Professional Training: Crucial Need to Enhance the Efficacy of Preschool Teachers in the Context of Bangladesh ()

1. Introduction
1.1. Background
In 1889, Japan had formulated its relevant rules, legal systems and specific educational goals for the development of Preschool Education; because Japan believes that Preschool Education plays a significant role in the sustainable development of the country [1]. Early education stage is a strong network of culture, customs, rules and social behaviors that affect the lifestyle of every individual [2]. But the goal of preschool education differs from country to country basing on their culture and socio-economic background [3]. Australia spends high level of investments in early years learning, especially in pre-primary education; because this learning makes effect on subsequent outcomes, i.e. academic success, labor market performance and socio-economic mobility [4]. In Bangladesh, the national education commission 2003 suggested pre-schooling for the age group of 4 - 5 years to ensure quality education at primary level; but like other developing countries, here also Early Childhood Care and Education programs are suffered by teachers with low qualification [5]. Along with other countries Bangladesh also started to focus on Early Childhood Education for the development of young aged children [6]. Here Preschool Education has been started its journey in the twenty-first century. Children are introduced to Pre-Primary Education (PPE) before they begin their formal school. PPE is considered as integral part of Primary Education in the “National Education Policy” that was approved in 2010. It is the most promising intervention in early childhood care and development in Bangladesh. It was approved by MoPME (Ministry of Primary and Mass Education) in 2008 for effective implementation of one year PPE for all children [7]. In the year 2010, The Directorate of Primary Education planned a yearlong PPE program for 5+ years old children, which was under Primary Education Development Program-2. Later from 2011, this program is extended under Primary Education Development Program-3 with remarkable levels of interventions to elevate the PPE up to a minimum quality standard for universal acceptance [8]. In PPE it has a rapid expansion from 895,000 (enrolled in 2010) to 2.86 million children by 2015 [9]. During a research study it was found that people outside have a tendency of thinking preschool teachers as babysitters. People do not understand the importance and developmental aspect of preschool curriculum [10]. The curriculum of preschool education or early childhood education has been designed to support children’s cognitive, physical, social and emotional development. Preschool teachers are responsible and hold the main power for the entire organizational educational process. Directly and indirectly teachers guide the children and create a psychological effect on them [3]. Preschool teachers are considered as “Critical Socializing Agent” of children’s social and emotional development. They have abilities to make effect on children’s psychological development. Children display their compassion level, when they are guided positively with sympathy during expressing their negative emotions [11].
1.2. Methodology
Using secondary data analysis method, this paper has opted for qualitative approach. Books, relevant scientific and academic articles, information from various sources, national and international reports and authorized websites have been utilized as secondary sources. After analyzing articles of related information and data, the main focus of the paper has been to arrive at deductive explanation. During collection of data from e-resources, unauthorized websites were carefully avoided. The research could have been more enriched if some survey or quantitative method had been applied along with qualitative method.
1.3. Objective
The objective of this paper is to highlight the importance of teacher’s EFFICACY for children’s development and to explore the ways of EFFICACY through professional development training in the context of Bangladesh. Pre-primary level of Government’s project is discussed here. In this article, the main focused part is “Lack of Teacher’s Training” of the mediocre preschools of city/metropolitan areas; which are showing poor standard in generating an enjoyable learning environment for the development of preschool children.
2. What Is “EFFICACY”
In a study, authors described three areas i.e. teacher’s professional background, classroom attain qualities and teacher’s job attitude by examining three groups of teachers basing on different categories. The indicators of “Professional Background” are teachers’ educational attainment, experience in early childhood education, special in-service training in child development area. “Classroom attain qualities” is defined by teachers’ emotional interaction with children, classroom management skills and instructional strategies. “Job attitude” is explained by job related stress, job satisfaction and commitment to the teaching. These all factors are inter-related with one another. Jeon et al. found out that an effective outcome of teaching is directly and indirectly effected by teacher-centered issues [12].
According to the study, teaching profession has some common characteristics, such as: knowledge, responsibility, ethics, training, continuing education, autonomy, professional organization, providing public service and prestige. These characteristics are defined in three dimensions of academic, ethical and systemic. “Professional Training” is mentioned as a prime requirement of “Academic Dimension” for being a teacher in this process [13]. Knowledge is related with training and it’s a continuous process. EFFICACY develops with knowledge, experience, sense of confidence and Training. EFFICACY means the ability to perform a responsibility to a suitable and expected degree. “Teacher’s Efficacy” is the level or state of confidence or belief that teacher has in his/her ability while teaching students. It is individual’s beliefs about own capacity to organize and exhibits a performance successfully. Efficacy is his/her self-confidence in offering effective education to students [14]. It makes teacher feel confident and competent. With the help of teacher’s efficacy, children achieve success and bring out the best objectives of their learning. Along with the social and academic attainment, teachers prepare students to develop confidence and self-esteem amongst them. For progressing these beliefs in students, teacher should possess this vision inside him/her. Knowledge and skills are the efficacies that indicate preschool teacher’s standard behavior. Occupational teaching efficacy also relates with teacher-students interaction, planning and organizing the lessons efficiently, skilled classroom management, developing and utilizing updated teaching strategies and evaluating of students’ output effectively [15].
In a study Senol and Ergun described the difference of self-efficacy beliefs in between pre-service preschool teachers (trainee) and preschool teachers. Authors wanted to state that teachers who have high efficacy beliefs, they can develop positive attitude among the students, which gradually make them successful in different stages in life. During this study, they used “Multi-Factor Self-Efficacy Scale for Preschool Teachers”, which is comprised of six sub-factors of Teaching and Learning process, Communication skills, Family Participations, Planning, The Regulation of Learning Environment and Classroom Management. After analyzing the study, it was found that preschool teachers scored high than pre-service preschool teachers. Because preschool teachers apply both the knowledge, information and skills they gained from university and from professional in-service trainings [16].
Self-efficacy does not grow abruptly. It requires time and experience in that field over the year. A teacher who has urge and patience to learn, to develop and has positive attitude towards teaching can achieve mastery in this field. Various in-service trainings, available of teaching resources, training aids, good environment of school, teacher’s mental health, teacher’s personality, teacher’s success, all these can put effect in building efficacy. School’s authority, colleagues, parents also play an important role by encouraging a teacher to gain that competence. Efficacy also can attain by In-service training, peer training, observing other teachers, discussions, reading, workshops, seminars, etc. In the USA, Guo et al. carried out a study on 48 preschool teachers to find out the main factors and their inter-relations behind teacher’s self-efficacy. Teaching experience, teacher’s collaboration, teacher’s influence on decision making and children engagement were discussed here with facts and figures, which act as main factors of self-efficacy [17].
3. Why Do the EFFICACY of a Teacher Is Necessary
Teacher’s attitude, personality and behavior have an enormous impact on children. The professional development of a preschool teacher does not mean the individual development, rather it means a total institutional development of culture and learning through that process of preschool stage [2]. When teachers possess a positive attitude, it makes a positive influence on the children of classroom. In Malaysia, Early Childhood Education (ECE) helps to promote cross cultural understanding and celebration of cultural diversity. Preschool teacher plays an effective role to establish cultural acceptance and positive racial interactions amongst the children. Before transmitting this belief to young aged children, teachers need to possess this belief in them. For minimizing the cultural prejudices, stereotype attitudes and biasness Malaysia offers effective teacher training on “Multiculturalism”. It ensures all preschool teachers develop multicultural education, understanding, positive attitudes and adequate pedagogical skills. Preschool teachers who completed the trainings, put positive impact on their practices and beliefs in multicultural classrooms [18].
A good teacher can positively affect children’s learning and makes differences in their academic outcomes. In preschool stage, very often teachers need to address young-aged children of challenging/negative behaviors. If these challenging/negative behaviors cannot be addressed properly in expected way (positively) then it creates problems in future or brings poor outcome later [19]. Managing challenging behavior of children is an complicated factor of classroom management process. Effective classroom functioning depends on how efficiently a teacher can manage children’s behavior [20]. A study in the USA was carried out on 1129 preschool teachers. Researchers had found that educational training specifically Bachelor’s Degree, Child Development or Early Childhood Education coursework put a positive and comparatively less-negative impact while responding to children. Educational program and courses that focus on Child Development Theory, help teachers respond positively to children’s social and emotional behavior [11]. Training always developed and upgraded the sense and introduced changes about the ideas. While determining the efficacy level of preschool teachers in Turkey (Malatya), the research has shown that teachers with special education training, knowledge of local laws and policies, experience and self-confidence in working with disabled students scored significantly good marks. They displayed very effective performance in class [14].
Self-efficacy is a tool of a teacher, which helps to understand and act with the situation. Children will receive high-quality experiences from preschool teachers who bear standard qualities. In Turkey Preschool Teacher Training program enriches teachers with knowledge, skills and positive attitude towards preschool teaching profession [15]. Many developed countries increased investments in preschool program considering the importance and future development of children’s education. In Japan, preschool teachers get specific training and learning activities for improving their professional skills and quality in teaching process [1]. Various science projects of the USA, Germany and Australia have recently introduced science-specific professional development programs for preschool teachers. These programs will help teachers to conduct science teaching to preschool student with competence [21]. In line with this we can assume, less qualified and non-trained teachers cannot show desirable and actual performance in class. These teachers limit the learning process and output of students. They demonstrate underrated performance when it comes to handle negative attitude of children or challenging situation in class. In many schools, it has been observed that preschool teachers are often undergraduate and less qualified; as they are recruited for teaching 3 to 5 years old children. Barnett focused in his article that four-year degree is prime requirement to be a preschool teacher. Higher education is linked with better teaching. Well educated and professionally trained teachers play an important role in aspect of children’s social, emotional, linguistic and cognitive development [22]. Again, many researchers also shown that teacher’s qualifications, academics major or credentials cannot ensure children’s success, this is basically teacher’s sense of self-efficacy significantly affect the high-quality classroom’s performance and children’s achievement [17].
A study on educational background and professional development of 151 preschool teachers and caregivers (in the Midwestern state of United States) was carried out who work with the children of 03 to 06 years old. It has been found that specific training and coursework of early childhood education made changes in thoughts and beliefs of preschool teachers and caregivers. They allow children more with their active participations, respect children’s individual interests and understand the importance of peer collaboration in play and learning activities. It has been found that teacher’s qualifications significantly affect the quality of care and education provided to young children; higher qualifications in teachers contribute more positively in this aspect. The diversity and less qualification of early childhood teachers and care givers may negatively affect the children [23]. A preschool teacher may often feel overwhelmed and frustrated if he/she does not have that behavioral understanding of children. A preschool teacher needs to gain a sense of mastery over student’s behavior and classroom management. Professional development is required to facilitate teachers’ understanding of the instructional behavior and student’s psychology. Pedagogical training can enhance the development of methodological part of teaching and learning. The result of a survey showed that preschool teachers who often attend external professional training, they displayed modern positive attitude towards teaching and professional development [2].
Efficacy comes with professional development. With the help of self-efficacy, a teacher can organize and apply his/her capacity in teaching. Basing on the situation, efficacy and competence are required to ensure a controlled management of class, to involve students with their active participation and to use effective teaching method. The results of the study (on 204 preschool teachers in Croatia) suggest that along with the experience, teachers need elective coursework and training in the area of Classroom Management to address challenging behavior of children and to efficiently manage the class. Teachers also need professional supports from expert personnel [20]. The process of teaching helps students in building up the academic life. Preschool teachers along with the teaching need to coordinate and work with other educators, therapists, psychologists and parents for the overall development of the children. In Israel, all preschool teachers (of both public and private sector) are trained under similar training and socialization process; that’s why the general perception of pedagogy of all teachers are in same line towards the teaching. For the professional requirement, teachers of public sector further need to participate in other professional development trainings. Thereby, public sector’s teachers remain more updated and positive toward any changes that are required in teaching techniques [13].
Learning takes place when the teacher and students are connected from both sides successfully and they understand each other. In line with this, another study showed that formal training and on-job-trainings are beneficial for preschool teachers. Participants of the study expressed that, training affects their attitude towards teaching. Thereby this positive attitude also affects the children positively in classroom. Educational leaders need to support the teachers by arranging adequate training for them, so that teachers can enhance their knowledge which will ultimately affect their attitude towards preschool education [10]. Although research showed that, except self-developmental training, there are other professional variables also which affect teacher’s competences; such as their graduated department, place of residence, economic competence, duration of professional experience, etc. [24]. Normally preschool teachers of Bangladesh convey traditional conceptions of preschool education [8]. Preschool stage is such a sensitive stage of children’s development where their learning process is totally different than traditional learning. Children always enjoy playing and joyful activities. Wisneski and Reifel showed that play has been at the center of the young aged children’s educational curriculum throughout the history of early childhood education; from Pestalozzi and Froebel’s Kindergartens to Montessori’s Method; and Rudolf Steiner’s Waldorf schools to Reggio Emilia Curriculum [25]. So, teacher’s efficacy will guide teacher to recognize this paly based, child-centered learning process while implementing the ideas and sharing knowledge with children of preschool.
4. Training Modules of Different Countries
To develop preschool teachers’ professional competencies, both formal and informal learning opportunities are important [21]. An effective teacher does not gain efficacy automatically over the period of time; rather in line with the teaching experience, it is the training what makes a teacher efficient and makes teaching effective. Training helps teachers to gain work-based learning and skills besides theoretical knowledge. In Turkey, Open Education Faculty of Anadolu University runs an Undergraduate Program for preschool teacher training. This faculty runs the same program in both ways of Formal Education and Distance Education. The program was prepared by Higher Education Council of Turkey. In order to admit to this training program, candidates have to be graduates from “Child Development”, “Children and Education” and “Children Development and Nurturing” department. Along with candidates also need to pass university entrance exam for placing in Preschool Teacher Training Program. This course consists of occupational knowledge of teaching, subject area knowledge and world knowledge. In this program, besides theoretical courses, two practical courses are also practiced, named “Teaching Practice” and “Practice in Preschool Education” [15].
A teacher can practice the outcome of the training in class combined with his/her experience. A motivated and skilled teacher has a significant role to play for students in Early Childhood Education. Describing the modern competencies in the training process of preschool education specialists, researchers showed the existing practices of Germany, United Kingdom and Ukraine. In Germany, preschool teachers are gone through Bachelor’s Training and Master’s Program Training. Here the process of training specialists in preschool education is determined by institution. In the United Kingdom, a detailed and comprehensive framework training is applied to achieve preschool teacher’s competence. Professionalism along with the standard combination of values, knowledge and skills are mainly focused here. In Ukraine, the main competence of training process for preschool teachers is based on professional basic knowledge and skills, values and attitudes, and motives of pedagogical activity [26].
In Croatia, for the professional development of preschool teachers, they focus on continuous learning and explore individual practices, such as taking part in external professional training (arranged by agencies, associations or universities), finding out the interests/limitation of each child of class, participating in internal training (workshops, seminars, lectures), practicing action research, meeting with other preschool teachers for exchanging views and ideas etc. [2]. Study confirms that mentor training of preschool teachers who directly involve and supervise students’ learning is very demanding and helpful. In Finland, Training of preschool teachers consists of 180-credit bachelor’s level degree program. The research-based training contains studies of educational science, approaches to childhood, pedagogy, sociology, psychology and the arts. It includes lectures, seminars, workshops, small group exercises and necessary practicums of preschools. The practicums and seminars focus on observing the learning environment, the children, the professional identity and ethics of preschool teachers, the pedagogy and curriculum work of early childhood education. It also focuses on the holistic responsibilities of preschool teachers’ works, their cooperation with other teams and parents. Through these professional training, the trainee teachers investigate the development process of preschool. Each of these practicums is guided by a university lecturer (A tutor) and a preschool teacher (a mentor) [27].
Zsofia and Serfozo explained in detail about the preschool teacher’s training of Hungary. From 2019 Faculty of Primary and Preschool Education of “Etovos Lorand University” launched the international kindergarten training in level of Bachelor’s Degree program (3 years duration) in Hungary. The preschools here are regulated by their government. Before starting the training, the trainee students seat for an entrance aptitude exam. As part of the exam, candidates must demonstrate physical fitness and singing skill. This practice-oriented training consists of both theoretical and practical lessons. The aspects focused in this training are as follow:
1) Professional and methodological knowledge regarding the harmonious and complex stages of health development of a child (3 to 7 years).
2) Adapting the knowledge of pedagogy, psychology and sociology; taking responsibility of children for the comprehensive development.
3) Working on developing the group experience, knowledge and attitude of children (3 to 7 years age group) [28].
To develop social side of children Executive Functions (EF) play a vital role. It also helps young learners with academic achievement and school success. German preschool teachers undergo a training program named EMIL to improve the EFs of preschoolers. Walk et al. carried out a study on eight preschools. Total number of 67 preschool teachers and 133 children participated in the study. They showed in the article that teachers’ training can put a significant contribution to improve the EFs of preschoolers. EMIL is an intervention program designed to enhance EF skills in children. The trg prog consists of eight sessions (28.5 hours). It covers four aspects; those are: a) Attitude (teacher’s mindset and child’s perception), b) Interaction and communication between teachers and children, c) Structures (timing, materials, rules, group structure) and d) Activities (games, physical activity, pretend play, mindfulness and relaxation techniques) [29].
Classroom Assessment Scoring System (CLASS) is an observational instrument or teacher-assessment tool that captures teacher’s behavior in classroom. It assesses the quality of teacher-child interactions in preschool classroom. It measures the emotional, organizational and instructional supports provided by teachers, which contribute to psychological, social and academic development of children. Many researchers found this system helpful to improve the understanding level of teachers specially in preschool level. This training process changes in teachers’ behavior across the domains of emotional support, classroom organization and instructional support. Casbergue et al. conducted a study that included seven preschool classrooms in urban area. Seven preschool teachers participated in that study who were observed by certified reliable observers in three 20-minutes period following CLASS observation protocol. Later on teachers joined weeklong professional development CLASS reliability training which consisted observation, coding, discussions on multiple examples of videotaped classroom’s interactions. It led to deep thoughts and understanding to the teachers and worked as indicator to improve the teacher-students interactions. After study, it is found that all teachers improved in their interactions as measured by CLASS but some made notable improvement in certain areas. CLASS training helps teachers to make changes contribute positively to children’s academic achievement [30].
An Academic Skills Training Program was carried out in Malaysia in December 2008 session. Twenty-three (23) teachers from different faculties, schools and centers participated in this program. This consisted of nine modules of classroom presentation skills (2 modules), teaching methods and techniques (2 modules), teaching and learning theories (1 module), assessment and evaluation (2 modules), outcome-based education (1 module) and micro-teaching (1 module). All these modules covered different aspects of teaching and learning sessions including self-assessment as teacher and assessment of students. The study was conducted with 2 modules of classroom presentation skills. At the end of the study, participants with prior teaching experience and fresh participants (with no experiences), all were benefited. They mentioned it in their post training feedback form. The teaching skills were facilitated by this training [31]. In Malaysia “Foundation Level Certificate Program”, “Post-graduate Diploma”, four years integrated “Bachelor Degree Course” on Early Childhood Educations are the trainings offered by various institutions and universities for preschool teachers [18].
In Israel, preschool teachers (both public and private sector) are trained in Teachers’ Education Colleges for four (4) years to receive a B.Ed. Degree (Bachelor of Education). Here, preschools are separately run under direct supervision of Ministry of Education, Pre-Primary School Education Department [13]. Training is the most effective forms of organizing methodological work. Psychological training along with pedagogy helps teachers to know about self-knowledge, self-perceptions, self-corrections and modification of pedagogical attitude in professional communication. It also improves communicative competence of preschool teacher. Other forms of training, e.g. business games (participants share their ideas about a given problem), certified courses, methodological associations (discuss and solve the problems, sharing innovative ideas, sharing experiences), internship (individual form of methodical work) are described here thoroughly. The objective of “Internship” is to explore in excellence, develop personal and professional qualities for performing upcoming responsibilities [32].
In Australia, NQF (National Quality Framework) provides and supervises a national approach to regulations, assessment and quality improvement of early childhood education and care. It sets out the qualifications and “educator to child ratio” requirements for children’s education and care services. The National Quality Standard focuses on 7 areas; such as: educational program and practice, children’s health and safety, physical environment, staffing arrangements, relationships with children, collaborative partnerships with families and communities, governance and leadership [33]. Australia also emphasizes on providing adequate training for preschool teachers and care givers, so that they can help children to develop socially, emotionally, intellectually and physically. For delivering education and care to young aged preschool children, there are three types of qualifications available in Australia. Those are: Early Childhood Teaching Qualifications, Diploma Level Qualifications and Certificate III Level Qualifications. They have also “Quality Improvement Plan” which helps providers to self-assess their performance while delivering education and for future improvements [34]. These qualifications depend on degrees; e.g. Bachelor of Education in Early Childhood (3 - 4 years course), Diploma in Early Childhood Education (1.5 years course), Masters of Teaching (Early years―2 years) and Masters of Teaching (Early childhood―2 years).
5. The Scenario of Preschool Level in the Context of Bangladesh
5.1. Pre-Primary Education Plan of Government
In Bangladesh, Early Childhood Education is provided by Government, NGOs and Private schools. The Government has announced “The Comprehensive Policy on Early Childhood Care and Development” in 2013 [6]. This policy was adopted by Ministry of Women and Children’s Affair, where it is aimed to nurture children (of all status) with security, dignity and care [35]. The Government of Bangladesh gives high priority in education sector to ensure the Education For All. A large portion of National Budget is kept to improve the educational sector. Though there are a lot of problems (political, social, environmental, transport and communication, economical etc.) but slowly and gradually it is developing this educational area including the pre-primary level [36]. The Government is committed to provide one year pre-primary education through the regular primary education system. These pre-primary activities are run by various programs of different national and international NGOs (Non-Government Organizations); e.g. GSS (Gonoshahajjo Shangstha), BRAC (Bangladesh Rural and Advancement Committee), Save the Children, Plan International, GS of GB, Care Bangladesh, Action Aid, Dhaka Ahsania Mission, FIVDB (Friends in Village Development Bangladesh), CARITAS (Churches Around Richmond Involved To Assure), Phulki and Bangladesh ECD (Early Childhood Development) Network. Pre-primary educational activities of government are planned basically for the children who are underprivileged and poor. Government focus on the children of urban area, rural village area, slum area, coastal area, haor area, tea garden area, brothels, central prisons, madrashas, maktabs and remote hilly areas of Chottogram. As per the report, the total number of pre primary education centers in 2012 was 88,225. Government was running 60,965 centers (69%); NGOs were operating 23,168 centers (26%) and ELCDP (Early Learning for Child Development Project) was running rest 5% centers [37].
5.2. Pre-Primary Teachers’ Training under Government
Rashid and Akkari evaluated and explained the policy, quality and impact of ECE (Early Childhood Education) of Bangladesh. In the study they mentioned that “more than half of the pre-primary teachers from all kinds of pre-primary service providers had any kind of teacher training and among them 35% had training particularly on pre-primary education” [6]. As per Country Report on Early Childhood Care and Education of Bangladesh, NCTB (National Curriculum and Textbook Board) developed National Pre-primary Education Curriculum and teaching learning package to be started from January, 2014. Here, it mentioned that all teachers need to have training on new curriculum with child development issues. NGOs and government projects have teachers who are having different academic backgrounds. Most of the government-trained teachers are SSC (secondary school certificate) qualified; as it is set as minimum qualification. Few teachers are also having the qualification of below SSC. NGOs usually arrange refresher’s training for their teachers. In operational framework of PPE (2008), government declared that the ideal ratio of teacher-children would be 1:30; which is normally above in most government schools. In Bangladesh there are total 649 teachers’ training centers are available; where government has 536 training centers. Government has 1603 trainers in PTI and Upazilla Resources Centers to provide teachers’ training. NGOs have 226 trainers and other projects have 35 trainers. NGOs have a regular system of supervision of this training and supervisors are also gone through training. Government does this supervision by Upazilla Education Officers. There are 68,200 trained teachers are supporting pre-primary education in 88,225 centers. DPE (Directorate of Primary Education) has trained 40,915 teachers; ELCDP project has trained 8731 and NGOs have trained 23,193 teachers [37].
From the year 2014, Government has been arranging training for PPE teachers. The Directorate of Primary Education (DPE) completed 15 days’ Special Basic Teacher’s Training for PPE teachers. The expansion plan of PPE mentioned that the training has a great influence on teachers for understanding the early grade teaching and child friendly teaching-learning process; but from different reports it is found that the trained teachers can not improve their classes utilizing the knowledge they accumulated from training. Thereby it cannot put any positive effect on children [8].
At present the education qualification of recruited/selected preschool teachers’ is bachelor degree or undergraduate degree. After getting selection teachers go through under a “Basic Training Course of Preschool Teacher” for 15 days. Here, teachers are taught and guided about joyful teaching methods, children’s psychology, various play-based teaching ideas etc. This training (of 15 days) includes theoretical and practical methods. The trainers of this course are selected by NAPE (National Academy for Primary Education). NAPE is run by Government, which conduct all relevant training activities for primary teachers, trainers, supervisors and other related officials of primary education program. After completing 15 days of training the newly recruited preschool teachers start conducting classes of pre-primary level. After six months of teaching, the teachers are sent for DPEd Course (Diploma in Primary Education) to PTI (Primary Training Institute). The duration of DPEd course is for 1.5 years (one and half years). This course is also run by NAPE. After completing this course teachers are qualified for teaching in primary level. So, preschool teachers are not only teaching in pre-primary level, but also in primary level. DPEd course is designed with both theoretical (one year) and practical (six months) parts. At the end of this course teachers are assessed with various exams, evaluations and different assessments. The certificate of DPEd is given by Institute of Educational Research (IER) Faculty of Dhaka University. The teachers who have completed BEd Course (Bachelor of Education) before joining in teaching, they do not require to complete DPEd course.
British Council also arranges professional development training for teachers. Selected teachers from nominated English medium schools can avail this opportunity of training from British Council. It basically offers the teachers relevant trainings on “Learning English Language” in effective way. British Council also works with government for training the teachers of government schools under various projects. But they do not have any special training or program to train preschool teachers.
5.3. Limitations of Pre-Primary Education Project
In most of the schools the teacher-students ratio is high. According to the government instruction the teacher-student ratio should be 1:30, whereas in most of the schools it’s found that 50 - 60 students are attending the preschool class. This is difficult for a single teacher to conduct the class properly with a large number of young aged students. In pre-primary level, the number of quality teacher is very less and insufficient. In the study, it is shown that large number of students, lack of teaching aids, shortage of quality teacher are the reasons behind inadequate care of children in pre-primary level of Bangladesh [36]. GroundWork (Washington, DC) prepared detailed series of reports (in collaboration with Creative Associates International, CARE, The George Washington University) on Bangladesh Education Sector for Basic Education and Policy Support (BEPS) Activity. In the fourth report, they mentioned about “Teachers and Teachers Training (Formal and Informal)” of educational sector. It is stated that poor quality of teaching is one of the key variables of low-level learning in primary level. Lack of initiatives, lethargic attitudes of teachers and staffs, lack of professionalism of teachers, lack of efficient trainers, lack of standard trainings, lack of incentives for the trainers and teachers, lack of facilities and overall lack of a good systematic culture of performing own responsibilities are the reasons of poor standard teaching-learning in primary level [38]. Sikder and Banu investigated and studied the policies, practices, challenges and contemporary research of the Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) in Bangladesh. They have indicated that the lack of reliable national dataset, poor service coverage, weak coordination among service providers, noncompliance of minimum quality standards, low parental awareness leading to low demand and utilization and low research base to guide policy and programmatic decisions for optimum efficiency and effectiveness; which altogether contribute to the non-achievement of universal coverage of ECCE services of good quality for all [39]. However, in a recent study participant teachers mentioned that continuous professional development training and refresher’s training, special training on crafts, arts, music and physical training can improve the professional skills of preschool teachers. Discussing problems with head teacher and education officer, maintaining accurate teacher-children ratio, providing necessary play materials, arranging adequate space for children’s play can improve the preschool education [8]. In Bangladesh, the formal quality training of pre-primary teachers is not in a standard satisfactory state. The participant teachers of a study (almost 70%) said that, they did not get any training facilities; only 30% of the teachers get training on pre-primary education system. The basic content of theoretical and practical knowledge of training needs to be more realistic and updated so that it can help teachers to develop the children in more creative and skilled way [36]. From the various researches, we came to know about the limitations of pre-primary education plan of Bangladesh Government. Poor quality of teaching, lethargic attitudes of teachers, lack of professionalism, stereotype mind-set of teachers, all these barriers are the result of absence of “Teacher’s Efficacy”. For developing “Efficacy”, standard teachers’ training is a prime requirement factor.
5.4. Non-Government Preschools of Metropolitan Areas
Other than Government pre-primary schools there are many private schools and kindergartens which run preschools as part of their school education. The number of these schools and kindergartens is very high in city and metropolitan areas. Because of the affordable educational expenses in these schools, parents and guardians of middle-class economic status select these schools for children. Most of the kindergarten schools do not have any prescribed common curriculum. The authority of the school decides the curriculum for students. Thereby children of these kindergartens face a huge pressure with overloaded study [36]. Private sector has its own arrangement and curriculum for preschool education. Renowned English Medium Schools have their experiences in preschool education. They mostly follow the international curriculum [5]. High-quality private schools are having good set-up in this regard. Various forms of professional trainings for preschool teachers are available in renowned English Medium schools. The school authority arranges it for their improvement. The educational methods, materials and ideas are well updated there. The educational expenses of renowned and standard quality private schools are very high, which are out of the range of middle-class economy.
In many schools of metropolitan areas play group, nursery level and kindergarten levels are available for children. Here preschool teachers simultaneously conduct classes of other higher grades/levels. In few institutions authority arrange some basic trainings, workshops or seminars for newly recruited teachers; but in most cases these trainings are absent. For teaching in preschool level, the importance and urgency of teachers special training (related to children’s behavior pattern, playful learning, children’s development, children’s care etc.) are ignored here. Thereby, the teachers of these schools are not well conversant with children’s learning process. They are not aware about children’s psychology. The best part of teaching the children with fun, playful and joyful activities are totally absent. In most of the schools, teachers conduct the classes with teacher-centered lecture method. Here, children are directed to memorize the lessons rather than understanding. The curriculum is totally biased with academic books and regular home works. While selecting curriculums and books for children, there is no prescribed instructions/guideline from government. So, “kindergarten class” of different preschools are having separate curriculum and they are following different books. The school authorities are deciding these at their own. And these create huge study-pressure on children.
For better understanding of early aged children “Play-based Learning” is recognized and approved by researchers, educators and specialists. It has pedagogical importance. German educator Friedrich Froebel was the creator of Kindergarten Education. For Froebel, play was the most important phase in the spontaneous development of the child. He saw the educational value of play and the use of non-book materials in the school [40]. Many countries follow play-based teaching learning process in early childhood education. In Bangladesh normally play-based teaching learning process is not very familiar and well practiced. Inadequate training of teachers, large no of students, lack of sufficient space and limited use of teaching aids or play materials etc are the reasons behind this [6]. Many teachers start the teaching profession with very little to no-training on teaching related issues or early child care, child development, early child education, classroom management, etc. No prior training is arranged for teaching the young aged children. In many cases, hardly preschool teachers completed their graduation or undergraduate degree. The common understanding of the society is, for teaching only alphabets, letters, numerical and drawing to the young aged learners, a teacher does not require graduation or undergraduate degree. On the other hand, it is mentioned in a study that insufficient training facility of teachers is a barrier for successful pre-primary education.
6. After Training Expected Impact of Preschool Teacher
Cognition is a consciousness, which is the process of obtaining knowledge and understanding through different activities, thought and experiences. Teacher’s training can improve teachers’ perceptions, attitude towards students, understanding, class management, teaching efficacy and intellectual functions; which will in turn produce effective learning.
Edwards and Newton showed in their study how cognitive coaching determines positive impact on teacher’s efficacy and empowerment. Here, while measuring teacher’s empowerment they have taken other factors incognizance like potency, independences, relatedness, motivation, values and joy of life. They sated that high efficacy teachers can give effective decisions in class while interacting or communicating with the students. They assist students to develop self-confidence. These teachers help young learners to do better in learning language, reading and mathematics. High efficacy trained teachers also carry a positive satisfied attitude towards the teaching career and to administration [41].
Training affects the overall psychological process of teachers; it changes the perspectives and thoughts regarding teaching the young aged children. Walk et al. described in their study that after completing EMIL training, the preschool teachers were expected to identify situations and opportunities in their preschools as they learned and discussed in training session. The teachers are expected to understand and support children individually for improving their EFs through group tasks, games and sports, etc. [29]. Preschool stage is a sensitive stage where a child needs to be attended with care. Rather than imposing rules and limits on children’s behavior, teachers’ who accept more child-centered beliefs, they can analyze children’s critical social and emotional attitude in gentle way [11].
Efficacy does not grow in a day. It’s a continuous and simultaneous combined effort. Teachers who possess self-efficacy, they are self-motivated, enthusiastic, positive and curious persons. While conducting classes or dealing with students they demonstrate confidence and competence in their attitude. They always try to display positive attitude in their activities. Teachers with self-efficacy help students achieve the maximum outcome from learning. From the researches and various studies carried out by researchers and professionals, we found that, EFFICACY is a joint outcome of three factors; i.e. “Personal Input of Teacher”, “Organizational Input” and “Social Input”. Though it’s a joint result, but teacher’s personal input plays an important role to link other two factors and makes the successful realistic outcome. As “Personal Input of Teacher”, primarily we understand educational degree (Bachelor/Masters), attending various pedagogical trainings/professional courses, will power, enthusiasm, motivation, initiative and verbal persuasion. All the three main factors mentioned are directly and indirectly affected by Professional Training of individual teachers. Professional training plays a vital role here.
After starting teaching career, teachers must go through professional development courses to improve pedagogical knowledge, which will gradually improve their skills. It will update the individual about teaching methodology, teaching techniques, classroom management skills and all other associated pedagogical issues. Professional Training means all kinds of trainings (both in-service and outdoor), seminars, workshops, discussions, conferences, online courses of distance learning, peer learnings, webinars, expert opinions etc. After achieving knowledge and skills a teacher with self-confidence can exercise innovative and playful teaching in class.
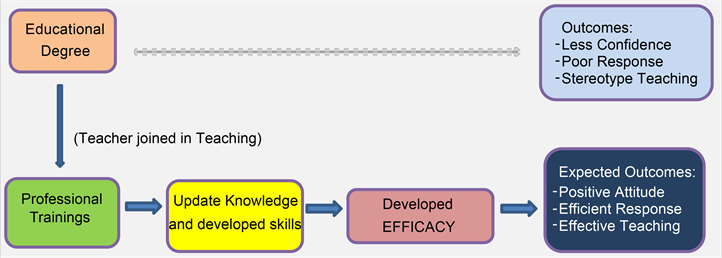
The expected behavior or outcomes of a preschool teacher, who possess self-efficacy are as follows:
1) The teacher will understand the importance of play-based learning for the children. So, as mentor being able to make the class lively and joyful with the children by creating an enjoyable playful learning environment.
2) Playing a role model of moral-values through his/her activities in class, so that children can learn moral-values and they can be inspired by teacher. Teacher can make the children understand about the necessity, requirement and effect of moral-values by storytelling, role play method or any other innovative ideas.
3) The teacher will gradually develop self-confidence amongst the young learners while communicating with them in class or on the play ground.
4) Teacher with efficacy will guide and encourage children to take effective decisions while interacting with them.
5) Preschool teacher’s emotional socialization is very important for developing children’s emotional and social competence. So, teachers need to act maturely and competently to attend children’s behavior and challenging issues both in class and outside the class.
6) Teacher can Inspire and motivate children in team work or peer learning. Teacher will help them to develop an attitude of acceptance, respecting other’s view, sharing and caring for others.
7) Increase the ability of handling negative behavior or environment of children. Teacher will take control over the class with good management skills.
8) Teacher can give proper necessary required attention to the special need children.
9) Play a vital role by establishing a strong, active, warm, comfortable and direct coordination with parents.
10) Assess the children and finding out the special qualities/interests/ limitations of the children and help them to grow up.
11) Apply a useful effective method of observations, preparing documentation, assessing the students for their overall development.
12) Teacher can be able to take control over own emotions in difficult situations, e.g. not exhibiting anger, handling own frustration or depression (if there any) etc.
13) A teacher with efficacy is self-motivated, enthusiastic in teaching and develops innovative ideas to make the teaching interesting for his/her students.
14) Satisfied with their teaching career and carry a positive attitude towards the profession.
7. Recommendations
A qualified, positive and motivated preschool teacher can identify the needs and the requirements of early young aged children. With the prudent guidance and effective behavior, he/she can shape up a child into a good human being. Training will enhance the knowledge and develop professional ideas of the preschool teachers. With this development, teachers will gain confidence and carry positive thoughts in their beliefs; which will be reflected through their behaviors and actions. In the context of our country few recommendations are mentioned below:
1) Preschool teachers must have completed their basic undergraduate degree (bachelor degree). It will be encouraging if teachers start their teaching profession with university graduate degree in respective field of education or with BEd degree (Bachelor of Education). In a survey on preschool teachers of Malatya, Turkey it is found that self-efficacy of teachers with graduate degrees were higher that the teachers with undergraduate degrees [14]. If a candidate does not have bachelor degree, then he/she must have completed Diploma in Education before applying as teacher.
2) Newly joined preschool teachers should go through some elementary short course/training curriculum related to young aged children to understand the young learners. Training on arts, crafts, music and physical training can be arranged for preschool teachers. NAPE (National Academy for Primary Education) and NCTB (National Curriculum and Textbook Board) can develop the training program and DPE (Directorate of Primary Education) can arrange the implementation of training [8].
3) Before conducting class as a regular teacher in preschool, fresh teacher can be gone through Internship under experienced or expert educator/senior teacher. It will help fresh teacher to gain practical experiences and understand the scenario of the junior classes.
4) Authority of school can arrange professional development training, lectures, conferences, workshops, seminars or discussion sessions (on children’s behavior, class management, counseling of children, early childhood care, etc) internally for preschool teachers.
5) At district level, all preschool teachers can gather for meeting to exchange, discuss and share their views, ideas and concepts of teaching. NAPE can help to arrange these sessions in Primary Training Institute three or four times a year.
6) The Primary and Mass Education Ministry through NAPE, in collaboration with IER (Institute of Educational Research) of Dhaka University can arrange formal and informal effective training curriculum for preschool teachers. After implementation of training, experts and educators of that program may often visit schools to monitor the performance of the trained teachers. The observations from experts will be more effective to aware them of their (preschool teachers) limitations to overcome it.
7) Capsule training, short courses on teaching methodology can be arranged with the help of authority/stakeholders at district level. External Trainings, seminars, workshops, conferences can be arranged by agencies, associations, universities in collaboration with school authority on child psychological development, early child care or child’s education issues.
8) Guest speakers or specialized persons from different sectors (e.g. pedagogy, child’s psychology, child’s care, etc.) can be invited by authority to train the teachers in respective fields. Specialists can enlighten the teachers by sharing their views, experiences, practical knowledge and discussing about the various sides of that field. It will work as an eye-opener for teachers.
9) Online training sessions, lectures, conferences, seminars and workshops can be arranged regarding children’s mental health and teaching related issues. Distance Education Program on teaching methods or child development can be arranged to train a good number of teachers in short time. In many countries, it is found very effective. Staying in workplace teachers can continue this program [15].
10) Teachers should be observed regularly by internal or external expert facilitator or professional educator for detailed observations. This feedback report will be constructive and evaluated. It will create teacher’s awareness about their performance and correct the negative attitude or misconduct in class. Regular observational feedback is associated with teachers’ emotional and social responsiveness [11]. In this process there will be chance to improve or do better in class.
11) Teachers can maintain “Reflective Dairy” where teachers will note down own performance, conduct, class management skills, teaching quality and interaction level with children. Gradually after the documentation, the overall performance of teacher will be reflected and necessary improvement or modification can be done accordingly. Self-motivation is very important factor in this process.
12) Lastly this is highly recommended that qualified and trained preschool teachers should be paid a handsome salary; so that it can be one of the driven forces to attract the trainees and freshers to this teaching profession. It is to be mentioned that salary of teachers, in our society are most often negligible. Most of the time the salary structure is unimpressive. To maintain an honorable standard life in society, a teacher should be paid accordingly as per social status.
8. Conclusion
In Bangladesh, preschool stage of children is yet to receive required attention and importance as basic part of education like other countries of the world. At preschool level, still we are struggling to establish the “IDEAL CONCEPT” of curriculum, playful learning of children and joyful environment in class. Other than Government’s pre-primary projects, the preschools of metropolitan areas should maintain a minimum standard (which will be suggested and monitored by Government) in preschool education while recruiting teachers, arranging teachers’ training, following the curriculum or prescribing the books. More training opportunities (both pre-service and in-service) should be created with available resources to enhance the quality of preschool teachers. As a developing country with many limitations, maybe it’s difficult to rapidly increase the opportunities of training; but we should put all efforts to develop qualified preschool teachers for constructing new generations with moral values and humanity. Government along with the educators, non-government organizations, stakeholders and policy makers should walk side by side to improve this sector. More research and studies with facts are required in this field to explore the problems and find out the possibilities. For a sustainable development of the country, we must nurture the younger generation, where the preschool teachers play a dynamic role. We should emphasize improving the qualities and abilities of preschool teachers so that they can raise young aged children properly.