Natural and Anthropogenic Influence in Water Quality: The Case of Linares City, NE Mexico ()
1. Introduction
Research on groundwater quality measurement and assessment is increasing over time due to its scarcity and its impairment by pollution, which can affect its availability for domestic, industrial and irrigation uses [1]. Studies on hydrological modeling [2-5] and groundwater vulnerability [6] are contemporary issues widely studied as well. The groundwater quality depends largely on the presence of natural and/or anthropogenic pollution sources, which must be considered when planning for the development of urban centers. Several related studies have been reported in Mexico, i.e., [7] analyzed the spatial distribution of groundwater hydraulic properties in the Queretaro Valley; [8] reported a numerical analysis depicting the evolution of the hydraulic gradient in fractured rocks in Mexico City; [9] carried out a water balance and water quality assessment in the Valley of Mezquital aquifer; and [10] evaluated the impact of anthropogenic practices on the groundwater quality in the Valley of San Luis Potosí.
Linares is the second largest city of the State of Nuevo Leon, NE Mexico, where development is steadily demanding increasing water supplies for several uses. In addition, in Linares, groundwater is the primary source for human consumption, irrigation and industrial use. Although Pablillo River crosses laterally the study area from SW to NE, it is only used for wastewater discharge. Earlier studies made in this area revealed that anthropogenic impact existed on groundwater quality because of high concentrations of coliform bacteria [11]. Moreover, in the landfill area, groundwater is polluted with high concentrations of nitrates and sulfates [12]. Reference [13] pointed out that Linares aquifer was vulnerable to several pollution sources related to anthropogenic activities. Reference [14] studied the Pablillo River basin, and they indicated that changes in hydrogeochemical faces were a function of lithology, solution kinetics, and flow patterns in the aquifer; also, they mentioned that nitrate concentration was higher downstream Linares, showing a clear impact of human activities due possibly to the use of pesticides and fertilizers, as well as sewage systems [15]. In 2013, [16] determined that groundwater types may be affected by factors such as natural salinization due to dissolution of halite and gypsum, as well as dolomite and carbonate. The main objective of this research is to identify whether water quality has been influenced either by natural environment or by anthropogenic activities.
2. Description of the Study Area
2.1. Location
The study area covers approximately 30 km2 and is located in the eastern periphery of Linares, 2,747,000 m - 2,750,000 m N and 444,000 m - 448,000 m E (Universal Transverse Mercator, UTM) at an elevation of 351 meters above sea level (Figure 1). The local watershed is an important water supply for the city of Monterrey and its metropolitan area, located up north at 135 km. The Linares region is characterized by subtropical to semiarid climate, with high temperatures and erratic precipitation in the beginning and at the end of the summer. Minor precipitation and severe frost also occur during wintertime. The region features a mean annual temperature and precipitation of 22.3˚C and 805 mm, respectively [17].
The Pablillo River flows in SW-NE direction, constituting a hydraulic connection with groundwater; it receives wastewaters from domestic, municipal and industrial sources. In S direction 2 km away, an old municipal landfill is located; it is an open trench that received around 300,000 tons of wastes (municipal, domestic and industrial) from 1980 to 2001. These wastes were deposited in direct contact with fractured rocks. A barite mineral processing plant is found 250 mW; pig farms are
located next to this plant, and agricultural land predominates on both sides of the old municipal landfill; the main population in study is located 750 m N from the old municipal landfill and along both sides of the river. The wastewater from La Petaca colony has been disposed of by latrines and septic tanks directly to the subsoil (Figure 1).
2.2. Geological Frame and Hydrogeology
The study area is located between a series of hills and plains forming anticlines and synclines with a general orientation of 10˚NW and immersions of about 7˚. The exposed rocks in the hills consist of a sequence of brownish-gray shale with 40 cm of thickness and, towards the top, occasional beds of 100 cm thick brown-red sandstone and calcareous sandstone, which are classified as part of the Méndez Formation (Campanian-Maastrichtian, Upper Cretaceous) (Figure 2). This unit exposes two systems of fractures assigned to hk0 and abc type, which have a preferential orientation of 8˚ SE and a dip varying between 85˚ to 88˚. In shales, the fractures expose joints that vary from 5 mm to 5 cm, whereas in sandstones, the joints vary from 1 cm to 10 cm. The fracture density observed in this unit varies from 4 to 15 fractures per meter. On the discharge zone in the valley, Quaternary fluvial terraces and lacustrine sediments are distributed on the channel of the Pablillo River and laterally on alluvial terraces (thickness varies).
The study area is flanked by the Sierra Madre Oriental, but the main surface is located within the valley discharge zone, where the aquifer inflow comes from the recharge zone in the Sierra Madre Oriental, by the Pablillo River, its tributaries, and by periodic annual precipitation. The surface runoff is determined by the topography, where its main direction is SW to NE, and the surface and ground-
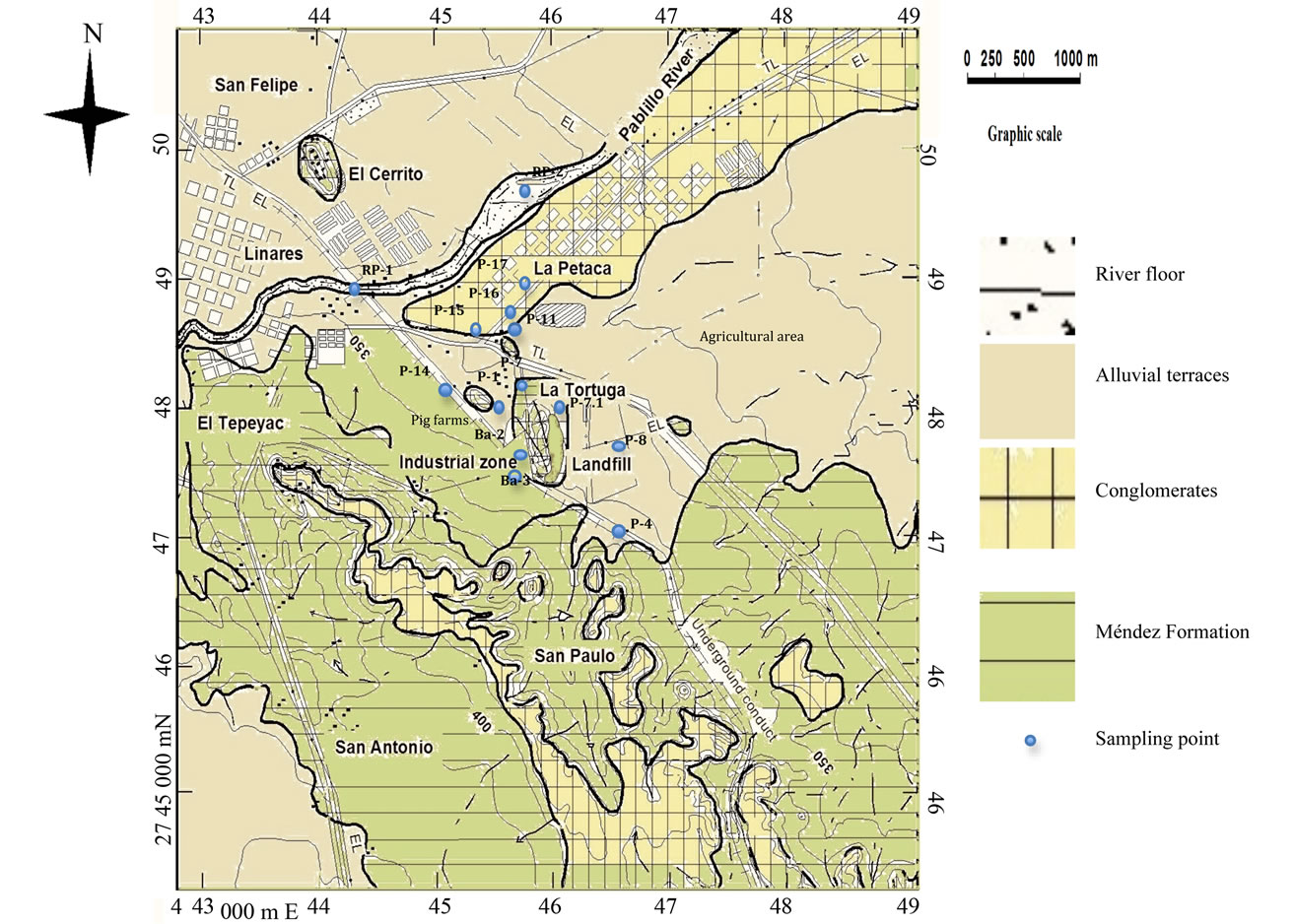
Figure 2. Geological map showing main pollution sources and sampling points (modified from [13]).
water flow is defined by the hydraulic gradient in the same direction. At the plain region, the Mendez Formation is discordantly overlaid by semi-consolidated polimictic badly sorted conglomerate, which represents alluvial terraces deposited during the Quaternary [18-20]. There are two interconnected aquifers: 1) The fractured aquifer covering 47.14% of the study area (W-SE), where groundwater flows through highly fractured rocks (Mendez Formation) within a saturated thickness of 70 m, where its medium permeability shows an average value of hydraulic conductivity of 2.5 × 10−5 m/s [21]. The phreatic groundwater level in different hydraulic wells varies from 11.64 m to 40.07 m. Its hydraulic gradient is of 1.6%, which indicates a low recharge index. The second aquifer is porous and covers 52.86% of the study area (NW-E); it permits groundwater flow in almost any direction (due to its topography). It is located mainly in the valley zone, characterized by Quaternary alluvial sediments of high hydraulic conductivity (0.995 to 0.89 m/d), and phreatic groundwater levels of 16.42 m to 5.75 m. Its hydraulic gradient varies from 0.74% to 0.93%, which indicates a good recharge index. Porous and fractured aquifers have different hydraulic parameters, however, both aquifers are hydraulically connected by the groundwater flow.
3. Materials and Methods
The adopted methodology comprises: an identification of contaminants present in a chemical analysis conducted previously by [13] and its comparison with national and international maximum permissible limits for human consumption and irrigation purposes; a hydrogeochemical modeling to evaluate the distribution of aqueous species; and an identification of the geochemical factors responsible for superficial and groundwater quality. The former study lacks of an interpretation of results to determine other natural or anthropogenic influences on the quality of superficial water and both aquifers, other than the old municipal landfill. The selection of the sampling points was made according to its location upstream and downstream the main pollution sources and accessibility.
3.1. Water Quality
Chemical analysis were conducted in 12 × 2 groundwater samples taken from wells (P-1, P-4, P-7, P-7.1, P-8, P-11, P-14, P-15, P-16, P-17, Ba-2, Ba-3), as well as 2 × 2 superficial samples taken from Pablillo River, downstream and upstream from the study area (RP-1, RP-2). Sampling campaigns were conducted during dry and rainy seasons (Figure 2). Electrical conductivitypH, and temperature were measured in situ. The samples were filtered using a glass fiber paper (0.45 mm), acidified to pH = 2 with nitric acid, and stored in polyethylene pre-washed bottles of 1 L, and refrigerated until they were analyzed.
The measurement of ion concentrations (sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, bicarbonate, chloride, nitrate, and sulfate) was determined by Ion Chromatography equipment. Elemental analysis of barium and mercury were performed by Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-OES). Analytical details are discussed in [13]. The average parameter concentrations from rainy and dry seasons for each sampling point are listed in Table 1 and is compared with maximum permissible limits stated in the following Mexican standards, for human consumption [22] and for irrigation purposes, [23] as well as with international standards for human consumption [24,25].
3.1.1. Irrigation Water Quality Indicators
The total concentration of soluble salts (salinity hazard) in irrigation water can be expressed in terms of specific conductance. Another important factor for irrigation water quality is the sodium concentration to express reactions with the soil and to know how it reduces the soil permeability (Table 2). Therefore, sodium absorption ratio (SAR) is considered as a better measurement of sodium (alkali) hazard in irrigation water. As SAR of water is directly related to the adsorption of sodium by soil, it permits to determine the suitability of water for irrigation.

Table 1. Summary of physico-chemical parameter (modified from [13]).

Table 2. Summary of salinity and alkali hazard in water samples.
SAR is computed as (Equation (1)):
 , (1)
, (1)
where the ion concentrations are expressed in miliequivalents per litre.
3.1.2. Chloro-Alkaline Indices
To determine whether the basic chemical groundwater composition is due to host rocks weathering or is influenced by hydrologic factors such as precipitation and evaporation, the methods of [26,27] have been widely used. From these, the presence of parameters such as sodium are calculated as follows (Equation (2)):
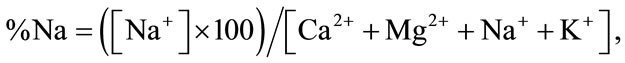 (2)
(2)
where the ion concentrations are expressed in miliequivalents per litre.
3.2. Hydrogeochemical Modeling
The computer program PHREEQC [28] using the database WATEQ4F was used to calculate the distribution of the aqueous species. PHREEQC has also been used to evaluate saturation and precipitation processes by means of saturation indexes calculations. The saturation index (SI) is defined as the logarithm of the ratio of the ion activity product (IAP) of the component ions of the solid in solution to the solubility product (K) for the solid (SI = log IAP/K). If the SI is zero, the water composition reflects the solubility equilibrium (saturation) with respect to the mineral phase. A negative value (<0) indicates under-saturation and a positive value (>0) indicates over-saturation. The ionic strength (I) has also been calculated with this software. It is a measurement of the ion shielding that occurs around charged dissolved species [29].
The I is calculated as follows (Equation (3)):
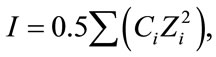 (3)
(3)
where Ci is the concentration in mol/L (M) of ion i, and Zi is the charge of ion.
3.3. Water-Rock Interaction
A chemical diagram proposed by [30] was used to depict the mechanisms controlling water chemistry for both aquifers (fractured and porous), as well as for the Pablillo River. This diagram permits to identify the relationship of chemical groundwater with their respective lithologies. Gibb’s ratio is calculated (Equation (4)):
ratio  for anions, (4)
for anions, (4)
and ratio 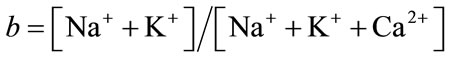 for cations.
for cations.
These ratios were plotted separately for each aquifer, as well as for the Pablillo River.
3.4. Natural and Anthropogenic Influence in Water Quality
A canonical correspondence analysis was performed to compare simultaneously spatial variations of phreatic level, chemical parameters, soil use, water use, sampling points location, as well as pollution sources (pig farms, barite mill, old municipal landfill, septic tanks and latrines, agricultural areas) by using the program STATISTICS v.8.0.
4. Results
A total of 14 sampling points were analyzed: 7 were located in the fractured aquifer (P-1, P-4, P-7, P-7.1, P-8,

Table 3. Mineral speciation and saturation indices.
Ba-2, Ba-3), 5 in the porous aquifer (P-11, P-14, P-15, P-16, P-17), and 2 in the Pablillo River (RP-1, RP-2).
4.1. Water Chemistry
The values for all the physico-chemical parameters measured and the maximum permissible limits for human consumption and irrigation purposes are shown in Table 1. The pH values in the fractured aquifer samples vary from 6.68 to 7.12 indicating circumneutral nature; in the porous aquifer vary from 7.03 to 8.01, and in Pablillo River range from 7.89 to 8.01, indicating slightly alkaline nature. The electrical conductivity values of the fractured aquifer are between 1003 and 2010 mS/cm, whereas in the porous aquifer they are between 800 and 1219 mS/cm, indicating fair quality. The electrical conductivity values in samples taken from Pablillo River range from 756 to 765 mS/cm, indicating good water quality.
According to the irrigation Mexican standard, the parameters that exceeded the maximum permissible limits were: total solids from four to nine times (P-7.1 > P-7 > P-16 > P-11 > P-8 > P-1 > P-15 > P-17 > P-4 > P-14 > RP-2 > RP-1), suspended solids once (P-16 > RP-2 > P-8 > P-1 > P-11 > P-17 > P-14 > P-4 > RP-1 > P-7.1), and mercury exceeded four times (P-4). For human consumption, dissolved solids exceeded maximum permissible limits once (P-7.1), chloride exceeded once (P-7.1), nitrate exceeded from one to five times (P-1 > P-7 > P-16 > P-7.1 = P-11 > P-14 > P-15 > P-4 > P-17), barium exceeded from four to twelve times (Ba-2 > Ba-3), and mercury exceeded three to sixty-seven times (P-4 > P-14 > P-1 > P-8).
4.1.1. Salinity and Alkali Hazards
From Table 2, 100% of samples are featured as medium quality for salinity hazard. The SAR index in the study area ranges from 0.2623 to 1.0174. This means that water can be classified as C3-S1 group, and is considered highly saline water. The most affected wells are P-4 and P-8 (SE to the old municipal landfill). Sodium percent ranges from excellent quality (P-16 and P-17) to good quality (P-1, P-7, P-7.1, P-11, P-14, P-15, RP-1, and RP-2). Wells that are in the urbanized area maintain excellent quality according to alkali (sodium) hazard.
4.1.2. Chloro-Alkaline Indices (%Na)
Sampling points in the fractured aquifer have negative chloro-alkaline indices, indicating that host rocks are the primary source of dissolved solids in cation-anion exchange reaction. Sampling points in the porous aquifer and in the Pablillo River, have positive chloro-alkaline indices, indicating a base-exchange reaction (evaporation process) (Table 2).
4.2. Mineral Speciation and Water Saturation
The distribution of the different species is depicted in Table 3, and it can be observed: 1) major calcium species in the surface and groundwater include in increasing order 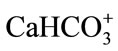 > Ca2+ > CaSO4 > CaCO3 > CaOH+ >
> Ca2+ > CaSO4 > CaCO3 > CaOH+ >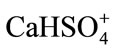 ; 2) major magnesium species in surface and groundwater include dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2); 3) major sulfate species are barite (BaSO4) and gypsum (CaSO4·2H2O); 4) major species of barium are barite (BaSO4) and witherite (BaCO3).
; 2) major magnesium species in surface and groundwater include dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2); 3) major sulfate species are barite (BaSO4) and gypsum (CaSO4·2H2O); 4) major species of barium are barite (BaSO4) and witherite (BaCO3).
The water is under-saturated with respect to anhydrite (CaSO4), mainly in the porous aquifer; water is oversaturated with respect to aragonite (CaCO3), calcite (CaCO3), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) and gypsum (CaSO4∙2H2O), in both aquifers (fractured and porous), while it is sub-saturated with respect to halite (NaCl) in both aquifers and the Pablillo River. The surface and groundwater ionic strength (I) is between 6.033 × 10−4 and 5.772 × 10−3 (mean 3.187 × 10−3). According to [31], the I for freshwater is normally less than 0.02, while seawater has I of about 0.7.
4.3. Water-Rock Interaction
In the study area, two aquifers with different lithologies control groundwater flow, and both permit infiltration of runoff as well as rainwater, that can contribute to different chemical reactions [32]. Figures 3(a)-(c) depict the chemical diagram proposed by [30].
Ratios a and b for fractured aquifer samples range from 0.08 to 0.35 and 0.38 to 0.65, with an average of 0.35; for porous aquifer range from 0.13 to 0.21, and 0.24 to 0.51, with an average of 0.27; and for Pablillo River range from 0.13 to 0.19, and 0.27 to 0.33, with an average of 0.23, respectively. Two field types are recognized in these diagrams: rock dominance for fractured aquifer, and evaporation dominance for porous aquifer and river flow.
4.4. Natural and Anthropogenic Influence in Water Quality
Results of canonical correspondence analysis are depicted in Figure 4. From these, several factors were identified that have influence in groundwater and superficial water. The spatial distribution of contaminants can be associated to several factors such as the distance to point (old municipal landfill, pig farms, barite mill) and diffuse pollution sources (agricultural land, septic tanks and latrines) with respect to the sampling points. The point pollution sources dominate the chemical parameters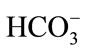 , Na+ and K+ in wells P-1, P-4, P-8, P-11 and P-14. The diffuse pollution sources can explain their influence in the presence of suspended solids, total solids,
, Na+ and K+ in wells P-1, P-4, P-8, P-11 and P-14. The diffuse pollution sources can explain their influence in the presence of suspended solids, total solids,
 (a)
(a)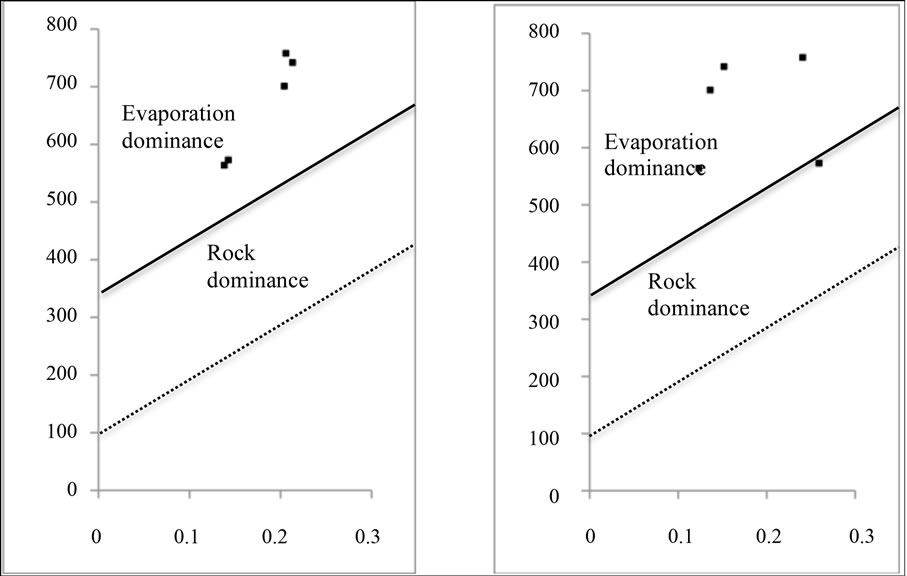 (b)
(b)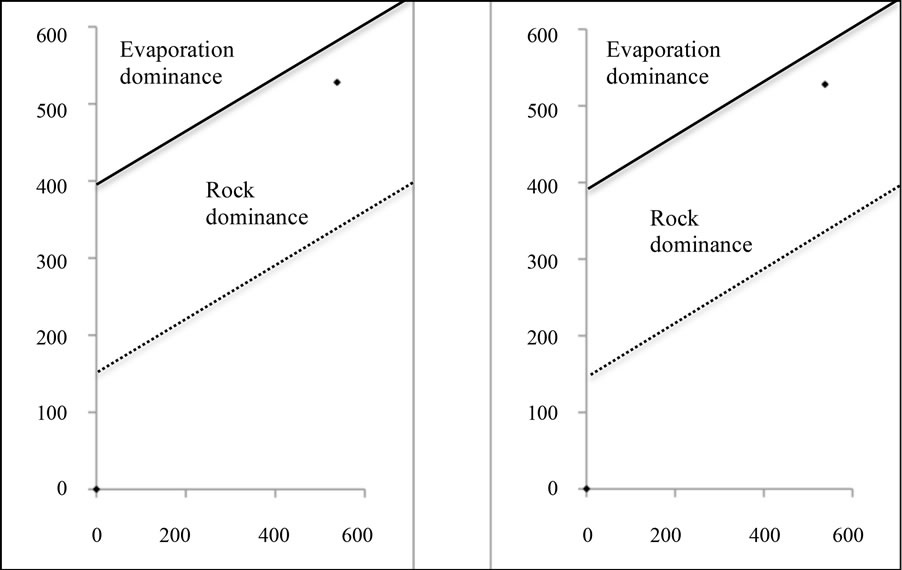 (c)
(c)
Figure 3. a) Rock dominance in fractured aquifer, b and c) Evaporation dominance in porous aquifer and in the Pablillo River, respectively (modified from [30]).
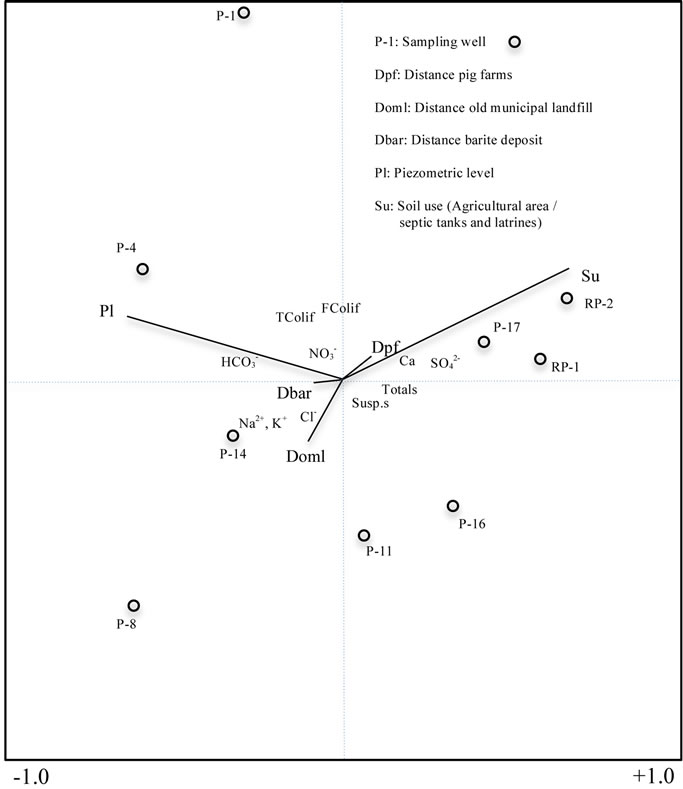
Figure 4. Relation between pollution sources and physicochemical parameters.
 , pH, and Ca2+ in wells P-16 and P-17, as well as on the Pablillo River (RP-1, RP-2). In the well P-1, fecal wastes generated by the activities of pig farms control its water quality, leading to the presence of biological parameters such as total and fecal coliforms, as well as the chemical constituents such as Mg2+ and
, pH, and Ca2+ in wells P-16 and P-17, as well as on the Pablillo River (RP-1, RP-2). In the well P-1, fecal wastes generated by the activities of pig farms control its water quality, leading to the presence of biological parameters such as total and fecal coliforms, as well as the chemical constituents such as Mg2+ and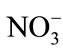 . Well P-8 is located downstream of the old municipal landfill, in the same direction of groundwater flow; therefore, leaching of wastes can contribute to the presence of Cl−, Na+, and K+.
. Well P-8 is located downstream of the old municipal landfill, in the same direction of groundwater flow; therefore, leaching of wastes can contribute to the presence of Cl−, Na+, and K+.
5. Discussion
There is an hydraulic interconnection in the study area due to the high fracturing of the Méndez Formation (4 to 15 fractures x m), the high permeability of the porous aquifer (0.999 to 0.89 m/d), and the proximity of both aquifers with the Pablillo River (20 m), that flow in the same direction SW-NE as the aquifers. Moreover, the water quality is being compromised by factors such as the distance of the sampling wells to point and diffuse pollution sources, water table, as well as rock weathering.
Due to the hydrogeologic characteristics of both aquifers, it is observed that a factor such as the evaporation (in the porous aquifer and the Pablillo River) exerts influence on the concentration of certain chemical indicators determined (positive chloro-alkaline indices). Additionally, in the fractured aquifer the concentration of some of the chemical indicators (negative chloro-alkaline indices) is due to the rocks weathering. Hence, subsaturation of minerals such as anhydrite is associated to the evaporation effect in the porous aquifer and the Pablillo River, while the rocks weathering can exert influence in the over-saturation of minerals such as aragonite, calcite, gypsum and dolomite (mainly in the fractured aquifer). The presence of contaminants determined for human consumption and for irrigation purposes can be explained as follows (Figure 4):
The canonical correspondence analysis explains a water quality gradient for the sampling points. The leachates infiltration from fecal wastes in the pig farms defines water quality in well P-1. The mobility of total coliforms, fecal coliforms, and nitrates, as well as the highly fractured rocks (hydraulic conductivity of 2.5 × 10−5 m/s) and the depth of the unsaturated zone (16.58 m), creates the ideal conditions to permit the migration of these contaminants through the fractured aquifer.
The change in land use, from native bushland (e.g. Leucophyllum texanum, Cordia boisieri, Porlieria angustifolia, Acacia rigidula, Pithecellobium brevifolium, Lycium Carolinianum) to agricultural land, as well as the distance from pig farms, exerts influence in the behavior of wells P-11, P-15, P-16, P-17, and RP-1, RP-2. The water quality in these wells is affected by the infiltration of suspended solids, total solids, and sulfates through the porous aquifer.
The distance of wells P-4, P-8, P-11 and P-14 to the old municipal landfill explains some of the variation in the parameters of water quality, but in an opposite direction to the gradient described for agricultural land (Figure 4). The influence in water quality is due to the location of these wells in the same direction of groundwater flow through the fractured aquifer. The presence of mercury (3 to 67 times exceeding the maximum permissible limits) in the fractured aquifer (P-4 > P-14 > P-1 > P-8) has not a well identified origin; however, in the case of P-4 and P-8, its presence can be associated to the leachate migration from the old municipal landfill, since these wells are located at a short distance in the same direction of groundwater flow. Additionally, in a previous study, [33] reported that methyl mercury could originate from microbial metabolism, as well as by chemical processes that not necessarily include microorganisms. Although, they report that anthropogenic activity such as leaching infiltration from landfills and from wastewater, these can be the sources of this pollutant. The presence of mercury in wells P-1 and P-14, is possibly due to the use of pesticides in agriculture land however, this remains under study. The two wells affected by barium (Ba-2, Ba-3) have a very clear source, since they are located in the barite mill facilities. Therefore, the high fracturing of rocks is favoring the infiltration of this contaminant through the fractured aquifer (average depth of 21 m). Although the water movement through fractures facilitates the migration of contaminants, barium was not detected in other wells due to the low solubility of barite.
6. Conclusions
In this study we concluded that natural conditions of the study area and anthropogenic activities exerted influence on superficial and groundwater quality. Water quality is affected by the following factors: a) water-rock interaction; b) permeability and water table depth; c) distance from wells to point sources (old municipal landfill, pig farms, barite mill) and diffuse (agricultural land, septic tanks and latrines). There are two aquifers that are hydraulically interconnected through their fractures and pores, respectively, allowing water to flow in SW-NE direction. Moreover, surface water is connected to the porous aquifer due to its high permeability that drains in the same direction.
The presence of some minerals (anhydrite) in the fractured aquifer is due to the slow dissolution of rocks, while evaporation favors the precipitation of other minerals (aragonite, calcite, dolomite) that predominates in the porous aquifer, as well as in the Pablillo River. The anthropogenic influence on the water quality is defined through the change from native bushland to agricultural areas, which have affected the quality in wells located in the porous aquifer and the Pablillo River. In addition, the presence of septic tanks and latrines also affects the water quality in the porous aquifer. It was more difficult to find a direct relationship between the pollution sources and contaminated wells in the fractured aquifer. However, the groundwater flows from pollution sources through contaminated wells, which allows determining that the old municipal landfill, pig farms, as well as the barite mill, exert influence on the contaminants detected.
Therefore, we recommend: 1) To place an impermeable layer over the old municipal landfill that prevents the contact of the wastes with rainwater, decreasing leachate infiltration, 2) to control the type of plants to grow, using saline plant tolerants, and irrigate them with water extracted far from the old municipal landfill, 3) to substitute latrines by modern sanitary facilities that transport their wastewater to a wastewater treatment plant, which is located at a few kilometers in NE direction, and 4) to take environmental measures in the barite mill facilities, protecting their mineral from weathering.
7. Acknowledgements
Thanks to the National Council of Science and Technology (Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología, Conacyt) for the scholarship number 159971; to the projects Conacyt-Conafor CO1 6231, Paicyt and Promep-2009- 2011 for financial support.
NOTES