1. Introduction
During the time of deglaciation, when the glacial isostatic uplift peaked at rates in the order of tens of cm per year, Sweden was a high-seismic region [1] -[3] . Even in the Late Holocene, there are several high-magnitude events recorded [3] -[5] . The latest high-magnitude event recorded is an event occurring around 900 BP [2] [4] . It faulted the Viking shoreline in SW Sweden and probably set up a tsunami wave that destroyed two Viking ships in the ancient harbour of Galtabäck. A C14-date of the ship gave 1172 ± 73 cal.yrs AD [6] , which is quite close to a major historical event at 1174 as recorded in the chronicles [7] .
Therefore, it may not be so strange that we are now able to present evidence of a major earthquake in SE Sweden [8] , which can be tied into the Late Bronze Age cultural history of the area [9] [10] .
Furthermore, there was a quite strong earthquake on December 16, 2008, in SE Sweden with a magnitude of 4.3, felt over an area of a radius of at least 200 km and with occasional fracturing of churches and other buildings in the vicinity of about 30 km.
2. Investigation Area
The present seismotectonic study refers to SE Sweden, an area often named “Österlän”. Figure 1 gives the geographic setting of the main sites discussed, and where the focus is on Brantevik where the prime evidence of an earthquake was first discovered [8] .
The geological setting will be discussed below in connection with the tectonics studies. The old fault patter is dominated by NW-SE and SW-NE trending faults.
3. Holocene Sea Level Changes
The sea level changes in the Brantevik area are presented in Figure 2 (cf. my precious curves for the Kivik-Vitemölle area and the Kåseberga area in [11] ). Holocene sea level peaked at +2.2 m 4600 cal.yrs BC and at +2.1 m at 1000-800 cal.yrs BC [12] . The last level constitutes an important marker level along the coasts and provides a reference level for the sea level in the Late Bronze Age of Österlän [9] .
4. Description
The main area is in the Brantevik-Järrstad-Simrishamn area with additional sites at Kåseberga 30 km to the SSW and at Lillehem 40 km to the NNW (Figure 1). The paleoseismic event has been discussed in a preliminary report [8] , like its relation to the Late Bronze Age archaeological development of the region [9] [10] . Additional fieldwork was undertaken in 2013 and 2014.
4.1. Branteträsk
Branteträsk is the key site [8] [9] . It was found in 2012. The site consists of a swampy depression and surrounding flat ground, which on the western side was found to consist of a bedrock of quartzite, strongly fractured in to big blocks (Figure 3). Furthermore, one block had been laid up in inclined position and this was obviously a human act. The swamp was cored at 21 points. In general, the bedrock surface of the basin is covered by half a metre of alder peat, suggesting that the swamp filling is of Late Holocene age. The idea that we might be dealing with an ancient quarry emerged [9] .
The fractured quartzite bedrock surface was cleaned over a large area. The quartzite surface is ice scoured and strongly weathered from postglacial exposure. The fracture surfaces on the other hand are fresh and have very

Figure 1. Geographical location of the main sites discussed.

Figure 2. Sea level changes at Brantevik during the last 5000 years [12] .

Figure 3. Branteträsk is a swampy, partly water filled, depression. To the northwest it is bounded by a heavily fractured bedrock of quartzite, partly broken up in big blocks by multi-directional extensional forces indicative of seismic deformation. Later, the blocks and the depression were utilized as quarry of monoliths for Ales Stones and flat blocks for the Late Bronze Ages graves at Brantevik. Yellow dot marks place of block laid up in inclined position. Red line and dots mark main coring section and sites.
sharp fracture edges. Figure 4 gives a typical picture of the sharp, open fractures. Obviously, we are dealing with a 3 dimensional extensional opening. This can only have been produced by a major earthquake.
A total of 70 fractures were measured: 33 in 355˚ ± 14˚, 19 in 283˚ ± 13˚, 12 in 57˚ ± 15˚, 4 in 324˚ ± 12˚ and 2 in 21˚ ± 3˚, which is quite different directions as those of the main old tectonic pattern.
The lithology of the quartzite is almost identical to that of the bow and stern stones in the Ales Stones megalithic monument some 30 km to the SW, suggesting that they were indeed collected in the Branteträsk quarry about 750 BC and transported by raft to the shore below the place of erection of the monument [9] .
At Brantevik, there previously was a huge grave from the Bronze Age known as “Brantarör” [13] . It is now gone, but we have a detailed drawing of it from 1777 showing a grave surrounded by, at least, 60 flat blocks and with a central sarcophagus of 14 large and flat block. All those blocks must consist of layered quartzite quarried in the vicinity, i.e. in Branteträsk. The grave contained some bronze tools and an urn, which by E. Jonson [13] was assigned an age of 800-500 BC. This fits perfectly well with an age of quarrying at Branteträsk of 800-700 BC [8] -[10] .
Only one core (7 in Figure 3) penetrated sediments going all the way back to the time of deglaciation (Figure 5). In this core there was a thin layer of angular pieces of fractured quartzite, which is likely to represent spall from a stone “industry” in the Bronze Age or Neolithic. The intension is to obtain a new core and sample the sediments just above and below the “spall horizon” for radiocarbon dating.

Figure 4. The fractured bedrock of Cambrian quartzite. The fracture surfaces are fresh and the fracture edges are knife-sharp. The bedrock surface, on the other hand, is strongly weathered with marks from glacial scouring. The main deformational force is extensional, indicating a seismic origin. A secondary deformation is recorded in the removal of blocks (top image) and lying-up of a big block in inclined position (in the back-ground of the top image), which can only have been achieved by man, transforming the site into a quarry.
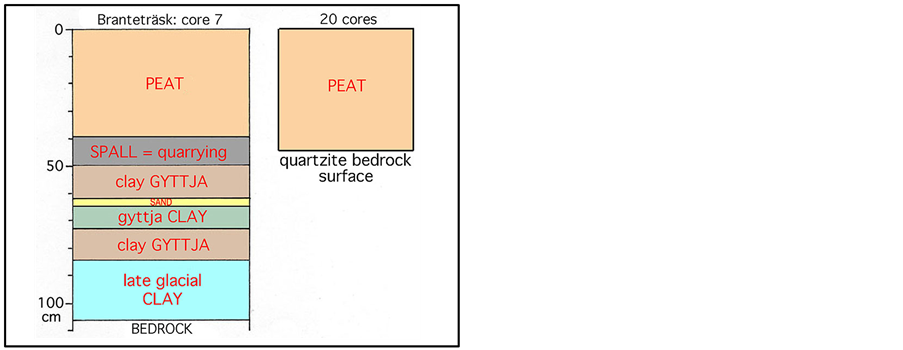
Figure 5. Core 7 penetrating the entire postglacial period after the deglaciation some 15,000 years ago and exhibiting a “spall horizon” of sharp quartzite fragments interpreted as a record of the quarrying in Late Bronze Age time. In all the other 20 cores, the quartzite surface is hit at a depth of about 0.5 m (equaling the depth of quarrying).
4.2. The Rocky Shores at Brantevik
The present coast around Brantevik is rocky consisting of lower Cambrian quartzite, known as “Hardeberga sandstone”. The bedrock is traversed by major open fractures in 72˚ - 76˚ and secondary fractures in 28˚ successively moving over into 326˚.
At the resting place just off the site of rock carving “Simris 19”, 2 km north of Brantevik, the fractures can be observed at a level not reached by the waves today, but well reached by the waves at the +2.1 m high-stand at about 1000-800 BC (Figure 2). The fractures are well washed and abraded by sea waves (Figure 6), in total contrast to the fractures at Branteträsk. This indicates that the fractures were formed at the latest part of the sea level high-stand, i.e. some 800-750 BC (and clearly before the rapid regression 700-650 BC).
This was also observed just south of Brantevik: the fractures are affected by the abrasion of sea waves up to the level of the waves of the high-stand at +2.1 m (Figure 2). Consequently, the fractures must be older than or time equivalent to this high-stand. This is in full agreement with an age of the earthquake in the order of 800- 750 BC.
4.3. Järrestad Rock Carving
Just north of Järrestad, a flat quartzite bedrock surfaces is exposed. It is covered by over 100 rock-carvings from the Bronze Age [9] [14] [15] . Already in 2003, I had noted that several pictures were traversed by fractures suggesting a post-carving paleoseismic fracturing [2] . Resumed investigations indicated that there must have been a seismic event of rock fracturing post-dating the carving [8] -[10] .
This post-rock-carving fracturing was documented at 6 additional sites of rock-carvings (petroglyphs) from the Bronze Age in the Simrishamn-Brantevik-Järrestad region (Figure 7), spanning an area of about 5 × 5 km [8] .
The surface of the quartzite bedrock is very smoothly polished by the glacial flow, and it contains excellent glacial striae and crescent-marks indicative of a main ice flow from the NE (measured value: 51˚ ± 3˚). The surface is traversed by a few large and open fractures in 34˚ and 316˚, and numerous minor fractures; viz. 63 in 290˚ ± 4˚ and 19 in 15˚ ± 8˚ (Figure 8).
Both glacial striae and crescent-marks are often cut by fractures indicating at least one phase of postglacial fracturing ([2] p. 267). Resumed investigations of the rock-carvings [15] indicated that several of the petroglyphs must have been affected by a late phase of post-rock-carving fracturing [8] . This is illustrated in Figure 9, Figure 10.
Consequently, there are good observational reasons documented in Järrestad and six additional sites for an

Figure 6. The abraded fractures just above the +2.1 m sea level highstand at 1000-800 BC (Figure 2) exposed at the resting place opposite the rock carving site “Simris 19” (compare with the very sharp-edged fractures in Figure 4).

Figure 7. Fractured rock-carvings (yellow dots) and sites of bedrock fracturing analyses (blue dots [8] -[10] ).
episode of general bedrock fracturing within an area of 5 × 5 km (Figure 7) occurring in the Late Bronze Age [8] -[10] . This, by itself, is indicative of an earthquake of an intensity of VIII [16] .
4.4. The Glimminge Hallar Area
Glimminge hallar area constitutes the eastern part of a local granite horst (Figure 11).
The northwestern side of the granite horst is full of structures indicating deformations in postglacial time. Two examples are given in Figure 12: open fractures of extension in the SW-NE direction with blocks tumbled down on the present land surface.

Figure 8. The smoothly glacial polished quartzite surface of the Järrestad rockcarvings, traversed by a few open fractures in 34˚ (central horizontal) and 316˚ (slightly winding from left top to bottom), and numerous parallel minor fractures in 290˚, traversed by a nearly perpendicular system in 15˚, which often cut across the pictures.

Figure 9. Postglacial fracturing of crescent-marks at site Simris 19 (A) and a post-carving fracturing of a foot picture from the Bronze Age at Järrestad (B).

Figure 10. Post-carving fracturing of petroglyphs at Järrestad [8] [11] [15] . (A) a pair of “shoes” cut by post-carving fractures. (B) the “sun-ship” severely fractures by post-carving fractures.

Figure 11. The area is a fault-bounded local granite horst of irregular (somewhat unclear) shape. Postglacially deformed bedrock occurs at sites 1 and 2. Site 3 is a small quarry of strongly fractured bedrock. Site 4 is a rock-carving traversed by minor fracture. Site 5 refers to a monolith (“Trollastenen”) of quartzite most probably originating from Branteträsk.

Figure 12. Fractured bedrock at site 1 due to a main extensional force in SW-NE direction. The picture to the right also indicates an anti-gravitational upward displacement. The deformation is clearly of postglacial age. Blocks tumbled out to the NW (right hand image) rest on the present land surface suggesting that the displacement might be of Late Holocene age.
Signs of postglacial deformation are present also on the eastern side of the horst. At site 2, there is a heavily fractured scarp (Figure 13, left) from where blocks have moved eastwards at a low angle in a loose higgledy-piggledy way suggesting a young age of deformation. Just outside there is a lake (Figure 13, right) where sediment coring was performed. Three cores were pushed down. All stopped at about 90 cm due to hard ground (probably bedrock). Beneath a 60 cm layer of coarse silt/fine sand, there is 30 cm of peat, the uppermost and lowermost 1 cm of which is under radiocarbon dating.
With the addition of the Glimminge hallar sites, the size and mode of bedrock deformation (Figure 7) may now be estimated at an earthquake of intensity IX [16] .
4.5. The Kåseberga Shore Sections
Figure 15 gives the setting of the 67 m long stone ship monument of Ales Stones [17] and the 4 sites here discussed (1 - 4) with the sections at the shore (1) in focus [9] [10] [17] .
The shore section was found in 2009 and described in [11] . In 2011, it was subjected to an excavation, GPR-studies, coring and radiocarbon dating [9] [18] . With the finding of the earthquake at Branteträsk [8] there were new reasons to revisit the site.
Right above the beach cobble of a sea level high-stand dated at around 1000-800 BC, there is a black layer of humus and charcoal, which was C14-dated at 785 ± 20 cal.yrs BC [12] . The organic layer is covered by sand, assumed to represent the eolian sand drift from around 500 BC, and later slid material.

Figure 13. Site 2 (the Glimmingehallar proper) with a strongly deformed bedrock hill of granite (left) and a lake outside (right). Yellow arrows give the view direction of the photographs; 1: Figure 13, left, 2: Figure 14, left and 3: Figure 14, right. Obviously the entire hill was strongly shattered and deformed with blocks sliding off in eastward and northward directions. A Late Holocene age of deformation is indicated. The final answer will come from the two C14-dates under measurement.

Figure 14. Left: the scarp seen from the north with a major open fracture (view 2). Right: the sliding-off of blocks on the northern side (as seen from view 3). The blocks are very sharp-edged and rest loosely on the present ground surface suggesting a Late Holocene age of deformation.

Figure 15. The Kåseberga area with the Ales Stone monument from the Late Bronze Age and four sites analyzed [9] [18] . 1: the main shore section, 2: liquefied and tectonized sediments, 3: excavation pit D with the cast of one of the stones in the monument, and 4: excavation pit F with some liquefaction-like structures.
At the 2011 excavation [18] it was observed that there at the base of the sand unit occurred some well-washed boulders, suggesting a possible sea level inundation. The study was followed up by six C14-datings [9] . A new date of the organic layer gave 775 ± 35 cal.yrs BC (i.e. almost identical to the previous date). Charcoal from a hearth in the sand layer was dated at 385 ± 35 BC (layer 5 in Figure 16).
After additional work in the section in 2013, it is now possible to identify the layer right above the organic bed as a layer of liquefied, tectonized and down-slid material; i.e. it is classified as a “seismite” (Figure 16).
The stratigraphy of Figure 16 includes the following layers cf. [9] .
7: base of a Viking Age midden [18] dated at 950 ± 50 AD.
6: eolian sand 2 with a strong humus soil of the Late Iron Age.
5: hearth with charcoal dated 385 ± 35 cal.yrs BC.
4: eolian sand 1 representing the general sand drift phase at 500-600 BC.
3: tectonized layer (i.e. a seismite) including down-slid boulders and a reworked bone dated at 1195 ± 85 cal.yrs BC (cf. Figure 18).
2: organic layer rich in charcoal dated 785 ± 20 and 775 ± 35 cal.yrs BC, further inland this land horizon is dated at 1285 ± 65 cal.yrs BC (Figure 18).
1: beach shingle representing the high-stand 1000-800 BC (cf. Figure 2).
Figure 18 provides a condensed section perpendicular to the shore. The layer 3 seismite is marked in brown. It consists of a liquefied basal bed with boulders in its upper part (Figure 17) that must have slid down from the nearby scarp. It also includes reworked material (Figure 18).
Close to the west (site 2 in Figure 15), there is a section of about 18 m of late glacial deposits. In the upper part, the sand and silt is tectonized, micro-faulted and liquefied (Figure 19). Earlier, it was assumed that this deformation was of late glacial age. Now, it seems reasonable to connect it with the earthquake deformation and seismites in the close-by shore section (30 m apart).
4.6. The Lillehem Sediment Deformations
In a road junction at Lillehem, there is a minor gravel pit. After cleaning, an interesting stratigraphy was exposed including an old ice wedge cast filled with organic material, humus and at the base a bed of precipitated carbonate (Figure 20 top). Laterally, the stratigraphy recorded tectonization and liquefaction (Figure 20 bottom).

Figure 16. Stratigraphy in the shore section at Kåseberga. Layer 3 (including the boulders) represents a tectonized horizon of liquefied material (flamed organic structures) and down-slid boulders (Figure 17). The event should have taken place shortly after the dates obtained from layer 2 (i.e. 775 ± 35 and 785 ± 20 cal.yrs. BC), and is here proposed to be a correlative to the earthquake fracturing recorded at Branteträsk. The erection of the Ales Stones monument is likely to have occurred shortly after; i.e. at around 750 BC.
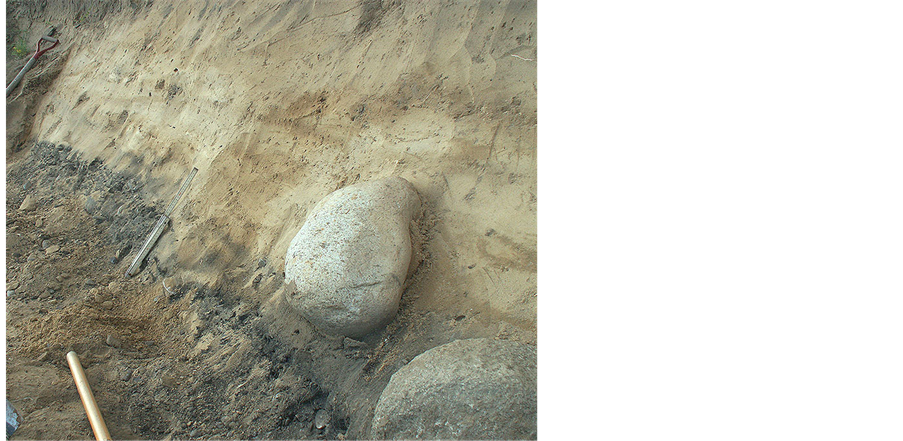

Figure 17. The black land surface (layer 2 in Figure 16) is covered by an irregular, partly liquefied, layer of humic sand (layer 3), in which the blocks rest. This layer contains reworked material (Figure 18) and constitutes a seismite of shaken and slid material.

Figure 18. Shore section cf. [18] with C14-dates in cal.yrs BC (red). The brown layer is a seismite of deformed (liquefied) sediments and slide material including reworked objects of mixed ages (bone 1195, land snail 2324 and a shell fragment 9638 BC).
The development of a strong humus soil in the ice wedge cast and the precipitation below of carbonate need a lot of time. This is consistent with the age obtained of the horizontal carbonate layer C14-dated at 4503 ± 43 cal.yrs BC.
The left side of the section is heavily tectonized with progressive down faulting (lower image). The tectonized beds include fragments of the carbonate bed dated at 4503 BC. Consequently, the tectonization must post-date this age.
The general down faulting in the order of 0.5 m is indicative of a significant liquefaction in the subsurface. All this suggests the effects from a major earthquake in Late Holocene time. It seems reasonable that this earthquake event is the same as the one identified in Branteträsk and Kåseberga.
5. Discussion
Multiple indications of a Late Holocene earthquake event have been presented above, and will now be considered together as to location, magnitude and age. In the first preliminary report, a magnitude of “M > 6” and an


Figure 19. Liquefied (above) and micro-faulted (below) deposits in the upper part of site 2 that may lead its origin from the same earthquake as that of the seismites in the shore section.
age “around 1000 BC” or “in the period 1000-800 BC” were proposed [8] [9] .
5.1. Fracture Pattern
The Glimminga hallar site (Section 2.4) documents extensional fracturing to the NE and the E, i.e. in directions off the granite horst.
The bedrock fracturing at Branteträsk follows a clear 3-dimentional extension. The main direction is perpendicular to the main fracture direction 355˚ - 175˚. This implies that the long axis of the strain ellipsoid must be in 265˚ - 85˚. The short axis should be perpendicular to this. The vector of the two additional fracture directions is 350˚ - 170˚, which is only 5˚ off the perpendicular direction of the long axis. If the long axis is extended westwards, it passes the granite horst (Figure 21).
At Järrestad, 63 fractures were measured in 290˚ and 19 in 14˚. It is this fracture system, which has fractured the petroglyphs (Figure 9, Figure 10). The corresponding strain ellipsoid would have had its long axis in 20˚ - 200˚ and its short axis in 110˚ - 290˚ (with a recorded value 104˚ - 284˚). If the long axis is extended southwards, is passes right west of the granite horst (Figure 21). The surface is also traversed by a few large and open fractures (Figure 8). The vector of these two directions is 356˚ - 176˚, which is not too far off the long axis of the strain ellipsoid. A southward extension of 176˚ passes just east of the granite horst.
The combined record (Figure 21) suggests that the granite horst might be the common point of ground motions; i.e. the epicenter of the earthquake and the point of primary faulting.
The tectonic map of the area [19] records the old, primarily Paleozoic and Mesozoic fault pattern. The granite horst sticks our as a special structure; a separate granite block within an elongated NW-SE fault block (Figure 21). Figure 22 gives a SW-NE profile across the granite horst.
5.2. Estimates of Intensity and Magnitude
The estimate of intensity and magnitude depends on the character of deformational structures and the spatial distribution of observations e.g. [16] .
Bedrock fractures in the order of centimeters to a decimeter suggest an intensity of about IX (on the IES scale; [16] ). The liquefaction structures at Lillehem may suggest an intensity of VII-VIII (maybe even IX).

Figure 20. Stratigraphy at Lillehem. There are minor structures of liquefaction in the main section. The left side is heavily tectonized (lower image) with down-faulting indicating the loss of some 0.5 m of space below, which can only be achieved by liquefaction and venting of liquefied sand. This event must post-date the 4503 ± 43 cal.yrs BC.
The accumulated extension of the 33 fractures at Branteträsk is 123 cm in 265˚ - 85˚ direction, and the opening along the two other directions is 48 and 47 cm. This seems rather to suggest an intensity of about X (or at least IX-X). At Järrestad 63 fractures were measures. Their width ranges form millimeters up to a centimeter at the most. This gives a total accumulated extension in the order of a decimeter. The spatial distribution (5 km from Järrestad and 4 km from Branteträsk to the granite horst) suggests an intensity of VIII-IX.
The spatial distribution of liquefactions provides a better mean of estimating intensity and magnitude. Lillehem lies 32 km north of the granite horst at Glimminge, and Kåseberga lies 20 km south of it. Applying the magnitude/spatial distance distribution relation (e.g. [2] , p. 39, Fig. 5), 32 km corresponds to M 6.3 - 6.8 and 20 km to M 6.0 - 6.4. Therefore, it seems likely that the magnitude of this earthquake had a magnitude in the order of 6.3 - 6.8 judging from the sites available.
5.3. Age of Event
The fracturing of the petroglyphs at Järrestad and six additional sites (Figure 7) indicated that the earthquake

Figure 21. The site 4 bedrock deformations indicate extension from the centre of the granite horst (light brown). The long axes of the strain ellipsoids at Branteträsk (1) and Järrestad (3) are also directed towards the granite horst. This suggests that the earthquake may have been located to vertical movements of this horst.
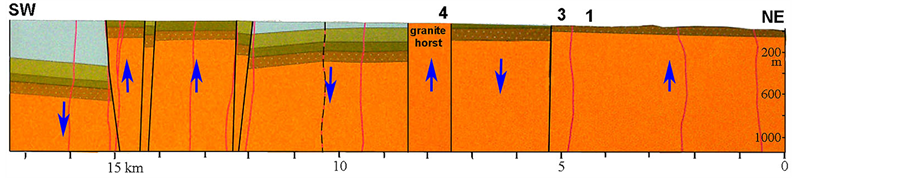
Figure 22. Cross-section over the granite horst with the positions of the Glimmingehallar site (4), Järrestad (3) and Branteträsk (1). It seems likely that the earthquake recorded might have had its epicenter located to vertical movements of the old horst block of granite.
must be younger than the Mid Bronze Age; i.e. younger than 1000 BC. The peat cover of the fractured (and quarried) quartzite bedrock at Branteträsk indicates quite some time back in the Late Holocene. The Brantarör grave seems to incorporate numerous blocks quarried at Branteträsk. Because the grave included bronze tools and an urn dated at 800-500 BC, the quarrying post-dating the earthquake fracturing is likely to have occurred in the Late Bronze Age at around 700 BC. Finally, if the quartzite megaliths were shipped out by boat or raft from Brantevik to Kåseberga, the natural harbor only existed at the sea level high stand 1000-800 BC up to about 750 BC (Figure 2; [12] ). The Brantarör grave had a location in direct association with the natural harbor [12] implying that it is likely to have been built before 700 BC and maybe around 750 BC.
At Kåseberga, charcoals just below the tectonized horizon are dated at 780 BC. Taking into consideration that the wood burned into charcoal must have some age, we may set the actual burning at abound 800 BC. The subsequent earthquake must have happened shortly after or at about 780-750 BC.
The earthquake deformation at Lillehem is dated as younger than 4500 BC. An age of 750 BC seems quite reasonable from the stratigraphic evolution. Besides, we have no reasons to infer a second seismic event for this deformation.
In conclusion, the age equation seems to provide a quite sharp age determination at around 780-750 BC.
5.4. Late Holocene Paleoseismicity
At the time of deglaciation, Sweden was a high-seismic area as a function of the very high rates of isostatic uplift [1] -[3] [5] . Even during the last 5000 years, when the isostatic uplift was not significantly higher than today, earthquakes much stronger than those of today were recorded [2] [4] [5] .
The Late Holocene records from NW Skåne may be of particular interest in comparison with the present record. A number of events of magnitudes well above M6 and maybe even reaching M7 were reported [2] [4] [20] . The strength of the documentation is that multiple criteria are applied for a congruent picture. So for example shoreline faulting, rock fracturing, rock avalanches, liquefaction and earth slides were shown to have occurred simultaneously at about 4800 C14-yrs BP. The youngest event recorded occurred at about 900 BP, maybe in 1174 (see above, section 1), with the documentation of a 1.1 m shoreline faulting, rock avalanches and possibly also a tsunami dated AD 1172 ± 73 yrs.
Because the instrumental seismic records do not exceed M 4.3 (for example the Dec. 16, 2008 event with epicenter 60 km west of the horst area here discussed), the seismological community has great difficulties in accepting any earthquake in the Late Holocene reaching M6 or above e.g. [21] . Coincidence in time between different events occurring at different sites or outcrops in nature is, for a geologist, a strong indication of a mutual driving force, whilst it, for a seismologist, might be just a matter of statistical coincidence. It is quite interesting that Gregersen and Voss [21] concluded: “one is left with a choice in the evaluation between coincidences or common cause: earthquake. The field trip convinced the participating seismologists that the claimed signs of earthquakes must be seriously taken into account”.
6. Conclusions
The present paleoseismic event is recorded by different geological and archaeological means (bedrock fracturing at 13 sites, fracturing of rock-carvings at 7 sites, liquefaction at two sites 43 km apart, and dating by radiocarbon, archaeology, sea level history, etc).
Analyses of measured fracture pattern suggest that the epicentre of earthquake is to be searched for in vertical movements of the local granite horst at Glimminge hallar.
The seismic intensity (on the IES scale) is likely to have been in the order of VIII-IX. The magnitude is estimated at M 6.3 - 6.8.
The age can be fairly well established at 780-750 BC. The following quarrying episode at Branteträsk must be older than 700 BC, and probably around 750-730 BC.
This investigation documents a new Late Holocene earthquake with a magnitude significantly higher than those with the maximum magnitudes recorded by seismological instruments. Hence it should affect our hazard assessment [5] .