A Pedagogical Agent as an Interface of an Intelligent Tutoring System to Assist Collaborative Learning ()
1. Introduction
Expert systems are a branch of applied artificial intelligence; the basic idea is to automate software through a certain cognitive processes related to decision making in. In this area there is one sub-area that refers to intelligent tutoring systems (ITS); have the facility to emulate human tutors with the aim of establishing what to teach, how to teach, when to interrupt and what advice to give, given in a certain cognitive state (Mora-Torres, Laureano-Cruces, & Velasco-Santos, 2011) by carrying out an assessment and a diagnosis on the basis of the components of ITSs and a graph of instructional targets. To get it, teaching material of instructional model is organized within it. Last is organized according to the instructional targets that must be covered in order to be able to teach the subject. This module interacts directly with the tutor model and is fed with data compiled trough the student module. Following is a brief explanation. For further information, please consult Laureano-Cruces & de Arriaga (2000) and Laureano-Cruces (2000).
The history and development of ITS may be summarized in two periods: the first corresponds to the foundation and crystallization of the technology. The second reflects advances and improvements in their constitutive elements (Laureano-Cruces & de Arriaga, 2000).
Conventional ITS, are based on a traditional or conventional architecture, formed by specific modules:
Domain or expert module: refers to the knowledge to be taught; student module: made up of two components: 1) the database that represents student behavior during the tutorial process, and 2) the diagnosis process that manipulates the database; tutorial module: has the facility to define the cognitive state of students during performance of the task to be assessed. This module, together with the student module and the expert, defines the interactions of what, how and when to show a certain concept or skill, or correct and advise (Laureano-Cruces, Mora-Torres, Ramirez-Rodríguez, & Gamboa-Rodríguez, 2010); user interface: provides an efficient user-ITS interaction facility. It also plays a teaching role (knowledge of how to present contents). In this case, the interface can be a pedagogical agent (Laureano-Cruces, Velasco-Santos, Mora-Torres, & Acevedo-Moreno, 2009; Velasco-Santos, Laureano-Cruces, Mora-Torres, & Herrera-Bautista, 2010).
The article is organized in this way: Section 2 explains the characteristics of different ITSs, taking into account aspects of the use of AI in education. Section 3 explains our proposal in terms of the collaborative aspects in the teaching learning process, and considers a pedagogical agent like interface. Section 4 explains the necessary characteristics of a collaborative teaching learning process. Section 5 describes the design of a pedagogical agent and the activities that it most considers, taking into account the characteristics described in Section 4. Finally we reach to the conclusions in Section 6.
2. Innovative Intelligent Tutoring Systems
We can detect some characteristics that result in different innovations. Subsections describe some of these. Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques are usually applied in one or two of the following domains: the system knowledge of the subjectand/or the tutorial process and its methods. The most classical ITSs are: SOPHIE I and II (Brown, Burton, & de Kleer, 1982), and GUIDON (Clancy, 1982).
2.1. Help and Advice Systems
Although the functionality of help and advice systems is similar to that of traditional ITS, they go further in the competence of these systems. They are first brought up as a friendly interface between the user and a system or product unknown to the user. The interface allows the connection or the communication with the system as well as the obtainment of different services, ranging from a simple consultation to getting written documents, to a guide of possible dialogues. Typical examples are: EXPLORA, it is an interface that offers adaptive support first at the level of navigation and then at the level of advice. It was designed to facilitate navigation in graph structures and documents in a virtual learning center. EXPLORA is generic and it may easily be adapted to represent the organization of tools, activities, concepts, or documents (Dufresne, Cosmova, Letran, & Ramstein, 1999).
2.2. Specific Tutorial Strategies Modeling
The need for specializing ITS in different subjects has encouraged the authors to include not only general tutorial strategies but also additional strategies and tactics, more closely related to the learning domain. A significant number of tutors have been developed which concentrate mostly on subjects such as science and computer science, among them we can describe: 1) the systems developed by Ferrero, Fernández, & Urretavizcaya (2000) at Basque Country University—SPAIN, this ITS focuses on the process of error diagnosis. Trying to obtain an exact diagnosis using error libraries imply a deep knowledge representation and a close relationship with the domain. It utilizes a model-tracing approach where exists of expert resolution models obtained from experts. In this case the tools are provided with a graphical user interface that helps in the collection of procedures and problems. The last set includes the problem resolution model that will used to diagnose the student problem in the solving activity, 2) statistics is another difficult subject to learn, in this case Finich, Cumming, & Les (1999) work with multiple representations in an ITS called StatPlay than can help. The intuition about fundamental concepts is often inaccurate: the natural language expression of statistical concepts is often inaccurate, there must to be an interface between the concepts and the real world that fails in the application and the interpretation. So StatPlay, provides striking, multiple dynamically-linked representations of statistical concepts and allow the user to explore different representation of a concept, and relations between representations of different concepts.
2.3. Student Modeling
Among the systems in this group we can find Pact Geometry tutor (Aleven, Koedinger, & Cross, 1999) requires to students explains their solutions. They develop a cognitive model, which captures the skills of an ideal student. It is expressed as a set of production rules. The tutor uses this model to assess the student’s solution steps and to provide feedback and hints (through model tracing). In this case the cognitive model is the basis for the student modeling, with this it maintains an estimate of the probability that the student masters each skill in the model. With this information the tutor uses the student model to utilize remedial problems targeting skills for which the student has not yet reached master, and also decide when the student may move to another section.
2.4. Pedagogical Agents
Educational technology are increasingly interested in the potential of the creation and use of this kind of interfaces with animated life, like persons or teachers. Last due that the interaction could make the learning more realistic. These agents express attitudes and moods, demonstrate the skills being learned, very important use nonverbal cues to help focus the learner’s attention (Mora-Torres, Laureano-Cruces, & Velasco-Santos, 2011). They can personify agents with a variety of possible roles in ITS, that can include: tutors, guides, peers, and team members. Like example of a pedagogical agent, is described Adele (Shaw, Ganeshan, & Johnson, 1999) who guides and assesses students as they work through clinical cases. The pedagogical agent consists of two components the animated person and the inference engine. The last one performs all monitoring and decision-making. Adele’s decisions are based on the case task plan and an initial state that are downloading from a repository when a case is chosen. The agent current mental state and the student model are also including. Adele monitors the student’s action and provides feedback. Depending of the instructional goals it can remark aspects of the case, suggests, corrects actions, provides hints and builds links for particular actions, makes reference to relevant background material, and provides contextual assessment.
2.5. Intelligent Agents
By the other side there are the intelligent agents that are a computer program that helps a user with routine computer task. Some of the applications implemented by intelligent agents are tutoring systems. According to Kearsley (mentioned in Les, Cumming, & Finch, 1999) agents could be used in education in different ways: 1) act as coaches or advisors giving individually-tailored explanations (Laureano-Cruces & de Arriaga, 2000; Laureano-Cruces, 2000), 2) different agents have different personalities and so offer different perspectives, 3) agents assist with navigation and other tasks incidental to the learning goals, 4) build agents into a programming environment so that students can create them directly (this a constructivist idea that learners build and use their own agents, and 5) agents interact with other users (and agents) giving a strongly collaborative view of learning. Like example of this kind there is an ITS called Makatziná (meaning tutor in TOTONACA, a Mexican pre-Columbian language), constructed according to this approach, which teaches the skills necessary to solve the truss analysis problem by the method of joints. This learning domain is an integration skill. The classical ITS work is based on explicit goals and an internal representation of the environment. The intelligent agent approach has reactive agents, which have no representation of their environment and act using a stimulus response behavior type. In this way they can respond to the present state of the environment in which they are embedded. With these elements, errors, and teaching plans, each agent behaves as an expert assistant that is able to handle different teaching (Laureano-Cruces & de Arriaga, 2000). Our work is based in the last way of use of AI in education; remark the strong characteristic of intelligent agent of its proactive behavior.
2.6. Collaborative Learning
A central point of recent research on collaborative learning is that certain types of communicative interactions between learners can be associated with specific interactive mechanisms and under certain conditions, specific forms of communicative interactions among students can be vehicles of conceptual changes. Ravenscroft and Hartley (1999) describe and implement a novel way of learning as knowledge refinement that addresses problems of conceptual change in sciences. They develop a collaborative framework for argumentation that supports the dialog process in ways that stimulate belief revision, hopefully leading to conceptual change and development.
3. Our Proposal
The distinguishing feature of an ITS is that it has the facility to be adapted to student’s shortcomings, therefore, the student model in methodology, design and development is a critical factor, as the ITS will adapt the teaching-learning process based on information of the student’s cognitive state. Shute (1995) proposes that the cognitive diagnosis in an ITS, is one of the most critical elements as the student model is achieved by means of the following parameters: errors made, style of learning, knowledge learned, and others (Sánchez-Guerrero, Laureano-Cruces, Mora-Torres, & Ramírez-Rodríguez, 2011). The following feature most referred to is adaptation to attendance, however, the joint work of all modules is what constitutes intelligence in an ITS.
The study comprised interdisciplinary research into the problem of how to design an interface for an intelligent tutoring system that has the facility to be adapted to a teaching process that improves the collaborative aspect, based on several views of knowledge, such as: 1) computer sciences, from the viewpoint of intelligent tutoring systems; 2) the interface design field (Laureano-Cruces et al., 2009), from a design process model, and 3) educational sciences. Based on this objective, the general-purpose instruction model developed by LaureanoCruces, Ramirez-Rodriguez, Mora-Torres, de Arriaga, & Escarela-Perez (2010) was analyzed, which includes teaching, learning and assessment. A number of adjustments were made to the model proposed so that it could be incorporated into the conception of a pedagogical agent (interface), in order to facilitate collaborative learning in a distributed computer environment.
The collaborative learning tutor model developed is represented by a pedagogical agent, this being the ITS interface, which is based on collaborative learning that constitutes one of the main contributions of this study. Based on the previous considerations, the importance of using a methodology to develop an interface in which students may interact dynamically with the pedagogical agent is emphasized.
Pedagogical agent model is based on the characteristics of the general-purpose intelligent tutor. It takes the following aspects into account: 1) presenting content according to the style of learning, 2) assessing students with regard to how to learn a certain content, and what the skills expected are; 3) helping students to meet the objective of the subject correctly and punctually, and 4) diagnosing performance and providing them the tools they need to increase their production.
The following features were developed and introduced in the particular case of the collaborative pedagogical agent: 1) ability to instruct users on the steps of the collaborative learning process; 2) ability to monitor, establishing application of the collaborative instructional methodology; 4) ability to implement instructional strategies for the group, adjusted to knowledge, and analyzing the combination of pedagogical techniques, in some cases geared to the teaching-learning process; 5) ability to promote development of mental models for group tasks backed by a cooperative and collaborative learning model; 6) assisting the tutor and pairs in collaborative working processes.
Animated pedagogical agents represent an ITS interface whit human features that enable the system and users to interact. Pedagogical agents can be used to increase channels of communication, the bandwidth between the ITS and student, and the ability of the system to commit itself and motivate students (Johnson, Johnson, & Holubec, 1999). Pedagogical agents simulate the manner in which humans teach. One of its pedagogical purposes is to break down knowledge into meaningful components and to use the knowledge in a similar way that humans do. Due to their aspect, they have greater ability to communicate with students more accurately.
4. Collaborative System
We used the Macaulay (1995) development model for this study, as it comprises a methodology centered on the design of interfaces for computer-supported collaborative systems. It suggests the use of a methodology that concentrates on the design of interfaces for group working systems, while at the same time taking into account the user interface analysis approach. According to Macaulay (1995), the purpose of this method is to put to the designer a way of thinking quickly and identifying these systems’ needs. Lewis and Rieman (1993) propose that the main idea in the interface concept is mediation between man and machine. From the design perspective, an interface provides the facility to use a system or machine for the purpose for which it was built. The authors explain that the interface is what measures, facilitates communication, interaction, between two different types of systems, human being and computer, for example. An interface is also an on-screen display that a system shows a user so that both may interact. According to Macaulay (1995), analysis requirements for setting up a system based on the computer-supported collaborative learning model are shown in Figure 1.
The Section 4.1 provides a brief explanation of the components of Figure 1 and relates them to our study case: 1) group analysis (in this case, analysis of a collaborative learning group), 2) overall system analysis (analysis of the instructional environment implemented), 3) user analysis (analysis of the user’s conduct in the instructional environment), 4) organization and types of user (human tutor, student, pedagogical agent), conceptual design for each user (student and pedagogical agent), specification of components (based on interface design models of Lewis & Rieman, 1993).
4.1. Group Analysis
A group analysis document is produced at this stage in sufficient detail so that the designer may describe the group under the terms of 1) what group members do, and 2) how they communicate with one another. In this sense, a table should be established that classifies and groups both aspects, as shown in Table 1.
4.2. Characterization of the Collaborative Learning Group
The collaborative learning group is characterized under the logic of a collaborative learning model planned by
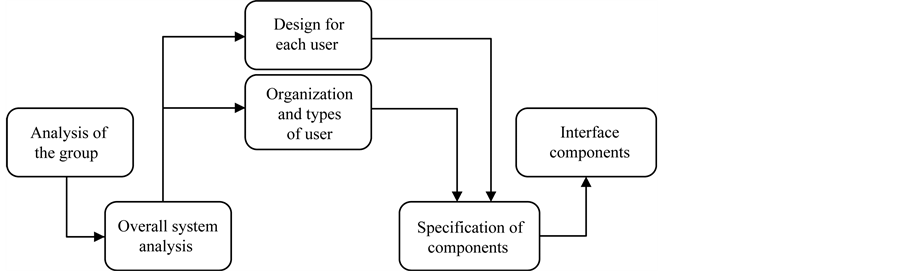
Figure 1. Analysis diagram of the basic requirements of a pedagogical agent-supported collaborative learning system.

Table 1. Classification of tasks and ways of communicating between the members of a collaborative learning group.
Johnson & Johnson (1990), with the following features: common learning objectives in line with the specific objectives of each member in order to achieve group success. These objectives are: 1) division of tasks and allocation of individual functions; 2) making use of personal skills; 3) encouraging interpersonal communication skills and self-assessment of the group; 4) encouraging reflection on the process in order to accomplish objectives. This analysis may be used to create a group model that reasonably represents the group user that will use the system. Table 2 shows the tasks of a collaborative working group during its teaching-learning process and assessment for the specific case of the design of our interface.
4.3. Overall Analysis of the Cooperation and Communication System
At this stage it is necessary to establish what level of communication and cooperation is needed in the application. There may be several particularities, depending on whether the work is: 1) synchronous or asynchronous; 2) distributed or presence based. The main question is to ascertain the level of communication to be used so that group members may interact.
In this study, the communications system depends on the stage of the collaborative learning instructional model developed by Adams (1996) in which communication is made (for example, if they are at the teaching, learning or assessment stage). Strategies for the collaborative teaching-learning process basically establish a face-to-face relationship, which means that students may communicate with one another directly and share information during the learning process. The teacher or instructor and groups of students make up this model of several tasks or activities that must be carried out, as shown in Table 3.
4.4. Analysis of User
Each group member and the types of tasks they carry out are considered at this stage. The user model takes into account their 1) knowledge, 2) skills, 3) experience, 4) motivation, 5) what tasks they carry out, and 6) their contribution to the group’s tasks. According to errors, in order to develop an interface on a typical software system, it is first necessary to: analyze the type of user that will use the system, specify the actions that the interface can support in order to meet the user’s objectives, specify the types of data (objects) on which action will be taken, define the plan or strategy by which potential users will achieve their targets or meet their requirements.
For our study, Table 4 shows the user analysis according to the approach of (Macaulay, 1995).

Table 3. Communication features of the system for a collaborative learning group.

Table 4. Analysis of type of user, actions taken and type of data or objects (for a collaborative learning group).
4.5. Organization and Types of Users
The role of each user comprises the privileges and functions allocated to him or her. The role that each group member plays at this stage must be specified. A system for an interface represented by a pedagogical agent that supports the collaborative teaching-learning process includes the following roles: students, human tutor and pedagogical agent.
4.6. Design for Each User
The individual task component that supports the user interface is related to the user’s individual task. The common task component supports the part of the user interface that is related to the group’s common tasks. The social interaction component supports interaction between group members, such as informal discussion. The interface may include, for example, pictures of group members, conference facilities, decision support facilities, social protocol, shares screens, etc. The social network interface is an efficient example to define collaborative interaction, as shown in Table 5.
4.7. Specification of Components
A diagram of tasks, table, etc., may be submitted in the form of a written document, and individual, common and social interaction tasks are described in this part (Macaulay, 1995). It is also necessary to describe other types of mechanisms, such as restricted access to sub-groups and cooperative editing. In our study we developed this section based on the analysis of the instructional model proposed and it describes how the model interacts with the user or a group of users. The model for this collaborative system is supported by an interface represented by a pedagogical agent, as shown in Table 6, which is also the interface that interacts with the user and directs the stages of development.
Table 7 summarizes the requirements for designing the pedagogical agent interface and its social interaction system.
5. Components for Designing an Interface for the Collaborative Teaching Process
Taking the above discussion into account, this section presents the main components for designing the interface of a collaborative system, assisted by a pedagogical agent (see Figure 2), also presented graphically: main interaction system interface, pedagogical agent interface at teaching-learning-assessment level (see Figure 2) and student interface (see Figure 3).
6. Conclusions
The interface’s components have been proposed in line with the criteria established on account of the needs of the instructional model implemented and the communication needs of the tutor, the pedagogical agent and students. Therefore, the requirements recommended for developing the interface are: distributed interaction, learning facility and collaborative use facility. Requirements have been developed on the basis of a methodology

Table 5. Characteristics of collaborative interaction.

Table 6. Specification of components and tasks.

Table 7. Requirements for designing a computer system for collaborative learning, assisted by a pedagogical agent.

Figure 2. Main system interface and main pedagogical agent interface.
geared to creating structures that facilitate teaching, learning and assessment, and to propose the requirement for assisting in monitoring the collaborative learning process and ensuring that the necessary conditions are in place to achieve successful learning.
Implementation of the interface concentrated on testing the requirements that represent the collaborative interaction system that will allow the system and users to interact. Some of the considerations regarding the interface are: human features which have proved to be effective in comparison with other forms of interface representation, such as animated desktop objects, animals, robots and other forms. We should bear in mind that an agent can not only impose its perspectives on students and oversee their cognitive process, but also stimulate learning and assist in and facilitate educational interaction between students so that they may achieve their learning objectives.
The instructional model of the pedagogical agent facilitates and guides the learning process and increases educational interaction between students. The distributed interaction system is the medium over which social interaction takes place between students and the pedagogical agent.
Acknowledgements
This work is part of the research undertaken by Enrique Acuña-Garduño to obtain the Ph.D. degree in Design, New Technologies, at the Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana-Azcapotzalco. It is also part of the Divisional Soft Computing and Applications project of the Intelligent E-Learning course funded by the same university.