Perceptions on the Implementation of the Philippine Development Plan in Ensuring Efficient Governance ()
1. Introduction
During the past five decades, the Philippine economic growth could have been more impressive than its neighboring countries, resulting in the formulation of the Philippine Development Plan (PDP). The Philippine Development Plan (PDP) provides a roadmap that will unlock inclusive and sustained growth for the Philippine economy despite the challenges brought by health, geopolitical, and other economic shocks. The Plan will provide a roadmap towards improving the country’s investment climate to generate more and higher-quality employment in the medium term and to transform the economy to make it more inclusive and resilient to unexpected shocks. Furthermore, the Plan serves as the government’s comprehensive guide in development planning for six years. It is formulated in collaboration with appropriate government agencies, the private sector, and local government units.
The National Economic and Development Authority (NEDA) is the lead agency in formulating plans, overseeing their implementation, and periodically reporting to the President and the Cabinet about the Plan’s progress (NEDA, 2022b) .
A continual enhancement of the nation’s health sector and social protection programs reduces the vulnerabilities of certain segments of the Filipino population. It enables the government to have a shared vision of where the country should be in the future and a concerted program of action to achieve this vision. The resources and investment are channeled to programs, projects, and activities that could best achieve the country’s goals and objectives.
1.1. Literature Review
The government has many missions. None is more important than public health. Collaborations, capacities, and finances are essential to effective responses to these missions. In addition, communications and cooperation are important, but so are capacities (Holzer & Newbold, 2020) . The next six years (2023-2028) will likely be a period of significant change, growing uncertainties, and great possibilities. It is essential to be familiar with the interrelated trends in various areas such as economics, politics, demographics, technology, and the environment at the international and regional levels to plan appropriately for the future. The Public Administration plays a vital role in Philippine economic development, ensuring efficient governance within the context of public sector governance and in measuring sustainable development is another factor in its importance. It aids the government in collecting information on the necessities and problems people experience on a daily basis.
Government employees can more successfully execute and monitor policies with the aid of public administration. Despite being a modality of study, public administration exposes students to a variety of managerial abilities. It serves as a gauge for how well policies are carried out and establishes a political divide between elected politicians and other public employees. On behalf of the government, public administrators conduct risk evaluations and reduce risk on specific projects (Guardian, 2021) .
As published in the Philippine Development Plan of 2017-2022 (2022), a high-trust society broadens the opportunities for inclusive growth as a high trust in governance promotes smoothness among business and official transactions. Trust in the government is the cornerstone of good management. A two-way process happens if there is a high trust; first, the citizens obey the law, and last, they willingly pay the correct taxes trusting that government will be equivalent in managing the fiscal resources appropriately. For the Filipinos to realize the objectives of the Philippine Development Plan, the “Ambisyon 2040” has been given birth. It collectively represents the long-term vision and goals of over 100 million Filipinos for themselves and the country. It aims to answer the questions of what kind of life and how the Philippines will be in 2040 with the concrete strategic plans involved (NEDA, 2022a) .
Resolution No. 03-01-2017, titled Approving and Adopting the Central Luzon Regional Development Plan (CL-RDP) 2017-2022, will adapt the PDP 2017-2022 development agenda. CL-RDP will highlight the regional role in achieving the national goal of a high-trust society and a globally competitive knowledge economy. It will also reflect the potential of Central Luzon to create massive opportunities for all segments of society through responsive and transparent governance. The challenge is to strengthen the public health function, system and sustain or surpass past achievements.
According to Bontá and Meredith (2009) , to perform crucial public health functions, societies must have the necessary infrastructure and resources. The governance and management of public health services serve as the foundation of this infrastructure for public health. The fundamental duties of public health management and governance are accomplished together. The challenges of governance and management include addressing concerns of social injustice and the need to get to the bottom of health disparities.
The Philippine Development Plan offers a comprehensive strategy with applicable policies and the intentions behind laws and initiatives, as it will allow the achievement of health-related goals and show how growth has benefited the Philippines in the years to come. It includes focusing primarily on improving the accessibility, provision of service of the highest quality, and effectively meets the medical requirements of the Philippine Healthcare System (Timogan, 2023) .
Investigating further, the researcher took an interest in studying the implementation of the Philippine development plan in ensuring efficient governance as the study aimed to explore how the implementation of the health-related goals of the Philippine Development Plan is perceived by people in the community, especially before and after its implementation.
1.2. Theoretical Framework/Paradigm of the Study
The development plan aims for clean, efficient, people-centered, and effective governance. Moreover, it aims to reduce corruption, achieve seamless service delivery, enhance administrative governance, strengthen the civil service, and empower and fully engage citizens (Course Hero, 2022) . Based on Chapter 7 of the Philippine Development Plan titled Good Governance and the Rule of Law (GovPH, 2022) , good governance sets the normative development standards as it ensures transparency, fosters participation, promotes efficiency and upholds the rule of law, which is known as the cornerstone of good governance. In addition, the Philippine Development Plan envisions promoting a long and healthy life, including a range of programs starting with quality and affordable universal healthcare.
1.3. Max Weber’s Bureaucratic Theory
A bureaucratic form of governance is an inescapable and omnipresent phenomenon in modern organizations. It is designed as the basis for the systematic formation of any organization to ensure efficiency and economic effectiveness. It is an ideal model for management and its administration to bring an organization’s power structure into focus. Weber’s Theory comprised some principles that governed the implementation of the Philippine Development Plan.
1) Task Specialization or Division of Labor is where tasks are divided and distributed based on functionalities. In the implementation of the Philippine Development Plan, tasks, particularly on its objectives, were subdivided into different agencies to facilitate its implementation.
2) Hierarchical Authority is a system in which different positions are related in order of precedence. The highest rank on the ladder has tremendous power, which is the President. The bottom layers (Provincial, Municipal, and Barangay Levels) of bureaucratic organizational structures are always subject to the supervision and control of higher layers. This hierarchy reflects lines of bureaucratic communication and the degree of delegation, laying out how powers and responsibilities are divided.
Figure 1 shows that division of labor is essential in bureaucratic governance since it allows the ample distribution of tasks or plans among the different implementing agencies. In this study, the health-related goals of the Philippine Development Plan were assigned to the Department of Health being the lead agency and in collaboration with other stakeholders. Each department has its administrator and flows down from the National to the Barangay Level. Hierarchical authority involves the centralization of power and a clear chain of command. Based on this study, establishing functional Epidemiological and Surveillance Units and reducing Stunting Prevalence came from implemented laws. These two are essential to address the health-related goals of the Philippine Development Plan.
For this study, the following are the operational definitions of the concepts used: The LGU Health Scorecard is a primary tool used to assess and monitor the performance of LGUs in implementing local health reforms within the province and city-wide health system. In this study, the researcher included the stunting prevalence—the proportion of child who is too short for their age results from chronic or recurrent malnutrition. Stunting is a contributing risk factor to child mortality. It is also a marker of inequalities in human development,
and one of the goals included in the Philippine Development Plan’s health-related programs is to improve the community’s health and nutritional status to achieve maximum productivity despite problems with limited budget, logistics and even manpower. It aims to utilize all available resources, and efficiency shall be observed.
Conceptual Framework
Figure 2 presents the conceptual framework of the study. The researcher gathered literature reviews pertinent to the study. In addition, the results of the 2021-2022 LGU Health Scorecard of the Municipality of Camiling were used as the main tool of the study and underwent Document Analysis. With the answers transcribed based on the informal interviews among the eight participants of this study, the researcher was able to generate themes after content analysis. Afterwards the creation of themes, the researcher concluded and was able to determine how the status of the health-related programs under the Philippine Development Plan is perceived before and after its implementation.
Since the Public Administration plays a vital role in Philippine economic development and ensuring efficient governance within the context of public sector governance, backed up with the gathered related literature and the conceptual framework, this study is essential so that the programs being implemented will be measured as to their efficiency and program implementation. This is important so that improvements based on the past literature that indicates gaps in program implementations, the results of previous studies, and answers to interviews will aid in the flourishing of programs. In addition, this study will be of use to address and formulate solutions to the identified existing problems.
1.4. Significance of the Study
As a study that focuses on the status of health-related programs under the Philippine Development Plan, this paper will serve as a reference for future readers regarding the differences brought about by the Philippine Development Plan, before and after its implementation. Specifically, the researcher sought to answer the following specific problems:
1) What is the standing of the implementation of the Philippine Development Plan?
2) What are the perceived negative effects of the Philippine Development Plan in terms of governance?
3) What are the perceived differences before and after the implementation of the Philippine Development Plan in terms of good governance?
4) What are the challenges encountered in the implementation of the Philippine Development Plan?
2. Methodology
2.1. Study Design
This article utilized a descriptive-qualitative research design. The researcher utilized this design to provide a straightforward description of the chosen topic and an in-depth view of the study by means of collecting and analyzing the gathered data from the review of related literature and documents and responses to the interview conducted. Furthermore, this research design is very useful to this study since the researcher wants to determine the in-depth perception of the respondents in the implementation of health-related programs under the Philippine Development Plan.
The primary sources of data are document analysis anchored on the Local Government Unit Health Score Card and informal interviews made among the eight (8) participants (six (6) barangay captains, Mayor, and the DILG Officer).
2.2. Population of the Study
The participants in this study are six (6) selected Barangay Captains through convenience sampling, the Municipal Mayor, and the DILG officer of Camiling, Tarlac. Initially, the study targeted ten (10) participants; however, due to personal circumstances, other participants who were supposedly included in this study refused to participate during the interview, resulting in only eight (8) participants.
The Barangay Captains included in the study are those who agreed to participate in the study without coercion, all of them are male and on their last term of service as they were able to be part of the Philippine Development Plan 2017-2022 implementation. Otherwise, those on their first and second term of service as barangay captains were excluded from the study. On the other hand, they help in the implementation of the Philippine Development Plan at the community level.
The Municipal Mayor served for the past six years, and this was his last term of service. And the length of service was enough to determine perceptions about the implementation of the Philippine Development Plan. Hence, being the local chief executive in their locality has a huge impact on implementing in the local government unit the directives coming from the national government.
The DILG Officer was also included as one of the study participants since they are one of the leading agencies that formulate policies, plans, and programs to enhance local autonomy, which mainly focus on the administrative, technical, and fiscal capabilities of every local government unit.
The researcher opted to choose the considered population depending on the availability and convenience of the said participants. As defined in the Principles of Sociological Inquiry: Qualitative and Quantitative Method (2022) , convenience sampling is when the researcher collects data from people to whom he or she has the most convenient access.
2.3. Data Gathering Tools
The primary tool used in this study is document analysis. With the help of the LGU Health Scorecard for the Municipality of Camiling, the researcher gained knowledge concerning the implementation and status of health-related programs under the Philippine Development Plan. Furthermore, the researcher conducted an informal interview with an interview guide.
On the data gathering tool, content analysis was applied. According to Columbia University Irving Medical Center (2022) , content ana lysis is used to determine the presence of certain words, themes, or concepts within some given qualitative data. Thus, the researcher analyzed and interpreted the data from the sources to formulate an in-depth understanding of the chosen topic, which was utilized to develop empirical knowledge. With this, the researcher quantified and analyzed the presence, meanings, and possible relationships of certain words and concepts found in interviews and communication between the participants. The researcher analyzed the following data on the LGU health scorecard:
1) The LGU’s performance in establishing a functional Epidemiological Surveillance Unit (ESU) in the years 2021 and 2022 was the main objective of the first tool. This was to determine, analyze, and interpret the data on the establishment of functional Epidemiological Surveillance Units (ESUs) so that a thorough analysis based on the program implementation would be made.
2) The LGU’s performance in terms of the stunting prevalence in 2021 and 2022 was also included on the data gathering tool. This was to gauge the improvement in the health status of the health program related to perceptions of the implementation of the Philippine Development Plan.
2.4. Data Gathering Procedure
Prior to the interview in April and May 2023, the researcher first sought the approval of the identified Barangay Captains who agreed to participate willingly in the study, the municipal mayor, who has served for the past six years, and the DILG officer, who is one of the lead agencies that formulate policies, plans, and programs to enhance local autonomy, which mainly focus on the administrative, technical, and fiscal capabilities of every local government unit. By asking for their time of availability, followed by the distribution of the signed letter to conduct the interview and the consent form, the objectives and purpose of the study are mentioned in the letter for them to become aware of the interview know-how. Along the way, the mayor and DILG officer were receptive to participating and immediately agreed with the researcher on the interview and let the researcher know their availability. Unfortunately, in the case of barangay captains, the researcher had trouble conducting the interview and selecting participants, as most of them begged off being included in the study when the interview date approached. After a series of rejections and negative updates coming from the first batch of barangay captains, the researcher opted to include another batch of barangay captains to be included in the study until six (6) barangay captains participated and expressed their willingness to become part of the study. Before the interview proper took place, the researcher introduced herself and stated the aim of the interview process. Brief background about the study was mentioned among the participants as well. Upon their approval, the researcher asked for their consent and proceeded with the interview.
Moreover, a document analysis was made on the LGU Health Scorecard. The result for the year 2021 and 2022 were scrutinized. Moreover, a document analysis was made on the LGU Health Scorecard. The result for the year 2021 and 2022 were scrutinized. Pertinent data about the status of stunting prevalence and the creation of the Epidemiological Surveillance Units (ESUs) was obtained, and the researcher made interpretations.
During the data gathering, the researcher used a cellphone as a recorder with a pen and paper to jot down pertinent answers from the participants.
2.5. Treatment of Data
To analyze the data, the researcher applied the content analysis, specifically the conceptual analysis. The researcher grouped similar responses and selected an appropriate theme. Based on the themes generated, the researcher came up with interpretations.
For the LGU Health Score Card reports from fiscal year 2021 to 2022, the researcher conducted a document analysis on the performance level in creating the Epidemiology Surveillance Unit (ESU) and the prevalence of stunting in the Municipality of Camiling. The researcher gathered relevant information about the contents and results of the LGU Scorecard, particularly from the administration and health perspectives focusing on epidemiological Surveillance Unit (ESUs) in 2021 which yielded a result of “No” and in 2021 which yielded a result of “Yes”; and Stunting Prevalence Decrease which shows “No” in 2021 and “Yes” in 2022.
2.6. Ethical Consideration
Before the conduct of the study and after the letter distribution, the researcher secured informed consent and explained to the participants the sole purpose of the research and that their answers were for the study alone. The researcher mentioned that results will be published, and a copy will be handed over to them once completed. In managing conflict of interest, the researcher adhered to the policies of the Barangays where the Barangay Captain resides and to the policy of the Local Government Unit of Camiling and the Department of Interior and Local Government. The participant’s voluntary participation and involvement in the study were also included and discussed with the study participants. More so, the researcher used initials in coding the transcribed answers of the participants.
3. Results and Discussion
The Philippine Development Plan aimed to reduce inequality among Filipinos so they would feel the changes in the public administration. To achieve such, one of the programs included in the medium-term plans is the improvement of the nutritional and health status by ensuring access to proper care at all life stages.
4. Health-Related Programs
LGU Health Scorecard
For 2020 and 2021, respectively, the Municipality of Camiling showcased a remarkable improvement in its health status. To monitor the progress and to track the national priorities to achieve responsive local health reforms, the Local Government Unit Scorecard (LGU Health Scorecard) was formulated (Administrative Order 2019-0027, 2019) . In terms of the health scorecard, a functional and organized Epidemiology Surveillance Unit (ESU) is required to meet some of the medium-term plans and achieve efficient governance. Based on Republic Act 11332 (2020), all the local health offices in every Province, City, and Municipality nationwide, including all the persons and entities required to do mandatory reporting of notifiable diseases under Rule VI, Section 2, of this IRR shall establish a functional Epidemiology Surveillance Unit (ESUs).
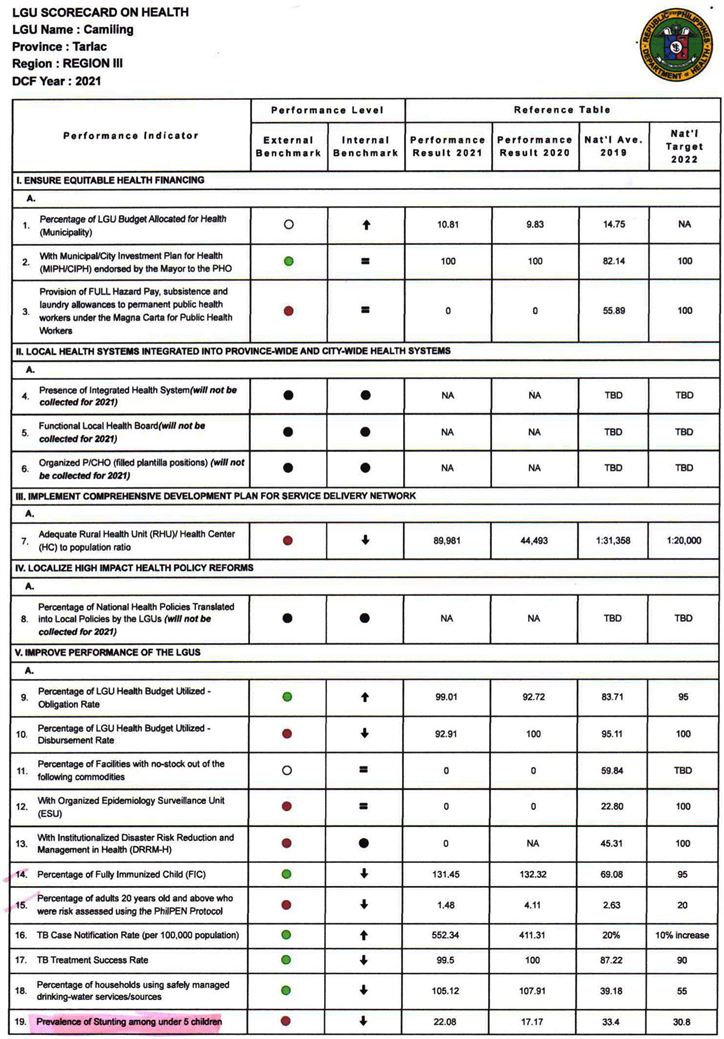
Table 1 shows the performance level of the Municipality of Camiling as published on the 2021 and 2022 LGU Health Scorecards. Based on its result, the researcher found that on the external and internal benchmarking, their performance in 2022 is better than in 2021, which means that the Local Government Unit of Camiling was able to comply with having a functional ESU that will contribute to the achievement of better health outcomes and surveillance management. Surveillance is vital in helping countries monitor and evaluate emerging
![]()
Table 1. LGU Health scorecard performance.
patterns and trends of disease. It is crucial because it contributes to preventing and managing non-communicable diseases.
In addition, the nutritional and health status will be improved by ensuring access to proper care at all life stages. The United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund calls on the government’s policymakers to work together towards robust health and nutritional services for children in the Philippines. According to National Nutrition Council (2022) , malnutrition remains a primary concern in the Philippines, and over the years, stunting and wasting in children under five years old continues to be a significant public health problem. As anchored on the Philippine Development Plan, improving the nutritional status is one of its aims. In 2022, the target of 21.4% was reduced from 33.4% of children under five years of age having high levels of stunting. To be able to achieve efficient governance as to the implementation of the Philippine Development Plan (PDP), the establishment of a functional Local ESU and monitoring of nutritional status will help support the promotion of a long and healthy life, a range of programs starting with quality and affordable universal health care. According to Naher et al. (2020) , the lack of efficient governance undermines the delivery of quality essential healthcare services equitably, makes it costly for the poor and disadvantaged, and results in poor health outcomes.
As shown in Table 2, the Municipality of Camiling has a decreased performance, resulting in stunting prevalence from 22.08% in 2021 to 18.90% in 2022. The collective efforts of the healthcare workers, policymakers, and community people coexist in lowering the stunting prevalence in the municipality. Activities such as growth monitoring, provision of micronutrient powder, and supplementation are being implemented to combat such problems.
According to Worldbank (2021) , the policymakers’ task was to create policies and programmatic actions to address the challenge of reducing childhood undernutrition. Furthermore, these include building a strong and more coordinated partnership for nutrition, securing adequate financing for nutrition, implementing at-scale, well-proven, direct nutrition interventions, addressing determinants of nutrition through multisectoral approaches, establishing geographic convergence of key sectors, and establishing geographic convergence of key sectors.
As to the responses from the participants, there were lots of ideas elicited based on the answers from the participants of this study on the implementation of the Philippine Development Plan in Ensuring Efficient Governance. From these answers, the tables below present the identified general themes (Table 3, Table 4).
![]()
Table 3. Themes—Perceived effects of the Philippine development plan.
![]()
Table 4. Significant changes before and after its implementation.
As to every programs being implemented, there are also challenges along the way.
5. Challenges Encountered
• Budgetary constraints—According to PDP (2022), the Philippines has made progressive improvements in its performance in various global governance indices, such as the e-Participation Index (EPI), Open Budget Index (OBI), and the Legatum Prosperity Index (LPI)-Political Accountability. However, the decline in the scores at the onset of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic in 2020 highlighted the disruption of transparency and participatory mechanisms when the government diverted resources to more urgent service delivery issues. Government budgeting is essential since it enables the government to plan and manage its financial resources to support implementation of various programs and projects that best promote the country’s development. Through the budget, the government can prioritize and put into action its plans, programs, and policies within the constraints of its financial capability as dictated by economic conditions. In order to realize the Philippine Development Plan’s objective to develop and protect the capabilities of individuals and families, the Budget Chief assured that the 2023 national budget has sufficient funding for the social services sector, which includes education with Php 896.08 billion—still the number one priority as mandated by the Constitution. Program longevity and continuity are also anchored on the budgetary requirement. With the LGU Health Scorecard, budgetary constraints on the formulation of a functional Epidemiological and Surveillance Unit (ESU) require a fiscal allocation as a dedicated staff shall be designated to oversee the functionality of the local ESU as mandated by Administrative Order 2021-0057 (2021) . On the other hand, the logistics to decrease the prevalence of stunting rate also faced budgetary problems. A low family income and poor living conditions increase the risk of child stunting because of high food insecurity, low access to health care, and unhealthy environments (World Health Organization, 2018) . To enable strategies to combat stunting among children, creating sustainable and resilient food systems for healthy diets is also one of the cross-cutting integrative areas defined. Adopting such food systems includes creating a diverse food supply that is affordable and geographically close to populations and improving local management of food systems. Being a complex problem, there is no single nutrition intervention to address stunting in children, but rather multiple, complex, and coordinated nutrition-sensitive and nutrition-specific interventions in partnership with other health and non-health actors in development. Some examples include programs for folic acid supplementation, multiple micronutrient supplementation, vitamin K administration, or exclusive breastfeeding.
• Combating Corruption—The Philippines has a long history of corruption in government—embezzlement of public funds, graft, and abuse of official power by elected officials is commonplace. A lack of legislative frameworks for strengthening political parties has led to a party system dominated by personalities and patronage. Another factor that fuels corruption is the lack of legal requirements for financial audits of political party expenditures. These findings are also reflected in public perceptions of corruption in the political party system—TI’s 2009 Global Corruption Barometer (GCB), a large-scale household survey that assesses general public attitudes toward and experience with corruption, found that political parties are perceived to be one of the most corrupt institutions by the Philippine people (Corruption Report, 2009) . Corruption, however, still costs Philippine government procurement 30% of its allocated budget, as reported by the Bertelsmann Foundation in 2008. Though no laws protect citizens’ freedom of information enacted in the Philippines, the Constitution contains “the right of the people to information on matters of public concern.” The speed with which information can be accessed is contingent upon personal connections within the government and suffers from a decentralized government data storage policy. In line with this, the Government Procurement Reform Act and other pieces of legislation address corruption challenges related to conflicts of interest. However, the enforcement of this legal framework is not uniform across all agencies and therefore has limited the success of this initiative (Transparency International, 2019) .
“Strategies that aim to foster an environment that penalize anti-competitive practices and strategies to aim to build a high-trust society “kasi sa implementation of the Philippine Development Plan, napakalawak po ang saklaw niyan na programa.” (For the implementation of the Philippine Development Plan, it covers a wide range of programs).
• Limitations in evaluation and program monitoring—Local autonomy has also been implemented with decentralization. Local autonomy is the ability of the local communities to govern, initiate, integrate, make decisions, and take actions with minimum outside direction from the national government. It involves, first, the right of local entities to administer their affairs freely in accordance with their own will and, second, the right of the local citizenry to determine that will. Its implementation with other programs implemented alongside resulted in limitations on program monitoring and evaluation.
“One common criticism is the challenge of effectively implementing the initiatives of the PDP.”
6. Analysis of the Study Findings
The themes above are based on the answers from the respondents. Out of the findings of the study, the researcher’s analysis is as follows:
• Uniformity in Direction—is one of the positive impacts since the PDP has been implemented. Having a uniform direction in governance provides a clear delineation to everyone. This also makes it easier for the Local Government Units to have a specified target that needs to be implemented and achieved. In connection with the LGU Health Scorecard results, the Local Government Unit follows the uniformity of direction through the establishment of ESU in the Republic Act No. 11332 Section 8, which mandates the uniform establishment of ESU in all levels of the DOH and its local counterparts, and in public and private health facilities and laboratories, as well as ports and airports in ah provinces, cities, and municipalities throughout the country.
• Collaboration—Collaboration among the stakeholders has a vital role in attaining successful public administration and efficient governance. The stakeholders could directly create success for the organization as a whole. With the continued implementation of the Philippine Development Plan as a medium-term plan, one factor for its success will depend on the stakeholders doing their part. In public administration, there is a term called collaborative public management, and this is a concept that describes the process of facilitating and operating in multi-organizational arrangements to solve problems that cannot be solved or easily solved by single organizations. Collaborative means to co-labor to achieve common goals, often working across boundaries and in multi-sector and multi-actor relationships. Collaboration is based on the value of reciprocity and can include the public, which is a dominant factor in the success of the Philippine Development Plan. The collective efforts of the RHU staff, Barangay Councils, Barangay Health Workers, Barangay Nutrition Scholars, community people, and the Local Chief Executive, together with the Sangguniang Bayan members in Camiling, lead to the successful creation of the Local Epidemiological and Surveillance Unit in town. Aside from that, programs to combat malnutrition were implemented all over town, prioritizing undernourished children resulting in decreased stunting prevalence among them.
• Corruption Reduction—If there was a positive effect of the implementation of the Philippine Development Plan, it is the decreased rate of corruption due to increased transparency, especially on government expenditures. The transparency of public institutions is essential as having access to information develops citizens’ trust in public institutions, enabling citizens to understand public policy decisions and monitor their implementation.
• Strengthened Local Governance—A well-functioning, strengthened local government has two accepted substantial objects: active participation and effective leadership. These are necessary for the governance of local government intuitions to be contented to its founding purpose. Strengthened local governance means proper decentralization, e-Governance, women, institutional and individual empowerment, effective leadership, and participation of the elected representatives. It is one of the schemes of decentralization of power for delivering government service to the door of citizens for their well-being.
The researcher also found out the negative effects of the PDP implementation.
• Financial Constraint—In public administration, fiscal administration is defined as managing financial resources and those activities and operations to generate revenue, make those available, and see that funds are wise entirely, lawfully, effectively, and efficiently spent. Every program to be implemented has corresponding funding to sustain the needed logistics and resources. The administration of finances is an intrinsic component of management responsibility. Nevertheless, that does not necessarily mean that the program will be granted automatically with equivalent funding so that funds misappropriation will be prevented. To prevent this, a review and approval by the administrative official of the line or operating agency of all requests for money releases and budgetary allotments, vouchers, and similar papers before payments are made so that expenditures follow policy and law and not irregular, unnecessary, excessive, extravagant and unconscionable.
• Corruption—Corruption is a systemic and adaptive phenomenon requiring comprehensive and multidisciplinary approaches for effective prevention and combat. In the government, critics believed that every program being implemented would be used as a channel to implement corruption in the process. One of the sole purposes of the Philippine Development Plan is to combat corruption, if not eradicate corruption. However, in reality speaking, it takes work to get rid of it. With the PDP implementation, the government aims for transparency to reduce corruption even on the grassroots level. Moreover, on the data published since its implementation, a significant decrease in corruption has improved, making the people trust the government more. It minimized the negative effects of the PDP I ensuring efficient governance and, in return, the people trust the government more.
• Implementation challenges—The Philippine Development Plan creates fast-paced program implementation. The problem is that along with its launching, implementation challenges have yet to emerge. However, it is common to observe a gap between what was planned and what occurs due to policy implementation. Policies are set at higher levels in a political process. They are then communicated to subordinate levels, charged with implementing the policy’s technical, managerial, and administrative tasks. Along the way, the researcher also found significant changes before and after its implementation.
• Good Public Affairs—Public affairs deal with noncorporate entities, such as government agencies, nonprofits, and trade associations. Advocacy plays a significant part in public affairs. Government and public advocacy are vital aspects of a successful public affairs strategy. Creating and maintaining relationships that benefit your industry or cause is vital to influencing laws and actions. Lastly, public affairs tend to focus on public policy, and with the implementation of the Philippine Development Plan, an excellent public affair has been observed.
• More Projects Implemented—Public administration is the backbone of a modern state. It shall implement programs and projects to elicit and generate a higher income to improve services provided to the people. When the PDP was implemented, health-related programs and programs to combat malnutrition were implemented to support the objectives of the PDP. In addition, the more projects being implemented, the more the economy will grow due to more public resources. In the case of combating malnutrition, the Department of Health, in collaboration with the National Nutrition Council, launched a program called “First 1000 Days” that mandates the different stakeholders starting from the Barangay level to formulate a barangay nutrition action plan, monitor its implementation and to reach out to the different partners to ensure that there is sustainability in the program implementation.
• Compliance to program implementation—Compliance with program implementation ensures that the standards are achieved. The why of a program being established shall always embody the reason for its implementation to gauge the satisfaction of the program recipients. More importantly, a program will have a higher success rate if compliance is observed since it enhances consistency in an organization.
As programs are implemented, challenges along the way also emerge.
• Budgetary Constraints—Despite the improvement in performance in budgetary problems, the Municipality of Camiling experienced a backlash on their budgetary allocation because of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Improving local governments’ financial status and operations to enable them to carry out their mandate is the foremost concern. This concern compels them to emphasize the administration of their fiscal and other economic resources. An efficient and effective local fiscal administration becomes imperative for them.
• Combating Corruption—Corruption is widely recognized as a social plague that affects most countries worldwide. In the Philippines, corruption issues in the public sphere have been a constant concern even though earlier and more recent leaders have won their seats under the battle cry of ending corruption. A collective effort from the government, policymakers, and the people is highly needed to combat corruption. Countering corruption means countering an environment that promotes might as right and repeatedly oppresses societies, particularly its vulnerable groups, through effective prevention strategies and programs developed through broad-based partnerships. The best way to combat corruption is to empower and strengthen the bodies that advance anti-corruption measures. The Philippines has a better chance of advancing integrity initiatives in the public sector through related reforms introduced and instituted by these organizations.
• Limitations in evaluation and program monitoring—The local government unit, since its devolution, experienced limitations not only on its resources but also on program monitoring. This limitation became one of the challenges they needed to overcome to implement efficient governance. Program monitoring should be iterative and integrated into the program from the start. This process can generate early warnings when things are not going as planned. It informs both continuous improvement and adaptations made to activities. Monitoring can provide the information needed to revisit decisions and change course in the program implemented.
7. Conclusion and Recommendations
7.1. Conclusion
This study focused on implementing the Philippine Development Plan to ensure efficient governance. In addition, the perceived positive and negative effects of the Philippine Development Plan to achieve efficiency in governance, the differences before and after its implementation, including the challenges that took place after implementing the program were included in this study.
With the document analysis made on the 2021-2022 LGU Health Score Card result, the study revealed an improvement in the health and nutritional status result in the municipality. This was by having an established Epidemiological Surveillance Unit (ESUs) as an integral part of the medium-term under the Philippine Development Plan and the improved stunting prevalence rate in the Municipality of Camiling from 22.08% to 18.90% with the National Target of 21.4% Nationwide.
Like any other program implemented, PDP brought significant changes not just on the national level but to the barangay level. In good public affairs, the government, or in this case, the Local Government Unit, must establish relationships between an organization and the people that interact with it, both directly and indirectly and become transparent with them.
More projects were implemented, ensuring that governance is efficient through being responsive to the needs of its citizens and increasing their awareness to establish their relationship with the general public.
Compliance with program implementation has improved. Since efficient governance requires continuous improvement, the government must realize that good governance requires constant improvement as internal and external circumstances change. The possible best practices shall be implemented for the benefit of its shareholders and stakeholders. These changes were attributed to the continuing development of infrastructures and program implementation here in the Philippines. With these significant changes that revolved around three themes identified, the researcher discovered that these are essential in ensuring efficient governance and implementation of the Philippine Development Plan.
Challenges are also encountered during the program implementation, bringing difficulty and mishaps.
7.2. Recommendation
Good governance creates a strong future for an organization by continuously steering towards a vision and ensuring that day-to-day management is always lined up with the organization’s goals. At its core, governance is about leadership. An effective board will improve the organization’s financial and social results and ensure the owners’ assets and funds are used appropriately.
Based on the themes elicited in this study, the following are recommended by the researcher regarding the implementation of the Philippine development plan to ensure efficient governance:
1) To Deepen the Participatory Governance—Deepening participatory governance means establishing functional participatory platforms that inform or consult citizens and ensuring that citizens and Civil Society Organizations have concrete roles and significant influence in all stages of public decision-making. Achieving this outcome will require a deeper understanding of the nuances and priorities of marginalized sectors such as women, children, indigenous peoples, overseas Filipinos, persons with disabilities, agricultural communities, and geographically isolated and disadvantaged areas.
2) To put in place the legal and institutional frameworks—Corruption is a significant obstacle to good governance in the Philippines. A recent literature review suggests that all levels of corruption, from petty bribery to grand corruption, patronage, and state capture, exist in the Philippines at a considerable scale and scope. Putting the legal and institutional framework create pathways that give citizens relevant tools to engage and participate in their governments to identify priorities, problems and find solutions.
3) Improve national governance assessments—The government must perform and conduct a timely governance assessment and improve the policy learning environment at all levels (Barangay to National).
4) To strengthen and rationalize the government functions, systems, and mechanisms—Bureaucratic efficiency improvement is a foundation that enables the environment for economic transformation. An efficient bureaucracy exercises the best use of its resources, including operational costs, time, and human resources (HR), while effecting coherence, rationality, and uncertainty reduction to deliver the intended results. Strategies for this outcome include rightsizing and digitalizing government functions while enhancing productivity.
5) To maintain integrity on all government offices and staffs—Integrity is a crucial determinant of trust. As government integrity is measured by the impartiality, openness, and accountability of its institutions, corruption may, in turn, erode trust in the public sector, thereby affecting the overall effectiveness of governance. Integrity policies, aimed at preventing corruption and fostering high standards of behavior, help to reinforce the credibility and legitimacy of those involved in policy decision-making, safeguarding the public interest and restoring confidence in the policy-making process.
Appendix A. LGU Health Scorecard Result—2021

Appendix B. LGU Health Scorecard Result—2022