Strategic Environmental Assessment to Improve Infrastructure Impact Assessments in Brazil ()
1. Introduction
Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) has been pointed as an important instrument to incorporate environmental variables into the decision process. The literature highlights the role of SEA as an instrument that informs decision-makers about the environmental consequences of strategic actions [1,2]. The most commonly perceived benefits of SEA are described as: the possibility of a wider consideration of effects on the environment and alternatives to be considered; the anticipation of public participation in discussions and the increased effectiveness of decisions related to development projects with savings in cost and time, as well as the consequent strengthening of strategic decision processes [3,4].
The practice of SEA is evolving with a greater awareness about the context and its influence in the results [5, 6]. Nevertheless to be effective the practice of SEA must be evidence-based and objective-led [4]; baseline-led [7]; flexible and adaptable to specific contexts [8]. It is recognized that the effectiveness of SEA is improved with systematic practice, as a consequence of organizational learning [9].
Through the last decades many developing countries are cumulating their own experience with the instrument. Although a few have a formalised system, SEA is still frequently applied without legal requirements that specify objectives and procedures to be followed downstreaming strategic levels of decision and non rare did not influence the concepts and alternatives to projects. In this context the implementation of development projects is often subject of court decisions, as a result of the wellrecognized limitations of project-EIA.
Therefore the present paper discusses the potential benefits from the use of SEA to promote the tier of strategic levels of decision in transport infrastructure plans and programmes. Through a case study applied to the state of Sao Paulo (south-eastern Brazil) the paper advocates for the systematic use of SEA in order to enhance impact assessments in the country.
2. Background
One of the most important aspects of SEA application deals with the concept of tiering, described as an important component in planning that is vitally related to the effectiveness of this instrument and its capability of influencing strategic decisions [10]. The ability to identify the significant effects to the environment caused by strategic actions and the interactions with other levels is a key aspect of SEA methodological framework.
The processes to formulate strategic actions in plans and programmes involve decisions that need to be legitimated within the political context [11]. In despite of that, the politic dynamics of the planning process can constitute an obstacle to strategic assessments due to the tradeoffs that are frequently imposed in order to balance different interests. As a consequence development projects are frequently threatened by impact assessment outcomes, especially when a mandatory project-EIA has to inform decisions.
Reflecting that, many conflicts over environmental licensing in Brazil have occurred in the energy sector, with complains about excessive procedural requirements and delays that lead to economic and political pressures diminishing the quality of environmental assessments [12]. A comprehensive overview of the Brazilian EIA system and its general strengths and weaknesses can be found in [13,14].
Regarding the Brazilian experience with SEA, there are three main contexts within which the instrument is applied: 1) environmental agencies that have the perception that EIA cannot deal with relevant issues that have emerged or will emerge from environmental studies; 2) groups of private investors who want to anticipate the likely conflicts that would emerge in a later EIA; and 3) multilateral funding agencies that require SEA to be conducted for deciding whether or not approve a request, as part of their safeguard policies.
It was observed elsewhere that SEA performance in Brazil was thoroughly influenced by what was referred as the “EIA rationality” [15]. An adequate performance was verified with regards to screening, establishment of baseline and description of mitigation actions, but serious deficiencies were observed in terms of the definition of SEA objectives, the identification of strategic alternatives, public participation and follow-up strategies.
Considering some enthusiasm with “new approaches” and the need for “flexibility” of SEAs coming from parts of the academic and practitioner communities [5], many of the shortcomings described to Brazilian SEAs are closely related to the lack of formal requirements in terms of SEA procedures [15].
In fact, Brazil has basically been working with SEA by adapting project-EIA procedures. Notably, SEA has been applied in Brazil to structural projects, large infrastructure projects that can significantly change the development of a region. In practice these SEAs are focused on filling the gaps of the environmental licensing process, using the same approach that of regular project-EIAs [16-18].
3. Case Study—Infrastructure Transport Plans in Sao Paulo State (Brazil)
Over the last decade Brazil had experienced an unprecedented period of economic growth supported by natural resources exploitation and the expansion of goods and services consumption. Therefore infrastructure development had become the priority to the government in order to maximize economic benefits.
In Sao Paulo state, the strategic development policy defined the state’s strategies to increase industrial production and consumption (Figure 1).
One of the main strategies is focused on the state’s transport policy, which aims to increase regional development through the investment in infrastructure and de-
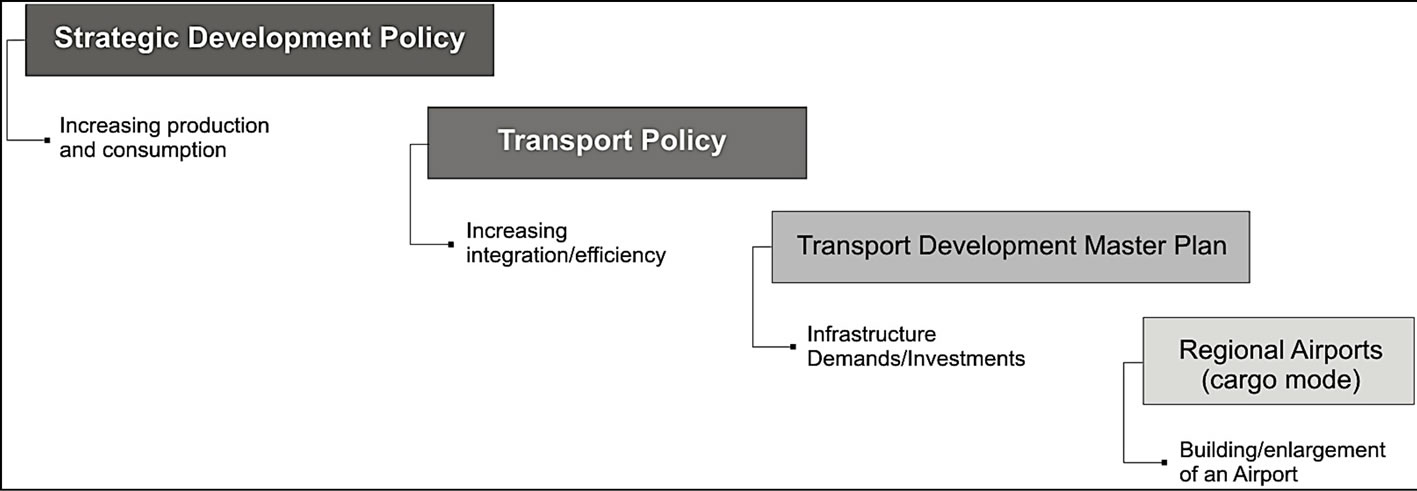
Figure 1. Tiered decisions related to the strategic development policy of Sao Paulo State.
centralization of transport operations, for example, stimulating the expansion of regional airports with both passengers and cargo transport facilities.
The situation we describe encompasses an airport expansion as one of the outcomes of strategic decisions that integrate at least three distinct and complementary groups of interest. The first one includes the local demand for the project itself, i.e., the need to increase the existing airport’s passenger transport capacity. Secondly it involves the intended regionalisation of the cargo transport system in the state of São Paulo. Finally, on state level, the internationalisation of the cargo terminal is added to the objectives of the expansion project.
Environmental Impact Assessment is required to verify whether or not a project can be implemented considering what is referred in Brazilian legislation as the project’s environmental acceptability. Basically the environmental agency verifies project’s compliance with legal thresholds considering the need of mitigation measures and the management of the impacts along the project’s life cycle. It follows, therefore, the classic framework of project—EIA as frequently described in literature presenting virtually the same strengths and weaknesses.
In our case study, the expansion of the airport’s terminal was merged with a subsequent expansion in its facilities to airplane landing, taxi and manoeuvre to increase its capability to receive bigger aircrafts, now including cargo transportation and customs facilities. After includeing all of commercial, economic and political demands that were imposed along the different levels of decision— local, regional and state—the project’s final layout was clearly much more than a simple expansion of the former airport.
From that moment on, the possibilities of integration of the strategic levels in a single decision informed by a project-EIA become very remote, because of the strategic character embedded in the chosen alternative (including project conception and locational alternative). The project submitted to approval was shaped by vertical driving forces that came from the state transport development policy pushing to the construction of a regional airport (or the expansion of an existing airport) with increased cargo transport capacity (Figure 2).
The state strategy had also defined that one of these regional airports, Leite Lopes Airport (sited in Ribeirao Preto city, northeast of state, nearly 400 km far from the city of Sao Paulo), would provide Viracopos International Airport with an international cargo connection, thus incorporating customs facilities as well as the expansion of passenger and cargo services.
Although Leite Lopes Airport was not the only alternative with aptitude to receive the investments, the regional leadership of Ribeirao Preto would virtually prevailed over any economic and political criteria. A rele-
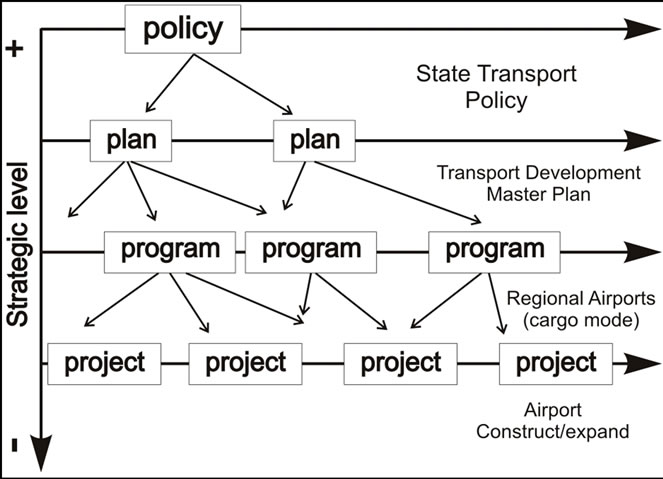
Figure 2. Horizontal and vertical strategic actions in the State Transport Policy.
vant aspect that supported this alternative was referred to the alleged economy with the expansion of an airport that already presented the basic infrastructure compared to the development of a new site.
Without alternatives assessment downstreaming each strategic level it was quite obvious that Leite Lopes Airport would be pointed as the preferred alternative in that region, despite the associated environmental and social costs. Given all of the political pressure for this site it was, therefore, considered to be the most cost-effective alternative (Figure 3).
In this case, the Environmental Impact Statement prepared to inform the decisions had showed to be very insensitive in terms of alternatives, cumulative and synergic impacts, as well as the integration with other plans and programmes, corroborating its already known low capacity to address environmental impacts related to the strategic levels.
In order to verify the adherence to the principles of EIA best practices described by the International Association for Impact Assessment [19] a content analysis was applied on the environmental report. This procedure allowed the identification of relevant deficiencies of the EIA process that were related to the airport’s new profile (Table 1).
Considering the methodological and procedural framework that is usual of project-EIA, it barely considers a compatibility assessment, what is significant in our case study due to the direct impacts in land use and the attractiveness of the project. When focusing on local level the impact assessment should exhaustively report to the conflicts with municipal land-use strategies, which is one of the main aspects to be addressed in this case together with the study of alternatives.
Some of the guidelines tied to the state strategies conflict with local strategies, what would be clearly observed with a broader scope to impact assessment brought by Strategic Environmental Assessment and a consequent analysis of the compatibility between other plans and
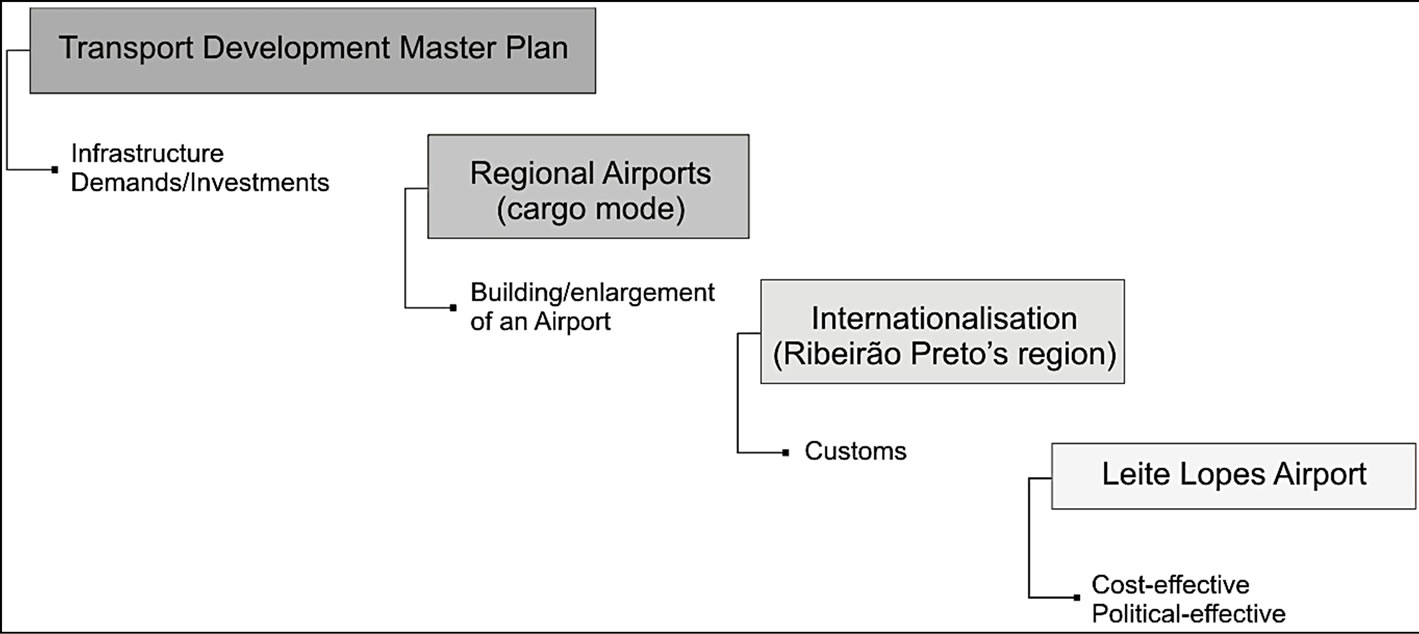
Figure 3. Decision without alternatives assessment.


Table 1. Main deficiencies of the Leite Lopes airport environmental impact assessment.
programmes. To this respect, some aspects of local plans and programmes that showed to be conflicting with the project’s implementation are presented in Table 2.
There is no coherence between the intended land-use and the existing traffic infrastructure. Despite the Local Master Plan had indicated the relocation of the airport in order to promote a better urban development of the surrounding areas, the guidelines that came with the internationalisation plan not only assumed the permanence of Leite Lopes Airport in the same site but also included the expansion of passengers and cargo transport capacity.
The lack of consistency in the criteria used to evaluate

Table 2. Compatibility assessment focused on local plans and programmes.
impact significance is evident in the situation showed in Figure 4. The main avenue to the airport is also an important access to the surrounding areas, and the proposed traffic solution describes a contour around the expanded area of the airport with a significant disruption of the main access.
Some of the measures proposed to mitigate impacts caused by the new demands need a proper assessment in terms of the potential impacts they would cause and subsequent costs to the whole society in order to be compared to other alternatives. In this specific case, the economic benefits that were supposed to follow the investments related to the State Master Plan for Transport Development are taken as the most important positive impact. The inclusion of top-down strategic objectives obscures the local guidelines to land-use with a progressive abandonment of the last in the name of the economic opportunity, but ignoring the previous efforts of local governments to implement their own strategies.
The Contributions of a Parallel SEA to Inform Decisions
The internationalisation plan of the Leite Lopes Airport followed similar trends as they happened in the airports of Manchester, England [21]; Beirut, Lebanon [22]; Zurich, Switzerland [23]; and Schiphol, The Netherlands [23,24]. In our case it can be synthesized as follows:
• Lack of public participation in decision-making;
• Failure in environmental compliance and compatibility with policies, plans and programmes, even within the local sphere;
• Absence of an environmental reference from a previously defined environmental baseline.
In situations where EIA is linked to the environmental licensing of projects, as it is found in Brazil, there are inherent difficulties to address all of the elements that need to be incorporated in decision-making, especially when strategic and project levels need to be contemplated.
Moreover, in our case the characteristics of the project imposes the assessment of cumulative impacts and compatibility with others plans and programmes, which is very difficult to be achieved by regular EIA procedures.
Figure 5 illustrates the procedures for decision-making with an SEA running in parallel to the formulation of strategic actions. Based on the case study, it is clear that the lack of alternatives assessment obstructs the desirable tiering of strategic levels of decision.
By accounting basically the positive economic impacts of the airport’s expansion, the decision taken at the state level overlays local strategies and justifies the maintenance of the airport in a site without balancing social and environmental costs.
The absence of a more accurate discussion about alternatives hampers the entire evaluation of the project’s acceptability and its potential with respect to the objectives of the airport’s internationalisation. The lack of environmental criteria to guide the assessments and the nonexistence of a broader scope to impact assessment that include the compatibility with other strategic actions and their cumulative effects are strong indicatives that could be satisfactorily fulfilled with SEA.
Based on [7], the procedural framework of an SEA running in parallel to the elaboration of the internationalization plan can be summarized in the following topics:
• It should establish general criteria that guide the study of alternatives in the region of Ribeirao Preto as a whole;
• It creates an opportunity to include environmental aspects in early stages of strategic decisions, thus collaborating to tiered decisions;
• It would be included in a long term vision of the State transport policies;
• There would be more space to search for compatible alternatives and solutions that fit environmental thresholds in first place and to each strategic level of decision;
• It should promote tiered decisions conciliating state,

Figure 4. Conflicts with local strategies: disruption of main accesses. Source: [20].
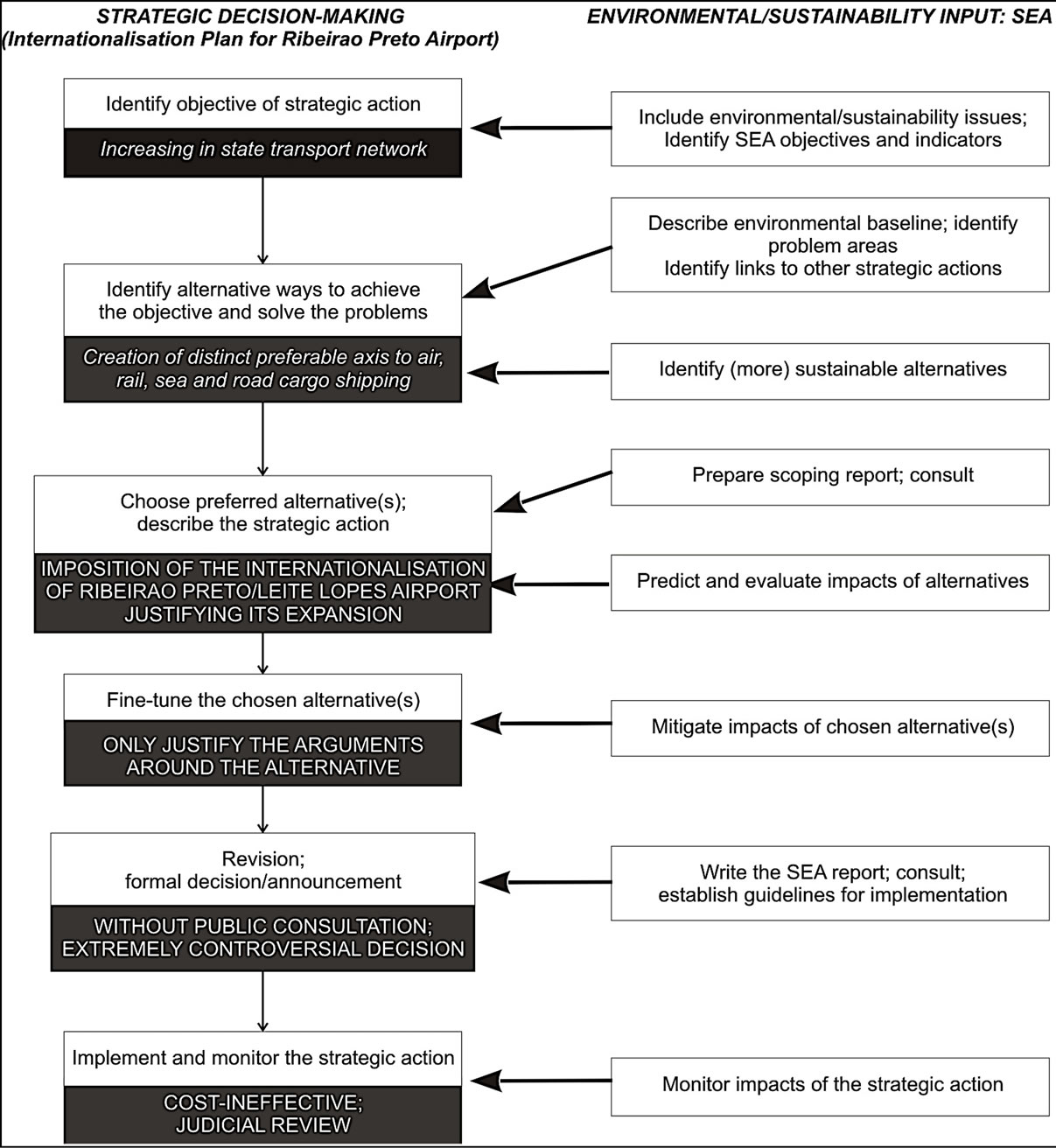
Figure 5. Procedures of strategic environmental assessment according to [7], indicating the obstructions in decision-making due to the lack of alternatives assessment.
regional and local strategies;
• It must include proactive actions focused on the enhancement of positive impacts of the different tiers of decision;
• It allows the assessment of sustainable alternatives not restricted to project specifications.
4. Final Considerations
The case discussed in the present paper stresses the potential of SEA to promote the connections between distinct plans and levels of decision, strengthening projectEIA by means of better conditions to the identification of relevant issues to be addressed. In our case study, it is evident that an internationalisation plan for a regional airport cannot be properly evaluated without considering the links to local and state strategies and its cumulative impacts.
With SEA the interaction with other plans would lead to the identification of feasible alternatives considering all levels of decision. This context would be favourable to promote the tiering based on sustainability criteria without losing its capability of focusing on the local strategies.
Therefore, we conclude that there is a need to adopt clear and well-defined SEA objectives, including formal competences and accountable procedures to fulfil the deficiencies of project-EIA. In a long-term perspective, a systematic use of SEA could contribute to social and institutional learning as described in [9], promoting tiered decisions. This would be a relevant contribution to infrastructure impact assessments in Brazil and other countries in order to streamline EIA procedures.
NOTES