HIV Infected Elderly Women: From Rhetoric to Reality—Experience from Eastern India ()
1. Introduction
Human immuno-deficiency virus (HIV)/acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) is a major public health issue which affects one person every six seconds and kills one person every 11 seconds [1] . Of the estimated 33.4 million people living with HIV/ AIDS (PLH), 47 percent are women and half of all new infections also occur among women [2] . Although most new HIV infections occur in younger people, due to growing and graying it is expected that, by 2015, half the people living with HIV infection in the United States will be 50 years of age or older [2] . Seniors represent an estimated 14 percent of total AIDS cases and senior women represent 18 percent of women AIDS cases in United States [2] . Moreover, the number of women over 50 years living with AIDS tripled in last decade [2] .
There is a growing evidence that women are disproportionately vulnerable to HIV/AIDS in South Asia [2] . Gender norms, gender inequality and gender violence propel increasing numbers of women to become infected with HIV [2] . At the end of 2011, 2.27 million PLH are living in India. In India the number of HIV/AIDS patients more than 50 years of age accounts for 13.2% whereas in West Bengal it accounts for 11.9% in 2009 and the figures are increasing over years [3] . Contrary to developed nations India lacks proper epidemiological data as well as targeted interventions centered on elderly HIV infected persons less so for women. Open discussion regarding prevention of HIV, methods of contraception, or any other sex-related issue among elderly individuals is considered as taboo. Poverty, patriarchy and low level of literacy have joined arms to fuel suffering from HIV/AIDS not only in India but also in many developing nations of South Asia [4] .
A lack of basic knowledge about HIV/AIDS is very common among older patients owing to the fact that education, research and clinical trials are focused on younger members [5] [6] . Contrary to popular belief, many seniors are involved in robust sex lives, often without using proper contraception [5] . In fact, western data indicate that 20 percent of people over 70 years of age engage in sexual activity at least once a week [5] . Seniors, meanwhile, are as one-sixth likely to use condoms as younger people and one-fifth likely to get tested for HIV, according to the National AIDS Behavior Surveys [6] . Only 5 percent of all HIV-positive people in the world are aware of their status [6] . So, the figures will be much more staggering in the near future.
Without the risk of an unwanted pregnancy, many older women also do not practice safe sex or even consider about sexually transmitted diseases [5] . Postmenopausal women may be more susceptible to HIV because low estrogen state renders increased opportunities for small tears and abrasions to occur during sexual activity [5] [6] . Many women and their medical care providers mistake the symptoms of HIV/AIDS as part of normal aging, and as a result are less likely to ask for testing or be advised to test for HIV unless the patients present to an advanced stage [5] . Women themselves appear even more reluctant to discuss an HIV concern or diagnosis with family members or friends and health-care workers and educators sometimes fail to talk with older patients about HIV [6] . Moreover, women always place their health issues after children and other family members. Once a diagnosis is confirmed, older women also tend to isolate themselves more than younger HIV-positive patients, and may struggle with severe depression [5] [6] .
Women with HIV are at increased risk for developing a range of conditions, including human papillomavirus (HPV), leading to cervical cancer, and severe pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) [7] . HIV associated non-AIDS (HANA) conditions like HIV associated neurocognitive diseases (HAND), cardiovascular disease, diabetes, dyslipidemia, cancer, osteoporosis are more pronounced in elderly population [7] . HIV-associated inflammation and immuno-senescence have been implicated in premature target organ damage and HIV-Tat down-regulates telomerase activity in the nucleus of human CD4T cells brings forth premature ageing by a novel mechanism proposed as “inflamm-aging” [8] .
The centre for disease control and surveillance (CDC) recommends routine HIV screening for all adults, aged 13 - 64 years, in health care settings, including women, and repeat screening at least annually for those at high risk [9] . However, in India, National AIDS control organization (NACO) has not yet followed the footstep of CDC in this regard. Making testing routine for older persons can help open a discussion about risk behavior as well as can detect undiagnosed cases. Older people are often overlooked in the HIV informational programs [5] . Coping with their illnesses in one hand and facing up to the stigma in other hand are challenging for HIV infected women [6] . With an escalating rate of HIV infected women, network of senior women AIDS activists is also proliferating in parallel [5] [6] . In India, various fostering partnerships, literacy programs, and legal services are rising up to uplift women’s needs and socio-economic status [3] .
The epidemiological and clinical data regarding HIV infected elderly are sparse in India and more so for women. Moreover in a country like India where gender bias is very common, studies exploring the epidemiological difference and clinical comparison among HIV infected men and women would be of immense importance. Our study from eastern India was an endeavor to turn this rhetoric into reality.
2. Methods and Materials
This cross-sectional study was conducted at the HIV clinic of a tertiary care hospital of eastern India, where more than 15 thousand HIV sero-positive patients are enrolled since its establishment. Following approval from institutional ethics committee 567 cases (men 457, women 110) that were detected to be HIV-positive at or after age of 50 years (are called “elderly” PLH), from 2008 to 2012, were analyzed on socio-demographical and clinical parameters. Our objective was to explore prevalence of HIV positivity among patients more than 50 years of age and to compare the distribution of socio-demographical parameters and clinical presentation with respect to gender.
3. Statistical Analysis
Data obtained from the study were analyzed in descriptive and statistical ways using Epi info software. Sociodemographic characteristics and clinical parameter were described using descriptive statistics. The univariate analyses were done by student’s t-test. To compare baseline characteristics between elderly men and women, student’s t-test for continuous variables and chi-square test or Fisher exact tests for categorical variables were conducted. Odds ratio, 95% confidence interval and p-values were calculated and p-value < 0.05 was taken as significant.
4. Results
Among the total of 5720 HIV sero-positive patients (men 3597, women 2123) detected from 2008 to 2012, 567 patients (men 457, women 110) were diagnosed sero-positive at or after the age of 50 years. Detection of HIV among elderly women was found to be increased over last 5 years (Figure 1) in our study. Among the total HIV infected elderly women 89% (n = 98) were within age of 50 - 60 years and the rest 11% (n = 12) were above 60 years old. Maximum observed ages of HIV diagnoses were found to be 70 years in women and 87 years in men. Illiteracy (p = 0.04) and unemployment (p =< 0.01) were seen more among elderly women. Death of spouse was noted more among elderly women (p = 0.01) when compared to men. Sero-concordance of spouse was observed more among elderly women (p = 0.02). Alcohol intake and smoking were found to be more common among
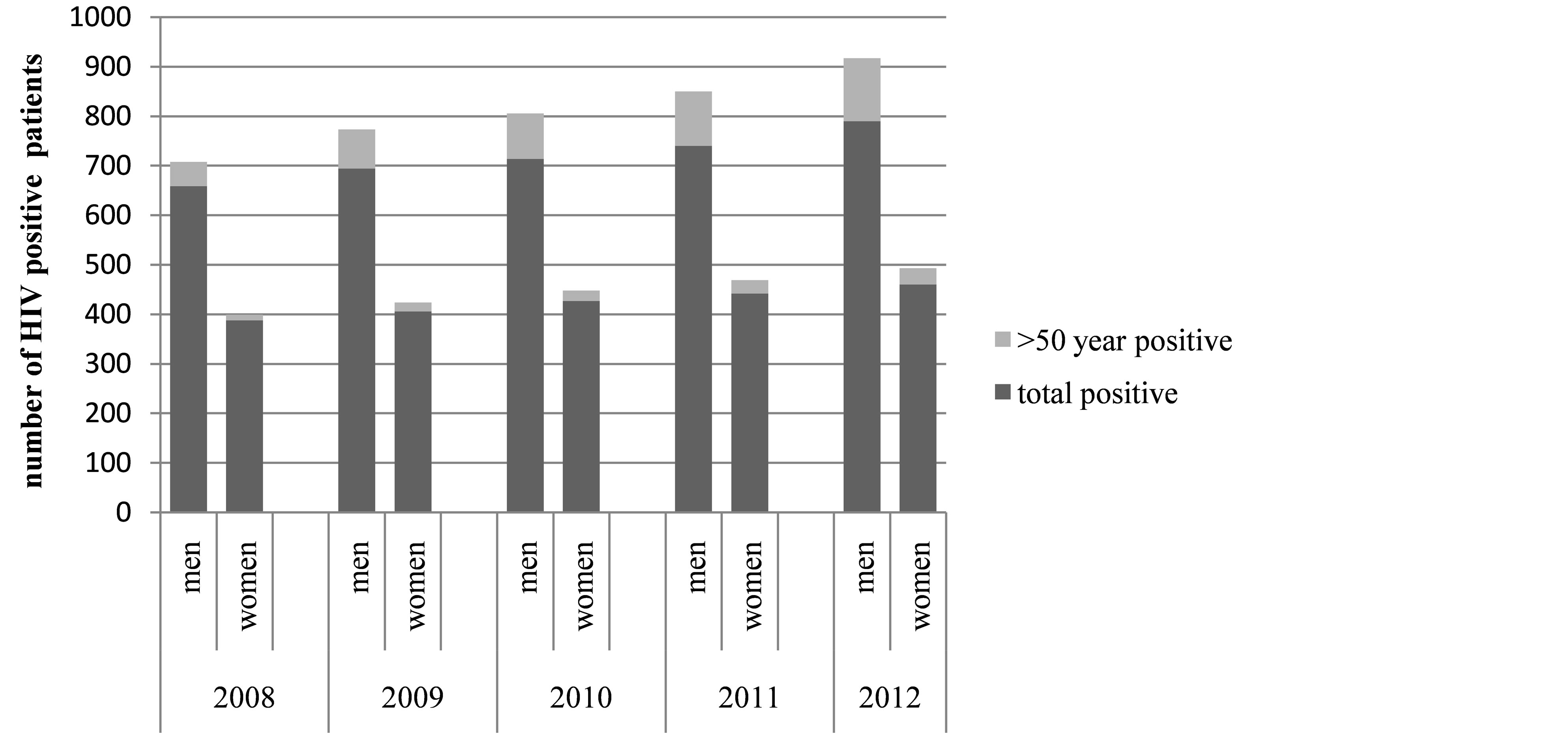
Figure 1. Bar diagram showing number of HIV sero-positive men and women who were diagnosed at 50 years of age or more among the total HIV sero-positive men and women respectively from 2008 to 2012.
men (Table 1). Commonest clinical presentation was frailty among elderly men (p =< 0.01) whereas most of the elderly women were asymptomatic (p =< 0.01) at the time of diagnosis (Table 2). Presentation with extra-pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) at the time of diagnosis was noted more commonly (p = 0.04) among elderly women (Table 2). Malignancy was noted among 13 HIV infected elderly men and 3 women. Non-TB chest infection (forty men, fourteen women), diarrhea (twenty six men, three women), fever of unknown origin (nine men, one woman) and skin and soft tissue infections (four men, one woman) were noted in fair number of cases. A lower mean CD4 count (112 and 137 cells/ dl for men and women respectively) and worse WHO clinical stage (p =< 0.01) were observed among the HIV sero-positive elderly men patients at the time of diagnosis (Table 2).
5. Discussion
The total number of people living with HIV (PLH) in India was estimated to be 22.9 million in 2009 with adult prevalence of 0.31% [3] . West Bengal, prevalence of HIV/AIDS has gone up from 0.21% to 0.30% from 2005- 06 to 2008-09 [3] . In India as per national AIDS control organization (NACO) HIV/AIDS patients more than 50 years of age constitute the “elderly” HIV-infected populations which accounts for 13.2% of the total PLH whereas in West Bengal it accounts for 11.9% in 2009 and the figures are increasing over years [3] . In addition, recent data suggests that prevalence and incidence of HIV infection is gradually tapering among younger individuals

Table 1. Demographical differences among HIV positive elderly men and women.

Table 2. Comparison of clinical presentation at the time of diagnosis among HIV positive elderly men and women.
#TB—Tuberculosis; $WHO—World Health Organization; *Others—described in text.
over years whereas increasing among people aged more than 50 years [3] . In our study detection of HIV was found to be rising among the patients aged 50 years or more over last 5 years.
There is discrepancy in men-women ratio (4:1) among study population. Under-diagnosis or underreporting of HIV/AIDS among elderly women can be one of the reasons. This difference could also be explained by the fact that as they both age, men have a greater chances of getting infected compared to women since men are polygamous and elderly men remarry upon widowhood and tend to marry younger women. NACO figures out that the adult prevalence is 0.25% among women and 0.36% among men in 2009 in India [3] . In a Tanzanian study conducted among elderly HIV patients, sero-positivity was found to be 15% (18.5% in men and 9.8% in women) [10] .
Elderly HIV infected patients originated from rural areas of West Bengal represented a lower portion in comparison to their urban counterpart. It can be explained partly by under-suspicion and under-diagnosis of HIV infection among rural elderly patients. Contrary to our observation in a Indian study from Jaipur, majority of patients were from rural area and were referred by treating doctors (97.5%) [11] . In our study illiteracy (p = 0.04) and unemployment (p < 0.01) were seen more among elderly women. However, the Tanzanian study failed to show any association between HIV sero-status to literacy, employment and residence [10] .
Most of husbands of women HIV patients were sero-concordant whereas sero-status of wives of elderly men were mostly sero-discordant (p = 0.02). This reflects men are engaged in heterosexual promiscuity whereas women are receiving them blindly. Death of spouse is an important issue among elderly HIV patients and proportion of widowhood was found to be significantly more among women. This can be explained by the facts that women have a longer life expectancy and in India it is a custom for men to have wives older than their age [12] . According to the 2001 census, 33.07% of the elderly in India were without their life partners. The widowers among men formed 14.98% as against 50.06% widows among women [12] . Single, divorced and widowed elderly PLH are expected to have a poor care, support and treatment.
Heterosexual contact was found to be the leading cause of HIV transmission among the elderly. In the Indian study from Jaipur, the mode of transmission was heterosexual in all sero-positive persons in our study [11] . While prevention and education dollars are concentrated toward young adult populations, seniors are not getting safer sex education and continue to get HIV infected.
Commonest clinical presentation was frailty among elderly men whereas most of the elderly women were asymptomatic at the time of diagnosis. Presentation with extra-pulmonary tuberculosis at the time of diagnosis is found to be commoner in elderly women. Elderly women presented at a better WHO clinical stage when compared to elderly men in our study. This suggests many women partner of the HIV infected men freely visited to voluntary counseling and testing centre (VCTC) and has become diagnosed HIV sero-positive in absence of any illness. Surprisingly WHO functional classification does not project suffering of the elderly HIV/AIDS patients as majority of our study population were functionally “working” at the time of diagnosis. This proclaims their ignoring attitude to physical suffering in the face of their helpless poverty-stricken situation as predominantly they hail from low economic strata.
Non-specific symptoms like weakness, easy fatigability and weight loss can mimic aches and pains of ageing and thus very easily ignored not only by the patient himself but also their family members and as a result they seek for medical assistance at a stage where they are extremely sick. The patients are hesitant to discuss their sexual behavior with doctors or social workers and physicians are also reluctant to consider HIV/AIDS as a possibility of their chronic illness. Thus diagnosis of HIV sero-positivity comes at a considerable delay and more importantly at the cost of progression of their illness to a worse clinical situation. In the study of Tanzania the main presenting feature among HIV positive patients aware wasting (44%), fever (39.5%), pallor (34.2%), weight loss (31.6%). Skin lesions, diarrhea and altered sensorium were noted in 23.7%, 18.4% and 5.3% of total elderly HIV patients of the study [10] .
In our study 92% of women were found to be having CD4 count below 350 cells/ dl which is similar to the figures observed among men. However, mean CD4 count at the time of HIV diagnosis was 137 cells/dl in elderly women and 112 cells/dl among elderly men. The lower mean CD4 count at the time of presentation indicates that there is considerable delay in diagnosis among the elderly HIV infected persons rendering them not only to worse clinical status but also at greater risks of transmission. Albeit beyond scope of our study, it has seen that ART causes a greater HIV RNA suppression in elderly than their younger counterpart [13] [14] .
Detection of HIV among elderly is increasing and this is going to be a major public health issue in recent future. At present all the HIV awareness programs are directed towards people of 15 - 49 years of age and some high risk groups. But elderly individuals especially women are at the end of dark tunnel deprived of these mass education. Social workers should come forward with newer modes of HIV awareness targeting chiefly elderly women with poor socio-economic background. Physician should be wiser to consider HIV/AIDS while attending elderly patients with frailty, neuro-cognitive impairment and constitutional symptoms. Policy makers should bring forth HIV testing more liberal and available for elderly individuals including asymptomatic spouse of sero-positive men. Addressing the issues of HIV among elderly and the need for potential insights regarding pathophysiology of aging and the care of older adults, September 18th has been designated National HIV/AIDS and Aging Awareness Day since 2008, and a White House Conference on HIV and Aging was also held in 2010 [15] .
6. Conclusion
An increasing proportion of HIV infections is occurring in older adults as members of this age group are the least likely to practice safe sex and changes in the reproductive tract and immune system may enhance susceptibility to HIV acquisition in seniors. HIV infection can be diagnosed after age of 50 years and it may present with atypical clinical picture. Our study demands attention of policy makers as well as social workers to addressing the emerging issue of HIV at the doorstep of geriatrics and considering wider awareness program and more liberal HIV testing among elderly men and women. Physicians also need to be wiser in considering and ordering HIV testing among elderly persons with risk factors and signs of premature ageing. The strength of the study being, it deals with an unexplored element of gender inequality in demographical and clinical profile among HIV infected elderly. The limitations are that it is a cross-sectional hospital based study consisting of heterogeneous study group with small number of cases. Moreover since the history regarding the possible exposure to HIV among the elderly sero-positive patients could not be retrieved due, expected duration of HIV infection could not assessed and thus severity of infection could not be correlated with the duration of disease. This study also points the need for larger multi-centric population based study involving elderly HIV infected persons in India.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.