A preliminary study on the treatment of bruxism by biofeedback therapy ()
KEYWORDS
Biofeedback; Bruxism; Splint
1. INTRODUCTION
Bruxism is a health problem that involves grinding or tightly clenching of the upper and lower teeth. The incidence of bruxism is 8% - 10% in adults [1]. It has serious negative impacts on peoples’ health conditions like tooth attrition, masticatory myofascial pain [2], headache, ear pain and disorders of temporomandibular joint. the noise produced by tooth grinding can be loud enough to disturb the sleep of anyone nearby [3]. Results from Nishigawa’s study on the bite force produced during bruxism episodes suggested that values as high as 1100 N have exceeded the maximum voluntary bite force. The aetiology of sleep bruism is multi-factors, such as psychosocial factors, genetical factors, and neurological factors or combined factors [4]. Treatment of bruxism such as behavioral treatment or splint treatment required long-term therapies and had slow effects. We bring biofeedback therapy to bruxism treatment which is reported to be effective. This study is therefore going to access the clinical efficacy of splint treatment by the wireless biofeedback therapy and to provide a new method for bruxism treatment.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1. Patients
The study included 15 bruxism patients from Department of Stomatolagy, Benq Medical Center, Nanjing Medical University. We obtained full consent from all patients in accordance with local ethics committees at Benq medical Center. They all enrolled and signed the informed consent form before the therapy. There were 8 men and 7 women, age from 20 to 40 years (mean 27.3 years). The primary diagnosis included several symptoms like: the night bruxism longer than 6 months and were confirmed by clinic examination and roommates sleep nearby, all full denture with/without tooth attrition, bruxism patients with/without temporomandibular disorders, with no history of neurotic and psychological disease.
2.2. Experiment Procedure
The wireless biofeedback instrument is mainly divided into two parts (Figure 1): the strain and the monitoring part, and the analysis and vibration part. When the patient was diagnosed as bruxism, we take the impression to make a maxillary occlusal splint using resin material. According to patient’s intercuspal position, embedded the strain gauge in the splint at the part of the mandibular canine which patient can contact with. The monitoring circuit (18 mm × 16 mm × 5 mm) and the button battery (CR2015, Panasonic, Indonesia, 20 mm × 2.5 mm) were all packed inside the splint. The margin of splint can be extended, so that the whole equipment can be all placed (Figures 2 and 3).
The stress strain gauge would gather the information about the grinding or clenching movement during sleep in patients, including the value of bite force, occurring time and the duration per 8 h sleep, the signals would be recorded in 3 nights without vibration so we can obtain the data about the patients to set the threshold from norm value to maximum. Then the data were sent to the analysis and vibration device in wireless mode. When information was accepted, meanwhile comparing with the threshold, when the value is exceeded the threshold for 3 seconds [5], the therapeutic instrument would vibrate to wake patients. The vibration equipment was designed for the wrist wearable, so that patients in sleep can sense the vibration if the value exceeded the threshold during sleep, thus awakened to relax the masticatory muscles and nervous system and stop the abnormal tooth movement.
The episodes and duration of bruxism were analyzed After 12 weeks and 24 weeks of continuous monitoring during 8 hours sleep, the difference between pre-therapy and post-therapy were accessed by univariate ANOVA, the comparisons with the significance set to two sides p < 0.05 in spss19.0 with least significant difference method (LSD).
3. RESULTS
The results about episodes and duration of bruxism before and 12 weeks and 24 weeks after treatment were shown in Table 1, and Figures 4 and 5.
3.1. Pre-Therapy
The average total episode of 15 bruxisers during 8 hours is (10.60 ± 1.23), the maximum is 14 times and the minimum is 9 times. The average duration of bruxism is (13.2 ± 0.74) s.
3.2. Post-Therapy
After 12 weeks treatment the average total episodes of 15 bruxisers during 8 hours is (6.60 ± 0.75), the maximum is 8 times and the minimum is 5 times. The average duration of bruxism is (6.50 ± 0.40) s.

Figure 1. The biofeedback therapy system.
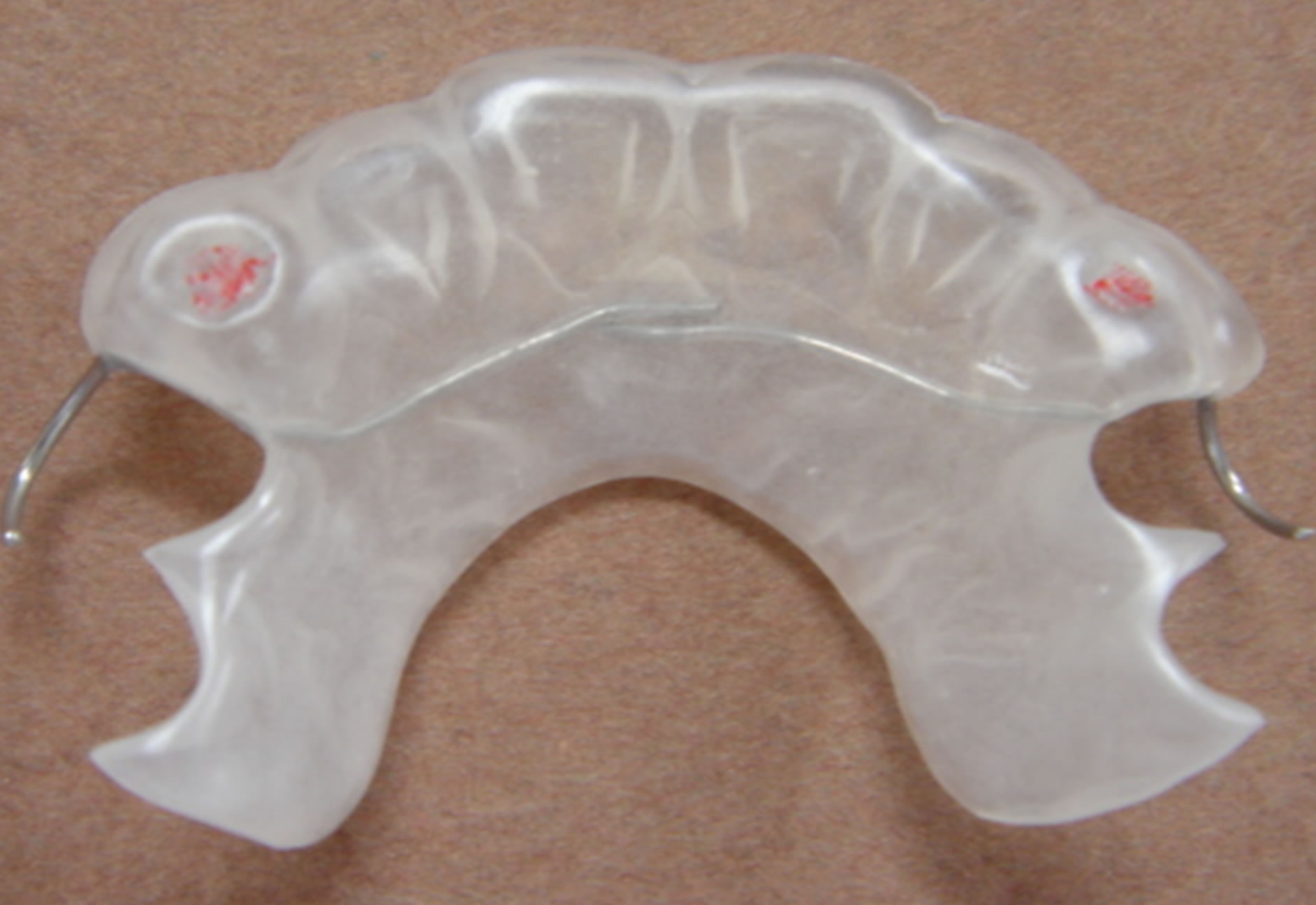
Figure 2. The maxillary biofeedback splint (Yin Xinmin Splint).

Figure 3. The monitoring circuit (18 mm × 16 mm × 5 mm) and the button battery (20 mm × 2.5 mm), and the receiver.
After 24 weeks’ treatment the average total episodes during 8 hours is (3.80 ± 0.64), the maximum is 5 times and the minimum is 3 times. The average duration of bruxism is (3.37 ± 0.34) s.
There was significant difference (p < 0.05) between pre-therapy and 12 weeks treatment of bruxism episodes and duration, so was significant difference (p < 0.05) between pre-therapy and 24 weeks treatment, but there are no significant difference between 12 weeks and 24 cant difference (p < 0.05) between pre-therapy and 24 weeks treatment, but there are no significant difference between
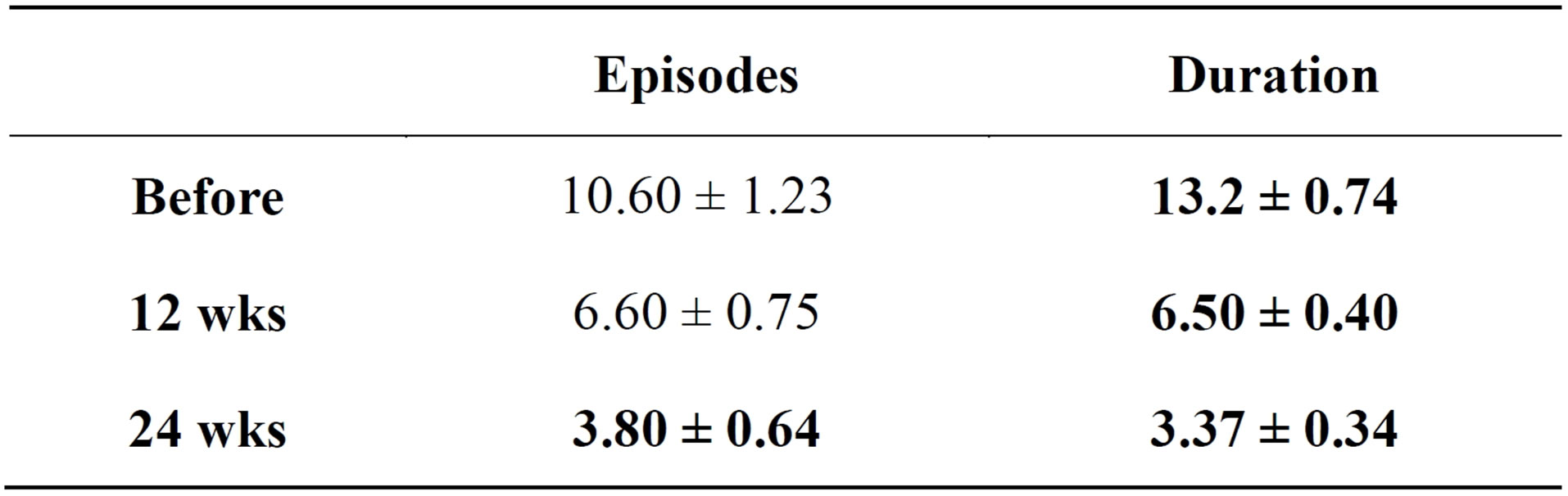
Table 1. Total episodes and duration of bruxism before and 12 wks and 24 wks after treatment .
.

Figure 4. The episodes of bruxism before and 12 wks and 24 wks treatment.

Figure 5. The duration of bruxism before and 12 wks and 24 wks treatment.
12 weeks’ and 24 weeks’ treatment (p > 0.05).
4. DISCUSSION
Most scholars believe that the etiology of bruxism is not well understood, and occlusal factors and mental factor may be the main causes of bruxism [6], which is commonly treated by drug treatment, psychological therapy and occlusal splint therapy. Occlusal splint treatment is still a common therapy in clinical treatment of splint [7], but it needs long-term therapy in order to have slow improvements in sleep bruxiam [8]. This study has focused on the treatment of a splint called “Yin Xinmin” splint. It was named by Major M. Ash [9]. It has been shown to have an effective prognosis in clinical treatment [10].
The other treatment of bruxism is the biofeedback therapy. It uses the conception of the neuromuscular system with electronic instrument activity. This information can be devised to be visual or auditory signals so as to give feedback to the patient, then the regulation of psychological and physiological changes about patients can achieve the therapeutic effect, including the EMG bio-feedback [11], aversive taste feedback method, psychological treatment combined with biofeedback method etc. The pressure strain and monitoring of miniature circuit were used in occlusal splint. When the patient wears the split, once in contact with the strain gauge, it can be collected in bruxism for episodes and duration, then the splint and vibration device can be connected in a wireless way. It is convenient and easy to be carried with, when the data are received higher than the set threshold, a vibration signal which would awake patients and stop the abnormal movement. According to the report, the awaken rate is about 3 - 4 times per 8 hours’ sleep without obvious interference of sleep, so the efficacy of biofeedback therapy is connected to the patients’ relaxation of learning and training. It depends on the buxisers’ unwilling behavior after awaking. There is no significant difference between 12 weeks’ and 24 weeks’ treatments, so the suitable therapeutic process can be obtained by the further experimental treatment.
Inclusively, 15 patients in this study were treated after 12 and 24 weeks. The brixism total episodes and duration have declined in the therapy. It suggests that biological feedback has a positive effect on the treatment of bruxism management, compared with traditional splint treatment.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like thank Doc WeiPing Gu from Nanjing Medical University and prof. ZhiYu Qian from Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics for their help. This project is funded by Nanjing medical science and technique development foundation (YKK10176).