Synthesis of New Mannich Products Bearing Quinoline Nucleous Using Reusable Ionic Liquid and Antitubercular Evaluation ()
1. Introduction
Tuberculosis (TB) is a global epidemic and an infectious disease caused by the pathogenic bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) [1] . According to the most recent World Health Organization (WHO) report on TB, there are estimated 8.6 million new cases and 1.3 million deaths from the disease, including 320,000 deaths among HIV-infected people in 2012 [2] . Among them, the vast majority of TB cases are reported in the Asian, African, and western Pacific regions. India and China together account for 40% of total cases [2] that represent that TB is no more disease of rich countries. Moreover, development of new virulent forms of TB, such as multidrug resistant ([MDR-TB, resistant to at least two frontline drugs such as isoniazid (INH) and rifampin (RIF)]) and extremely drug resistant (XDR-TB), and its synergistic effects with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) have become a major threat to human kind [3] - [6] . TB is at its peak recent years, largely owing to HIV infection, immigration, increased trade, and globalization [7] . The increasing occurrence of drug-resistant TB, especially multidrug-resistant TB, is particularly alarming. MDR-TB has already caused several lethal outbreaks [8] and has posess a substantial peril to the treatment and control of the disease in several parts of the globe, where the incidence of
MDR
-TB can be as high as 14% [7] . There is much apprehension that the TB situation may become even shoddier with the spread of HIV globally, a virus that significantly weakens the host immune system and allows latent TB to reactivate and makes the victim more vulnerable to reinfection with either drug-susceptible or drug-resistant strains. The fatal combination of drug-resistant TB and HIV infection is a growing problem that presents serious challenges for effective TB control. In view of this situation, in 1993 the WHO declared TB a global emergency [9] .
Over the past few decades, Mannich bases of heterocyclic molecules have found to show versatile pharmacological activities [10] - [12] . In addition to this, various quinoline containing molecules have been synthesized tested for anti-TB activity all over the world. D. Sriram et al. [13] synthesized 48 novel 6-nitroquinolone-3- carboxylic acids derivatives and compound having sustitution (4-((benzo [d] [1] [3] dioxol-5-yl) methyl) piperazin-1-yl) was found to be the most active compound in vitro with MIC of 0.08 and 0.16 μM against MTB and MDR-TB, respectively. They also extend their work to synthesized various 2-(sub)-3-fluoro/5-nitro-1,2-dihydro- 5-oxobenzothiazolo [3,2-a] quinoline-6-carboxylic acid and evaluate for in-vitro against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv (MTB), multi-drug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MDR-TB), and Mycobacterium smegmatis (MC2). Compound bearing 2-(3-(diethylcarbamoyl) piperidin-1-yl)-) is found to be the most active compound with MIC of 0.18 and 0.08 μM against MTB and MTR-TB [14] . 3D-QSAR analysis has been employed by Rahul Jain and co-worker to understand the relationship between structure and anti-TB activity. They develop new 4-(adamantan-1-yl)-2-substituted quinolines derivatives, the most potent analog of the series produces 99% inhibition at 1.00 μg/mL against drug-sensitive strain, and MIC of 3.125 μg/mL against isoniazid resistant TB strain [15] .
Recognizing these facts and continuation of our earlier work based on u. v. absorbing materials as well as heterocyclic moiety [16] - [28] , we set upon a program of achieving significant antitubercular molecules, using phenol aldehyde and various amide derivatives to achieve Mannich products bearing quinoline nucleus.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Melting points were determined in open capillary tubes and are uncorrected. Formation of the compounds was routinely checked by TLC on silica gel-G plates of 0.5 mm thickness and spots were located by iodine. IR spectra were recorded Shimadzu FT-IR-8400 instrument using KBr pellet method. Mass spectra were recorded on Shimadzu GC-MS-QP-2010 model using Direct Injection Probe technique. 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra were determined in DMSO-d6 solution on a Bruker Ac 400 MHz spectrometer. Elemental analysis of the all the synthesized compounds was carried out on Elemental Vario EL III Carlo Erba 1108 model and the results were in agreements with the structures assigned. All chemicals were purchased from commercial sources and used without further purification.
2.2. Synthetic Procedures for Synthesis of Substituted Mannich Products Bearing Quinoline Nucleous (4a-f)
A mixture of 2,4-dihydroxybenzophenone 1.07 gm (0.005 M), 2-chloro-6-methoxyquinoline-3-carboxaldehyde 1.105 gm (0.005 M), various amides 0.30 gm (0.005 M) and EAN 30 ml (1 M) was refluxed with stirring at 80˚C temperature. The completion of reaction was monitored by TLC with using solvent system chloroform/methanol (v/v = 70:30). On completion of reaction, the reaction mixture was extracted thrice with 20 ml ethyl acetate. The extract was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, evaporated under vacuum and the residue was purified via recrystallisation from methanol or ethyl acetate to obtain pure new Mannich products 4(a-f) (Scheme 1).
2.3. Spectroscopic Data for New Mannich Products (4a-f)
1-((5-benzoyl-2,4-dihydroxyphenyl) (2-chloro-6-methoxyquinolin-3-yl) methyl) urea (4a)
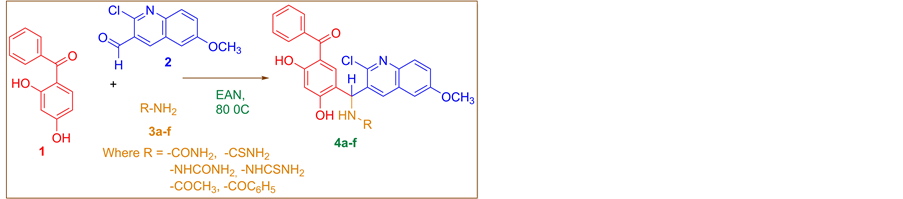
Scheme 1. Synthesis of new Mannich products 4(a-f) bearing quinolinenucleous.
It was obtained as yellow solid color, yield: 84%; decomposition temperature 188˚C - 192˚C; IR (KBr, υmax/cm−1): 3463, 3440 (Ar-OH), 3198 (-NH), 3072 (CH, aromatic), 2974, 741 (CH aliphatic), 1705, 1628 (C=O, diaryl), 1605 (C=N), 1519 (C-N), 1481 (C-C, aromatic), 1212-1024 (C-O-C), 1101 (C-O), 732, 584 (for substituted benzene); 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ = 8.25-7.01 (4H, m, H-4, H-5, H-7, H-8, -CH for substituted quinoline), 7.97 (1H, s, Ar-OH, -intra), 7.84 (1H, d, J = 7.8 Hz, -NHCO-), 7.01-7.78 (7H, m, H-3’, H-6’, H-2”, H-3”, H-4”, H-5”, H-6”, Ar-H), 7.01 (1H, s, Ar?OH), 7.05 (1H, dd, J = 10.5, 3.5 Hz, -CHNH), 6.86 (2H, s, -CONH2), 4.06 (3H, s, -OMe); 13C NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz,): δ = 203.1 (C, -C=O, benzoyl), 163.2 (C-4’, Ar-OH), 160.1 (C, NHCONH2),159.4, (C-2’, Ar-OH), 155.9 (C-6, C-OCH3), 150.2 (C-2,C-Cl), 148.6 (C, C-10), 132.7 (C, C-1”), 132.2 (C, C-9), 132.0 (C, C-8), 131.8 (C, C-4), 131.7 (C, C-1’), 131.6 (C, C-6), 130.5 (2C, C-2” & C-6”), 128.1 (C, C-4’), 122.8 (2C, C-3”& C-5”), 119.7 (C, C-5’), 109.4 (C, C-7), 107.5 (C, C-5), 104.1 (C, C-3’), 101.8 (C, C-3), 55.2 (C, -OCH3), 51.2 (C, aliphatic-CH); EI-MS m/z: 477 (M+1)+; Anal. Calc. for C25H20ClN3O5 (%): C, 62.83; H, 4.22; N, 8.79% found: C, 62.80; H, 4.19; N, 8.71%.
1-((5-benzoyl-2,4-dihydroxyphenyl) (2-chloro-6-methoxyquinolin-3-yl) methyl) thiourea (4b)
It was obtained as pale yellow solid color, yield: 88%; decomposition temperature 180-1840C; IR (KBr, υmax/cm−1): 3463, 3440 (Ar-OH), 3198 (-NH), 3072 (CH, aromatic), 2974, 741 (CH aliphatic), 1705, 1630 (C=O, diaryl), 1605 (C=N), 1519 (C-N), 1481 (C-C, aromatic), 1329 (C=S), 1212-1024 (C-O-C), 1101 (C-O), 732, 584 (for substituted benzene), 691 (C-S); 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz,): δ = 8.25 - 7.25 (4H, m, H-4, H-5, H-7, H-8, -CH for substituted quinoline), 7.97 (1H, s, Ar-OH, -intra), 7.85 (1H, d, J = 7.8 Hz, -NH), 7.2-7.78 (7H, m, H-3’, H-6’, H-2”, H-3”, H-4”, H-5”, H-6”, Ar-H), 7.01 (2H, s, -CSNH2), 6.76 (1H, s, Ar-OH), 5.96 (1H, dd, J = 10.5, 3.5 Hz, -CHNH), 4.08 (3H, s, -OMe); 13C NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz,): δ = 203.1 (C, -C=O, benzoyl), 176.5 (C, NHCSNH2), 166.0 (C-4’, Ar-OH), 158.7(C-2’, Ar-OH), 155.8 (C-6, C-OCH3), 152.1 (C-2, C-Cl), 150.0 (C, C-10), 135.4 (C, C-1”), 135.2 (C, C-9), 133.3 (C, C-8), 132.9 (C, C-4), 132.4 (C, C-1’), 131.9 (C, C-6), 131.7 (2C, C-2” & C-6”), 1128.6 (C, C-4’), 124.0 (2C, C-3” & C-5”), 122.1 (C, C-5’), 112.9 (C, C-5), 112.4 (C, C-3), 103.9 (C, C-7), 103.5 (C, C-3”), 57.4 (C, -OCH3), 55.2 (C, aliphatic-CH); EI-MS m/z: 493 (M+1)+; Anal. Calc. for C25H20ClN3O4S (%): C, 60.79; H, 4.08; N, 8.51%; found: C, 60.72; H, 4.03; N, 8.47%.
2-((5-benzoyl-2,4-dihydroxyphenyl) (2-chloro-6-methoxyquinolin-3-yl) methyl) hydrazine carboxamide (4c)
It was obtained as yellowish green solid color, yield: 82%; decomposition temperature 260˚C - 264˚C; IR (KBr, υmax/cm−1): 3463, 3440 (Ar-OH), 3198 (-NH), 3072 (CH, aromatic), 2974, 741 (CH aliphatic), 1705, 1629 (C=O, diaryl), 1605 (C=N), 1519 (C-N), 1481 (C-C, aromatic), 1212-1024 (C-O-C), 1101 (C-O), 732, 584 (for substituted benzene); 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz,): δ = 8.25 (1H, s, Ar-OH, -intra), 7.97-7.55 (4H, m, H-4, H-5, H-7, H-8, -CH for substituted quinoline), 7.84 (1H, d, J = 7.8Hz, -NHNHCO-), 7.68-7.15 (7H, m, H-3’, H-6’, H-2”, H-3”, H-4”, H-5”, H-6”, Ar-H), 7.45 (1H, d, J = 8.1 Hz, -NHNHCO), 7.44 (2H, s, -CONH2), 7.03 (1H, s, Ar-OH), 6.69 (1H, dd, J = 10.5, 3.5 Hz, -CHNH), 3.96 (3H, s, -OMe); 13C NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz,): δ = 203.1 (C, -C=O, benzoyl), 163.9 (C-4’, Ar-OH), 160.1 (C-2’, Ar-OH), 159.4 (C, -NHNHCONH2), 155.2 (C-6, C-OCH3), 150.7 (C-2,C-Cl), 148.1 (C, C-10), 132.4 (C, C-1”), 132.2 (C, C-9), 132.0 (C, C-8), 131.8 (C, C-4”), 131.4 (C, C-1’), 131.2 (C, C-6), 130.3 (2C, C-2” & C-6”), 128.8 (C, C-4), 122.4 (2C, C-3” & C-5”), 119.9 (C, C-5’), 109.2 (C, C-5), 107.9 (C, C-3’), 104.1 (C, C-7), 101.1 (C, C-3), 55.2 (C, -OCH3), 51.2 (C, aliphatic-CH); EI-MS m/z: 492 (M+1)+; Anal. Calc. for C25H21ClN4O5 (%): C, 60.92; H, 4.29; N, 11.37; %; found: C, 60.89; H, 4.22; N, 11.32%.
2-((5-benzoyl-2,4-dihydroxyphenyl) (2-chloro-6-methoxyquinolin-3-yl) methyl) hydrazinecarbothioamide (4d)
It was obtained as pale yellow color, yield: 86%; decomposition temperature 176˚C - 180˚C; IR (KBr, υmax/cm−1): 3463, 3440 (Ar-OH), 3198 (-NH), 3072 (CH, aromatic), 2974, 741 (CH aliphatic), 1705, 1633 (C=O, diaryl), 1605 (C=N), 1519 (C-N), 1481 (C-C, aromatic), 1329 (C=S), 1212-1024 (C-O-C), 1101 (C-O), 732, 584 (for substituted benzene), 690 (C-S); 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ = 8.20-7.14 (4H, m, H-4, H-5, H-7, H-8, -CH for substituted quinoline), 7.98 (2H, s, -CSNH2), 7.85 (1H, s, Ar-OH, -intra), 7.78-6.48 (7H, m, H-3’, H-6’, H-2”, H-3”, H-4”, H-5”, H-6”, Ar-H), 7.44 (1H, dd, J = 7.8Hz, -NHNHCS-), 6.99 (1H, dd, J = 8.1 Hz, -NHNHCS-), 6.79 (1H, s, Ar-OH), 6.00 (1H, dd, J = 10.5, 3.5 Hz, -CHNH), 3.96 (3H, s, -OMe); 13C NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ = 203.13 (C, -C=O, benzoyl), 176.1 (C, -NHNHCSNH2), 166.7 (C-4’, Ar-OH), 158.8 (C-2’, Ar-OH), 155.8 (C-6, C-OCH3), 152.9 (C-2, C-Cl), 150.2 (C, C-10), 135.3 (C, C-1”), 135.2 (C, C-9), 133.1 (C, C-8), 132.6 (C, C-4”), 132.3 (C, C-1’), 131.4 (C, C-6’), 131.0 (2C, C-2” & C-6”), 128.4 (C, C-4), 124.8 (2C, C-3” & C-5”), 122.9 (C, C-5’), 112.6 (C, C-5), 112.1 (C, C-3), 103.4 (C, C-7), 103.2 (C, C-3’), 57.4 (C, -OCH3), 55.2 (C, aliphatic-CH-); EI-MS m/z: 508 (M+1)+; Anal. Calc. for C25H21ClN4O4S (%): C, 58.99; H, 4.16; N, 11.01; %. found: C, 58.93; H, 4.12; N, 10.06%.
N-((5-benzoyl-2,4-dihydroxyphenyl) (2-chloro-6-methoxyquinolin-3-yl) methyl) acetamide (4e)
It was obtained as yellowish green color, yield: 89%; decomposition temperature 216˚C - 220˚C; IR (KBr, υmax/cm−1): 3463, 3440 (Ar-OH), 3198 (-NH), 3072 (CH, aromatic), 2974, 741, 650 (CH aliphatic), 1705, 1628 (C=O, diaryl), 1605 (C=N), 1519 (C-N), 1481 (C-C, aromatic), 1212-1024 (C-O-C), 1101 (C-O), 732, 584 (for substituted benzene); 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ = 8.85-6.83 (4H, m, H-4, H-5, H-7, H-8, -CH for substituted quinoline), 7.87 (1H, s, Ar-OH), 7.84 (1H, d, J = 7.8 Hz, -NHCO-), 7.68-6.78 (7H, m, H-3’, H-6’, H-2”, H-3”, H-4”, H-5”, H-6”, Ar-H), 6.47 (1H, s, Ar-OH), 6.60 (1H, dd, J = 10.5, 3.5 Hz, -CHNH), 4.00 (3H, s, -OMe), 1.84 (3H, s, -CH3); 13C NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ = 203.1 (C, -C=O, benzoyl), 169.4 (C, C=O, acetamide), 166.5 (C-4’, Ar-OH), 157.9 (C-2’, Ar-OH), 154.2 (C-6, C-OCH3), 152.0 (C-2, C-Cl), 150.2 (C, C-10), 135.4 (C, C-1”), 135.3 (C, C-9), 132.3 (C, C-8), 132.0 (C, C-4”), 131.6 (C, C-1’), 130.1 (C, C-6’), 129.8 (2C, C-2” & C-6”), 128.1 (C, C-4), 124.7 (2C, C-3” & C-5”), 122.8 (C, C-5’), 112.1 (C, C-5), 109.8 (C, C-3), 102.6 (C, C-7), 102.2 (C, C-3), 55.2 (C, -OCH3), 39.3 (C, aliphatic-CH), 23.9 (C,-CH3); EI-MS m/z: 476 (M+1)+; Anal. Calc. for C26H21ClN2O5 (%): C, 65.48; H, 4.44; N, 5.87%; found: C, 65.46; H, 4.41; N, 5.82%.
N-((5-benzoyl-2,4-dihydroxyphenyl) (2-chloro-6-methoxyquinolin-3-yl) methyl) benzamide (4f)
It was obtained as yellowish green color, yield: 85%; decomposition temperature 188˚C - 192˚C; IR (KBr, υmax/cm−1): 3463, 3440 (Ar-OH), 3198 (-NH), 3072 (CH, aromatic), 2974, 741 (CH aliphatic), 1705, 1627 (C=O, diaryl), 1605 (C=N), 1519 (C-N), 1481 (C-C, aromatic), 1212-1024 (C-O-C), 1101 (C?O), 732, 584 (for substituted benzene); 1H?NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ = 9.23 (1H, d, NH), 7.14-8.20 (4H, m, H-4, H-5, H-7, H-8,-CH for substituted quinoline), 6.48-8.03 (12H, m, H-3’, H-6’, H-2”, H-3”, H-4”, H-5”, H-6”, H-2”’, H-3”’, H-4”’, H-5”’, H-6”’, Ar-H), 6.16 (1H, dd, J = 10.5, 3.5Hz, -CHNH), 5.35 (2H, s, Ar-OH), 3.83 (3H, s, -OMe); 13C NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ = 203.1 (C, -C=O, benzoyl), 168.1 (C, -C=O, NHCOC6H5), 166.6 (C-4’, Ar-OH), 157.9 (C-2’, Ar-OH), 154.2 (C-6, C-OCH3), 152.0 (C-2, C-Cl), 150.2 (C, C-10), 137.1 (C, C-1”), 135.4 (C, C-9), 135.0 (C, C-8), 132.2 (C, C-4”), 131.6 (C, C-4”’), 130.7 (C, C-1’), 130.1 (C, C-6), 129.9 (2C , C-2” & C-6”), 129.8 (C, C-4), 129.5 (2C, C-3”’ & C-5”’), 128.1 (2C, C-2’” & C-6”’), 126.4 (C, C-5’), 124.2, (C,C-3” & C-5”) 122.8 (C, C-1”’), 111.6 (C, C-5), 109.8 (C, C-3), 102.6 (C, C-7), 102.2 (C, C-3’ & C-6’), 55.2 (C, -OCH3), 41.5 (C, aliphatic-CH); EI-MS m/z: 538 (M+1)+; Anal. Calc. for C31H23ClN2O5 (%): C, 69.08; H, 4.30; N, 5.20%; found: C, 69.01; H, 4.27; N, 5.17%.
2.4. Antituberculosis Activity
All the newly synthesized compounds were evaluated for their in vitro antitubercular activity at the Tuberculosis Acquisition Antimicrobial Coordinating Facility (TAACF) screening program, Alabama, USA. Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was determined against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv by using the radiometric BACTEC [29] and broth dilution [30] assay methods.compounds 4b, and 4d found most active with percentage inhibition of 95, and 96, respectively, at minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 6.25 µg/mL, among the synthesized compounds. Whereas compounds 4a, 4c, 4e, and 4f exhibited considerable antitubercular activity with percentage inhibition of 71, 79, 55, and 68, respectively, at MIC of >6.25 µg/mL. The results of in vitro antitubercular screening of newly synthesized phenothiazines bearing nitrogen mustard are presented in Table 1.
3. Results and Discussion
The promising results obtained on 2-chloro-6-methoxyquinoline-3-carboxaldehyde, 2,4-dihydroxybenzophe-
![]()
Table 1. Invitroantitubercular screening data in µg/mL of (4a-f).
none and various amides using 1 M EAN as catalyst at the 80˚C temperature encouraged us to investigate the feasibility of solvent-free MCRs protocol to a wide range of chloro substituted aldehydes, amides/carbamates/ urea and 2,4-dihydroxybenzophenone for the synthesis of new Mannich products 4(a-f).
A bromo derivative of hetrocyclic aldehydes, amides/carbamates/urea possessing various electron donating and electron withdrawing functional groups reacted smoothly with 2,4-dihydroxybenzophenone under neat reaction conditions to give desired products in excellent yields over EAN at 80˚C temperature. The results illustrate that the one-pot three component condensation reactions show excellent performance irrespective of the presence of electron withdrawing or electron donating groups on aromatic/hetrocyclic aldehydes and hence solvent- free MCRs protocol is highly effective, promising and general for the synthesis of new Mannich products 4a-f. The substituted aromatic aldehydes with electron withdrawing group reacted with 2,4-dihydroxybenzophe-none and different amides provided desired products in excellent yields. The recovery and recyclability of EAN was still investigated for the synthesis of new Mannich products 4(a-f) by one-pot three component condensations of above said aldehyde, phenol and different amide as model substrates in the presence of EAN is under progress. The high yield of new Mannich products 4(a-f) using EAN at milder reaction condition compared to other ionic liquid can be rationalized due to high acidity associated with it (pH = 5) along with its capacity to absorb water formed during course of the reaction.
All the synthesized compounds 4(a-f) were purified by re-crystallization with suitable solvents and characterized by spectral FT-IR, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR and elemental analysis. The results of elemental analyses of each new Mannich products 4(a-f) were consistent with the predicted structure, as shown in Scheme 1 and Table 1. The IR, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR spectrum of each compounds comprised the important features of aromatic, methoxy, hydroxyl, keto and chloro and different amide groups. The IR spectra of all compound 4(a-f) showed absorption band at around 3463, 3198, 3072, 2974, 741, 1705, 1628, 1605, 1519, 1481, 1212-1024, 1101, 732, 584 cm−1 regions, conforming the groups presence in each compounds are retained. In all compounds, phenolic -OH group gives absorption band between 3450 to 3463 cm−1 and carbonyl groups of diaryl shows 1620 to 1628 cm−1. Mannich product has characteristic functional group (-CH-) which shows band at 3032 to 3066 cm−1. The presence of aliphatic (-CH group) in each compound shows 1H-NMR spectra 6.16 δ is confirmed obtained Mannich reaction. The 1H-NMR spectra of all the new compounds based on 2,4-dihydroxybenzophenone, chloroderivatives of quinoline and amide group show important signals at their respective positions, confirming the structures of 4(a-f), as shown in Scheme 1 and Table 1. Methyl group protons gave a singlet between 1.84 δ ppm in compounds 4e, Out of two hydroxy groups in all compounds, one -OH shows signals at 5.35 δ where as another -OH gives signals between 7.8 to 8.25 δ which confirmed the intramolecular hydrogen bonding. As far as -OCH3 group is concern it appears at4.06. 4c and 4d compounds having -NH group gives doublet signals between 7.8 to 8.0 δ and -NH of amide group shows signals at 7.8 δ. 13C-NMR spectra of all compounds showed characteristic signals appearing for aliphatic -CH is 47.2 to 54.8 δ which confirmed the all new Mannich products 4(a-f). Another groups also appears as 106.6 δ for C-Cl, 157.2 δ for methoxy group (C-OCH3), 158.2 to 159.7 δ for phenolic (C-OH). Amide andthioamide appears at 159.9 (CONH2) and 184.3 δ (CSNH2) respectively. In the case of semicarbazide and thiosemicarbazide for 4c and 4d appears at 154.6 and 170.8 δ. Carbonyl and methoxy group of all compounds 4(a-f) shows 198.6 δ and 55.8 δ respectively. The results of spectral analysis indicated that the compounds are pure.
The results from in vitro antitubercular screening against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv were very much encouraging. It may be predicted that Mannich base linkange would increase the lipophilicity of molecule hence help molecule to penetrate in the mycobacterium cell wall, and quinoline would generate reactive oxygen species. The compounds 4b and 4d found most active with percentage inhibition of 95 and 94, respectively, at minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 6.25 µg/mL, among the synthesized compounds. Whereas, compounds 4a, 4c, 4d, and 4e, exhibited considerable antitubercular activity with percentage inhibition of 71, 79, 55, and 68, respectively, at MIC of >6.25 µg/mL. On evaluation of antitubercular screening data, it can be seen that extent of percentage inhibition is largely affected by the type of substitutions at phenyl ring irrespective of positions of substitution. Electron withdrawing group at phenyl ring considerably enhanced the antitubercular activity whereas electron releasing groups on phenyl ring strongly diminished the antitubercular activity, which can be evident by antitubercular screening results.
4. Conclusion
In the present paper, we report the synthesis, characterization and antitubercular activity of new Mannich products bearing quinoline moiety. The results indicate that quinoline moiety with increased lipophilicity and ability of Benzophenone to general reactive oxygen species make the molecule suitable candidate against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The promising results from antitubercular screening make quinoline moiety as important class in the area of tuberculosis research. Moreover, incorporation of quinoline moiety will offer new possibilities of this class apart from conventional biological activities.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by University Grant Commission, New Delhi, and File No. 41-300/2012 (SR). The authors wish to thank UGC for its financial support to the scheme. The authors are indebted to Micro Care Lab for biological tests. Authors are also thankful to C.V.M. for providing research facility.