Temporal Optimality of a Via-Posture on Trajectory during Sit-to-Stand and Back-to-Sit Movements ()
1. Introduction
Rising from a chair, or sit-to-stand (STS), and back-to-sit (BTS) movements are important human movements among the activities of daily living. Because many degrees of freedom of the musculoskeletal system are involved in these motions, it is necessary to master the redundant degrees of freedom to perform a coordinated movement pattern [1] . Optimization hypotheses are important approaches to accounting for motor coordination. The maximum smoothness models, for instance, have succeeded in explaining the pattern of endpoint kinematics [2] and joint movements [3] - [6] in reaching movements.
Recent studies have shown that the optimization approach can be adopted for the movements of other parts of the human body, such as finger movements [7] , gait [8] [9] , STS movement [10] - [12] , and kip movements of a gymnast [13] . For example, Yamasaki et al. [11] demonstrated that the minimum torque-change criterion could predict the joint trajectory as well as the center of mass (COM) trajectory in STS movement after the seat-off (the instance the buttocks leaves the seat), indicating that the joint movements are optimized to yield a coordinated movement pattern in STS. However, whether the prediction of the optimization can explain the pattern of the joint movement before the seat-off in STS and during BTS has not been well examined.
Another unknown about the motor coordination in STS and BTS is the determinant of temporal consistency of the kinematics. For example, Pai and Rogers [14] demonstrated that the timing of peak horizontal velocity of the COM was consistent across movement speeds, and the horizontal momentum of the COM that is generated by the trunk flexion remained constant across different speeds. Dubost et al. [15] also showed that maximum trunk flexion occurs around the middle period during STS, and that its maximum angles in young and elderly subjects were similar. This stereotypically, temporally constrained invariant characteristic of the joint movement during STS suggests that the movement is planned and executed in terms of the optimal sequence of the movement events. The temporal optimality of the kinematic events in STS and BTS has not been fully explained.
The purpose of this study was to examine the hypothesis that the optimal trajectory formation model, especially the minimum jerk and minimum angle-jerk with via-point models, could account for the temporal consistency of kinematics in STS and BTS movements. The minimum angle-jerk model has been regarded as a good approximation of the minimum torque-change criterion [4] [16] . An advantage of the minimum angle-jerk model is the independence of the biomechanical parameters of the musculoskeletal system.
2. Method
2.1. Subjects
Five male subjects (mean age 24.2 ± 6.3 years) without musculoskeletal or neurologic impairments took part in the experiment after giving informed consent. The study protocol was approved by the institutional ethics committee.
2.2. Tasks
The subjects performed the STS task from a standardized sitting posture on a chair in two speed (fast and natural) conditions. They were told to cross their arms in front of their chest throughout the duration of the task. In the natural speed condition, the subjects were asked to stand at a comfortable speed after receiving a signal from the experimenter. In the fast speed condition, the subjects stood as fast as possible. The subjects gazed at a point presented in front of them during the tasks. They were also instructed to stand still at the end of the movement task until receiving another signal from the experimenter. This second signal indicated the start of the BTS movement task at the same speed condition. The height of the seat was set to two different positions, i.e., Low and High positions that yield knee angles at 80 degrees and 50 degrees flexion, respectively. Angle of the ankle joint was 10 degrees dorsiflexion for both positions. All subjects started STS tasks in the Low-natural speed conditions, followed by the fast speed condition. Tasks in the High position were always examined after all the tasks in the Low position were completed. The subjects performed 10 trials in each condition, thus a total of 40 STS trials and 40 BTS trials (2 speed conditions by 2 seat-height positions) were recorded. There was a 3minutes rest period between each test. The subjects were allowed remain seated during the rest.
2.3. Motion capture
The schematic diagram for the motion analysis process was shown in Figure 1. The positions of reflexive markers attached to the bony landmarks were captured using seven VICON MX cameras at a sampling frequency of 200 Hz (Vicon, UK). The markers were taped bilaterally on the acromion, greater trochanter, lateral epicondyle of the femur, lateral malleolus, and the head of the fifth metatarsal. A three-link rigid body model
![]()
Figure 1. Schematic diagram for data analysis.
composed of HAT segment (Head, Arms and Trunk), thigh, and shank in the sagittal plane was assumed to calculate the anatomical joint angle of the hip, knee, and ankle joints and position of the COM of the subject. The angular velocity and acceleration as well as the linear velocity of the COM were also calculated by numerical differentiation. The length and weight of the links for each subject were estimated using the height and weight of each subject [17] . Movement time was determined as the duration when the velocity of the COM exceeded 5% of its peak velocity. For the convenience of data processing, the data length of kinematics was normalized by the movement time (one hundred points). Raw kinematic data were low-pass filtered using a second-order Butterworth filter with a cut-off frequency of 5 Hz [18] .
The ground reaction force (GRF) under the seat was monitored using a Kistler 9287B force plate (Kistler, Switzerland) at a sampling frequency of 1 kHz to determine the moment of seat-off during STS, i.e., when the GRF reduces to zero, and the moment of seat-contact during BTS, i.e., when the GRF increased above two standard deviations of the unloaded period.
2.4. Cost functions and computation of the optimal trajectory
Two criteria were adopted to compute the trajectories. First, the cost function for the minimum jerk trajectory of the COM was determined as
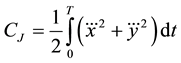 (1)
(1)
where 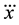 and
and 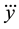 represent the jerk (third derivative) of the COM position in the Cartesian coordinate system,
represent the jerk (third derivative) of the COM position in the Cartesian coordinate system,
and T denotes the movement time. The optimal time sequence of COM positions, 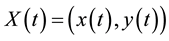 mini-
mini-
mizes the cost function under the boundary conditions 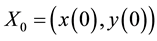 and
and 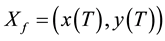 with
with
via-points,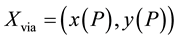 . As described later, timing of a via-point P was selected based on the kine-
. As described later, timing of a via-point P was selected based on the kine-
matic events. Second, the cost function for minimum angle-jerk trajectory of the joints was determined as,
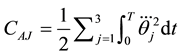 (2)
(2)
where 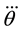 denotes the angle jerk (third derivative of the joint angle), and subscript j indicates the joint number.
denotes the angle jerk (third derivative of the joint angle), and subscript j indicates the joint number.
The optimal angular trajectories, 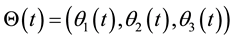 minimizes the cost function under the boun-
minimizes the cost function under the boun-
dary conditions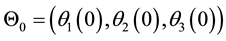 and
and 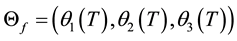 with via-points
with via-points
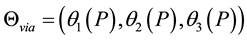 . In this study, the boundary conditions were obtained from measured data aver-
. In this study, the boundary conditions were obtained from measured data aver-
aged for ten trials in each speed condition. The problems were solved as the dynamic optimization with interior -
point equality constraints, as described by Flash and Hogan [2] .
2.5. Selection of the Via-point (Via-posture)
To examine the temporal optimality of the movement kinematics, some position datasets during movement, i.e., via-points, were selected in the computation. Because the via-point is not evident a priori, the candidate positions were selected as the via-points based on the important components of the STS and BTS suggested by previous studies; i.e., hip flexion, and extension and COM movement velocity [19] - [21] . In this study, six candidate positions were identified:
・ Position at peak velocity of the hip flexion (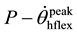 );
);
・ Position at maximum angle of the hip (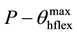 );
);
・ Position at peak velocity of the hip extension (![]() );
);
・ Position at seat-off for STS or seat-contact for BTS (P-seat);
・ Position at peak horizontal velocity of the COM (![]() );
);
・ Position at peak vertical velocity of the COM (![]() ).
).
The optimal time to pass through a via-point or via-posture was determined in the optimization process [2] .
2.6. Quantification of the correspondence
To quantify the correspondence between the optimal COM trajectory and measured COM trajectory, the norm of the difference in each data point was calculated as the residual,
![]() (3)
(3)
where superscript opt denotes the data of the computed optimal trajectory, and superscript meas denotes the data from the measured trajectory averaged over 10 trials. Subscript n means the data number within a total number of m (m = 100). The correspondence between angular kinematics can also be quantified by a similar equation,
![]() (4)
(4)
where j represents joint number. All numerical computations were performed using custom programs of MATLAB (The MathWorks, Inc., USA).
2.7. Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was carried out using SPSS version 17. Differences in the residuals and effects of speed and seat height were tested using analysis of variance (ANOVA) tests. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Movement times
Mean and standard deviation of movement times during STS in the Low condition were 0.98 ± 0.12 (s) and 1.58 ± 0.19 (s) for the fast and natural speed conditions, respectively. For BTS, the movement times for the fast and natural speed conditions were 1.26 ± 0.10 (s) and 1.88 ± 0.40 (s), respectively. Two-way ANOVA (speed, seat height) was performed separately for both task direction (STS or BTS). The main effects of speed were significant for task direction (p < 0.01). The main effects of height and interactions were not significant. These results confirm that the subjects performed the tasks at different speeds according to the instructions.
3.2. Boundary joint angle
To examine the effect of the condition on the initial and final joint angles, two-way ANOVA (speed, seat height) was performed separately for each task direction (STS, BTS) and the joints (ankle, knee, and hip). A significant main effect of seat height was found on the knee and hip joints for both task directions (p < 0.01 for initial and final) but not on the ankle joint for both STS and BTS. The effect of speed was not significant for all joints for both task directions, indicating the boundary joint angles were independent of the speed conditions.
3.3. Timings of the candidate Via-points
As shown in Table 1, the timings of the candidate positions, i.e., the occurrence of measured kinematic features
relative to movement time, are distinguishable for all conditions except for between ![]() (at peak hori-
(at peak hori-
zontal velocity of COM) and ![]() (at peak vertical velocity of COM) in the BTS task. According to
(at peak vertical velocity of COM) in the BTS task. According to
two-way ANOVA (speed and candidate positions), there were significant main effects candidate positions (p < 0.01 for both STS and BTS) on the timing. The main effect of speeds and interaction effect were not significant for the STS and BTS. Bonferroni post-hoc analysis confirmed a significant difference among all six candidate
positions for STS and BTS (p < 0.01) but not for the difference between ![]() and
and ![]() in the BTS.
in the BTS.
Hence, six candidate positions for the STS task and five positions for the BTS task (![]() ,
,![]() ,
,
![]() , P-seat, and
, P-seat, and![]() ) were temporally discriminated as via-points. The
) were temporally discriminated as via-points. The ![]() was unused for
was unused for
the BTS task.
3.4. Temporal consistency
Linear regression analysis revealed that there were highly consistent temporal relationships between the timings of the candidate positions and movement time. Table 2 summarizes the slope and the determinant coefficient of the linear regression lines, showing that the timings of candidate positions are highly dependent on the move-
ment times (![]() ).
).
3.5. Optimal trajectory
Given the candidate positions for via-points, six different optimal trajectories for STS and five optimal angular trajectories for BTS could be computed by the minimum angle-jerk model for each speed and seat-height condition. Figure 2 shows an example of angular profiles and computed optimal trajectories for the Low-fast speed condition for one subject. Selected original points as via-points are indicated by square markers and computed optimal via-points (and its timing) are plotted using circle markers. An optimal via-point computed for the hip
joint at ![]() in STS is clearly different from the original via-point in terms of timing. On the other hand,
in STS is clearly different from the original via-point in terms of timing. On the other hand,
computed optimal via-points at ![]() as well as the optimal trajectories for these via-points in both STS
as well as the optimal trajectories for these via-points in both STS
and BTS are relatively close to the measured ones. In addition to the angular trajectories, optimal trajectories of the COM are also computed for the via-points. Figure 3 shows the time profiles of the COM displacement and
the optimal trajectories computed by the minimum jerk model. The trajectory computed for ![]() (a
(a
via-point at peak velocity of the hip flexion) in STS is found to be close to the measured trajectory for both the horizontal and vertical directions. As for the BTS trajectories shown in Figure 3(b), on the contrary, the computed trajectories for all via-points are not compatible with the measured kinematics.
Figure 4 shows the residuals of difference, or the degree of correspondence between the computed optimal trajectory and measured trajectory in terms of the angular (![]() ) and COM (
) and COM (![]() ) trajectories for all conditions and subjects. On average,
) trajectories for all conditions and subjects. On average, ![]() was small when the optimal trajectories were computed using the via-point at the maximum hip flexion for both STS and BTS. This trend was also true for the residuals evaluated on the COM kinematics (
was small when the optimal trajectories were computed using the via-point at the maximum hip flexion for both STS and BTS. This trend was also true for the residuals evaluated on the COM kinematics (![]() ) except for the BTS. Two-way ANOVA (height and via-points) was performed separately for each direction (STS, BTS) and type of residuals (
) except for the BTS. Two-way ANOVA (height and via-points) was performed separately for each direction (STS, BTS) and type of residuals (![]() ,
,![]() ). As for the
). As for the ![]() in STS, the main effects of the height (p < 0.01), via-point (p < 0.01), and interactions (height * via-points, p < 0.01) were
in STS, the main effects of the height (p < 0.01), via-point (p < 0.01), and interactions (height * via-points, p < 0.01) were
significant. Bonferroni post-hoc analysis found that ![]() at
at ![]() was significantly smaller than
was significantly smaller than ![]() s at
s at
![]() , P-seat,
, P-seat, ![]() , and
, and![]() . Main effects of height (p < 0.01), via-points (p < 0.01), and inte-
. Main effects of height (p < 0.01), via-points (p < 0.01), and inte-
raction (height * via-points, p < 0.01) were also significant for ![]() in STS. Differences among s of
in STS. Differences among s of
![]() , and
, and ![]() were not significant, but these residuals were significantly smaller than the
were not significant, but these residuals were significantly smaller than the ![]() s
s
![]()
Table 1. Relative timing of kinematic events (% of movement time).
![]()
Table 2. Slope (β) and determinant coefficient (R2) of the regression lines of the relative timing of the kinematic event against the movement time.
of ![]() and
and![]() . As for the
. As for the ![]() in BTS, the main effects of the height (p < 0.01), via-
in BTS, the main effects of the height (p < 0.01), via-
point (p < 0.01), and interactions (height * via-points, p < 0.01) were significant. Differences among the ![]() s
s
of P-seat, ![]() , and
, and ![]() were not significant, but the residuals were significantly smaller than
were not significant, but the residuals were significantly smaller than
the residuals at ![]() and
and![]() . The main effects of height was significant (p < 0.01) for
. The main effects of height was significant (p < 0.01) for ![]() in
in
BTS, but post-hoc analysis failed to show significant differences among residuals at the via-points. These results indicate that the optimal angular trajectory computed using the via-points at around the maximum hip flexion fit the measured angular kinematics well.
4. Discussion
The results of the present study showed that the residual of the angular trajectory (![]() ) was smallest when the trajectory was computed using the via-point around the hip flexion posture in the early period of the STS movement, and in the latter period of the BTS movement. The similarity of angular trajectories computed with the via-points will be discussed in terms of the functional significance of the via-point and temporal optimality of the points.
) was smallest when the trajectory was computed using the via-point around the hip flexion posture in the early period of the STS movement, and in the latter period of the BTS movement. The similarity of angular trajectories computed with the via-points will be discussed in terms of the functional significance of the via-point and temporal optimality of the points.
The present results on coincidence of the optimal joint trajectory with the measured trajectory may shed light on the functional significance of the hip flexion posture before the seat-off in STS. Considering these results and those of previous studies [11] [12] , the hip flexion posture before the seat-off, which is an important boundary of the optimal angular trajectory formation, may be related to dynamic balance during the movement. Indeed, it is hypothesized that the subjects placed more importance on achieving postural stability at the seat-off [22] [23] . Though there have been differences in the operational definition of the instance of seat-off, as noted by Etnyre and Thomas [24] , the present study proposes the via-posture hypothesis in which the optimal trajectory is
planned to pass through the dynamic hip flexion posture at around the seat-off for STS.
It should be noted that the optimal time to pass through the via-posture, i.e., optimal via-time, is determined in the optimization procedure. Matsui et al. [25] proposed an optimal control model that reproduces movements of humans when rising from a chair. Their model switches its dynamics equation at the time when the body moves away from the chair, which is close to the instance of maximum hip flexion. The present study supports the idea that the coordinated STS movement would be generated with a set of temporal information of the via-posture before the seat-off.
The via-posture hypothesis also accounts for the temporal consistency of the BTS kinematics. The residuals on the COM trajectory (![]() ) were relatively larger than the residuals on the angular trajectory (
) were relatively larger than the residuals on the angular trajectory (![]() ) for BTS. Therefore, the optimality of the COM trajectory could not be explained by the minimum jerk trajectories computed with the via-point at any candidate positions during the movement. As opposed to the COM control notion of the rising movement [26] - [28] , the present study suggests that the angular movement of the joints is controlled during the BTS movement as well as the STS movement. In fact, it is shown that both movements have a common critical posture, i.e., the via-posture around the maximum flexion angle of the hip joint, corresponding to the via-point of the optimal trajectory.
) for BTS. Therefore, the optimality of the COM trajectory could not be explained by the minimum jerk trajectories computed with the via-point at any candidate positions during the movement. As opposed to the COM control notion of the rising movement [26] - [28] , the present study suggests that the angular movement of the joints is controlled during the BTS movement as well as the STS movement. In fact, it is shown that both movements have a common critical posture, i.e., the via-posture around the maximum flexion angle of the hip joint, corresponding to the via-point of the optimal trajectory.
As noted above, the via-posture may provide the subject with dynamic balance during the movements. Dubost et al. [15] showed decreased trunk flexion in elderly subjects during BTS, and they suggest it may be an adaptive strategy to minimize the forward body displacement and thus decrease the risk of anterior disequilibrium. Their results support the idea that the hip flexion posture at around the seat-contact may represent dynamic via-posture during movements. The present study expanded the previous understanding on the functional optimality of the hip flexion movement in BTS. It might also be optimal in terms of timing as the via-posture for the minimum angle-jerk trajectory.
5. Conclusion
The present study showed that coordinated angular trajectories of the joints during STS and BTS movements were well reproduced by the minimum angle-jerk criterion with via-point, namely the via-posture around the hip flexion in the early period of the STS movement, and in the latter period of the BTS movement. The result indicates that the pattern of STS and BTS movements is organized in terms of smoothness of the joint rotations with a via-posture. The present study revealed the significance of temporal invariance found in the pattern of STS and BTS by the posture-based optimization model.
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by a grant from Showa University. The author is grateful to Dr. Satoshi Nishizawa for helpful comments and discussions on the original manuscript.