i components,
, where Ri is a set of the subsystem i components, . Also, we assume that
. Also, we assume that ,
,  , and
, and .
.
Let  be the availability of the component j in subsystem i, improved by reducing its failure rate
be the availability of the component j in subsystem i, improved by reducing its failure rate  by the factor
by the factor . One can easily derive
. One can easily derive
 (4)
(4)
Therefore, the availability of subsystem i improved by reducing the failure rates of a set Ri components by the factor , denoted
, denoted , can be written as
, can be written as
 (5)
(5)
where 
 is the set of all subsystem i components,
is the set of all subsystem i components,  ,
, .
.
Finally, the availability of the system improved by reducing the failure rates of a set R components by the same factor , denoted
, denoted , can be derived as
, can be derived as
 (6)
(6)
3.2. The Increasing Method
It is assumed in the increasing method that the system can be improved by increasing the repair rates of a set S components by a factor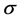 ,
,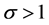 . We assume that
. We assume that , where Si is a set of the subsystem i components,
, where Si is a set of the subsystem i components, . Also, we assume that
. Also, we assume that  and
and 
 .
.
Let  be the availability of component j in subsystem i after increasing its repair rate
be the availability of component j in subsystem i after increasing its repair rate  by the factor
by the factor ,
,  and
and  be the availability of subsystem i which is improved by increasing the repair rates of a set Si components by the same factor
be the availability of subsystem i which is improved by increasing the repair rates of a set Si components by the same factor ; and
; and 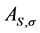 be the availability of the system improved by increasing the repair rates of a set S components by the same factor
be the availability of the system improved by increasing the repair rates of a set S components by the same factor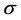 . One can derive these availabilities in the following forms
. One can derive these availabilities in the following forms
 (7)
(7)
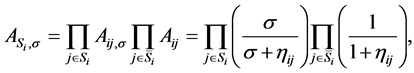 (8)
(8)
 (9)
(9)
where , for
, for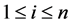 .
.
3.3. The Hot Duplication Method
It is assumed in the hot duplication method that the system can be improved by connecting every element in a set B components with an identical component in parallel. We assume that  where Bi is a set of the subsystem i components,
where Bi is a set of the subsystem i components, 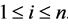 Also, we assume that
Also, we assume that ,
,  , and
, and 
 .
.
Let  be the availability of the subsystem i which is improved by improving a set
be the availability of the subsystem i which is improved by improving a set  components,
components, ; and
; and  be the availability of the system improved by improving a set B components according to the hot duplication method. One can derive
be the availability of the system improved by improving a set B components according to the hot duplication method. One can derive
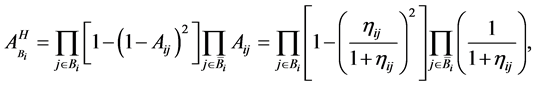 (10)
(10)
 (11)
(11)
where 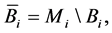 for
for .
.
3.4. The Warm Duplication Method
We say that, a component j in subsystem i is warm duplicated if it is connected in parallel with a non-identical component, having a failure rate , in parallel via a perfect switch. In the warm duplication method, it is assumed that the system can be improved when every component in a set B components is warm duplicated. We assume that
, in parallel via a perfect switch. In the warm duplication method, it is assumed that the system can be improved when every component in a set B components is warm duplicated. We assume that  where
where  is a set of the subsystem i components,
is a set of the subsystem i components, . Also, we assume that
. Also, we assume that
 ,
,  , and
, and 
Let  be the availability of the component j in the subsystem i when it is improved according to the warm duplication method. Using Markov process,
be the availability of the component j in the subsystem i when it is improved according to the warm duplication method. Using Markov process,  can be obtained as follows, see [21] ,
can be obtained as follows, see [21] ,
 (12)
(12)
where  for
for  and
and .
.
Let  be the availability of the subsystem i improved by improving Bi subsystem components according to the warm duplication method. Therefore, one can derive
be the availability of the subsystem i improved by improving Bi subsystem components according to the warm duplication method. Therefore, one can derive
 (13)
(13)
Finally, let  be the availability of the system improved by improving a set B components according to the warm duplication methods. Using Equation (13), we get
be the availability of the system improved by improving a set B components according to the warm duplication methods. Using Equation (13), we get
 (14)
(14)
3.5. The Cold Duplication Method
It is assumed in the cold duplication method, that each component of set B components is connected in parallel with an identical component via a perfect switch. We assume that  where Bi is a set of the subsystem i components,
where Bi is a set of the subsystem i components,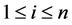 . Also, we assume that
. Also, we assume that ,
,  , and
, and 
Let  is the availability of the component j in subsystem i when it is improved according to the cold duplication method;
is the availability of the component j in subsystem i when it is improved according to the cold duplication method;  be the availability of subsystem i, which is improved according to cold duplication method; and
be the availability of subsystem i, which is improved according to cold duplication method; and  be the availability of the system improved by improving set B components according to the cold duplication method. Using Markov process theory,
be the availability of the system improved by improving set B components according to the cold duplication method. Using Markov process theory,  is, see [22] ,
is, see [22] ,
 (15)
(15)
Using Equation (15) and the nature of the series subsystem i, one can derive
 (16)
(16)
Finally, using Equation (16) and the nature of the parallel connection of the subsystems, we get
 (17)
(17)
4. Availability Equivalence Factors
In this section, we derive the availability equivalence factors of a repairable parallel-series system with independent, non-identical and repairable components. Two types of availability equivalence factors will be discussed. These two types are referred as availability equivalent reducing factor and availability equivalent increasing factor. Following the definition of reliability equivalence factors introduced in [1] .
4.1. Availability Equivalence Reducing Factor
Availability equivalence reducing factor, in short AERF, referred as  D = H, W, C for hot, warm and cold, respectively, is defined as the factor
D = H, W, C for hot, warm and cold, respectively, is defined as the factor  by which the failure rate of a set R components should be reduced in order to get equality of the availability of another better design which can be obtained from the original system by assuming hot, warm and cold duplications of a set B components. That is,
by which the failure rate of a set R components should be reduced in order to get equality of the availability of another better design which can be obtained from the original system by assuming hot, warm and cold duplications of a set B components. That is,  for D = H, W, C, is the solution of the following equations in
for D = H, W, C, is the solution of the following equations in ,
,
 (18)
(18)
In what follows, we give the non-linear equations needed to be solved to get the three possible AERF’s.
1) Hot availability equivalence reducing factor (HAERF): Substituting Equations (6) and (11) into Equation (18),  is the solution of the following non-linear equation in
is the solution of the following non-linear equation in ,
,
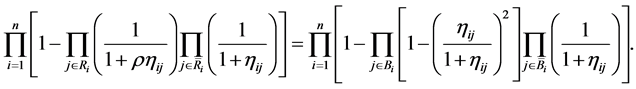 (19)
(19)
2) Warm availability equivalence reducing factor (WAERF): Substituting Equations (6) and (14) into Equation (18),  is the solution of the following non-linear equation in
is the solution of the following non-linear equation in ,
,
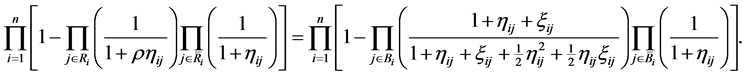 (20)
(20)
3) Cold availability equivalence reducing factor (CAERF): Substituting Equations (6) and (17) into Equation (18),  satisfies the following non-linear equation
satisfies the following non-linear equation
 (21)
(21)
Equations (19)-(21) have no closed solutions, therefore, a numerical technique method is needed to get their solutions.
4.2. Availability Equivalence Increasing Factor
Availability equivalence increasing factor, in short AEIF, referred as  D = H, W, C for hot, warm and cold, respectively, is defined as the factor
D = H, W, C for hot, warm and cold, respectively, is defined as the factor  by which the failure rate of a set S components should be reduced in order to get equality of the availability of another better design which can be obtained from the original system by assuming hot, warm and cold duplications of a set B components. That is,
by which the failure rate of a set S components should be reduced in order to get equality of the availability of another better design which can be obtained from the original system by assuming hot, warm and cold duplications of a set B components. That is,  for D = H, W, C, is the solution of the following equations in
for D = H, W, C, is the solution of the following equations in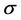 .
.
 (22)
(22)
In what follows, we give the non-linear equations needed to be solved to get the three possible AEIF’s.
1) Hot availability equivalence increasing factor (HAEIF): Substituting Equations (9) and (11) into Equation (22), 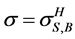 is the solution of the following non-linear equation
is the solution of the following non-linear equation
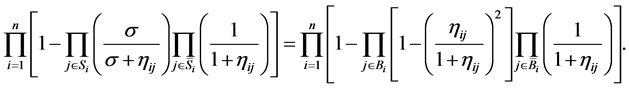 (23)
(23)
2) Warm availability equivalence increasing factor (WAEIF): Substituting Equations (9) and (14) into Equation (22),  is the solution of the following equation in
is the solution of the following equation in 
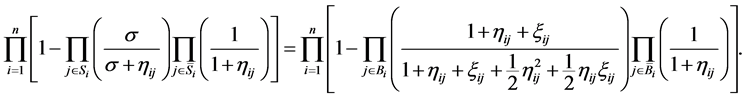 (24)
(24)
3) Cold availability equivalence increasing factor (CAEIF): Substituting Equations (9) and (17) into Equation (22),  is the solution of the following equation in
is the solution of the following equation in ,
,
 (25)
(25)
The above Equations (23)-(25) have no closed-form solutions in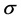 , so a numerical technique method to get the value of
, so a numerical technique method to get the value of .
.
5. Numerical Results
To explain how one can utilize the previously obtained theoretical results, we introduce a numerical example. In such example, we calculate the two different availability equivalence factors of a general repairable parallel- series with n subsystems. Each subsystem consists of mi,  , non-identical components, under the following assumptions:
, non-identical components, under the following assumptions:
1) The parallel-series system has two subsystems, n = 2;
2) The subsystems have the components, m1 = 1, m2 = 2 then N = m1 + m2 = 3;
3) The values of the system parameters ,
, 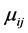 , and
, and  are presented in Table 1.
are presented in Table 1.
The objective is to improve the repairable parallel-series system by improving the performance of some components instead of increasing the number of these components.
We give the values of availability of the original system and of the design obtained using the duplication methods for the example considered in this section.
Table 2 shows the availability of the original and improved system obtained from the original system by applying hot, warm and cold duplications using all possible set B components, where 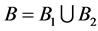 and ϕ is the empty set.
and ϕ is the empty set.
From the results shown in Table 2, one can easily see that:
1)  for all possible set B components when
for all possible set B components when ;
;
2)  for all possible set B components when
for all possible set B components when ;
;

Table 1. Set values of the system parameters.

Table 2. The availability of the improved system,  D = H, W, C.
D = H, W, C.
3) Improving the only one component in subsystem 1, according to the duplication method, provides a better design than that can be achieved by improving one component from the subsystem 2, according to the same method;
4) Duplicating two components, one from each subsystem, produces a better design than that can be obtained by duplicating the two components in subsystem 2, according to the same method; and 5) Cold duplicating all components in the system provides the best design, in the sense of having the highest availability.
We used Mathematica Program System to calculate all possible availability equivalence factors of the studied system. Table 3 and Table 4 give the hot, warm and cold (D = H, W, C) availability equivalence reducing factors, 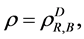 and the hot, warm and cold availability equivalence increasing factors,
and the hot, warm and cold availability equivalence increasing factors, 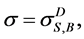 respectively, for all possible sets R, S and B.
respectively, for all possible sets R, S and B.
From the results presented in Table 3, Table 4, we can immediately conclude that:

Table 3. The AERF ( D = H, W, C) for different R, B, when
D = H, W, C) for different R, B, when .
.

Table 4. The AEIF ( D = H, W, C) for different S, B, when
D = H, W, C) for different S, B, when .
.
1) Hot duplication of the only one component in subsystem 1, 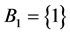 and
and 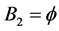 increases the system availability from
increases the system availability from  to
to 
 , see Table 2. The improved system with
, see Table 2. The improved system with  0.99888 can be achieved by performing one of the following:
0.99888 can be achieved by performing one of the following:
a) Reducing the failure rate(s) of (see Table 3): i) the only component in subsystem 1,  , where
, where  and
and , by the HAERF
, by the HAERF , ii) the only component in subsystem 1 and the first component in subsystem 2,
, ii) the only component in subsystem 1 and the first component in subsystem 2,  ,
, 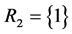 , by the HAERF
, by the HAERF , iii) the only component in subsystem 1 and the second component in subsystem 2,
, iii) the only component in subsystem 1 and the second component in subsystem 2, 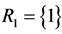 ,
,  , by the HAERF
, by the HAERF , iv) the two components in subsystem 2,
, iv) the two components in subsystem 2,  and
and , by the HAERF
, by the HAERF , v) all the three components,
, v) all the three components,  ,
,  , by the HAERF
, by the HAERF .
.
b) Increasing the repair rate(s) of (see Table 4): i) the only component in subsystem 1,  , where
, where  and
and , by the HAEIF
, by the HAEIF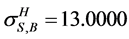 , ii) the only component in subsystem 1 and first component in subsystem 2,
, ii) the only component in subsystem 1 and first component in subsystem 2,  ,
,  , by the HAEIF
, by the HAEIF , iii) the only component in subsystem 1 and second component in subsystem 2,
, iii) the only component in subsystem 1 and second component in subsystem 2,  ,
,  , by the HAEIF
, by the HAEIF , iv) all the three components,
, iv) all the three components,  ,
,  , by the HAEIF
, by the HAEIF .
.
2) Warm duplication of the only component in subsystem 1,  and
and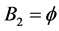 , increases the system availability from
, increases the system availability from 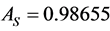 to
to ,
, 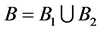 see Table 2. The improved system with
see Table 2. The improved system with  0.99879, can be achieved by performing one of the following:
0.99879, can be achieved by performing one of the following:
a) Reducing the failure rate(s) of (see Table 3): i) the only component in subsystem 1, 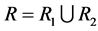 where
where  and
and , by the WAERF
, by the WAERF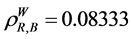 , ii) the only component in subsystem 1 and the first component of subsystem 2,
, ii) the only component in subsystem 1 and the first component of subsystem 2,  ,
,  , by the WAERF
, by the WAERF , iii) the only component in subsystem 1 and the second component of subsystem 2,
, iii) the only component in subsystem 1 and the second component of subsystem 2, 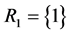 ,
,  , by the WAERF
, by the WAERF , iv) the two components in subsystem 2,
, iv) the two components in subsystem 2,  ,
,  , by the WAERF
, by the WAERF , v) all three components,
, v) all three components,  ,
,  , by the WAERF
, by the WAERF .
.
b) Increasing the repair rate(s) of (see Table 4): i) the only component in subsystem 1,  where
where  and
and , by the WAEIF
, by the WAEIF , ii) the only component in subsystem 1 and first component of subsystem 2,
, ii) the only component in subsystem 1 and first component of subsystem 2,  ,
,  , by the WAEIF
, by the WAEIF , iii) the only component in subsystem 1 and second component of subsystem 2,
, iii) the only component in subsystem 1 and second component of subsystem 2, 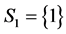 ,
, 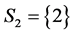 , by the WAEIF
, by the WAEIF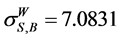 , iv) all three components,
, iv) all three components,  ,
,  , by the WAEIF
, by the WAEIF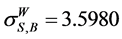 .
.
3) Cold duplication of the only component in subsystem 1,  and
and , increases the system availability from
, increases the system availability from 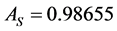 to
to , see Table 2. The improved system with
, see Table 2. The improved system with , can be achieved by performing one of the following:
, can be achieved by performing one of the following:
a) Reducing the failure rate(s) of (see Table 3): i) the only component in subsystem 1,  where
where  and
and  by the CAERF
by the CAERF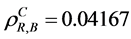 , ii) the only component in subsystem 1 and first component of subsystem 2,
, ii) the only component in subsystem 1 and first component of subsystem 2,  ,
, 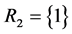 , by the CAERF
, by the CAERF , iii) the only component in subsystem 1 and second component of subsystem 2,
, iii) the only component in subsystem 1 and second component of subsystem 2,  ,
,  , by the CAERF
, by the CAERF , iv) the two components in subsystem 2,
, iv) the two components in subsystem 2, 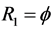 ,
,  , by the CAERF
, by the CAERF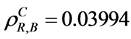 , v) all three components,
, v) all three components,  ,
,  , by the CAERF
, by the CAERF .
.
b) Increasing the repair rate(s) of (see Table 4): i) the only component in subsystem 1,  where
where  and
and 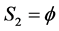 by the CAEIF
by the CAEIF , ii) the only component in subsystem 1 and first component of subsystem 2,
, ii) the only component in subsystem 1 and first component of subsystem 2, 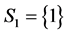 ,
,  , by the CAEIF
, by the CAEIF , iii) the only component in subsystem 1 and second component of subsystem 2,
, iii) the only component in subsystem 1 and second component of subsystem 2,  ,
, 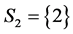 , by the CAEIF
, by the CAEIF , iv) all three components,
, iv) all three components,  ,
,  , by the CAEIF
, by the CAEIF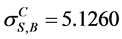 .
.
4) In the same manner, we can illustrate the rest of results shown in Table 3 and Table 4.
5) The notation NA, means that there is no possible equivalence between the two improved systems that can be achieved by reducing (increasing) the failure (repair) rates of the set 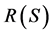 of system components and that can be achieved by duplicating elements of set B of system components.
of system components and that can be achieved by duplicating elements of set B of system components.
6. Conclusions
This paper discusses the availability equivalence factors of a general repairable parallel-series system with independent but non-identical components. The system studied here generalizes several well-known systems such as a repairable parallel-series system with independent and identical components; repairable series and repairable parallel systems with independent and non-identical or identical components. We derived two types of the availability equivalence factors of the system. We presented a numerical example to illustrate how the theoretical results derived in the paper can be applied.
Indeed there are several possible extensions of this work. As an example, the case of a general repairable parallel-series system with non-constant failure rates can be studied.