Toxicity and feeding response of adult corn earworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to an organic spinosad formulation in sucrose solution ()
1. INTRODUCTION
EntrustTM is a natural insect control product formulated from the spinosyn family of insecticides for the organic growers. The spinosyns are fermentation by-products of the soil borne actinomycete bacterium, Saccharopolyspora spinosa Mertz and Yao [1]. Spinosad consists of two principal fermentation factors, Spinosyns, A and D and is a fast acting broad spectrum chemical that acts on the insect primarily through ingestion or contact with the sprayed surface [2]. It affects the nervous system of the insect and activates the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and causes loss of muscle control, exhaustion and culminates in the death of the insect. In the tobacco budworm larvae, Helithis virescens (F), Spinosyn A causes diuresis and widespread tremors of the extremities and the larvae curl up and lay on their sides [3].
Public awareness of the hazards associated with pesticides has burgeoned consumer interest in organically produced farm products in the United States [4]. This has resulted in the organic farming sector to continuously increase its market share each year and has now become a $30 billion industry [5]. Organic farms have increased from 11 million ha in 1999 to 37.2 million ha in 2011 worldwide [6]. Concomitant with these developments in organic farming, there has been a renewed interest in the reformulation of pesticides that are compatible for usage in organic farms. For instance, the inert ingredient, propylene glycol, contained in SpinTor® 2SC was replaced with more ecologically compatible kaolinite clay in EntrustTM (SpinTor® 2SC; MSDS 2012; EntrustTM 80 W; MSDS 2013, Dow AgroSciences, Indianapolis, Indiana). With the approval from the Organic Materials Review Institute (OMRI) for use in organic farming and gardening, Entrust is also classified as an organic substance by the USDA National Organic Standards Board, and is in conformity with the FAO/WHO “Codex Alimentarius” and IFOAM (International Federation of Organic Agriculture Movements) standards.
Pesticide control of heliothine insect pests is traditionally conducted targeting larval instars which feed on fruiting structures of host plants. However, several researchers contend that adult control of highly mobile heliothine insects would be more beneficial compared to traditional method of control of larvae with broadcast application of synthetic pesticides. For instance, heliothine adults were 10 to 100 times more susceptible to insecticides compared to larvae, and that adults were much less likely to develop resistance to insecticides compared to larvae [7]. Also, higher detoxification associated with cuticular penetration, internal accumulation, excretion of applied toxicants and their metabolites occurred more rapidly in larvae compared to that in adults [8].
Adult females upon emergence from pupal cells in their natural habitat disperse in quest of carbohydrate-rich food source, usually obtained from plant exudates, before resuming their reproductive activity [9-11]. This nocturnal behavior of H. zea has the potential for exploitation in developing pest management strategy for organic farming systems. Researchers have developed attractants for several noctuid species of Lepidoptera and that when the attractant composition is mixed with a toxicant, it could serve as a lethal food source [12]. However, despite the worldwide growth of organic agriculture, there has been a lack of research-based information on arthropod pest management strategies suitable for such farming systems [13].
Objectives of this study were to determine rate of ingestion, toxicity and proboscis extension response of adult corn earworm, Helicoverpa zea (Boddie) relative to an organic formulation of spinosad, Entrust when mixed with sucrose solution as a feeding stimulant. The intent of this study was to determine whether Entrust, when mixed with a sugar solution as a feeding stimulant, could serve as a cynosure of attraction, delivering a lethal food source for foraging moths.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1. Test Solutions
We weighed 1.25 g of EntrustTM 80 W (EPA Reg.# 62719-282; 80% spinosad and D, 3.4% kaolin, 2% silica gel and the balance 14.6%; MSDS 2013; Dow AgroSciences, Indianapolis, Indiana) in a Sartorius balance (Model No. LA 120S). Using 10% sugar (Sigma Chemical Co., St Louis, Missouri) solution as a feeding stimulant, we prepared a stock solution of the pesticide at 10,000 mg∙L−1. The sugar solution was prepared by weighing 100 g of sugar and made up to a volume of 1 L. Various concentrations of test solutions were then prepared by appropriate dilution with the sugar solution.
2.2. Laboratory-Reared Test Insects
Corn earworm eggs were obtained from Department of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology, Entomology and Plant Pathology, Mississippi State University, Mississippi. Eggs were held for hatching in the laboratory maintained at 23.9˚C ± 0.38˚C, RH 64.5% ± 4.6% with a photoperiod of 14:10 L:D. Larvae were reared on a soybean-wheat germ diet [(Stonefly Heliothis Diet, Ward’s Natural Science (www.wardsci.com)]; using similar techniques described earlier [14]. During the rearing procedure, approximately 4 g of the diet was dispensed into a 22.2 ml plastic soufflé cup using a caulking gun and an individual larva was placed on the diet and sealed with a lid. About 250 cups were prepared each time and were stored in a 1/6- 57# paper bag in the laboratory. About 3 wks thereafter, pupae were harvested, sorted by gender, and male and female pupae were placed separately in 4 L jars for moth emergence.
2.3. Field-Collected Test Insects
The natural populations of corn earworm comprised of those captured in pheromone-baited wire cone traps baited with Zealure®, the synthetic male sex attractant (Hercon Environmental, Emigsville, Pennsylvania). Traps were established in an agricultural production area in the Brazos Bottom Region in Burleson County, southwest of College Station, Texas (30.6278˚N, 96.3342˚W). Males captured during the previous night were collected early in the morning and were placed in a BugDorm-1 (www.megaview.com.tw) insect rearing cage, and kept in the laboratory for testing.
2.4. Feeding Mechanism
The feeding apparatus used in this study was described earlier [15,16]. Amount of Entrust ingested by each corn earworm was determined by providing test solutions of the chemical in a 0.5 ml disposable centrifuge tube. Test solutions were weighed on an electronic balance before and after feeding. To account for the evaporation loss during the feeding period, extra tubes containing the test solutions on which the moths did not feed were used to obtain the amount loss between before and after feeding. Each moth was placed in an apparatus equipped with alligator clips to hold the wings in a vertical position. Test solutions in centrifuge tubes were placed in a hole drilled in a Plexiglass® block. Immediately, thereafter, the moths extended their proboscides to feed on the test solutions. Moths that did not extend the proboscides were teased with an insect pin to initiate feeding and to ensure adequate feeding, insects were teased multiple times.
2.5. Determination of Lethal Concentration (LC) Values
Both male and female laboratory-reared corn earworms that emerged overnight in the laboratory and feral males captured overnight in pheromone-baited traps were used in this study. Each test consisted of moths fed various sub-lethal concentrations of Entrust at 0.1875, 0.375, 0.25, 0.50, 1.0 mg∙L−1. Control moths were fed 10% sucrose solutions alone. These sub-lethal concentrations were determined after conducting preliminary tests to assess the range of concentrations that would provide appropriate mortality data. In each test, six moths were fed Entrust at each concentration, and the test was replicated 22 times. Immediately after cessation of feeding, moths were sorted by treatment and were placed in a 946 ml jar where 10% sugar solution was provided in a 22.2 ml soufflé cup closed with a lid through which a cotton wick in contact with the sugar solution was inserted. Two strips of paper towel were left hanging inside the jar to enable the moths to rest and move around within the jar. Mortality was determined 24, 48 and 72 h after feeding.
The assessment of mortality is usually based upon the criterion that the moths could not right themselves when placed upside down [16]. In this study, we observed variant symptoms of poisoning between individual moths after the ingestion of Entrust by the corn earworm. Often the moths which fed to satiation had bloated abdomen, the proboscides were extended with the terminal end being rolled in and the wings were lifted up. Some moths had their genitalia extruded, and lay on their sides inside the cup with the wings lifted up and the body twitching. We considered moths showing such symptoms of poisoning dead because they were incapacitated and were moribund.
2.6. Determination of Mean Lethal Time
In order to determine mean lethal time, we chose the 50 mg∙L−1 concentration of Entrust, the minimum spray application rate at 46.8 L∙ha−1 for control of corn earworm larvae in sweet corn (Specimen Label, Dow AgroSciences, Indianapolis, IN). We conducted two tests relative to the determination of mean lethal time. In test 1, we determined ingestion of Entrust at 50 mg∙L−1 by feeding feral males captured overnight in pheromone-baited traps using the feeding apparatus described earlier. A total of 156 moths were fed Entrust in groups of 6 and were compared to control moths fed 10% sucrose solution alone. In test 2, moths fed at 50 mg∙L−1 were placed individually in a 22.2 ml soufflé cup after feeding, and were examined every 15 min. for mortality. A total of 66 moths were fed in groups of 6 and were compared to control moths relative to mortality.
2.7. Feeding Response at Lethal Concentrations
Moths were fed Entrust at concentrations of 0.1, 1.0, 10, 100 and 1000 mg∙L−1 in order to determine the effect of lethal concentrations of the pesticide relative to ingestion. Control moths were provided only 10% sucrose solutions. Test moths comprised of both laboratory-reared and field-collected corn earworm. These moths were grouped into two categories. Group 1 comprised of corn earworm that emerged overnight in the laboratory as well as those captured overnight in pheromone-baited traps. Similarly, group 2 comprised of both laboratory-reared and field-collected corn earworm held for 24 h without feeding. A total of 30 to 36 replications were conducted in each group.
2.8. Proboscis Extension Bioassay
The proboscis extension response assay measures the taste behavior of H. zea and is a useful technique to measure the sense of taste. Stimulation of gustatory receptor neurons on the antennae, the tarsi and the mouthparts elicits the proboscis extension response in tobacco budworm, H. virescens [17]. The methods used to determine the proboscis extension response were similar to those described earlier [18]. Briefly, they comprised of holding a moth with the index finger and the thumb and touching the front tarsi to the test solutions in a porcelain multiwall plate by raking the front legs across it while avoiding contact of other body parts with the test solution. The proboscis extension response comprised of three phases. If the proboscis was completely extended (a positive response), a rating of 2 was assigned, and if the proboscis was partially uncoiled but was retracted without fully extending (a partial response), a rating of 1 was recorded and if there was no extension of the proboscis (a negative response), a rating of zero was recorded.
The proboscis extension response was evaluated in the laboratory in the afternoon using H. zea captured overnight in pheromone-baited traps and those held for 24 h without feeding. Moths comprising of the two age groups were exposed to concentrations of the chemical at 0.1, 1, 10, 100 and 1000 mg∙L−1. Five replications comprising of 20 males per concentration were conducted for each age group of the insect. A total of 100 males per concentration were used in each test.
2.9. Data Analysis
All statistical analyses of the data were conducted using SAS 9.3 version [19]. Lethal concentration data were analyzed using the Proc Probit log10 procedure with LACKFIT and INVERSECL options. The failure of 95% fiducial limits to overlap was used as a criterion to separate LC50 values between 24-, 48- and 72 h responses in the dose-response models [20]. Statistical validity of this criterion to separate LC values for data with large sample size and approximately equal standard errors was demonstrated by Payton et al. using a computer simulation model [21]. Data reported here include tests with large sample size (N = 204 to 372 moths) and nearly equal standard errors (See Tables 1-3) between the slopes of probit regressions. Traditionally, we assume a dose response relationship between the levels of a factor representing increasing amounts x of Entrust and the response y (mean % proboscis extension or the feeding response), and execute the regression of y on x. In this study, neither the feeding response nor the proboscis extension response exhibited a normally expected functional relationship between y and x. Instead, we found that variations between individual moths predominated in each of these test variables without any apparent dose response relationship. For instance, some moths fed to satiation at higher concentrations of Entrust to the extent that they succumbed soon after ingestion of the toxicant. This behavior demonstrated that regression analysis is not appropriate for this study and that a variance analysis instead will adequately describe the relationship between the variables. Therefore, data on proboscis extension response and feeding studies were analyzed using PROC GLIMMIX model. When means were significant (p < 0.05), least square means were separated using PDMIX800 letter grouping procedure with adjust = Tukey (p < 0.05) [22]. Variability in the amount of Entrust ingested and the concentrations of pesticide offered to the insect was equalized by transforming the data into natural log before conducting ANOVA procedure. The corn earworm lethal time data relative to the rate of ingestion of Entrust was conducted using the PROC REG procedure.

Table 1. Probit statistics relative to toxicity of Entrust 80 W mixed with 10% sucrose solution fed to male corn earworm, H. zea captured overnight in pheromone-baited trap.
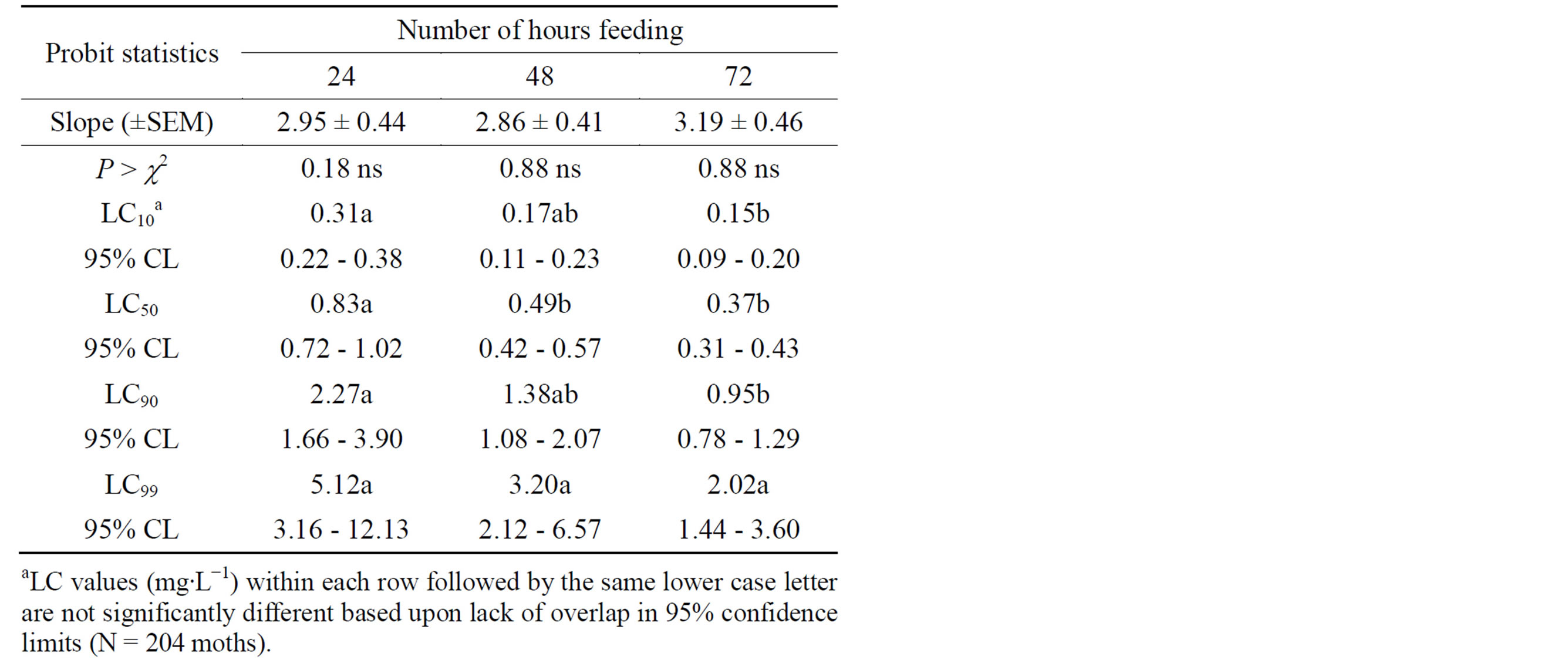
Table 2. Probit statistics relative to toxicity of Entrust 80 W mixed with 10% sucrose solution fed to laboratory-reared male corn earworm, H. zea which emerged overnight.

Table 3. Probit statistics relative to toxicity of Entrust 80 W mixed with 10% sucrose solution fed to laboratory-reared female corn earworm, H. zea which emerged overnight.
3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1. Toxicity
Table 1 shows that for natural populations of male corn earworm captured overnight in pheromone-baited traps, the dosage mortality equations were in agreement with the probit model for 24-, 48- and 72-h responses (Table 1). The LC50 (95% CL) was 0.48 (0.43 - 0.53) mg∙L−1 for 24 h response and was significantly different from those for 48 and 72-h responses with 0.31 (0.26 - 0.35) and 0.26 (0.23 - 0.30) mg∙L−1, respectively. There was, however, no significant difference between 48 and 72 h responses for both LC50 and LC90 values. In an earlier study with spinosad (Tracer® 44.2% spinosyn A and D; inert ingredients including propylene glycol ≈ 55.8%;
MSDS 2001) mixed with 2.5 M sucrose solution, we reported that LC50 and LC90 values for feral male corn earworm were 4.96 (4.29 - 5.67) and 21.83 (17.35 - 29.84) mg∙L−1 for 24 h responses, respectively [23]. Compared to spinosad, Entrust is 10- and 20-fold more toxic to feral male corn earworm, respectively, as indicated by LC50 and LC90 values. The increased toxicity of Entrust to H. zea is more likely due to a 2-fold increase in concentration of the spinosad A and D in Entrust compared to that in spinosad.
Table 2 shows that the LC50 and LC90 values of Entrust for laboratory-reared male corn earworm which emerged overnight were 0.83 (0.72 - 1.02) and 2.27 (1.66 - 3.90) mg∙L−1, respectively. These values were significantly greater than those for the pheromone trap-captured males. It is likely that the feral corn earworm might have been leaner compared to the laboratory-reared moth, and that the corn earworm probably responded to the toxicant in direct proportion to body weight. This is in agreement with Australian researchers who reported that pyrethroid susceptible old world bollworm, H. armigera (Hübner) pupae were lighter than those of the resistant pupae, although differences in resistance frequencies were not significantly related to body weight of pupae collected from maize, pigeon pea and cotton [24]. However, researchers have cautioned against unquestioned use of proportional adjustment of dose to body weight without testing the hypothesis that the response is proportional to body weight. This may result in erroneous conclusions about relative toxicities [25].
Table 3 shows LC50 and LC90 values of Entrust for laboratory-reared female corn earworm which emerged overnight were 0.77 (0.68 - 0.92) and 1.92 (1.46 - 3.05) mg∙L−1, respectively. These values were not significantly different from those reported for laboratory-reared males (Table 2).
3.2. Proboscis Extension Response
Entrust concentrations tested in this study did not significantly influence the proboscis extension response for the moths captured overnight in pheromone-baited traps for any of the three phases of the response: positive, negative and partial (F = 0.76, p > 0.59 for positive; F = 0.47; p > 0.79 for negative and F = 0.55; p > 0.74 for partial, each with 5, 20 df), respectively. However, the frequency of extending their proboscides positively upon contact with Entrust solutions for moths captured overnight was significantly different from that for moths held for 24 h (F = 171.51; df = 1, 24; p < 0.0001; Table 4). Similarly, the negative response of the moths not responding to Entrust solutions upon contact varied significantly between 24 h old moths and those captured overnight (F = 140.61; df = 1, 24; p < 0.0001); however, the response was conversely related. Entrust did not significantly in-
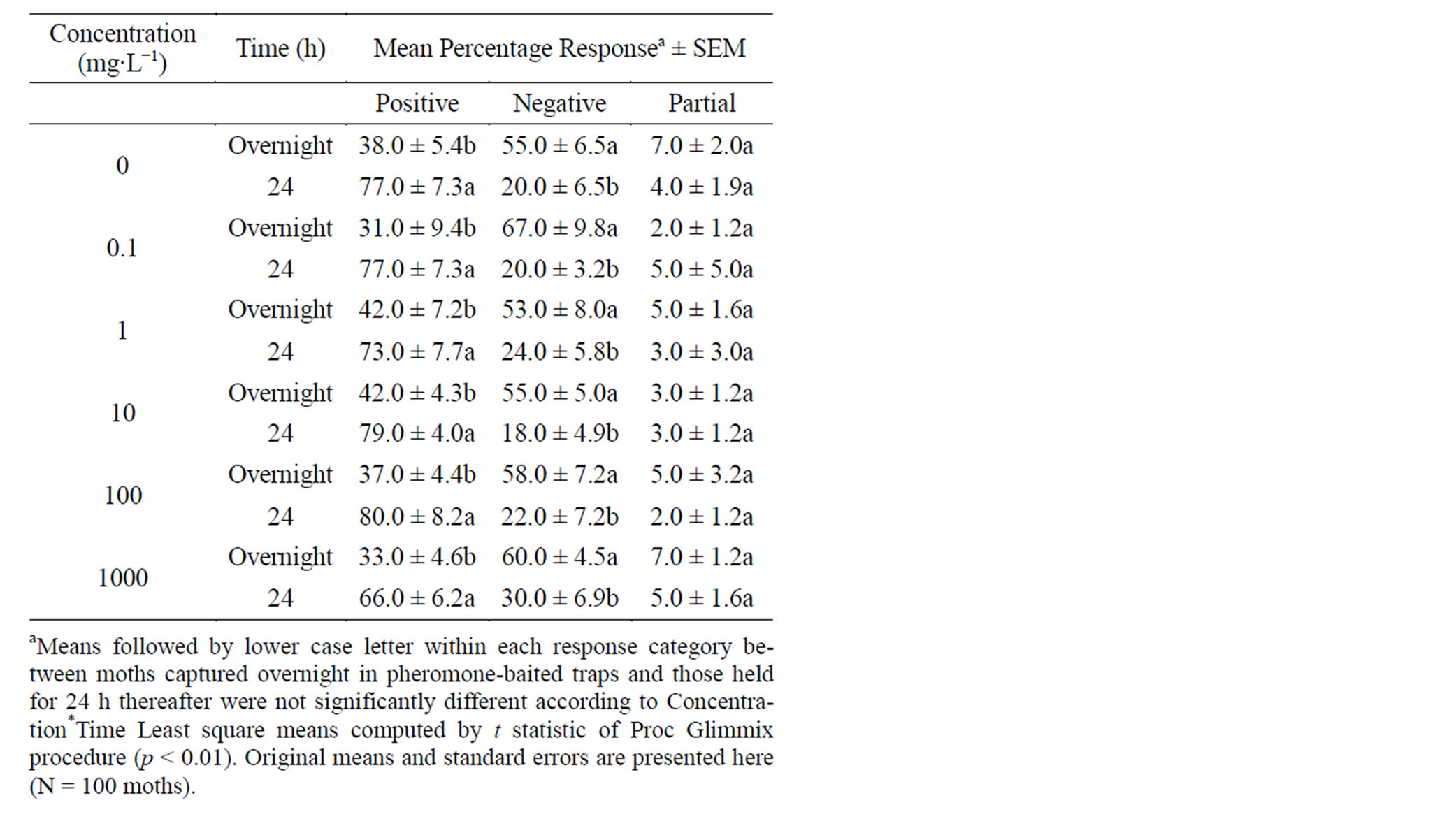
Table 4. Proboscis extension response (±SEM) of H. zea males captured in pheromone-baited traps to various concentrations of Entrust 80 W mixed with 10% sucrose solution.
fluence partial extension of the proboscis for feral corn earworm captured overnight in pheromone-baited traps when compared to those held for 24 h thereafter in the laboratory (F = 0.89; df = 1, 24; p > 0.36). There was no significant interaction between moths captured overnight and those starved for 24 h relative to any of the components of proboscis extension response (F = 0.49, p > 0.78 for positive; F = 0.76, p > 0.59 for negative; F = 0.56, p > 0.73 for partial, each with 5, 24 df).
The ability of the moth to extend its proboscis upon contact with a toxicant solution is indispensable for feeding initiation. Regardless of concentrations, 24 h old h old corn earworm positively responded to Entrust solutions by extending their proboscides completely more frequently compared to moths captured overnight in pheromone-baited traps. This suggests that 24 h old moths were more appetitive compared to moths captured overnight in pheromone-baited traps. Also, the 24 h starvation time appears to have brought the corn earworm to a proper responsive state. The frequency of deterrence of the corn earworm to feed on Entrust solutions was significantly more common for corn earworm captured overnight in pheromone-baited traps than for those held for 24 h without feeding. The percentage of moths that exhibited partial response to Entrust solutions was minimal with less than 10% of the moths extended their proboscides, but retracted soon thereafter.
The proboscis of the tobacco budworm, H. virescens exhibited 100% positive response to 1.0 M sucrose, but showed a weak or no response to an insect deterrent, 1.0 M sinigrin monohydrate [17]. Stimulation of gustatory receptor neurons located in the antennae and the proboscis of the moth elicits the proboscis extension response in H. virescens [26]. Data reported here demonstrate that the lethal concentrations of Entrust did not inhibit neural transmission of information from the gustatory receptor neurons in the corn earworm to elicit proboscis extension response.
3.3. Feeding Response at Lethal Concentrations
Figures 1 and 2 show that the feeding response of laboratory-reared female corn earworm to concentrations of Entrust did not significantly differ for moths that emerged overnight (F = 2.25; df = 5, 165; p > 0.05) as well as for moths held for 24 h without feeding (F = 1.10; df = 5, 187; p > 0.36) when compared to female fed 10% sucrose solutions alone. Similarly, the feeding response of 24 h old laboratory-reared male corn earworm to Entrust did not vary significantly between concentrations (F = 1.23; df = 5 and 191; p > 0.29) when compared to control male fed 10% sucrose solution alone (Figure 3).
Nevertheless, the feeding response for male moths captured overnight in pheromone-baited traps did vary
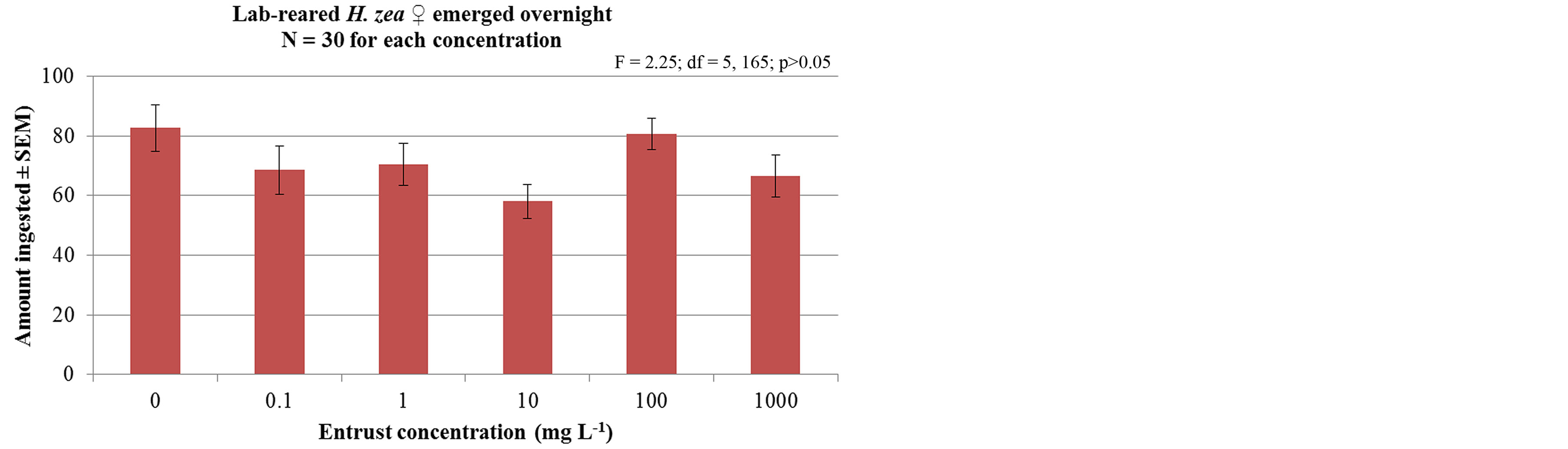
Figure 1. Mean (±SEM) amount of Entrust ingested by labreared H. zea female emerged overnight when fed various concentrations of the chemical mixed with 10% sucrose solution.

Figure 2. Mean (±SEM) amount of Entrust ingested by 24-h old lab-reared H. zea female when fed various concentrations of the chemical mixed with 10% sucrose solution.

Figure 3. Mean (±SEM) amount Entrust ingested by 24-h old lab-reared male H. zea when fed various concentrations of the chemical mixed with 10% sucrose solution.
significantly between concentrations of Entrust (F = 2.28; df = 5, 183; p > 0.049) when compared to control moths fed 10% sucrose solution alone (Figure 4). Corn earworm male moths fed significantly less Entrust at 1000 mg∙L−1 compared to those fed Entrust at 0.1 mg∙L−1. There was no significant difference in ingestion between moths fed Entrust at 0.1 mg∙L−1 and those fed 10% sucrose solution alone. Ingestion of Entrust at 1, 10 and 100 mg∙L−1 was comparable to one another, and did not vary significantly from control moths as well. However, there was no significant difference in feeding response between moths captured in pheromone-baited traps and held in the laboratory for 24 h without feeding and control moths fed 10% sucrose solutions alone (Figure 5; F = 1.63; df = 5, 210; p > 0.15). Data show that the inhibition of ingestion of Entrust at the lethal dose of 1000 mg∙L−1 occurred only with H. zea male captured overnight in pheromone-baited traps and that inhibition was not evident in any of the other more exhaustive tests conducted in this study. This suggests that the inhibition of feeding of Entrust at the lethal dose may not be a genuine phenomenon but that it is likely to be an artifact.
3.4. Mean Lethal Time
Figure 6 shows that in test 1, corn earworm consumed significantly less Entrust at 50 mg∙L−1 compared to control moths fed 10% sucrose solution only (F = 4.96; df = 1, 232; p > 0.027). In test 2, the analysis of the data relative to ingestion of Entrust at 50 mg∙L−1 and lethal time revealed a significant curvilinear relationship which leveled off asymptotically (Figure 7). There is a decided tendency, as shown in Figure 7, for the corn earworm to succumb to the ingestion of the pesticide within 5 h. With the X variate converted to natural log, the regression of lethal time on ingestion of Entrust showed that lethal time decreased as the amount of Entrust ingested by the corn earworm increased (Figure 8). The regression model was Y = −0.857ln(X) − 0.2303 with R2 = 0.3587. The regression model indicated that only 36% of

Figure 4. Mean (±SEM) amount of Entrust ingested by male H. zea captured overnight in pheromone-baited traps when fed various concentrations of the chemical mixed with 10% sucrose solution. Least square means were separated using PDMIX800 letter grouping procedure with adjust = Tukey (p < 0.05). Bar with the same lower case letter is not significantly different from each other.

Figure 5. Mean (±SEM) amount of Entrust ingested by 24-h old male H. zea captured in pheromone-baited traps when fed various concentrations of the chemical mixed with 10% sucrose solution.

Figure 6. Mean (±SEM) amount of Entrust at 50 mg∙L−1 ingested by corn earworm compared to 10% sucrose solution.
the variation in the ingestion of the chemical was explained by the variations in lethal time. The low R2 value

Figure 7. Relationship between amount of Entrust at 50 mg∙L−1 ingested and lethal time for H. zea male captured overnight in pheromone-baited traps. Arrows show two moths which each ingested 106.4 and 113.5 mg∙L−1 of Entrust had a lethal time of 1.5 h, and another moth which ingested only 44.7 mg∙L−1 of Entrust died within 0.5 h.

Figure 8. Relationship between log amount of Entrust at 50 mg∙L−1 ingested and lethal time for H. zea male captured overnight in pheromone-baited traps.
appears to be due to considerable variability in lethal time between individual corn earworm relative to ingestion of Entrust. For instance, Figure 7 shows that two moths which ingested 106.4 and 113.5 mg∙L−1 of the chemical took 1.5 h each to die, while one of moths which consumed 44.7 mg∙L−1 of the pesticide died within 0.5 h. Fourteen percent of the moths, which died at 2 h, exhibited 5.3-fold difference in the ingestion of the pesticide between individual insect. Overall, mean lethal time for the corn earworm was 2.56 ± 0.13 h with ingestion of Entrust at 50 mg∙L−1. We reported earlier that a similarly negatively linear relationship existed between lethal time and ingestion of spinosad for feral corn earworm captured in pheromone-baited traps in the Brazos Bottom region in Texas [23]. Mean lethal time was 5.3 h with the ingestion of spinosad at 73 mg∙L−1. Our data are in agreement with researchers in Australia who found that spinosad produced very high mortality of the old world cotton bollworm, H. armigera and H. punctigera, but that moths took much longer to die [27]. Rapid incapacitation or mortality of test moths is important for sampling dead moths near treated rows while evaluating the efficacy of insecticidal baits in an attract-and-kill management strategy [27]. They, Del Socorro et al. [27] found significantly more dead moths near rows treated with methomyl compared to those treated with spinosad. This suggests that quick acting Entrust would be preferable over spinosad in field trials during development of a behavioral-based pest management strategy for heliothine insects.
4. CONCLUSION
Recent trend in increased awareness of organically produced fruits and vegetables concomitant with the public willingness to pay premium prices for these products has attracted many growers to organic farming. Organic food market grew at 12% per year from 2000 to 2010 with sales of natural and organic foods exceeding $40 billion in 2010, and is expected to grow at 8% from 2010 through 2013 [28]. Nevertheless, the organic farms are not growing fast enough to meet the surging demand for organic meat and dairy products in the United States. For instance, in order to meet the domestic needs of this industry, the value of organic soybean imports from China and India to the United States doubled last year and is expected to surpass $100 million in value in 2013 [29]. Data reported here indicate that Entrust will be a useful tool as applicable to attract-and-kill technology to control heliothine insects in organic farming systems. This technology is not gender specific and targeting virgin females before they mate and reproduce will be an effective management program. Furthermore, organic farms are usually small scale operations and treating small acreage of vegetation with syrup-based feeding stimulant/toxicant mixture using a backpack sprayer will annihilate large populations of reproducing of H. zea on host crops. It was estimated that in the Coastal Plains area of Texas that nearly a million moths could be killed by treating one ha of row of corn using only 20 g of toxicant and 190 L of a sugar-syrup-based feeding stimulant [30]. Soon after the emergence of H. zea from pupae in corn fields, moths climb up corn stalks and feed on exudates from the stalks [10]. Furthermore, the corn earworm moths do not oviposit until 2 d after emergence [10,31]. This behavior provides some windows for conducting spray applications, and can be exploited for the development of an attracticide-based insecticidal bait formulation for controlling corn earworm on its host crop. Even though our results show encouraging trends in the control of heliothine species, additional studies are needed to ascertain the efficacy of attract-and-kill technology in field plots.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We appreciate the assistance of Curtis Hubbard who serviced and maintained the pheromone traps. Parker Knutson helped in conducting the tests on ingestion, toxicity and proboscis extension response reported in this study.
DISCLAIMER
Mention of a commercial or proprietary product does not constitute an endorsement for its use by the US Department of Agriculture. USDA is an equal opportunity employer.