Improvement of decocting method for Kampo medicines using a microwave oven to extend its applications in clinical practice ()
1. INTRODUCTION
Kampo medicines have been used to treat diseases from ancient times. It is still an important part of the current medical system in Japan, where 83.8% of doctors prescribe Kampo medicines to patients, and about 70% of these doctors consider Kampo medicines have good effects [1]. Kampo medicines used clinically can be divided into decoction and extract. Decoction plays an important role in clinical practice. Since the composition of medicines can be adjusted when using decoction, doctors can form the most suitable prescriptions for their different patients; that is, decoction can enable individualization of treatment. Also, because of its variability, decoction has a wide treatment range. Therefore, decoction is valuable in clinical practice.
However, in Japan, Kampo extract product is used mostly because of the inconvenience of decocting Kampo formulas. Decoction usually requires a long time, 30 - 60 min daily. When decocting Kampo formulas with a gas burner, the regulation of the flame is difficult and requires some experience, and patients must take care to avoid accidents. Of course, patients can buy a special electric device which is safer, but it costs about 20,000 yen, far more expensive than the Kampo medicines themselves. Thus, a long decocting time and complex process are the biggest obstacles to wider application of decoction. Improvement of the decocting method for Kampo formulas is quite necessary to extend the application of decoction in clinical practice and thereby benefit patients.
Recently, microwave technology has been applied to extraction, processing, desiccation and sterilization of crude drugs [2-4]. Microwaves are an efficient heat source; microwave ovens require less heating time than traditional heating methods. In addition, microwave ovens are widely used (97.5%) in Japan [5]. If microwave ovens can be used to decoct Kampo formulas, patients can avoid dangerous fire and don’t need to buy special electric devices; they only need to prepare a teapot which costs about 1500 yen. Therefore, in this study, we devised a method for decocting Kampo formulas using a microwave oven.
We chose kakkonto (Gegentang in Chinese), which is the most widely used Kampo formula in Japan [1], and keishikabushito (Guizhijiafuzitang in Chinese), which contains Processed aconite root (has to be paid attention in clinical practice because of toxic components though it has been processed) as study formulas. Regarding the contents of 8 characteristic components in the kakkonto decoction and 6 toxic components (Figure 1) in the keishikabushito decoction as indices, and with extraction and detoxification effects equal to those of the conventional decocting method as targets, we determined the optimal decocting conditions of the new decocting method for the two formulas with Response Surface Methods (RSMs) [6] to validate the feasibility and safety of this new decocting method.

Figure 1. The detoxification of diterpene alkaloids by two-step hydrolysis.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1. Crude Materials and Chemicals
Kakkonto (daily dose) [7]: We used the same crude drugs (Pueraria root 4 g, Ephedra herb 3 g, Jujube 3 g, Cinnamon bark 2 g, Peony root 2 g, Glycyrrhiza 2 g, Ginger 2 g) followed our previous methods [8,9].
Keishikabushito (daily dose): Cinnamon bark 3 g (Cinnamomum cassia Blume, Lot No. 002811006), Jujube 4 g (Zizyphus jujube Miller var. inermis Rehder, Lot No. 007111015), Peony root 3 g (Paeonia lactiflora Pallas, Lot No. 005311009), Glycyrrhiza 2 g (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisher, Lot No. 002011023), and Ginger 1 g (Zingiber officinale Roscoe, Lot No. 005812002) were purchased from Tochimoto Tenkaido (Osaka, Japan); Processed aconite root 1 g (Aconitum carmichaeli Debeaux, Lot No. B2L0514, Processed aconite root 3 in the Japanese Pharmacopoeia, 16th edition, JP16) was purchased from Uchida Wakanyaku Co. Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan).
The standard compounds paeoniflorin, puerarin, glycyrrhizic acid, cinnamic acid, cinnamaldehyde, 6-gingerol, aconitine, mesaconitine, hypaconitine and benzoylmesaconine were purchased from Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan). The standard compounds ephedrine hydrochloride, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, benzoylaconine and benzoylhypaconine were purchased from Zelang (China). Acetonitrile (HPLC grade) was from Sigma-Aldrich (Tokyo, Japan). Methanol (HPLC grade), phosphoric acid, ammonium acetate, aqueous ammonia, 37% hydrochloric acid, diethyl ether and ethyl acetate were from Wako. Distilled water was prepared by the purification system of Millipore. Tap water (pH 7.2; 24.7 mg/L Ca2+, 6.3 mg/L Mg2+, measured with a polarized Zeeman atomic absorption spectrometer, Z-5300, Hitachi, Japan) was used to prepare the decoction.
2.2. Instruments and Chromatographic Conditions
A MRO-JV200 microwave oven (Hitachi, Japan) and XCK-1000 teapot (Hario Glass, Japan) were used in the new decocting method, and an HMJ3-1000W electric decocting device (Hario Glass, Japan) was used in the conventional decocting method.
The analysis was performed on an HPLC system (Shimadzu, Japan) followed our previous methods, including column, mobile phase and gradient elution conditions for the kakkonto decoction [9]. However, the mobile phase for the keishikabushito decoction was composed of A-40 mM ammonium acetate buffer solution (pH 10.0, adjusted with aqueous ammonia) and B-acetonitrile. The gradient elution conditions were as follows (shown as the percentage of B): 0 - 10 min, 22%; 10 - 18 min, 22% - 24%; 18 - 30 min, 24% - 30%; 30 - 34 min, 30% - 38%; and 34 - 70 min, 38% - 56%. The injection volume was 20 μL. The signals were collected at 234 nm.
2.3. Preparation of Kakkonto Decoction Sample
Conventional decocting method: Kakkonto (daily dose) was decocted with the electric decocting device in 500 mL tap water at 600 W for 40 min followed by filtration through gauze. The volume of decoction was adjusted to 600 mL with tap water after cooling to room temperature. The decoction was then filtrated through filter paper under reduced pressure; the subsequent filtrate was retained and filtrated through a 0.45 μm syringe membrane filter before injection.
New decocting method: Kakkonto (daily dose) was decocted with a microwave oven and teapot at 500 W. Water volume from 500 mL to 700 mL and decocting time from 20 min to 40 min were tested in 13 runs by Central Composite Design (CCD) of RSM. Decocting time of Cinnamon bark from 1 min to 15 min was tested in 6 runs by One Factor Design of RSM. The preparations after decocting were same as those in the conventional decocting method.
2.4. Preparation of Keishikabushito Decoction Sample
Conventional decocting method: Keishikabushito (daily dose) was decocted with the electric decocting device in 500 mL tap water at 600 W for 60 min followed by the filtration through gauze, and the volume of decoction was measured. Then, we filtered the decoction through filter paper under reduced pressure, measured 25 mL of the subsequent filtrate, adjusted the pH to 1 with 37% HCl and extracted with ethyl acetate 3 times (20 mL each time); the mixture was separated by centrifugation (2500 rpm, 5 min), and the ethyl acetate layer was discarded to remove the non-alkaloid components. Then, the acidic aqueous solution was basified with 28% ammonia solution to pH 10 and extracted with diethyl ether 3 times (20 mL each time). The mixture was separated by centrifugation (2500 rpm, 5 min), and the diethyl ether layer was kept and dried with a rotary evaporator. The residue was dissolved with 0.5 mL of methanol containing 0.1% (v/v) HCl. The sample was filtrated through a 0.45 μm syringe membrane filter before injection.
New decocting method: Keishikabushito (daily dose) was decocted with a microwave oven and teapot at 500 W. Water volume from 700 mL to 800 mL and decocting time from 40 min to 60 min were tested in 13 runs by CCD of RSM. The preparations after decocting were same as those in the conventional decocting method.
2.5. Preparation of Standard Solutions
A stock solution of standard for kakkonto was prepared followed our previous methods [9]. A stock solution of standard for keishikabushito decoction was prepared by accurately weighing the standard compounds aconitine, mesaconitine, hypaconitine, benzoylmesaconine, benzoylaconine and benzoylhypaconine, and dissolving them in a volumetric flask with methanol containing 0.1% (v/v) HCl. The standard solutions for keishikabushito were diluted from the stock solution of standard with methanol containing 0.1% (v/v) HCl and filtrated through a 0.45 μm syringe membrane filter before injection.
2.6. Optimization Methods
The optimization of decocting conditions was performed with Design Expert software. CCD of RSM was used to optimize the water volume (from 500 mL to 700 mL) and total decocting time (from 20 min to 40 min) for kakkonto. The decocting time of Cinnamon bark, which contains the volatile component-cinnamaldehyde in kakkonto, was optimized from 1 min to 15 min with One Factor Design of RSM. The optimization of the water volume (from 700 mL to 800 mL) and decocting time (from 40 min to 60 min) for keishikabushito was performed by CCD of RSM.
3. RESULTS
3.1. Feasibility Research of Decocting Kampo Medicines with a Microwave Oven
3.1.1. Decocting Kakkonto with the Conventional Decocting Method
Kakkonto was decocted with the conventional decocting method. The contents of the 8 characteristic components are shown in Figure 2. These data were regarded as targets in optimization of decocting conditions of the new decocting method for kakkonto.
3.1.2. Optimization of Water Volume and Total Decocting Time of Kakkonto Using CCD
According to the results of optimization experiments, we found that the volatilization loss of cinnamaldehyde was serious (Figure 3). Therefore, we decided to put Cinnamon bark into the teapot after other drugs had been decocted for some time to decrease the volatilization loss, and optimized the decocting time of Cinnamon bark with One Factor Design. Regarding the contents of characteristic components (except for cinnamic acid and cinnamaldehyde in Cinnamon bark) as indices, water volume and total decocting time were optimized with CCD of RSM. The decocting conditions under which we could obtain almost the same extraction effect as with the conventional decocting method were a water volume of 700 mL and a total decocting time of 35 min. The fitted equations and p-values of ANOVA for response surface models are shown in Table 1 (p-value is the misfit of fitted equation and reality. When p < 0.05, they fit very well in statistics. The p-values in Tables 2 and 3 are same as here), and the response surface is shown in Figure 4 (Desirability is a desirable value. When optimization, a goal is set for each response-component content by researcher freely; Desirability is the approach extent (0 - 1) to the goal. The closer to 1, the closer to goal. Here, goals of the 6 responses were combined into one desirable value to show the total effect. The desirability in Figures 5 and 6 is same as here).
3.1.3. Optimization of Decocting Time of Cinnamon Bark Using One Factor Design
The decocting time of Cinnamon bark from 1 min to 15 min was optimized with One Factor Design. The

Figure 2. Contents of the 8 characteristic components in kakkonto decoction. Data represent mean ± S.D., n = 6; *μl/daily dose.
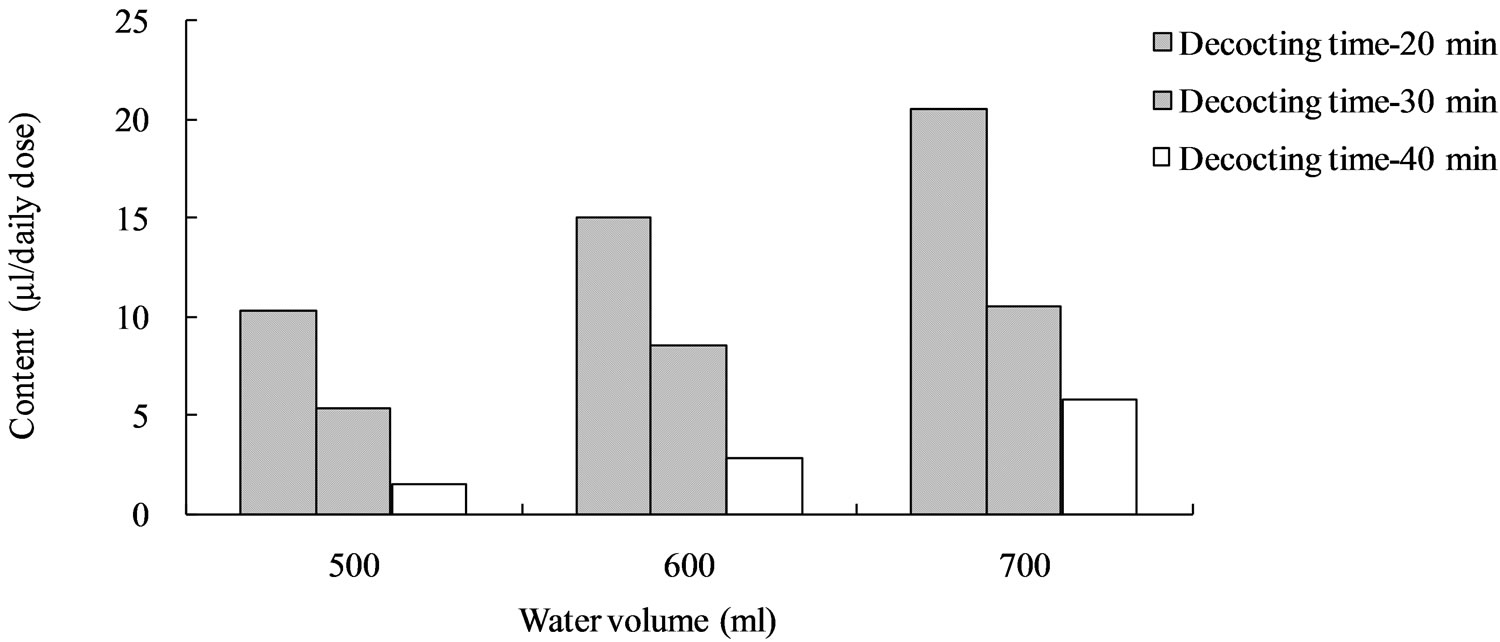
Figure 3. Cinnamaldehyde content in kakkonto decocted with the new decocting method.

Figure 4. Response surface for the effect of water volume and total decocting time on characteristic components (except for cinnamic acid and cinnamaldehyde) content in kakkonto decoction.

Table 1. Fitted equations and p-values of ANOVA for response surface models of the 6 components in kakkonto decoction.
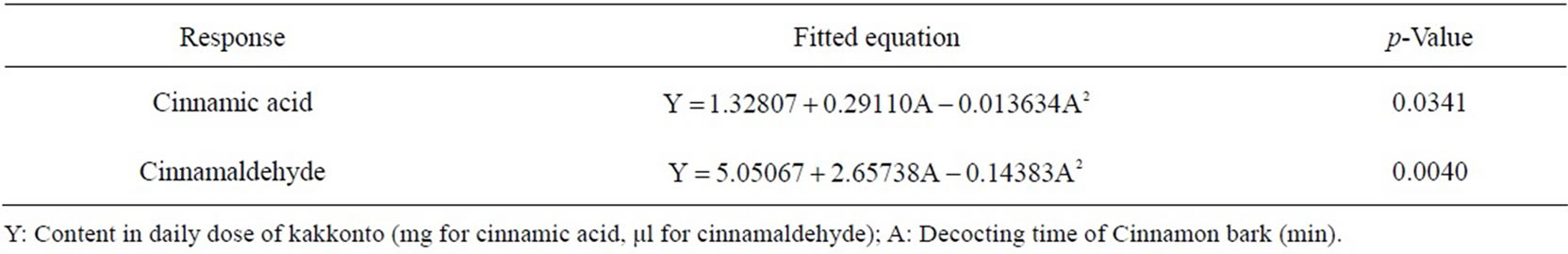
Table 2. Fitted equations and p-values of ANOVA for response curve models of the 2 components in Cinnamon bark in kakkonto decoction.

Table 3. Fitted equations and p-values of ANOVA for response surface models of the 6 toxic components in keishikabushito decoction.
optimal decocting time was 8 min, under which we could obtain almost the same cinnamic acid and cinnamaldehyde contents as with the conventional decocting method. The fitted equations and p-values of ANOVA for response curve models are shown in Table 2, and the response curve is shown in Figure 5.
3.1.4. Decocting Kakkonto under Optimal Decocting Conditions
According to the results of optimization, we decocted kakkonto with the new method in 700 mL tap water at 500 W for 35 min, and Cinnamon bark was decocted later for 8 min. About 385 mL of decoction was obtained. The resulting contents of the 8 components are shown in Figure 2. We could obtain almost the same extraction effect as with the conventional decocting method (600 W, 500 mL water, 40 min, about 364 mL of decoction).
3.2. Safety Research of Decocting Kampo Medicines with a Microwave Oven
3.2.1. Decocting Keishikabushito with the Conventional Decocting Method
Keishikabushito was decocted with the conventional decocting method. The contents of the 6 toxic alkaloids are shown in Figure 7. These data were regarded as targets in the optimization of decocting conditions of the new decocting method for keishikabushito.
3.2.2. Optimization of Water Volume and Decocting Time of Keishikabushito Using CCD
Regarding the contents of the 6 toxic alkaloids as indices, the water volume and decocting time for keishikabushito were optimized with CCD. The decocting conditions under which we could obtain almost the same detoxification effect as with the conventional decocting method were a water volume of 750 mL and a decocting time of 45 min. The fitted equations and p-values of ANOVA for response surface models are shown in Table 3, and the response surface of CCD is shown in Figure 6.
3.2.3. Decocting Keishikabushito under Optimal Decocting Conditions
According to the results of optimization, we decocted keishikabushito with the new method in 750 mL tap water at 500 W for 45 min. About 350 mL of decoction was obtained. The resulting contents of the 6 toxic alkaloids are shown in Figure 7. We could obtain almost the same detoxification effect as with the conventional decocting method (600 W, 500 mL water, 60 min, about 346 mL of decoction).
4. DISCUSSION
In this study, we devised an improved decocting

Figure 5. Response curve for the effect of decocting time for Cinnamon bark on cinnamic acid and cinnamaldehyde content.

Figure 6. Response surface for the effect of water volume and decocting time on 6 toxic alkaloids content in keishikabushito decoction.

Figure 7. Contents of the 6 toxic alkaloids in keishikabushito decoction. Data represent mean ± S.D., n = 4. AC: aconitine, MA: mesaconitine, HA: hypaconitine, BA: benzoylaconine, BMA: benzoylmesaconine, BHA: benzoylhypaconine.
method using a microwave oven and validated its feasibility and safety.
In the feasibility research, we chose kakkonto, the most often prescribed formula as a study formula [1]. Kakkonto is a typical formula for the common cold and influenza. It is composed of 7 crude drugs. We chose 8 characteristic components that are usually studied in quality-control researches as indices [10-13]. Regarding the extraction effect of the conventional decocting method as a target, we optimized the water volume and decocting time with RSMs. Microwave ovens are produced at several grades of power. The most common grades are 200 W and 500 W, which are available options on most microwave ovens, while other grades may only be obtained on expensive microwave ovens. However, the 200 W setting cannot sustain boiling water. Thus, considering our goal for wide application of this new decocting method, we chose the operating power of 500 W.
According to the results of CCD optimization we found that the volatilization loss of cinnamaldehyde is serious because of the violent boiling. The microwave oven is an efficient heating source; the boiling is much more violent and the water evaporation capacity is much greater than those in an electric decocting device; thus, the volatilization loss of cinnamaldehyde in a microwave oven is serious. In this instance, we decided to put Cinnamon bark into the teapot after other drugs had been decocted for some time to decrease the volatilization loss. This also conforms to the Traditional Chinese Medicine theory: drugs which contain volatile components should be decocted later. We optimized the decocting time of Cinnamon bark with One Factor Design.
In the safety research, we chose keishikabushito, which contains processed aconite root as a study formula. Processed aconite root is used widely and largely in Asia. It is prepared from the roots of certain species of Aconitum. The raw roots of Aconitum plants have high toxicity on the nervous system and cardiovascular system; consuming them can even lead to death [14]. Therefore, only processed and detoxified ones can be administrated orally in Japan and China [15]. Aconitine, mesaconitine and hypaconitine are 3 main diester alkaloids with high toxicity in Aconitum, but they are also active components. When processing or decocting, the ester bonds on C-8 of aconitine alkaloids are hydrolyzed and the acetyl groups are lost, yielding benzoylaconine alkaloids with less toxicity. After the further hydrolysis of the other ester bonds on C-14, benzoyl groups are lost to obtain aconine alkaloids with a little toxicity (Figure 1). Wada et al. [16] reported that the LD50 values of aconitine in mice were 1.8 mg/kg p.o., 0.308 mg/kg i.p. and 0.12 mg/kg i.v., those of benzoylaconine were 1500 mg/kg p.o., 70 mg/kg i.p. and 23 mg/kg i.v., and the LD50 value of aconine was 120 mg/kg i.v. This clearly demonstrates that the loss of the acetyl as well as the benzoyl group significantly decreases the toxicity. Though the toxicity is greatly reduced, the pharmacological activities are maintained, because the hydrolysates also have activities [17]. In clinical practice, though processed aconite root has been detoxified, doctors and patients still have to pay attention to its toxic components. A formula contained processed aconite root must be decocted for no less than 60 min. Therefore, the change of decocting method may affect the toxic components, so the safety of this new decocting method must be carefully studied. We chose the 6 toxic alkaloids (aconitine, mesaconitine, hypaconitine, benzoylaconine, benzoylmesaconine and benzoylhypaconine) as indices. Regarding the detoxification effect of the conventional decocting method as a target, we optimized the decocting conditions for keishikabushito with CCD.
5. CONCLUSIONS
In this study, we improved the decocting method for Kampo medicines using a microwave oven to shorten the decocting time and promote convenience, and validated its feasibility and safety. With this new method, it took 35 min (500 W, 700 mL of water), to obtain almost the same extraction effect for kakkonto as that of the conventional decocting method, which takes 40 min (600 W, 500 mL of water); also, it took 45 min (500 W, 750 mL of water) to get almost the same detoxification effect for keishikabushito as that of the conventional decocting method, which takes 60 min (600 W, 500 mL of water).
In conclusion, decocting Kampo formulas with a microwave oven is feasible and as safe as that with the conventional decocting method. Indeed, this method is a convenient, efficient, safe, time-saving, and electric energy-saving decocting method for Kampo medicines. With this method, patients don’t need to buy special decocting devices but rather only use kitchenware they already own. This method may be applied widely in clinical practice; thus, more patients will benefit from decoction and the individualized treatment it offers.
6. ACKOWLEDGEMENTS
Our work was partially supported by Research Grants from the Uehara Memorial Foundation, Japan.