Modeling and Analysis of Pumping Motor Drives in Hardware-in-the-Loop Environment ()
1. Introduction
Pumping systems used worldwide for fluid transportation represent a significant sector of industry. Nowadays, about 22% of the energy supplied to electrical motors is acquired by the pumping systems [1] . In different fields, from 20% to 60% of the total electrical energy is going to the clear and wastewater treatment. The increased water market, growing energy costs and competition require new solutions in the pumping design and research technologies.
Motor drives play a major role in the pumping systems. They provide a broad range of functionalities, like speed adjustment, power quality improvement, as well as technology management [2] . They run pumping equipment, perform automatic and manual control, process the data, monitor the fluid flow, pressure, and power, and realize communication between the sub-systems and external equipment.
Optimal control for such kind of applications is one of the most challenging tasks the designers face. Unfortunately many operators choose to employ all their equipment at the maximum power full time rather than to apply the flexible control potential. As a result, in many applications pumps are running outside their recommended minimum or maximum flow that ultimately leads to reduced reliability and efficiency.
This paper is devoted to enhancements in the development and exploration of the variable speed drives of centrifugal pumps, to improvements in analyzing and assessment of the processes in the complex assemblies consisting of induction motors, pumps, and control devices, and facilitating in taking the pump characteristics.
Different modeling and simulation methods can be used for the system exploring and design. In the beginning, the mathematical models are effective that describe the studied system by a set of logical and mathematical relations between the system variables. While such model is simple enough, an accurate analytical solution of the problem is accessible. When the systems are more complex, an analytical solution becomes problematic. In this case, the model is explored using an imitational simulation that is the process of computer experimentation upon the mathematical model to explore and forecast its performance.
In contrast to the mathematical modeling and imitational simulation, at the hardware-in-the-loop simulation the real studied system is replaced with its physically scaled analogue intended for the laboratory exploration. The results obtained in such a way can be applied to the real system using the theory of similarity.
A hardware-in-the-loop approach discussed in this paper assumes the study of the system using the analytical models, in which the components of real equipment are included. Along with the real apparatus, such models often contain set-point and disturbance imitators as well as environment simulators the mathematical description of which is unclear. Real equipment in the simulation loop helps to explore the processes that have no clear analytical characteristics. Here, the advantages of mathematical and natural simulations can be combined successfully using the optimal interaction of both approaches.
In the described research, a hardware-in-the-loop simulation of pumping motor drives is proposed. Unlike architectural, shipbuilding, or airplane designs, in which this approach is very popular, to study the pumping applications the real control system is used whereas industrial pumps are replaced with the specially developed imitators.
The paper is organized as follows. First, the mathematical model of the centrifugal pump subjected to the hardware-in-the-loop simulation is presented. Next, the definition of the system curve family is explained. Further, the double-motor test stand intended for simulation is described. Finally, the simulation results are discussed and the conclusions are drawn.
2. Mathematical Model of the Pumping Process
Centrifugal pumps represent the most common type of pumps applied in different industrial applications [3] . They constitute about 80% - 90% of all water treatment equipment [4] . Being a sub-class of the dynamic asymmetrical absorbing turbo machinery, they are used to transport liquids by means of converting the rotational kinetic energy of the fluid to the hydrodynamic energy. A topology of the traditional centrifugal pumping system is shown in Figure 1. The system includes the pump fed by the variable speed drive (VSD). The supply grid, fluid pipe, and a sensor producing the pressure feedback are the obligatory parts of the system. The VSD incorporates an electric motor directly connected to the pump. Other important units of the VSD are the frequency converter and controller. Usually, the fluid enters the pump along the rotating axis and, after acceleration by the impeller, flows outward into a diffuser or volute chamber from which it exits.
Every pump is described by the fluid flow rate Q (m3/s) and the fluid head H (m) at the definite rotational speed n (rpm) of the motor shaft and fluid density r (kg/m3). The non-linear relation between the fluid flow rate and head known as the performance characteristics, or the QH curves, are usually provided by the pump manufacturers at the rated rotational speed. Some examples of the performance curves for Ebara CDX pumps from ABB are presented in [5] . Similar data can be found in [6] [7] for other vendors.
Being an electromechanical system, the pump is defined by the following output mechanical power P, electrical supply power Psup, and efficiency η:
 , (1)
, (1)
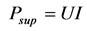 , (2)
, (2)
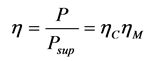 (3)
(3)
where:
U—supply voltage, V;
I—supply current, A;
ηC—efficiency of the frequency converter;
ηM—efficiency of the motor;
g—acceleration due to gravity, m/s2.
According to the flow-head (QH) and flow-power (QP) curves, for all types of the centrifugal pumps the head decreases as the flow rate increases whereas the power grows along with the flow rate. As the efficiency is concerned, it increases to some extend and then starts to drop.
On the motor shaft the following mechanical torque T is developed:
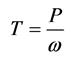 (4)
(4)
where:
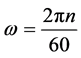 —angular frequency, 1/s.
—angular frequency, 1/s.
An important property of hydraulic systems is expressed with the affinity laws [8] that describe the relationships between variables involved in pump performance, such as flow rate, head, torque, and power at the changing speed:
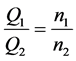 , (5)
, (5)
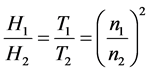 , (6)
, (6)
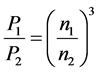 (7)
(7)
where index 1 denotes the initial states and index 2—the final states of the process variables.
Every set of points found using the affinity laws defines a locus of constant speed useful for prediction the pump characteristics basing on the known characteristics measured at a different speed. The only requirement is the pump similarity at which the ratios of the forced fluids are to be the same.
Using affinity transformations, the family of the performance curves can be designed. Such a family calculated with (5), (6), (7) for Ebara CDX 120/12 on the basis of [5] is shown in Figure 2. Here, the curves H2800 to H500 describe the flow-head relations at 2800, 2200, 1800, 1500, 1000, and 500 rpm correspondingly. The
![]() (a)
(a)![]() (b)
(b)![]() (c)
(c)
Figure 2. Performance and system curves of Ebara CDX 120/12.
curves P2800 to P500 describe the flow-power relations at the same speeds, and the curves T2800 to T500 describe the flow-torque relations within the same speed range.
3. Obtaining the System Curves
To proceed from the mathematical to the hardware-in-the-loop model, all the dependences which describe the pump and motor behaviors are converted in such a way that the study of the real pump could be replaced with the study of the similarly loading motor.
Applying the pump QH ratios to the real pumping system affects the pressure in the pipeline which can be found from the Bernoulli’s equation [9] dependently on the system topology as follows:
 , (8)
, (8)
where:
p—fluid pressure, N/m2;
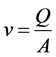 —fluid velocity in a pipeline, m/s;
—fluid velocity in a pipeline, m/s;
A—cross-sectional area of the pipeline, m2;
z—elevation of the point above the reference plane, m.
Generic shapes and slopes of the system curves cannot be provided with the pump datasheets because they vary along with the consumer’s environment changing. Variation in the household daily consumption is one of the factors affecting the shape of the system curve which tends left when the resistance is high and tends right since the resistance falls. Particularly, if the pump discharge valve is closed, the provided head will be at its maximum and the flow rate will be at the zero point.
For variable-speed pumping applications, every system curve is superimposed upon the family of performance curves. The intersection of a pump performance curve with the system curve indicates the working point of pumping known as a pump operating point [10] [11] . Commonly, such points are the key subjects of the semi-natural simulation. By plotting the points of intersection of the system curve with pump performance curves, a set of operating points can be found, one for every speed along the system curve. From these points, different pump operating regions can be defined, such as the best efficiency region, maximum productivity region [12] , etc.
In this study, to find the system curves an experimental ABB manufactured pumping station has been used. The station is accomplished with the pumps EBARA 120/12 feeding with the frequency converters ABB ACQ 810, the discharge valves for the consumer’s environment emulation, the pressure sensor and the manometer, digital switches, potentiometers, relay circuitry, wiring, and data cables for RS485 connection. All the pumps are of nominal power 0.9 kW, current 3 A, voltage 400 V, and speed 2800 rpm. This station includes all the required computing hardware and software to perform the pump speed adjustment and process monitoring. The toolkit Drive Studio provides the distance station control and data acquisition.
The main variables for the experimental study are the desired speed and the actual system variables, such as voltage, current, torque, and pressure. The Drive Studio adjusts the speed reference for the pump, providing the speed required for every measurement level. To study different system curves, the operator changes the discharge valve position thus providing the pipe cross-sectional area regulation. As the VSD executes the commands, the Drive Studio collects continuously updated data needed for experimentation. Depending on the operational state of the pump and the process system characteristics, the minimum required time interval for such estimations can vary from hundreds of milliseconds to several seconds.
Basing on the above family of the performance curves, the system characteristics at different discharge valve positions were taken from the pumping station. To this aim, using the torque measurement, the total head was acquired from the QH diagram at the requested speeds. Further, following the flow rate determination, the total head was acquired. Next, applying the Bernoulli’s equation the pressure was located which depends on the flow rate as (1) shows.
The obtained family of the system curves is shown in Figure 2 above the pump performance curves. Here, the curves 2.2 cm2 and 0.8 cm2 bound the area of the studied system curves. From now, all the required torque- speed relations connected with the concrete pumping application are ready for emulation in the semi-natural environment.
4. Laboratory Setup for Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulation
The sketch of the test setup developed in the Electrical Drives Laboratory of Tallinn University of Technology is presented in Figure 3 [12] [13] . It incorporates two motor drives of ACS800 series from ABB, the testing drive and the load drive of the similar structures consisting of induction motors, power converters, remote consoles, cabinet, housing, measuring, and cabling equipment. The machine shafts are mechanically coupled to each other via the clutch to provide their joint rotation. The working machine has the nominal power of 5.5 kW, voltage of 400 V, and current of 11 A. The loading machine has the nominal power of 15 kW, voltage of 400 V, and current of 29 A.
The power converters are the low-harmonic cabinet-mountable motor supplying. Each of them includes the motor-side inverter and the line-side active rectifier connected via a DC link. A converter cabinet contains the frequency converter with the cooling system, the control panel mounted on the front cover, the heat sink on the back side, and the connection box placed under the bottom cover. Both the motor-side inverter and the line-side active rectifier are built on six IGBTs with freewheeling diodes. In the motoring mode, the three-phase AC voltage feeds the intermediate DC link via the rectifier. Further power goes to the motor through to the motor-side inverter. In contrast, in the braking mode the energy returns back from the motor via the motor-side inverter and the DC link to the supply lines through the line-side rectifier. The current and voltage harmonics are suppressed with an input filter placed ahead the line-side active rectifier. For the IGBT gating, the space vector modulation principle is used. In this way, both the scalar converter adjustment and the direct torque control (DTC) can be executed.
ABB ACS800 power converters are the middle-power class devices with broad control possibilities. There are two main control modes of the drive, namely the direct torque control (DTC) [14] and the scalar control supporting the constant voltage-frequency ratio. To control the load drive, the DTC was chosen, and for the pumping drive the scalar mode was used.
The converters possess several predefined macros with factory settings allowing flexible drive tuning for a user.
![]()
Figure 3. ACS800 laboratory stand for hardware-in-the-loop simulation.
Additionally, ABB ACS800 is equipped with the model-based measurement tools allowing the real-time parameter tracing. It includes the built-in logical controller for programming the converter outputs and inputs to fulfil the basic operations. Both drives are connected to the computer through a set of optical wires. To obtain accurate data, the readings from the measuring devices are compared with the information displayed by the ABB toolbox Drive Window which provides the remote control of the tested and the loading drives, their tuning, monitoring, graphical trending, and registration of the drive parameters. The output data from the Drive Window software can be presented and saved in graphical and numerical forms for the following analysis. During the tests, the data related to the measuring parameters are recorded for further estimation and analysis. After receiving the data, characteristics of the simulated pump system can be drawn up.
The test stand permits simulation of different loads to study the steady-state and dynamic modes of the system operation or to keep them constant for making static measurements. The following research problems can be solved with the help of the platform described:
· Comparative analysis of the tools to identify and test the drive components.
· Experimentation on the static and dynamic operation modes using the developed physical prototypes.
· Application of the library of the motor drive models that support the experimental study and identification procedures.
· Combination of both the marketable simulation instruments and the author’s original software in the drive exploration.
· Load-dependent and speed-dependent study of the drives for the search of optimal equipment configurations.
· Evaluation of the most economical performances to choose the best application modes of operation.
5. Adaptive Programming and Simulation
An ABB adapting programming methodology [15] [16] was used to create the loading diagrams basing on the above mathematical model. The Drive AP toolkit from ABB has become the suitable instrument to build the programs from the function blocks the maximum number of which approaches 15. The programs mainly consist of several separate functions some of those are presented in Table 1.
![]()
Table 1. Function blocks of the library.
By applying these functions, the models of the pumping system resistances [9] were realized as shown in Figure 4. Here, the starting pulse and the referred time durations come to the program inputs. Then, the positive and negative signal amplitudes are assigned. The summarized and ramped converted levels assign the output torque reference of the required acceleration and deceleration rates.
To check the developed models, a series of tests was performed in the test stand. During these tests, a researcher selected the proper loading diagrams and uploaded them to the loading drive. Using the ABB Drive Window toolkit, the torque and speed values were explored, documented, and saved. In such a way, the speed of the driving motor and the torque of the loading machine were assessed.
Some results are presented in Figure 5. Here, the speed-torque characteristics obtained from the pumping station are shown with the bold curves, green for the 2.2 cm2 pipeline and black for the 0.8 cm2 pipeline. The characteristics resulted from the semi-natural simulation are shown with the thin lines within the range of 20% to 100% loading. Their comparison show that the dependence between the speed and the torque stays actually the same as given in (7) within the full range of applied torques.
![]()
Figure 4. Realization of the loading diagram.
![]()
Figure 5. Speed-torque curves for the torques of 20% to100% of nominal.
6. Conclusion
The proposed hardware-in-the-loop simulation approach allows obtaining multiple characteristics of the pump drives at varying speeds and load torques within their operating regions. The new model has been developed and the set of the speed-torque curves has been found. Information about the system performance at normal operation, underloading or overloading dependently on the simulation conditions has been described and explained.