Imperfection of Domain Knowledge and Its Formalization in Context of Design of Robust Software Systems ()
1. Introduction
The 1930’s theoretical work in computer science proved, not just claimed, that most of the problems, human beings may encounter, will be either unsolvable or infeasible (together to be called “difficult”) by using only computational/algorithmic means, even by the most advanced computer to be ever developed in future. One significant consequence of the theoretical work is recognition of the fact that man-machine combination is essential for attempting solutions of difficult problems.
The fact of human intelligence―over and above the capabilities of the machine for solving complex problems―being essentially required for solving difficult problems and for development of complex software has been emphasized and re-emphasized by the pioneers from time to time. According to famous “No Silver Bullet” paper [1] , the process of developing complex software involves two types of tasks: 1) the accidental repetitive tasks that could be automated and 2) the essential tasks that unavoidably require syntheses of human expertise, judgment, and collaboration. The human aspect in designing software, and hence, software metrics has also been emphasized by psychologists and others including [2] .
The significance of human intelligence in solving complex problems through software means and the need for modeling human intelligence through AI and other relevant disciplines has appropriately been expressed by [3] .
Another consequence of the 1930’s theoretical work and of the emphasis on requirement of the human intelligence essentially in solving difficult problems and in developing complex software is the birth of a number of disciplines including Software Engineering (SE) and Artificial Intelligence (AI). SE, like any engineering discipline, is concerned with designing and developing complex systems, and additionally, it is also concerned with developing systems that are most abstract (non-material) systems, viz. Software. AI, on the other hand, is concerned with developing tools, techniques and computational models for embedding in machine (human-like) intelligence to find optimal, if not the best, solutions of difficult problems.
In AI, from the very beginning, it was discovered that the exploitation of knowledge of the problem domain is essential for solving difficult problems. However, knowledge, so far, being mainly the product of human mind or human intelligence, is full of imperfections. Rather, knowledge of domains for sufficiently complex problems has to be imperfect―incomplete, uncertain, vague, imprecise, approximate, obsolete or inconsistent etc. This is true, especially, in view of the fact that the human capabilities, including the ones for acquiring and storing knowledge, are finite and discrete, whereas problem domains, being part of the real world, are infinite and continuous. On more concrete level, it can be said that knowledge, whether in the human mind or embedded in the machine through human efforts, has to be imperfect in view of the facts: 1) knowledge is essentially grounded in common sense and 2) the carrier of knowledge (between human beings, and between man and machine) at fundamental level is some natural language. Both common sense and natural languages involve almost all sorts of imperfections. Hence, in view of these facts, imperfection of various types in knowledge of a problem domain is a rule, rather than an exception ( [4] - [7] ).
Also, software development, from the initial stage of requirement analysis to final stages of deployment and maintenance is human-driven. Thus, human-centricity of both SE and AI, and hence, of the whole enterprise of attempting solutions of difficult problems with the help of computers, makes the task of modeling the software development processes and software quality concerns, genuine challenge [4] .
One of the qualitative requirements for software to be developed, is that it be robust i.e. it does not break down while encountering unpredictable situations. A robust system (man or machine) has to be an intelligent system in the sense that it should be able to find an optimal, if not the best, solution when the knowledge of the problem domain is uncertain/incomplete/imperfect/unpredictable. Thus, for designing and developing a robust software system, the system must have in-built mechanisms for handling imperfect knowledge of the problem domain/context, especially in view of the fact that imperfection of knowledge of problem domain is a rule, rather than an exception. The assets from AI and SE interleave, apart from in other aspects of software enterprise, in attempting to develop robust software.
Knowledge, possible imperfections in knowledge and development of appropriate conceptual frameworks for designing robust software systems & metrics for imperfect knowledge domains form the basis of the reported research work. In the next section, various issues related to knowledge are briefly discussed. Formal Approaches & Models for Handling Imperfections in Knowledge are discussed in Section 3. The discussion provides ground for exploring various possibilities for conceptualization of imperfect knowledge domains and for setting an agenda for research in this area. Finally, the Section 4 concludes the presented work.
2. Knowledge & Imperfect Knowledge: Types and Models
In order to develop intelligent and robust software, the knowledge that needs to be represented (in computer system) may include objects, states, situations, events, and time; properties and categories of these entities, and relations between entities. Also, knowledge may also include causes and effects of actions in certain situations, knowledge about knowledge and many other relevant entities.
Knowledge can be classified from different perspectives including from organizational management, from library & information science, and from psychological ones. Here, the classification of knowledge is discussed from computational perspective and that also within the context of software development enterprise.
In this respect, first, various forms of human knowledge are enumerated, and then sources and types of imperfections in knowledge are discussed.
2.1. Types of Human Knowledge
One of the most difficult problems in knowledge representation is the breadth of common sense knowledge, especially in view of the fact that the number of atomic facts an average person knows is very large, rather, is potentially infinite. Still more difficult is the representation of the sub-symbolic part of common sense knowledge, which cannot even be expressed in terms of verbally expressible facts and statements.
To begin with, the subconscious knowledge is discussed, which is the most difficult part of human knowledge from the point of formal knowledge representation. Next, the discussion of the other knowledge types which are considered successively less difficult from computational perspective and/or from the perspective of formal representation follows.
At the top level, various forms of human knowledge include:
1) Unconscious/sub-symbolic/Tacit/Implicit Knowledge: It is the type of knowledge the possessor of which exhibits behaviors that indicate the possession of such knowledge but possessor seems unaware of that possession and is unable to verbalize it. A substantial part of such knowledge is in the form of cognitive processes involved in carrying out various activities including acquisition of the explicit knowledge. This type of knowledge informs, supports and provides a context for symbolic, conscious knowledge. It includes habits, vague intuitions and gut feelings. Unconscious knowledge is repeatedly used, but is not explainable, communicable to other human beings and to machine and may or may not be visualizable. (e.g. procedure, if any, for each of a) composing a poem by a poet, b) getting a novel research idea and working on it, and c) preparing of tasty, but novel dish, by an expert cook, cannot be described in words).
2) Common Sense Knowledge: Common sense may be considered as basic human attribute possessed by most people, pertaining to ability to perceive, understand and judge things, and also to possession of, mostly implicitly, collection of facts and information enabling this ability. A substantial part of human knowledge is in the form of Common Sense, and further a large part of it is in sub-symbolic form and is used unconsciously. This part of subconscious knowledge is covered under 1) above. But, there is also substantial part of common sense which can be stated, of course with some effort, explicitly. Despite the fact, or rather because of the fact, that common sense is shared by almost all human beings, it is difficult to transmit/imbed common sense knowledge and reasoning in the machine. The difficulty may arise because of the fact that common sense knowledge and reasoning is so deeply imbedded in human psyche that one hardly becomes aware (think consciously/explicitly) of using these, whenever using such knowledge. For example, a person charged with theft in some town, is exonerated by the judge, on ascertaining the fact that the person at the time of commitment of theft, was in some other town. The judge, without explicitly stating the fact, or even without being explicitly aware of having used the fact, uses the common sense fact that a person cannot be at two different places at the same point of time. Thus, difficulty in imbedding common sense knowledge and reasoning in machine may be because of the fact that most of the time these are used implicitly or unconsciously; however, these can be explicated also. For imbedding common sense knowledge and reasoning in the machine, these must be explicated first.
3) Conscious Knowledge: This type of knowledge may be in any of the following forms:
・ Visualizable/image-like form: knowledge in the form of an image, whether of a scene from the real world or purely creation of the human mind, is infinite and continuous. On the other hand, human capability for communication through some language (even within equivalence of meaning) is only finite and discrete; and computer is also a finite and discrete system. Hence, visualizable knowledge may not be communicated in its entirety to the computer through some symbolic means.
・ Verbalizable/symbolizable form: knowledge that can be communicated to other human beings through some natural language.
・ Justifiable/rationalizable form: knowledge that may not be available directly through senses or that is a plain statement of a fact, but, that which requires some (mental) rationalization.
・ Mathematical form
a) Mathematical theories; and
b) Mathematical models.
・ Formalizable: that part of conscious knowledge which is or can be put, through human efforts, in a form readable by a computer, but which may or may not be computer-executable. The situation is somewhat analogous to that of a person who may read/understand a recipe for preparing a dish, but may not be able to actually prepare the dish.
・ Computational theories and computable models
a) Computer-executable form: that part of conscious procedural knowledge which is or can be put, through human efforts, in the form of a computer program which is first computer readable and then is such that the instructions in the program can be acted upon by a computer system. However, the execution of program may not terminate.
b) Computer-decidable/feasible/answerable form: that part of the programmable knowledge, which leads to a required answer or a solution.
(In each of the last three cases: formalizable, computer-executable and computer-decidable form, it may be noted that a part of Human capacity/knowledge that enables man for teaching a computer respectively to read, to execute and to decide may include some unconscious knowledge, and is a higher level of knowledge―sort of meta-knowledge).
2.2. Sources of Imperfections in Knowledge
The following three are major sources of imperfection in human knowledge:
1) The first source may be traced to the fact that human mind is finite and discrete, too limited to grasp the problem domains in their entirety, because domains are generally parts of the infinite and continuous real world. An example of finiteness and discreteness of human mental and physical capacities is the well-known fact that if more than 16 frames per second of a script are received, the frames cannot be distinguished from each other.
2) Second source of imperfections in human knowledge may be traced to the fact that a natural language is primary source for human beings of acquiring, expressing and communicating knowledge, and which, either as a consequence of 1) above or otherwise, has a number of shortcomings to be an adequate tool for representing knowledge perfectly.
3) Final major source of imperfection is common sense―a major source of human knowledge and problem solving capabilities and, which is mostly used unconsciously―is constituted of knowledge pieces which are ambiguous, possibly mutually conflicting, imprecise, and having other blemishes of imperfect knowledge.
Apart from the above, so far as equipping the computer with problem solving assets is concerned, there is a large part of human problem solving assets that cannot be transferred to computer. As mentioned above, a substantial part of human knowledge is unconscious, i.e. is purely-procedural or is stored in human system in the form of habits, vague intuitions and gut feelings. This unconscious knowledge is not communicable, and hence cannot be transferred to computers.
2.3. Types of Imperfections in Knowledge
Imperfections in Knowledge include the following types:
1) Uncertain: The knowledge is uncertain, when, e.g., it is about diagnoses of problems/diseases, predictions (e.g. about weather), historical facts (possibly biased) and conclusions based on sampled data. Also, knowledge in respect of each of the following types of scientific matters is also uncertain: a) the path of an electron in an atom, b) existence of the most fundamental particles, c) existence of life somewhere other than earth, d) existence of other universes having different physics, chemistry, and if relevant, biology etc., i.e. universes having different physical/chemical/biological properties and phenomena different from the ones known to humanity.
Knowledge―including the one, some cases of which are mentioned above―may be uncertain, particularly, when the underlying phenomenon is random, i.e. when knowledge of the phenomenon is group determinable, but is individually non-determinable (e.g. in tossing of a coin, the outcome is certain to be a head, a tail, or rarely standing; but, in a particular trial which one will be the outcome cannot be determined). However, repeated observation of the phenomenon leads to approximate, but uncertain, knowledge of the phenomenon.
2) Incomplete: sampled data for a massive phenomenon is, by its very definition, incomplete representation of the phenomenon. And, so is the knowledge of a natural phenomenon based on any scientific model/theory/ex- planation of the phenomenon, e.g., based on Newton’s theory (because a theory is finite representation of large, generally infinite, phenomenon). History, how so ever detailed it is, is about only some aspects, say political or scientific etc., and further, for each aspect also it cannot be complete representation, in fine detail, of the whole past.
3) Vagueness: The knowledge is vague when there is difficulty of making sharp or precise distinctions in the problem domain, e.g. when knowledge involves linguistic/qualitative variables, like tall. Other terms used for vagueness include fuzziness, indistinctiveness, unclearness, and sharplessness.
4) Imprecise/Approximate/inexact: Imprecision arises when values of a continuous/real variable―like time, length and area―are attempted to be represented in terms of some computer/discrete numbers. In such cases, all the values in the range [n − ε, n + ε], where n is an integer and ε is machine-epsilon, may be represented by the single value n.
5) Ambiguous: Knowledge is ambiguous when it involves some word/situation for which there are many possible interpretations/meanings, generally resolved by context, e.g. the word “bank” or the phrase “for a long time” (as is illustrated by the three sentences: a) I waited in the doctor’s room for a long time, b) It has not rained for a long time, c) Dinosaurs ruled the earth for a long time. Thus, the phrase “for a long time” represents time periods ranging from a few hours in a) and to millions of years in c)). Other terms used for ambiguity include divergence, one-to-many relationship, non-specificity and generality.
6) Paradoxical/Inconsistent: when a given set of statements constituting knowledge, involves mutually conflicting statements. Knowledge of social sciences, among other disciplines, frequently involves mutually conflicting/contradicting theories.
7) Subjective: knowledge is subjective when source of the knowledge is also significant component of the knowledge. For example, the knowledge, generally in the form of beliefs and opinions, in respect of political and economic state of a country, varies from person to person, and hence is subjective.
8) Dynamic: when problem domain changes with time, the knowledge becomes imperfect when the changes are too subtle or too fast to be captured by human beings or by the system meant for monitoring changes.
It may be noted that above mentioned types are neither exhaustive, nor mutually exclusive―a knowledge piece may involve more than one of the above mentioned types.
3. Formal Approaches & Models for Handling Imperfections in Knowledge
In Subsection 3.1, the computational approaches and models for handling appropriately various types of the imperfections in knowledge enumerated above, are discussed in general. Though commonsense knowledge and the unconscious knowledge involve all types of imperfections mentioned above, to which the discussion of Subsection 3.1 may also be valid; yet in view of the specific nature and the specific role each of the two plays in problem solving and other mental and intellectual tasks, the computational aspects of the two are discussed in the next two subsections. In Subsection 3.2, various approaches and models for computation of commonsense are discussed. And, finally, approaches and models for computation of the unconscious knowledge are discussed in Subsection 3.3.
3.1. Computational Approaches and Models for Imperfect Knowledge
In the recent past, a number of approaches have evolved and (mathematical) models have been developed for representing and handling various types of imperfections in knowledge of problem domains for developing robust software systems. The approaches/models may be classified according to the three criteria: 1) quantitative vs. qualitative 2) deductive vs. inductive and 3) symbolic vs. sub-symbolic.
In the quantitative approach, an information piece may be represented as say “100 km/hour” whereas, the same information may be qualitatively represented by stating “very fast”. In the deductive approach, the rules for processing are provided by discipline experts, and an output is determined by the application of appropriate rule(s) for each of the inputs. In the inductive approach, the rules are discovered by the system itself, instead of being provided by some expert [6] . In the symbolic approach, the information for input, the output and processing for drawing inference is in symbolic form. In the sub-symbolic approach, processing may involve sub-symbolic processes, as is done by human brain.
The approaches for handling imperfection of knowledge include probability theory, fuzzy set theory; fuzzy measures and its special cases belief measure, plausibility measure, probability measure, possibility and necessity measures―all of which are symbolic and primarily numeric, but may involve inductive and/or deductive reasoning in the matter of providing rules or discovering rules. Modal logics, belief models and non-monotonic logics are mainly non-numeric, symbolic and follow deductive approaches. Rough set theory is primarily an inductive, qualitative and symbolic approach. Chaos theory, neural network, genetic algorithms, swarm intelligence etc. are sub-symbolic and quantitative approaches, in which Chaos theory is primarily deductive, whereas the others are inductive ( [4] - [8] ).
Next, various models conceived to handle different types of imperfections in knowledge, are mentioned. Probability theory (mathematically) models the phenomenon of randomness, where a phenomenon may be considered as random if individual outcomes are uncertain; however, there is a regular distribution of outcomes when the phenomenon is repeated a large number of times.
As mentioned earlier, fuzzy set theory models the phenomenon of vagueness, which is associated with the difficulty of making sharp or precise distinctions in the world; a domain of interest is vague if it cannot be delimited by sharp boundaries. As an illustration, consider X as the set of persons in an Indian town. Then fuzzy subset Tall of X may be defined as the ordered pair consisting of X and the function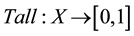 , where, it may be assumed that Tall (person x with height 5’) = 0, Tall (person x with height 5’ 6”) = 0.5, Tall (person x with height 5’ 11”) = 0.9 etc.
, where, it may be assumed that Tall (person x with height 5’) = 0, Tall (person x with height 5’ 6”) = 0.5, Tall (person x with height 5’ 11”) = 0.9 etc.
Formally, a fuzzy set may be specified as follows: For universal set X and a given subset S of X, S is a fuzzy subset of X if for each element x of X, x is assigned a degree of belonging to S, to be denoted by say , with
, with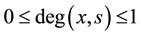 . Thus, for given universal set X, a fuzzy set is a pair
. Thus, for given universal set X, a fuzzy set is a pair , with
, with  and
and 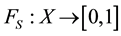 is a function, specifying degree of belonging to S of each element of X.
is a function, specifying degree of belonging to S of each element of X.
On the other hand, Fuzzy measure and its special cases viz. belief measure, plausibility measure and probability measure, possibility and necessity measures etc. model another type of uncertainty, viz. ambiguity, when the uncertainty is about membership of an element of X in crisp subsets of X. A measure, in general, is about our belief (based on some evidence) in the truth of an element to be in some subset of Universal Set. For example, a person is suspect of having committed a crime. He is either innocent or guilty, but not both; he cannot be either partially innocent or partially guilty of say degree 0.6. On the basis of evidence or additional information, it is to be decided to exactly which one of the two crisp sets I or G the person belongs, where I denotes the (crisp) set of innocent persons and G denotes the set of guilty persons.
Formally, fuzzy measure may be specified as follows: For universal set X and a given set 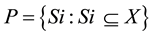 of (crisp) subsets of X, a fuzzy measure specifies the degree to which an arbitrary element x of the universal set X is believed, on the basis of evidence, to belong to Si, an arbitrary element of P. Thus, a fuzzy measure is a pair (P, FP) such that
of (crisp) subsets of X, a fuzzy measure specifies the degree to which an arbitrary element x of the universal set X is believed, on the basis of evidence, to belong to Si, an arbitrary element of P. Thus, a fuzzy measure is a pair (P, FP) such that 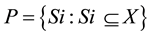 and
and  is a function, specifying the degree of an element x of X of belonging to Si, an element of P.
is a function, specifying the degree of an element x of X of belonging to Si, an element of P.
Modal logics, belief models and non-monotonic logics are extensions of propositional and predicate logics to handle different types of imperfections in knowledge. Modal logics model situations represented by statements which involve phrases like “It is possible that X” and “It is necessary that X” (the use here of “possible” and “necessary” is quite different from the use of these words in “possible/possibility measure” and “necessary/necessity measure”). “It is possible that X” represents a sort of story, which may or may not be true, but which is consistent, i.e. X is not self contradictory. On the other hand, “It is necessary that X” represents the dual of “It is possible that X” in the sense that “negation of X” is impossible or self-contradictory. Some of the well-known formal modal systems include S4, S5, B and T.
Belief logic deals with not necessarily what is factual, but with beliefs, many of which are subjective; and it prescribes (formal) rules for consistent believing and willing [8] . The conventional logics―propositional and predicate―are monotonic in the sense that as the set of facts grows so does the set of conclusions derivable from facts. However, in many of the situations, addition of a fact may force withdrawal of an earlier conclusion. For example: It is a well-known fact that birds can fly. Hence, one may conclude Twitty, a bird can also fly. But later, with the addition of the knowledge that Twitty has both its wings broken, one is forced to withdraw the earlier conclusion. This type of reasoning is called non-monotonic. Some of the well-known approaches/models for non-monotonic reasoning include abductive reasoning, autoepistemic logic, belief revision, paraconsistent logics, default logics and circumscription.
Similar to, but, distinct from probability theory, fuzzy theory and belief theory etc, [9] has proposed “uncertainty theory” as a formal model for handling a distinct type of imperfect knowledge. Three fundamental concepts of the theory are 1) uncertain variable, used to represent imprecise quantities 2) uncertain measure, used to represent the measure of our belief in the truth of an uncertain event and 3) uncertainty distribution, used to describe uncertain variables in an incomplete but easy-to-use way.
Chaos Theory is a (mathematical) approach for representing and handling chaotic phenomenon in nature. A phenomenon is said to be chaotic which is sensitive to initial conditions, i.e. slight difference in the initial conditions/inputs may lead to quite different outputs. However, in a chaotic phenomenon, under exactly same initial conditions, the output must be the same. A chaotic phenomenon differs from a random phenomenon in the sense that in the case of latter, even under exactly same initial conditions, the outcomes may be quite different. Another way of stating the difference is that in both types of phenomena, the appearances are irregular, however, in the case of chaotic phenomenon, the underlying rules are deterministic, whereas in the case of random phenomenon, the rules are probabilistic, i.e. non-deterministic [6] .
Neural networks, Genetic Algorithms and Swarm intelligence are attempts at and approaches to imbedding intelligence in machine by simulating the functioning respectively of a human brain, a biological system in general, and a colony of ants/bees/insects etc. Each of human brain etc. is capable of performing tasks which even an advanced computer may not be able to perform.
The discipline of Numerical Methods & Analysis is about dealing with approximate/inexact knowledge.
To deal with Paradoxical/Inconsistent knowledge, [10] [11] have proposed two paradox logics: Diamond Paradox Logic & Delta Paradox Logic.
Situation Calculus was introduced and developed by [12] , for representing knowledge about dynamic systems. The basic entities of Situation Calculus include 1) objects 2) the actions that can be performed on the objects of the problem domain and its environment to change to new states 3) situations, where a situation is not a state, but is a finite sequence of actions. According to [13] , a situation is not a snapshot, but it is ahistory, and 4) fluents, which may be functions or predicates, the values of which distinguish between different states of the dynamic system under consideration.
In Situation Calculus, a problem domain and its environment are formalized by various types of formulae including the following ones: 1) Action precondition axioms, which state conditions under which an action can be carried out 2) Successor state axioms, which state conditions which must be satisfied by the values of functions and predicates of a fluent and 3) Axioms describing the problem domain and environment in various situations.
3.2. Approaches and Models for Computing “Commonsense”
In view of the fact that common sense reasoning plays pivotal, rather indispensible, role in human problem solving to the extent that hardly any human intelligent behavior is possible without having its basis in common sense; one of the central goals of Artificial intelligence is to develop computer systems capable of exhibiting human-like common sense behavior. But the formalization of commonsense reasoning is so far an elusive goal. Reasons for the difficulty in formalising common sense reasoning include 1) the number of common sense facts―millions and even more―that people know and reason with and 2) most of these millions of commonsense facts are used by human beings implicitly―without their being consciously aware of having actually used some of these common sense facts in realizing some intelligent behavior. One of the prerequisites for developing commonsense reasoning systems is making this knowledge explicit. In view of these facts, in the following, attempts at formalisation of specifically common sense knowledge & reasoning are briefly discussed independently; despite the fact that various approaches and models for formally representing and handling imperfections found in common sense knowledge have been discussed above. But the earlier discussed approaches and models were generic for any type of imperfection in knowledge. The discussion below is specifically in context of common sense.
There are two well-known strategies in respect of formalization of common sense knowledge & reasoning viz. 1) logical and 2) encyclopedic. The logical strategy for the purpose is based on extensions of Propositional Logic and Predicate logic and includes temporal and spatial reasoning ( [14] - [17] ), non-monotonic reasoning ( [18] [19] ), logics of knowledge, belief, desire and intention ( [20] [21] ), default logics [22] , and logics of obligation [23] [24] .
The encyclopedic strategy is based on constructing a massive knowledge base of millions of common sense facts. The strategy is used in the well-known Cyc Project ( [25] [26] ).
3.3. Approaches and Models for Computing “Unconscious”
For similar reasons as were given for the need of independent discussion of attempts at formalization of common sense, next, brief sketch of attempts at formalization of the “unconscious” is given. It is also done in view of the fact that latest relevant research establishes that substantial part of human intelligent behavior is rooted in the unconscious. Discussion of issues regarding computing the conscious/unconscious and creativity is at least as old as the design of Analytical Engine by Charles Babbage. In [27] , it is mentioned that in a memoir by Lady Lovelace (1842), she states, “The Analytical Engine has no pretensions to originate anything. It can do whatever we know how to order it to perform”. Turing further discusses objections, raised up to 1950, by different scholars to the possibility of computing even the conscious, what to talk of the unconscious. There have been serious attempts―by cognitive scientists, cognitive neuroscientists, cognitive psychologists, psychophysiologists and AI specialists―at revealing the secrets of the unconscious mind.
The subject matter is very vast and interdisciplinary in nature covering a number of disciplines including physiology, psychology, cognitive science, neuroscience, computer science, AI and even philosophy. The subject even has some relevance to or overlaps with other well-known disciplines/sub-disciplines including computer- human Interface (CHI), affective computing and robotics. Just for a glimpse in field, only a very small, rather negligible, fraction of the available literature is mentioned here.
Out of a number of theories and architectures that provide scientific and engineering foundations to the attempts at formalizing and computing the conscious and unconscious cognition, only the following three are sketched:
1) Global Workspace Theory (GWT), proposed in [28] - [30] , is an architecture that simulates computationally various conscious and unconscious cognitive processes. GWT consists of two types of memories a) Working Memory(WM)―sort of storage for transitory events―that are momentarily active for a few seconds only and are subjectively experienced―that may be considered as sort of atoms of what constitutes human unconscious behavior, and b) Global Workspace(GW), sort of storage simulating human consciousness, or totality of conscious experiences. The contents of GW are broadcast to large number of unconscious processes in WMs, for providing control over and information to various unconscious processes about conditions for possible actions/ behaviors. Other unconscious processes in coalitions may become inputs to GW. Thus there is continuous communication between the unconscious cognition and conscious cognition. The claim of GW modeling consciousness appropriately is based on facts including its capability to handle novel situations, its sequential nature and capability to specify context, which though is not a part of consciousness but it shapes consciousness.
GWT is not accepted uncritically. For example, in [31] [32] , objections are raised to the model on various grounds including to the assumption of consciousness being assumed to be continuous stream of rich and detailed experiences.
2) Another cognitive architecture, known as LIDA, was proposed and developed in [33] - [36] , which stands for Learning Intelligent Distribution Agent, attempts to model large number of elements and processes of cognition which range from low-level perceptions and actions to high-level reasoning, including the capability to provide plausible explanations for various cognitive processes.
3) Unconscious Thought Theory (UTT): was first proposed in [37] in 2006. One of the most significant, and also the most controversial, hypothesis of the theory is that in the matter of solving complex problems having large number of parameters, unconscious thought is better than conscious thought. The hypothesis is diametrically opposite to the findings of research over a number of decades previously. According to the findings of earlier research, unconscious processes by themselves are incapable of accomplishing complex tasks.
The findings under UTT have been challenged and criticised by a number of researchers including [38] - [43] .
4. Conclusion
In order to develop robust software, it is essential that imperfectness of knowledge of the problem domain and its environment be taken into consideration. Further, for handling each of the various types of imperfections, only some of the available tools and approaches may be appropriate. In this communication, various types of knowledge and types of imperfections in knowledge are discussed from computational perspective within the context of software development enterprise. For handling each type of imperfections, various approaches, models and methods are proposed. The work can be further extended by refining the existing tools and approaches and proposing new ones for incorporating and handling of imperfect knowledge appropriately for robust software development.
Acknowledgements
Our thanks to Prof. Manohar Lal, SOCIS, IGNOU, New Delhi (India) for his valuable suggestions.