Structural Analysis and Static Simulation of Coastal Planktonic Networks ()
1. Introduction
The Coastal Zone―CZ―is the area where interaction between the sea and land processes occurs giving rise to a number of habitats often characterized by high biological activity [1] . In Brazil, the CZ is a geopolitical concept and a territorial unit defined in legislation for the purpose of environmental management [2] to attempt to achieve sustainability. Along the Brazilian coast, the CZ of Rio de Janeiro state is of special interest since it presents four coastal sectors [3] according to its management challenges such as 1) the estuarine complex of Ilha Grande bay with harbors, nuclear power plants and a petroleum terminal in the green South Coast; 2) a high population pressure and two outfalls on the Coast of the Bay of Guanabara, as well as much of the petrochemical industries of the state beyond the port of Rio de Janeiro (middle coast); 3) a strong urbanization process and high touristic activity in the Coastal Lakes Region where an upwelling process takes place giving a great marine productivity; and 4) high oil prospecting activity in the North Coast besides the estuary of Paraíba do Sul river that cross the largest agricultural area of the state. Thus, some of the biggest obstacles for an effective coastal management of this state are the limited experience in coastal management; limited understanding of the interconnectedness of coastal and marine processes; low conservation of marine biodiversity; supervision inadequate; shortage of trained human resources, relevant technologies and appropriate monitoring equipment.
So, the aim of this paper is to contribute to the Information System of the Coastal Management―SIGERCO, developing a system for monitoring the marine environment based on real time information. The main goal is to gain knowledge about the biological community structure through graphs that are representative of the interactions among the planktonic organisms. We recently began investigating the use of network analysis based upon natural environmental co-occurrence patterns to examine the complex interactions among plankton communities.
In the same way many authors [4] -[7] have used different approaches to evolve food web structures in order to analyze their many features. One of the most important is the interaction strength that has shown to be typically characterized by few strong interactions embedded in a majority of weak links whose arrangement according to [8] promotes community-level stability. However, in real food webs these interactions are very dynamic once for each time they present a different value giving a factor of great imprecision and uncertainty. In this way, [9] [10] have demonstrated the use of fuzzy cognitive maps to build prototype models of complex food webs.
We stick to the restrictive use of the term food web because we recognize the diversity of other possible ecological interactions that can be represented in a multigraph structure. For this reason it is not intended to generate a directional graph which is characteristic of the traditional food webs that indicate who eats whom.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Studied Area
The Ilha Grande bay (Figure 1), southern of Rio de Janeiro state, is a system formed by a large retract of the shoreline and has two access bars, one from 23˚06'13.35''S 43˚59'44.17''W (Marambaia tip) and another from 23˚17'20.64''S 44˚29'06.85''W (Juatinga tip) due to location of the Ilha Grande island. Inside there are other smaller bays as of Sepetiba (northern part), Ribeira (middle) and Parity (southern part), a large number of coves, beaches and islands of great natural beauty that make the region a major tourist hub. Its shores are mountainous with a dense rainforest whose slopes plunge into the sea. This estuary is considered to be a biodiversity hotspot and includes a high number of protected areas [11] . Within the Ilha Grande bay are found the Itaguaí hub port, an oil terminal (TEBIG), the Verolme shipyard, two nuclear power plants for electricity generation besides an expanding industrial park [12] . Because of it, this region has undergone a significant increase in pollution over the last decades [13] [14] which has resulted in worsening of the degradation scenario.
2.2. Data Acquisition and in Situ Flow Cytometry
For real time data acquisition the CytoSense flow cytometry (CytoBuoy bv, Worden, The Netherlands) was used with the same configurations of [15] . This device is connected to the computer by Wi-Fi connection and data transferred by the Internet for remote operation. It can detect and record large suspended particles (>1 - 1000 mm diameter) in relatively large volumes of water (more than 4 cm3 per sample).
The CytoSense is equipped with a solid blue laser providing 20 mW at 488 nm, one frontal sensor named forward scatter (FWS) which measures the light deviation angle according to the passage of the particle through the laser, one side scatter (SWS, 446/500 nm) detector measuring the reflected light that has interacted with structures within the cells giving a sense of its granularity, and three others sensors to detect the red fluorescence produced by the amount of chlorophyll-a (FLR, 669/725 nm); one orange/yellow (FLO, 601/651) sensor and a green/yellow (FLY, 515/585 nm) sensor that measure the amount of phycocyanin and phycoerythrin fluorescences respectively [15] .
The CytoSense is equipped with a solid blue laser providing 20 mW at 488 nm, one frontal sensor named forward scatter (FWS) which measures the light deviation angle according to the passage of the particle through

Figure 1. The Ilha Grande bay, south of Rio de Janeiro state—Brazil. 1 is the location of the two nuclear power plant for electricity generation, 2 is the TEBIG, an oil terminal and 3 is the CytoSub monitoring site.
the laser, one side scatter (SWS, 446/500 nm) detector measuring the reflected light that has interacted with structures within the cells giving a sense of its granularity, and three others sensors to detect the red fluorescence produced by the amount of chlorophyll-a (FLR, 669/725 nm); one orange/yellow (FLO, 601/651) sensor and a green/yellow (FLY, 515/585 nm) sensor that measure the amount of phycocyanin and phycoerythrin fluorescences respectively [15] .
In addition to the 5 basic parameters (FWS, SWS, FLR, FLO and FLY), some simple mathematical models were assigned to each signal shape: inertia, fill factor, asymmetry, number of peaks, length, and apparent size (FWS size) [16] . All these values were summarised in cytograms to facilitate the identification of groups of cells or organisms with similar optical properties derived from these models. However, data acquisition was performed using the CytoUSB software provided by the manufacturer.
2.3. Data Preparation
As a result the CytoBuoy generated a file with a matrix of 30 columns and 2.700 lines regarding to integrated values of each cytometric parameter of pulse shape. This matrix is the result of the six mathematical model applied to the 5 primary parameters (sensors). Then, to reduce the matrix dimensionality without however losing information the first approach was to discard those variables with low variation, it means min and max values near its average value. A second approach was to perform a statistical correlation in order to determine which variables are the most important, in this case to retain those variables without statistical significance.
2.4. Graphs and Networks Generation
A network can be described as consisting of nodes (individuals) and edges (interconnections between them) usually displayed through graphs enabling analyze the patterns it contain. However, although the amount of collected data, there is no information on these pattern of connection. Therefore it is necessary to choose a method that can establish these edges. Given the dynamic nature of these interactions we have adopted a fuzzy logic based approach.
A fuzzy relationship 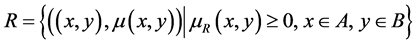 has its degree of relevance given by
has its degree of relevance given by
 , which makes
, which makes  to be the strength of the relationship between x e y [17] . So any fuzzy relationship
to be the strength of the relationship between x e y [17] . So any fuzzy relationship 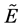 in a fuzzy subset
in a fuzzy subset  of a set
of a set 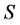 can denote a weighted graph, or fuzzy graph, so that the edge
can denote a weighted graph, or fuzzy graph, so that the edge 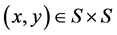 has a weight or force, as expressed by [18] . Formally, a fuzzy graph
has a weight or force, as expressed by [18] . Formally, a fuzzy graph 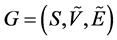 is a not empty set
is a not empty set 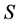 associated with a pair of functions
associated with a pair of functions 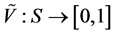 and
and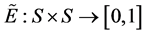 , such that for every
, such that for every
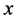 and
and  belonging to
belonging to 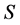 has
has , considering
, considering  as negligible [18] . In most general case, vertices and edges have relevance values, but in this work is used the special case assumption
as negligible [18] . In most general case, vertices and edges have relevance values, but in this work is used the special case assumption , which gives meaning to the use of values relevance only to the edges. Therefore, the fuzzy graph notation will simply be
, which gives meaning to the use of values relevance only to the edges. Therefore, the fuzzy graph notation will simply be . It was used a triangular membership function according to the following criteria:
. It was used a triangular membership function according to the following criteria:
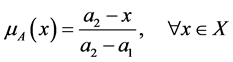 (1)
(1)
in which the maximum value  is the maximum distance found between the set target and all other particles in the sample while the minimum distance, assumed by
is the maximum distance found between the set target and all other particles in the sample while the minimum distance, assumed by 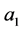 is zero. The strategy is as the following steps:
is zero. The strategy is as the following steps:
1) normalizing the data using the amplitude;
2) creating a square matrix of distances using the Euclidean distance;
3) create a triangular pertinence matrix, considering in turn each particle as a collection target unit;
4) combine the pertinences through the operation of algebraic product, once the logic the above step establish two pertinences for each pair of particles;
5) apply an alpha cut off as arbitrated in accordance with the desired granularity, so that the network is formed only by particles, which will be nodes, whose relevance is greater than alpha.
2.5. Network Metrics
All tasks of network generation, extraction of key features and application of indices were performed on Java programming language used with the JUNG (Java Universal Network/Graph) framework, both free license. The network metrics used was:
Degree is the number of links (edges) from a node with whom it is directly affiliated—obtained by the arithmetic mean of all degrees [19] .
Degree of variance, is a measure of how much the nodes differ in terms of activity [20] —calculated as:
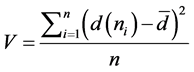 . (2)
. (2)
Density is a global measure that represents the proportion of existing edges in relation to the maximum possible edges [20] , calculated as:
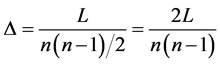 . (3)
. (3)
Connectance is a special case of density that allows inferences about the network complexity and dynamics. Here it is measured as:
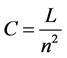 . (4)
. (4)
Diameter and Average degree of separation is the shortest path that separates node x from node y, If there are disconnected nodes will be zero-valued paths making  The greatest distance between any two nodes defines the network diameter [19] . The average degree of separation can be calculated in an undirected network as:
The greatest distance between any two nodes defines the network diameter [19] . The average degree of separation can be calculated in an undirected network as:
 . (5)
. (5)
Complementary cumulative distribution function (CCDF) [21] denotes the probability of a random variable X having a behavior given by:
 . (6)
. (6)
The degree distribution is an important structural property on any real network whose fraction of nodes with degree k is given by:
 . (7)
. (7)
however the complementary cumulative distribution of the degree is more interesting since the CCDF graph provides good visualization of the degree distribution with heavy tail or power law patterns. So, applying (4) in (5), the complement can be obtained from:
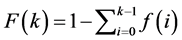 . (8)
. (8)
Clustering coefficient determine whether a graph is a small-world network [22] . It is a local measure of a node that quantifies how close its neighbors are to being a clique (a subset of nodes). Ultimately it gives the average probability of two neighboring nodes of a node are also neighbors [23] and it is given by:
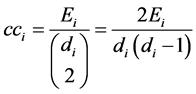 , (9)
, (9)
while the overall coefficient is obtained dividing the sum of the local coefficients and the total network nodes [23] as follow:
 . (10)
. (10)
Degree centrality is a simple measure, with exactly the degree of the node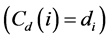 , but allows interpretations, as the assumption that more connected nodes have more influence on the network [23] . Getting high degree a node also indicates the location of the points of greatest activity on the network [20] .
, but allows interpretations, as the assumption that more connected nodes have more influence on the network [23] . Getting high degree a node also indicates the location of the points of greatest activity on the network [20] .
Betweeness centrality quantifies the node participation in the shortest path between any pair of nodes in the network ranking those exerting greater control over the interactions between non-neighboring nodes within a network [20] . The numerical value of intermediation, for a given node i, is the sum of the ratios between the number of shortest paths between a node s and a node t that pass i and the total amount of existing shortest path between s and t. expressed by:
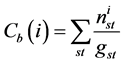 . (11)
. (11)
Closeness centrality is based on the concept of distance and the subject is to measure how close a node is to all others in the network, indicating the potential speed of your interactions [20] . To calculate the average geodesic distance of a node i, it is commonly used divide the sum of the geodesic distances between it and all other network nodes by the number of nodes minus 1, the node i itself:
 . (12)
. (12)
However, this average shows lower values for more central nodes, and high values for most peripheral nodes. To maintain harmony with other measures of centrality, a proximity is calculated as the inverse of the mean:
 . (13)
. (13)
3. Results and Discussion
Table 1 present the set of 20 selected variables after the data preparation procedure so that for the Length parameter, only the FWS was selected. The fluorescences FLY, FLO and FLR were selected to the Total, Inertia and Number of cells parameters while all the primary five variables (FWS, SWS, FLY, FLO, FLR) were selected for both Fill Factor and Asymmetry.
The distribution of these twenty variables is present in the appendix and the correlation matrix between then can be seen in Table 2.
First, regardless to the level of correlation, Table 2 demonstrate all variables are reasonably correlated each other. The greatest correlation coefficient is 0.92 and 0.77 between the variables Total FLO and Total FLR, and variables Total FLY and FLO respectively. The occurrence two (FLR and FLO or FLR and FLY) or three (FLR, FLO and FLY) fluorescences in the same particle is a feature of cyanobacteria. Second, the positive correlation between the Length FWS that determine the apparent size and the Number of Cell fluorescences is an indication of the occurrence of filamentous algae or colonies or aggregates of micro algae cells and/or cyanobacteria. Another interesting information in Table 2 is the negative values of the Number of Cell fluorescences and its asymmetry indicating a heterogeneous pattern on pigments distribution within the cells.
The components or nodes of the planktonic network (Figure 2) represent many sort of marine planktonic or-ganisms, notedly coming from phytoplankton (eukaryotic algae, diatoms, cyanobacteria, dinoflagellates and coccolithophores) that support photosynthesis and zooplankton (small protozoans and metazoans) that feed on the other plankton and detritus generally with smaller sizes. So that the body size determines the position of organisms in plankton food webs [24] . Their classical size distribution are picoplankton with sizes less than 2 µm, nanoplankton comprising sizes between 2 and 20 µm, microplankton ranging from 20 to 200 µm and mesoplankton above 200 µm until 2 mm. It is worth to say, the maximum size detectable by the CytoSub instrument is 1mm. Thus, the graph of Figure 2 depict different sized and colored circles representing a high diversity of auto-fluorescent particles, species of phytoplankton, and gray ellipses and rectangles referring to the primary and secondary consumers. An important observation is the phytoflagellates, any member of a group of flagellate protozoans, that have many characteristics in common with algae. They contain chlorophyll and various accessory pigments enjoying a photosynthetic type of nutrition, although many organisms included in this group also exhibit heterotrophy or mixotrophy.
Figure 3 shows the size distribution of all network nodes based on their forward scatter signals that was previously calibrated in accordance to [25] . Therefore any one can verify that 12.93% of the occurrences (323 particles) belongs to picoplankton individuals, a great dominance is exhibited by nanoplankton with 86.43% (2159 particles) and only 0.64% (16 particles) representing the microplankton species.
The nanoplankton particles suggest, according [26] , it is a dynamic “food web”. However, this is also a feature of oligotrophic systems which are usually dominated by flagellates as the main grazers of pico-sized autotrophs [27] despite this site being an estuary where heterotrophic dinoflagellates (mixotrophic as well) with high feeding plasticity is another potential grazer [28] . In fact the plankton abundance and distribution are strongly dependent on factors such as nutrient concentrations and the physical state of the water column.
Table 3 presents the network properties values according the applied indexes. In networks, we call degree of a node the number of edges which are adjacent to it. So, the basic structure of this network present a total of 2498 nodes interconnected by 107,741 edges which would give an average of 43.131 edges per node. However, the edge distribution is not uniform. There are many nodes connected by a single edge (minimum degree = 1), while others have many ones (maximum degree = 555) resulting in a network mean degree of 86.262. This fact reveals topological differences in the network architecture. In another way, in relation to the network heterogeneity, differences in node activity can be represented by the variance degree values that, in our network, is 9220.385. The overall density or the ratio of the existing edges and the maximum possible edges in the network, is 0.035. It gives a sense of network cohesion. Another measure widely used in ecological networks analysis is the connectance. It is the proportion of possible trophic links that are actually observed [29] . Essentially it is the density of interactions, that in our planktonic network, has a connectance value of 0.017. On the other hand, this network presents a diameter value of 13 that means it is larger number of paths connecting two nodes within the network. The characteristic path length and the clustering coefficient are another two index of the small world property that have been identified [30] -[34] .
The clustering coefficient not only proves the existence of triangles, expected in any real network, but the

Table 1. Cytometric variables selected to each mathematical model.

Table 2. Correlation of the 20 selected variables performed in the Statistica 9 package software. Significance in red numbers. Level of significance p < 0.5.
value of 0.437 is compatible with other biological networks, such as that 16 food webs analyzed by Dunne and colleagues whose coefficients vary from 0.02 to 0.43. The average degree of separation of these networks, that is equivalent to the characteristic path length, were set around 2.2, while the test with our one showed a value close to 3.204. In the same way the marine microbial network analyzed by [35] , present a clustering coefficient of 0.265 and an average degree of separation of 0.3 that are both values near that found in our planktonic network.
Figure 4 shows us the degree distribution of the generated planktonic network.
The long tail depicted in Figure 4(a) shows a high occurrence of nodes with low degree at the same time many nodes having high degree in accordance with a power law distribution characteristic of free scale pattern also verified by [30] [36] in food webs. Figure 4(b) presents the same but in a log-log plot with the R2 values allowing seeing the adjustment of all degrees to its straight-line.
The ultimate goal in environmental management is the impact assessment. It can be achieved by simulation. In this way Table 4 present the values of a series of network properties according to progressive node deletions chosen by their highest degree, betweeness and closeness centralities.
Table 4 show us that while the network nodes were progressively deleted, consequently their respective edges, the network diameter (the distance from any given node to another) remain almost the same or had a

Figure 2. Representative graph of the planktonic network. Green and Yellow circles refer to chlorophylla and phycoerythrin fluorescence particles. Circle sizes refer to particles whose length is based on its forward scatter signal. Gray rectangles and ellipses refer to non-fluorescent particles as carnivores and herbivores respectively. Lines are edges linking two or more organisms.
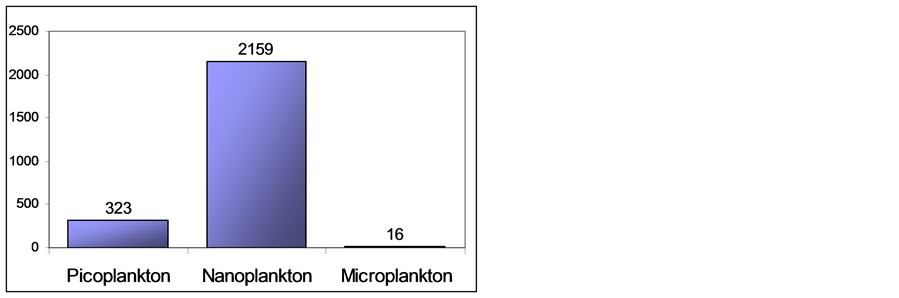
Figure 3. Number of individuals within each classical size class based on forward scatter signals.

Table 3. The planktonic network properties.
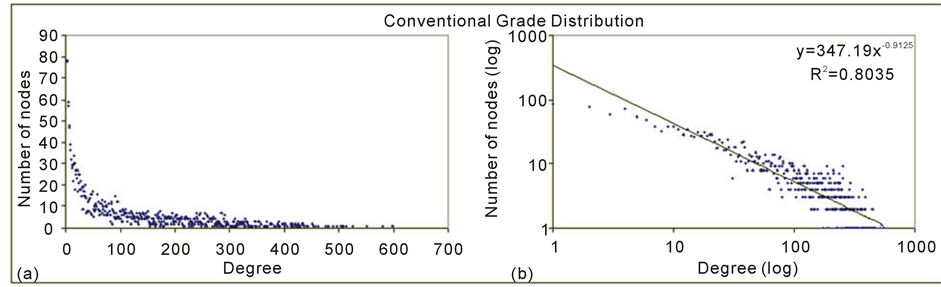
Figure 4. Degree distribution of the planktonic network.

Table 4. Values of network properties according progressive deletions of nodes.
small increasing. However, it was verified a marked increase in the characteristic path length and a slack decrease in the clustering coefficient. This follows from the fact that most shortest paths between nodes flow through hubs instead of peripheral. The clustering coefficient reduction indicates the loss of triangles and other possible clicks. Table 4 still present the R2 values of each simulation that can also be graphically observed in Figure 5.
From Figure 5(a) to Figure 5(i), are showing the deletions effect of the network core nodes. This set of simulation present a similar behavioral pattern. At 10% and 25% level of deletions there are progressive loss in the adjustment of points to the power law pattern but a recovery is also verified when the 50% deletion level are reached, may be due to more permanence of nodes with smaller degree.
On the other hand, the Figure 5(j) to Figure 5(l) present the results if the causative agent of environmental impact was more effective upon nodes with lowest degree. In this case the adjustment of points is always decreasing since the distribution has become much less dispersed, with the degree of the remaining nodes near the network average. The network diameter underwent a sharp decline followed by slight decrease in the characteristic path length values and a lazy increasing of the clustering coefficient and connectance (Table 5) showing that some highly connected nodes still maintains relations with varied roles within the network.
4. Conclusions
The planktonic fuzzy network evolved in this work showed most of nodes having small degree despite many of them with high degree values in addition to high clustering coefficient can be taken as a sign that these structural features suggest it is a small-world network. It has been hypothesized that the prevalence of small world networks in biological systems may reflect an evolutionary advantage of such an architecture. One possibility is that these structures are more robust to perturbations than other architectures. All species are embedded in complex networks of interactions [37] , so understanding species interactions and the robustness of interaction

Figure 5. Graphical visualization of the progressive network node deletions in logarithm scale.

Table 5. Values of network properties according progressive deletions of lowest degree nodes.
within networks to species loss is essential to understand the effect of species decline and extinctions.
Whether our results are ecologically meaningful depends crucially on our ability to attack an ecological interpretation the decisive properties that are identified.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Brazilian Research Agencies (CAPES and CNPQ) for the financial support and the transportation sector of the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ) by logistical support.