Vismodegib Provides a Novel Treatment for Advanced Basal Cell Carcinoma ()
2. Pharmacology
Vismodegib is a selective inhibitor of the Hh signaling pathway. It acts by binding to Smoothened (SMO), a 7- transmembrane protein, which in turn prevents the intracellular signaling of Gli family proteins and inhibits the activation of Hh target genes downstream [5,6]. While the Hh pathway plays a key role in embryogenesis, in most adults the Hh pathway is inactive [7]. However, its reactivation has been linked to many cancers, including BCC and medulloblastoma [6]. By inhibiting SMO, vismodegib hinders cancer cell growth and survival [8].
3. Pharmacokinetics
In a two-stage phase I study, daily dosing of oral vismodegib reached steady state within 7 - 14 days, regardless of the dose [3,9]. Vismodegib has nonlinear kinetics due to its high protein binding affinity (99%), especially for α1-acid glycoprotein (AAG) [3,5]. It also binds to human serum albumin at a lower binding affinity, leaving less than 1% unbound in the serum [3,10]. Bioavailability of oral vismodegib is low, at about 32% after a single oral dose. In the phase I trial, absorption was found to be saturable, since an increase in dosing from 150 mg to 270 mg or 540 mg did not cause a proportional increase in drug exposure [5,9]. With over 98% of the drug eliminated unchanged, vismodegib is scarcely metabolized. The main metabolic pathways used are oxidation, glucuronidation, and pyridine ring cleavage. The two largest oxidative metabolites recovered from the feces are produced from recombinant cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C9 and CYP3A4/5 [3,5,11]. Elimination of vismodegib is primarily through the liver, with 82% of the drug recovered in the feces and 4.4% found in the urine [11]. The elimination half-life is about 12 days after a single dose, but decreases to 4 days with daily continuous dosing [3,5,12].
4. Clinical Trials
4.1. Phase I Trials
In a two-stage phase I clinical trial, researchers assessed the safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of vismodegib in patients with locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors, with a focus on patients with BCC [9,13]. The first stage was a dose escalation stage to determine the maximum tolerated dose. Patients took a single oral dose of 150 mg (n = 7), 270 mg (n = 9), or 540 mg (n = 4) on day 1, and then began daily administration on day 8. Results showed no dose-limiting toxic effects, and a dose of 150 mg per day was determined for Stage 2, since larger doses did not provide higher drug plasma concentrations. Stage 2 included a 12 patient expansion cohort to further study pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety data [9,13].
Based on the preliminary data from Stage 1, the study was amended to include two additional cohorts. The first was a 20 patient cohort of individuals with advanced BCC, added due to the clinical efficacy seen in two patients with BCC from Stage 1. These patients were treated with either 150 mg or 270 mg per day depending on dose availability. A second cohort of 16 patients with solid tumors, 10 of which had BCC, was added to study a new 150 mg oral formulation of vismodegib [13]. Out of 68 total patients, responses were only observed in patients diagnosed with advanced BCC or medulloblastoma [9]. Of the 33 patients diagnosed with mBCC or laBCC, the objective response rate, including complete and partial responses, was 58% (19 out of 33), and the median duration of response was 12.8 months [9]. Response rates are broken down by specific cancer in Table 1. While no dose-limiting toxicities were observed, the most frequently reported adverse events were muscle spasms, dysgeusia, fatigue, alopecia and nausea (Table 2) [9,13].
Due to the findings of this phase I study, further studies looking at the safety and efficacy of oral vismodegib in patients with mBCC or laBCC were conducted.
4.2. Phase II Trials
After the success of the phase I trial, several studies looked further at the effects of vismodegib on different cancers associated with Hh expression. The most noted phase II study was the ERIVANCE BCC trial that evaluated the safety and efficacy of vismodegib in advanced BCC. The ERIVANCE BCC trial was a single arm study with no control group [14]. Of the 104 patients enrolled, 33 patients with mBCC and 63 patients with laBCC who had received a daily oral dose of 150 mg vismodegib were included in the results. The objective response for mBCC was 30% (p = 0.001), with all responses being partial responses. The objective response in laBCC was 43% (p < 0.001), with a complete response in 13 out of 63 patients. For both groups, the median duration of response was 7.6 months and the median progression free survival was 9.5 months (Table 1). During this study, all patients experienced at least one adverse event, with 57% having experienced only grade 1 or 2 adverse events. The most commonly reported adverse events of any grade were muscle spasms, alopecia, dysgeusia, weight loss, fatigue, and nausea (Table 2). Thirteen patients discontinued use due to adverse events, with the most commonly cited being muscle spasms [14]. Based on the results of this trial, the FDA approved vismodegib in January 2012 for the use in otherwise untreatable BCC [15].
In another phase II study, the effects of vismodegib were studied in patients with ovarian cancer who were in their second or third remission [16]. In total, 104 patients were randomized to either 150 mg/d oral vismodegib (n = 52) or placebo (n = 52), stratified by their second versus third remission. The primary endpoint was progression free survival (PFS) from time of randomization to first occurrence of progression or death. Patients in the treatment arm had PFS of 7.5 months compared to 5.8 months in placebo (p = 0.39) (Table 1). The most com

Table 1. Efficacy of vismodegib in clinical trials.
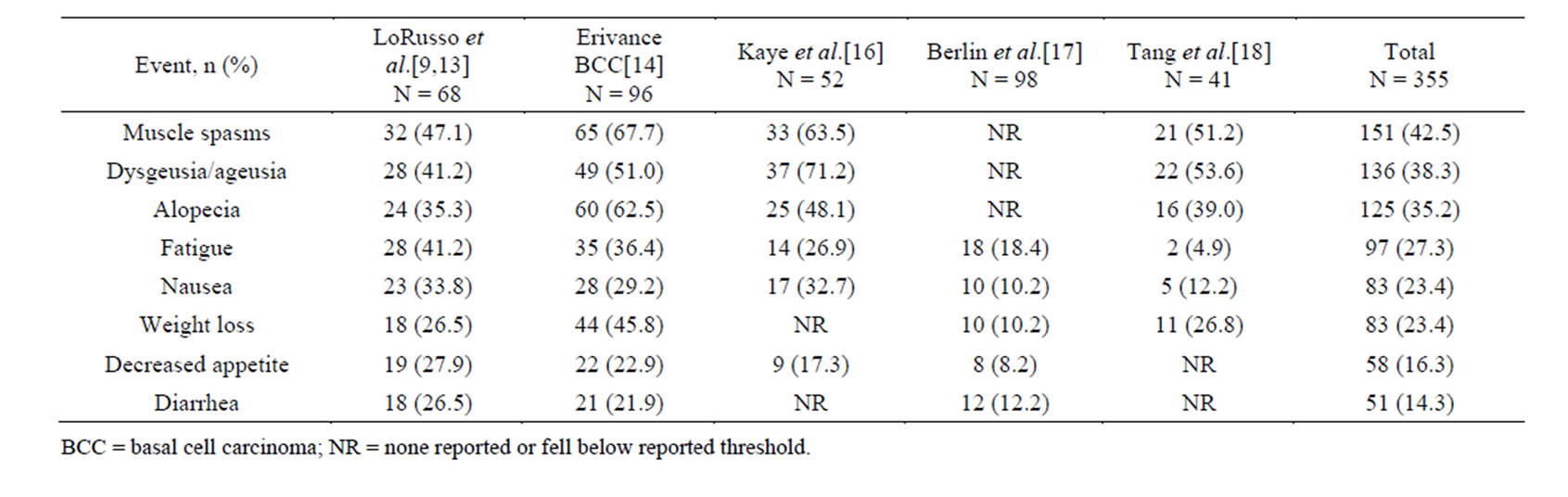
Table 2. Adverse events occurring in 10% or more of vismodegib patients.
mon adverse events reported in the treatment arm were dysgeusia/ageusia, muscle spasms, and alopecia (Table 2). The results of this study suggest that Hh pathway activity may be less meaningful in the treatment of ovarian cancer [16].
A third phase II study looked at the use of vismodegib in conjunction with standard care regimens for treating previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) and its effect on PFS [17]. Patients were randomized to vismodegib 150 mg/d orally or placebo and stratified based on standard of care regimen. Vismodegib or placebo was started on cycle 1 day 3 and continued until disease progression or intolerable toxicity occurred. A total of 97 patients received vismodegib and 99 received placebo. It was found that vismodegib combined with the standard treatment regimen did not bestow a clinical benefit by PFS or objective response rate (ORR). Median PFS for patients on vismodegib was 9.3 months while it was 10.1 months for placebo. ORR for placebo was 51%, whereas for vismodegib it was 46%. It was also noted that patients complained of vomiting, asthenia, weight loss, decreased appetite, dehydration, muscle spasms, and dysgeusia greater than 10% more frequently on vismodegib than on placebo. The results of this study suggest further testing in this setting should not be pursued [17].
An additional phase II study looked at the efficacy of vismodegib specifically in patients with basal-cell nevus syndrome (BCNS) [18]. This study randomly assigned 41 patients to receive placebo or vismodegib 150 mg/d orally, and monitored for reduction in incidence of new BCCs eligible for reduction via surgery. The placebo arm was ended after interim analysis due to the statistically significant differences in efficacy with vismodegib compared to placebo. The study found that vismodegib significantly reduced the per-patient rate of new BCCs that were eligible for surgery compared to placebo (p < 0.001) and decreased the size of surgically eligible BCCs that already existed (p = 0.003) (Table 1). Patients on vismodegib also had fewer surgeries to remove tumors compared to placebo (mean, 0.31 vs. 4.4, p < 0.001). Adverse events related to vismodegib led 54% of patients to discontinue the medication. The most commonly listed adverse events were dysgeusia, muscle cramps, hair loss, and weight loss (Table 2). Overall this study found vismodegib to be effective at reducing the surgically eligible tumors for patients with BCNS [18].
5. Dosage Recommendations
After a two-stage phase I study found that doses greater than 150 mg did not provide increased drug exposure, it was recommended patients receive a starting dose of 150 mg/d orally [3,5,9]. This medication can be taken with or without food, however most clinical trials dosed vismodegib on an empty stomach [19]. Thus far, there has been no study information looking at vismodegib in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, so it is not known if a dosage adjustment is needed in these populations [3,5]. Vismodegib carries a black box warning due to its teratogenic potential, with the possibility of embryo-fetal death and severe birth defects. Females of reproductive potential should use two methods of contraception for the entire duration of treatment and continue for 7 months after treatment [6]. Males with female partners of reproductive potential should also use protection up to at least 2 months after treatment [6]. While it is unknown whether vismodegib is excreted in the breast milk, it is not recommended to breastfeed while on this medication [3]. Pediatric use is currently being studied in patients with medulloblastoma, but developing young children may still require normal Hh pathway activation so use of vismodegib could cause adverse effects not seen in adult studies, including closure of the epiphyseal growth plate and abnormal development of the incisor teeth [3,20].
6. Drug Interactions
Drugs that increase the pH of the upper GI tract, such as proton pump inhibitors, histamine2-receptor antagonists, and antacids, can decrease the solubility of vismodegib and lead to decreased absorption [3,5]. However, as of yet there are no studies that look at the effect of these medications on systemic exposure to vismodegib [5]. While vismodegib is mostly excreted unchanged, it is a substrate of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4/5; however, in clinical trials, CYP3A4 inhibitors and inducers did not affect steady state plasma concentrations when taken concomitantly with vismodegib [11]. In addition, although vismodegib has the potential to inhibit CYP2C8 and 2C9, it does not seem to affect systemic exposure to substrates of these enzymes. In a study focused on drug-drug interactions, rosiglitazone, a substrate of CYP2C8, was given to patients alongside vismodegib but there were no observed changes to systemic exposure [21]. In the same study, no interaction was found with oral contraceptives that are substrates of CYP3A4 [21]. Vismodegib was also found to be a substrate of the p-glycoprotein transporter (p-gp), so administration of drugs that inhibit p-gp, such as clarithromycin, erythromycin, or azithromycin, can lead to an increased systemic exposure to vismodegib and an increased incidence of adverse events [3,5,11].
7. Formulary Considerations
Currently, vismodegib is the only approved therapy for mBCC or laBCC that has recurred after surgery or where surgery or radiation is not a treatment option [5]. The current cost for a one-month supply of vismodegib is $7500 – approximately $250 per capsule [5]. While it is unknown for sure the length of treatment necessary, the average length of treatment is 10 months, making the average total cost of therapy $750,000. As of now, vismodegib is only available in specialty pharmacies [5].
8. Conclusion
Currently vismodegib is the only Hh pathway inhibitor approved by the FDA, although similar SMO inhibitors are presently in development. Due to the current lack of proven alternative treatments for mBCC or laBCC, vismodegib offers this small population of patients an effective and well-tolerated option. It is still unknown whether resistance mechanisms will limit the long-term efficacy of vismodegib or if vismodegib will prove helpful in treating other cancers. However, current evidence warrants further studies to investigate these possibilities.