We investigate the violation factor of the original Bell-Mermin inequality. Until now, we have used an assumption that the results of measurement are
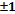
. In this case, the maximum violation factor is as follows:
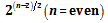
and
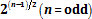
. The quantum predictions by
n-partite Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger state violate the Bell-Mermin inequality by an amount that grows exponentially with
n. Recently, a new measurement theory is proposed [K. Nagata and T. Nakamura, International Journal of Theoretical Physics, 49, 162 (2010)]. The values of measurement outcome are
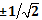
. Here we use the new measurement theory. We consider a multipartite GHZ state. We use the original Bell-Mermin inequality. It turns out that the original Bell-Mermin inequality is satisfied irrespective of the number of particles. In this case, the maximum violation factor is as follows:
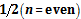
and
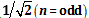
. Thus the original Bell-Mermin inequality is satisfied by the new measurement theory. We propose the following conjecture:
All the two-orthogonal-settings experimental correlation functions admit local realistic theories irrespective of a state if we use the new measurement theory.