1. Introduction
Organizations are often considered as living systems. These living systems are vulnerable to pathogens as humans. Beer commented that an organization might be quite ill and its condition may be pathological [1]. Organizational diagnosis is the process of diagnosing an organizational health, by finding any pathogens and suggesting a cure for those pathogens. The purpose of this paper is to create an understanding of the system; this understanding provides a basis of determining if any change is required [2].
Similar to a medical practitioner an organizational diagnostician diagnoses an organization by first examining the current state of an organization and tries to answer the question “what is happening now?”. Once the answer to this question is found the diagnostician then moves to the next question i.e. “what needs to be done?” Practitioners in the organizational change field often run organizational diagnosis to analyze the current functioning level of the organization [3-5]. The information collected from the diagnosis is then fed to develop an appropriate change intervention to enhance the organizational performance [6]. We define an organization’s health state as the “condition of leadership, strategy, systems and structure encapsulated within the environment”.
2. Organizational Pathologies
We have defined an organization’s health as the “condition of leadership, strategy, systems and structure encapsulated within the environment”. The health of an organization can be measured through extended diagnostic model developed by us but it is for the moment unpublished work. We have identified that organizations can be, in any period of time, performing, stable or disarranged. The characteristics of these states are discussed in the following subsections along with the corrective actions. These characteristics are shaped through the leadership, strategy, structure and systems of an organization.
2.1. Performing Organizations
In a performing organization virtually no pathogens exist and hence it does not need any corrective action apart from maintaining the current performance. In a performing organization the mission is clear. The leadership articulates a mission or purpose. At the same time the employees understand that how they can contribute towards the attainment of the mission. Senge states that “building a shared vision” creates a creative tension that leads to organizational learning [7]. The clarity of mission also leads to the identification of values and employees conforming to those values [8].
In a performing organization the leadership is committed to the organizational goals [9]. The performance standards are well set and the optimal performance is recognized by giving rewards and incentives in a timely manner. The leadership is effective at communicating what they need from the employees. Delegation of authority (where needed) is a common practice and there is a common belief that the people can do it. The leadership promotes teamwork and builds passion for group work. The leadership is always open to constructive criticism, admits their mistakes.
The strategy of any organization has been in the limelight and is mostly the focal point of literature and is also closely associated with organizational performance [10, 11]. The strategies of a performing organization are prioritized so as to ensure the selection of the right goals at the right time. These strategies are realistic and are always related to a measurable outcome hence ensuring the performance standards. The organizational strategic plans include detailed operational plans which support the execution of the organizational strategy.
McCormack and Johnson argued that managing any organization means managing its processes or systems [12]. The different systems or operations running inside a performing organization are well defined. The different resources (e.g. human, capital, etc.) are made available on time and are managed effectively. The running systems are constantly checked and maintained for the optimum performance. The different operations in the organizations show consistency and are flexible to adapt to the changing technologies. Research and development is a common practice, and the relevant tools and techniques are applied to perform any operation. The demands of the customers are kept in mind and the quality is never compromised.
Organizational structure plays a vital role in organizational performance, may it be fiscal or non-fiscal, directly and also through the organizational learning and innovation [13]. The structure of a performing organization is well developed. The teams and different groups are empowered to make necessary decisions. The workload is evenly distributed to ensure employee commitment and job satisfaction. The tasks are divided in a logical manner and are given to people who are expert of that field. The structure also accommodates responsibility and promotes accountability [14]. The different teams are self managing so that they can solve their problems in their working domains.
2.2. Stable Organization
A stable organization can also be termed as half performing because it has certain features of a performing organization. In a performing organization there is somewhat consistency to be observed in performance. In a stable organization the following pathogens are found and these pathogens are discussed in the following paragraphs.
• Empowerosis
• Decisionosis
• Alignosis
• Domainosis
• Maintainosis The leadership is successful in setting short term priorities. This type of organization emphasizes more on short term performance and neglects long term performance [15]. The mission is not in line with the processes and procedures (alignosis). The leadership is not effecttive in valuing people and is also unable to provide them directions.
The strategy is also not very well developed hence goals are not that clear. This leads to less developed performance standards. Similarly in the organizational structure the working domains are not clear (domainosis) and an objective might be partly missed out. This can also create redundancy which leads to resource wastage. The different teams are not self managing and are not empowered hence hindering them to make decisions necessary for the performance (empowerosis and decisionosis). In a stable organization resources are available to perform a certain task. The different running systems are not well maintained and are not thoroughly checked leading to extra costs (maintainosis).
Remedy
An organization, which is suffering from empowerosis, decisionosis, alignosis, domainosis and maintainosis, requires the remedy involving the following steps:
• Align process and procedures with a mission to fulfill the organizational purpose
• Value people to keep them motivated
• Create an environment of shared decision making to keep the people involved
• Empower employees to enable to make decisions related to their work
• Clarify working domains
2.3. Jumbled Organization
A jumbled organization can also be termed as disarranged or chaotic. Jumbled organization is the one in which almost no or very less performance and growth is observed. The diseases found in this type of organization are:
• Leaderitis
• Strategitis
• Structuritis
• Systemitis The leadership of an organization fails to give direction and align the process with the mission and core purpose [16]. Ineffective leadership is considered to be as the silent killer of organizational effectiveness [17]. Similarly Schyns and Schilling elaborated in their study that destructive leadership gives rise to poor organizational culture eventually giving poor organizational performance [18]. It is also noted that in a jumbled organization the leadership does not delegate authority and power leading to less motivated workforce. Calculated risks are not taken leading to decreased innovation. Communication channels are not set and vertical communication is almost impossible. The performance standards are not set hence a reward system and positive motivation are not observed.
The strategies are reactive rather than proactive. There is no linkage of strategies with the overall organizational vision. The direction of the organization is not clear. No matter how the strategy is conceptualized, a bad strategy will always lead to poor organizational performance [19]. Priorities are not set leading wrong goal at the wrong time. The goals set are also not related to a measurable outcome and are not realistic. While developing a strategy the employees are not consulted.
The different operations or the running systems are not managed effectively. Employees are not provided with the resources required to perform a certain task. Research and development is almost never observed. People are not aware of the relevant advances in their field. Quality is almost never the organizational objective and demands of the customers are not well satisfied.
The organizational structure in a jumbled organization is poorly developed and the work load is not evenly distributed [20]. The tasks are not distributed logically and given to people who are not expert in that field. The managers are overburdened with large number of reporting employees. The teams and groups are not self managing and adjusting hence does not have the power to solve work related problems. The observed structure does not have any room for accountability.
Remedy
Jumbled organization can be treated by following the steps stated as below:
• Leadership should create shared vision and collective sense of success
• Strategies of the organization should define policies and procedures in line with the overall mission
• Define clear rules of success and define clear (SMART) goals and objectives
• Performance standards should be well articulated
• The resources for performing a certain task should be made available
• Communication channels should be open and well developed
• Quality should never be compromised and customer always comes first
• Research and development should be a common practice
• There should be clear working domains
• Pick the right people for the right task at the right time and empower them
3. Conclusions
In this paper we have classified the state of an organization through a diagnosis model. The diagnosis is performed through the examination of leadership, strategy, systems and structure of an organization. After the diagnosis and finding the pathogens the organization is classified as performing, stable or jumbled. The remedies proposed can be used to remove the pathogens and transform the organization into a performing one.
A summary of the diagnostic process is shown in Table 1.
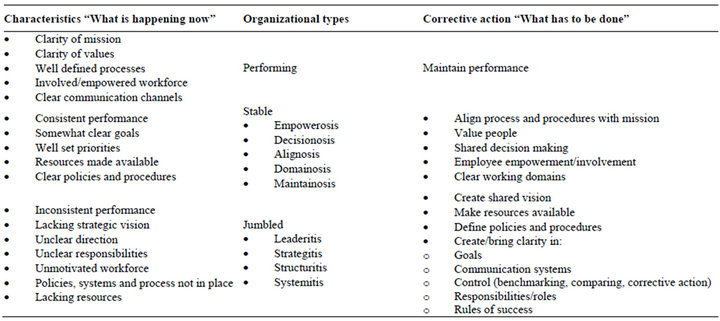
Table 1. Summary of the diagnostic process.