A Brief Report Investigating Subjective and Objective Memory Pre- and Post-Memory Training in 70- to 96-Year-Old Individuals with Mild Memory Deficit ()
1. Introduction
Subjective memory impairment is a major complaint among older adults. Interestingly, research is conflicting regarding the relationship between subjective memory impairment and objectively measured memory loss [1] -[4] . For example, one study reported the extraordinary finding that 94% of memory-impaired older adults had no subjective memory complaints; furthermore, there were no differences between “complainers” and “non-complainers” in objective memory performance [2] . Conversely, another study examined healthy individuals who did not show an objective memory deficit, but who reported a subjective memory deficit that was problematic enough that they self-referred to an aging/dementia clinic [5] . After 3 years, participants who subjectively described impaired memory, but did not show deficits on objective tests, demonstrated no decline in memory. Strangely, despite the maintenance of their memory ability over time, their complaints did not diminish.
Despite conflicting literature, most studies do report that increased complaints about memory are in fact predictive of poorer objective memory task performance in older, mild, cognitive impairment (MCI)-diagnosed individuals [6] - [11] . Furthermore, at least in some cases, subjective memory complaints may be more accurate than objective measures regarding memory ability. For example, Erickson et al. noted that early-stage, disease-related cognitive decline might be predicted better by self-evaluation of impaired memory, than by objective memory tests [12] .
Given the uncertain relationship between subjective and objective memory deficit, it is also not clear whether subjective memory improvement is predictive of improvement in objective measures. In one of the few studies investigating this issue, Valentijn et al. examined subjective and objective memory improvement 1 week and 4 months following a memory intervention in healthy older adults [13] . Following the memory intervention, individuals both subjectively reported their memory to be more stable, and demonstrated objectively superior memory. However, the predictive value of self-assessed memory to objective memory performance is not clear. In a meta-analysis, it was reported that memory interventions do indeed result in increased self-assessed memory, but that subjective memory improvement is lower than that found by using objective measures [14] .
The current study examined the relationship between subjective and objective memory in individuals with mild memory deficit (MMD), who underwent memory training for three months. The goals were to determine whether 1) subjective memory is related to objective memory and; 2) objective memory can be altered via a memory training paradigm.
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
Participants, recruited from assisted living communities, volunteered for memory training or were referred by staff/family, and were found on initial evaluation (Time 1 testing) to have an objective memory deficit (n = 95, 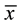 age = 84.08, SD = 5.58, range 70 - 96 years). Individuals were free from sensory deficits, as reported via a medical history and conditions questionnaire at the initial evaluation. Presence of memory deficit was determined at Time 1 testing via the Mini Mental Status Exam (MMSE) [15] and the Dementia Rating Scale (DRS-2) [16] . The mean MMSE score was 22.04 (SD = 5.05), indicating a low level of cognitive disturbance. Additionally, all participants had a memory deficit without reaching Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Revision [17] criteria for dementia as measured via the DRS-2.
age = 84.08, SD = 5.58, range 70 - 96 years). Individuals were free from sensory deficits, as reported via a medical history and conditions questionnaire at the initial evaluation. Presence of memory deficit was determined at Time 1 testing via the Mini Mental Status Exam (MMSE) [15] and the Dementia Rating Scale (DRS-2) [16] . The mean MMSE score was 22.04 (SD = 5.05), indicating a low level of cognitive disturbance. Additionally, all participants had a memory deficit without reaching Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Revision [17] criteria for dementia as measured via the DRS-2.
Participants were enrolled in a memory training program with the expectation that they would participate for at least 3 months in order to complete two evaluations (an initial evaluation [i.e. Time 1], and a follow-up [Time 2]). Despite expectations, 9 participants dropped out over the course of the study (Time 2; n = 86).
2.2. Materials
2.2.1 Subjective and Objective Memory Tests
In addition to the above, participants completed tests of subjective and objective memory (The authors realize that the DRS-2 and MMSE are indeed tests of objective memory, however previous work [18] suggests that memory training in neuropsychologically impaired individuals does not necessarily remove individuals from a designation of “impaired”; thus, a more sensitive test of cognition, the Cognistat [described below], was used here to analyze objective memory change in response to memory training). Subjective, self-evaluation of memory was conducted via the Memory Complaint Questionnaire (MCQ) (Appendix A) [19] - [21] . This scale requires yes/no responses to ten items listing the experience of deficits in different memory situations.
Objective memory was assessed via the Cognistat [22] . The Cognistat is a measure of cognitive functioning that encompasses these ability areas: Orientation, Attention, Language Comprehension, Sentence Repetition, Naming, Visual-Spatial Constructional Praxis, Memory, Numerical Calculations and Reasoning. The Memory subtest is composed of 4 words that are repeated until learned, with participants asked to recall the words 10 minutes after an intervening task. Only performance on the Memory subscale was analyzed here.
2.2.2. Memory Training Material
Memory training materials consisted primarily of commercially available memory training computer exercises. Games used were: Moraff’s Concentration Game (The World of Games, 2003), Improve Your Memory (Think Active, 2001), Brain Builder (Advanced Brain Technologies, 2003), Think Fast (Brain. com, 2003), and Train Your Memory (Happy Neuron. com) [23] - [27] . It should be noted that many of these games are no longer available, and internet/contact sites could not be determined, as a result of the fast-paced nature of computerized gaming development. It is also worth mentioning that exercises to strengthen attention and concentration were included, in addition to those involving memory directly, as these cognitive functions are required to store and retrieve new information (i.e. to engage in successful memory function). In addition to the computer-generated exercises, clinicians provided interactive exercises, such as 3 and 4-word retrieval games, inquiry regarding recent events (supported by cues to encourage the patient’s ability to retrieve information), and other interactive memory-exercises based on the participant’s training goals and/or areas of interest. Lastly, clinicians also engaged participants in developing compensatory skills to strengthen independent and confident functioning. Some examples of these practical strategies were: helping participants identify places in their apartment to keep important items (that were otherwise frequently misplaced), use of a calendar, wearing a watch, utilizing appointment cards, and carrying a schedule of the day’s activities.
2.3. Procedure
Clinicians administered an initial testing session (Time 1) in one setting, lasting about one hour, followed by the second session, occurring after three months (approximately 13 sessions), also lasting approximately 1 hour. Both the MCQ and the Cognistat were administered at Times 1 and 2.
During the three-month memory training period, participants were trained by different clinicians, and were assigned homework to complete during other days of the week. Specific computer programs used by a given participant were determined by the clinician. That is, participants were trained on a variety of computerized memory training programs until the one most useful/interesting to the individual was determined. Memory training sessions took place, on average, twice weekly, for 55 minutes. The clinician presented stimuli on the computer, and participants responded, with responses then entered into the computer by the experimenter (in some case a participant insisted on performing the computer tasks unaided, and that was permitted).
2.4. Data Analyses
Results were analyzed by first dividing participants into two groups based upon Time 1 performance on the MCQ. A “High Complaint” Group (HCG; n = 39) consisted of those reporting 4 or more “yes” responses on the MCQ, while the “Low Complaint” Group (LCG; n = 56) was defined as reporting fewer than 4 “yes” responses. The difference between groups on Cognistat performance was examined. Second, we divided participants into two groups based on change in memory score from Time 1 to Time 2. The Improved Memory Group (IMG; n = 19) demonstrated an increased memory score (remembered more items on the Cognistat Memory subscale), whereas the Non-improved Memory Group (NMG; n = 13) demonstrated a decreased memory score (Those whose memory score did not change from Time 1 to Time 2 were excluded from analyses, n = 61). Differences between groups in MCQ responses were then examined.
We acknowledge that there are serious limitations in the analyses described below. Specifically, a catastrophic data retention failure prohibits any analyses beyond those described in the Results. That is, paired and unpaired t-tests were used to examine the data. However, we further acknowledge that correlational examinations and repeated ANOVAs would have been appropriate to conduct, but that we are unable to do so. Because of these limitations, we strongly suggest that any conclusions drawn are suggestive only, and in need of replication in order to be considered valid. Nevertheless, we believe the findings are worth publishing because of the relatively rare population on which the work was conducted (mild memory impaired older adults), because they are in line with previous work demonstrating relationships between subjective and objective memory assessments, and because they may hold clinical importance.
3. Results
Participants were divided into 2 groups based upon Time 1 performance on the MCQ. A “High Complaint” Group (HCG; n = 39) was defined as 4 or more “yes” responses, while the “Low Complaint” Group (LCG; n = 56) was defined as reporting fewer than 4 “yes” responses (MCQ 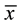 = 4.06). Complaint Groups did not differ in age (HCG
= 4.06). Complaint Groups did not differ in age (HCG 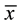 = 84.04, sd = 5.76; LCG
= 84.04, sd = 5.76; LCG 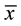 = 80.04, sd = 5.14), MMSE (HCG
= 80.04, sd = 5.14), MMSE (HCG 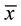 = 21.61, sd = 5.07; LCG
= 21.61, sd = 5.07; LCG 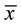 = 23.16, sd = 4.49) or DRS-2 performance (HCG
= 23.16, sd = 4.49) or DRS-2 performance (HCG 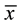 = 61.42, sd = 14.83; LCG
= 61.42, sd = 14.83; LCG 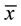 = 58.96, sd = 15.12). Comparison of the two complaint groups on performance of the Cognistat Memory subscale at Time 1 revealed that HCG (
= 58.96, sd = 15.12). Comparison of the two complaint groups on performance of the Cognistat Memory subscale at Time 1 revealed that HCG (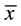 = 4.44; sd = 3.32) scored significantly lower than LCG (
= 4.44; sd = 3.32) scored significantly lower than LCG (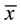 = 6.26, sd = 3.13; t (93) = 2.72, p ≤ 0.001), indicating that individuals with a larger number of memory complaints performed worse on a memory test (the Cognistat) at Time 1, prior to any training.
= 6.26, sd = 3.13; t (93) = 2.72, p ≤ 0.001), indicating that individuals with a larger number of memory complaints performed worse on a memory test (the Cognistat) at Time 1, prior to any training.
After 3 months of training, the HCG (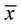 = 6.05, sd = 3.32, n = 33) and LCG (
= 6.05, sd = 3.32, n = 33) and LCG (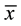 = 5.08, sd = 3.48, n = 53) did not differ (t (84) = 0.76, p = 0.20; Note attrition and thus smaller n’s in the groups at Time 2). Although numerically the HCG increased, and the LCG decreased, their respective memory performance from Time 1 to Time 2, these changes were not significant (p > 0.05). See Table 1.
= 5.08, sd = 3.48, n = 53) did not differ (t (84) = 0.76, p = 0.20; Note attrition and thus smaller n’s in the groups at Time 2). Although numerically the HCG increased, and the LCG decreased, their respective memory performance from Time 1 to Time 2, these changes were not significant (p > 0.05). See Table 1.
We next asked whether a change in memory performance, either positively or negatively, was reflected in number of memory complaints, with increasing memory predicted to be associated with decreasing complaints, and decreasing memory predicted to be associated with increasing complaints. Participants were divided based on change in memory score from Time 1 to Time 2. The Improved Memory Group (IMG; n = 19) demonstrated an increased memory score (remembered more items on the Cognistat Memory subscale), whereas the Non-improved Memory Group (NMG; n = 13) demonstrated a decreased memory score (Those whose memory score did not change from Time 1 to Time 2 were excluded from analyses, n = 61). Score on the MCQ was analyzed as a function of IMG versus NMG. As can be seen in Table 2, IMG decreased their complaints, and NMG increased their complaints. Due to catastrophic data retention failure, we were unable to statistically test this latter comparison. However, independent t-tests comparing IMG versus NMG at Times 1 and 2 revealed a trend toward significant between group differences at Time 1 (t (32) = 1.94, p = 0.06), but not at Time 2 (p > 0.05).
4. Discussion
With regard to our initial goals, subjective memory assessment does seem to be related to objective memory performance. Specifically, at Time 1, individuals with more memory complaints performed worse on the memory
![]()
Table 1. Cognistat Memory Score as a Function of Complaint Group and Test Time.
*HCG versus LCG at Time 1, p < 0.05.
![]()
Table 2. MCQ as a function of Memory Change and Time.
*IMG versus NMG at Time 1, p = 0.06.
scale of the Cognistat, compared to those with fewer memory complaints. Additionally, individuals who demonstrated increased Cognistat memory performance at Time 2 relative to Time 1 also reported decreased subjective memory complaints, compared with those whose performance on the Cognistat decreased from Time 1 to Time 2 (Though due to data loss we were unable to perform inferential statistical analyses). These findings suggest that memory complaints, in relatively healthy older adults, should be taken seriously and as a potential indicator of objective memory disturbance, and with the possibility that cognitive rehabilitation therapy might improve memory deficits. Thus, memory complaint may be a positive prognostic sign that should decrease with an improvement in memory function as a result of treatment.
With regard to whether objective memory can be altered via the memory training paradigm used here, the answer is a slightly equivocal “yes”. In support of training program induced memory improvement, both high and low memory complaint groups performed the same at Time 2, suggesting that memory training modified memory. However, paired comparisons between Times 1 and 2 for each group did not reveal any significant differences and, in addition, there is the possibility of regression toward the mean resulting in Time 2 equivalent performance between groups. Thus, although suggestive, further research is necessary.
The application of memory training and use of subjective memory complaints as indicators of objective memory impairment in individuals residing in assisted living communities would potentially benefit older adults in such care settings. For example, research suggests that 58% of assisted living residents can be diagnosed with cognitive impairment and, of these, 41% can be diagnosed with dementia but remain without treatment [28] . Thus, the finding that memory complaints may be indicators of memory impairment, and that memory training may reduce both complaints and cognitive decline, are of clinical value as well as an indicator of future memory problems.
5. Conclusion
Despite the obvious and acknowledged limitations of the work presented here, the results suggest that memory complaints in older adults with mild memory impairment may be indicative of actual memory, with increased versus decreased complaints associated with decreased versus increased memory, respectively. Furthermore, these findings imply that older memory impaired adults, despite their memory impairment, are indeed able to judge, and may be accurately concerned with, the extent of their own memory loss. Finally, future work is necessary to determine whether the memory training paradigm used here has clinical utility. Again, given the limitations of the statistical analyses reported here (as described in the Data Analysis section), the findings must be viewed cautiously and, prior to being considered valid, with an eye toward replication.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Ruth Propper for statistical advising and assistance with manuscript preparation. The authors are employed by Memory Training Centers of America (MTCA). Because this company provides memory training to older adults, we acknowledge that a financial conflict of interest may exist. Research is sponsored and funded by MTCA.
Appendix A
MEMORY SELF-REPORT QUESTIONNAIRE
Have you often experienced any of the following problems during the past 6 months?
1. Forgetting the name of a friend or family member?
YES ___ NO ___
2. Difficulty finding the right word when speaking?
YES ___ NO ___
3. Problems doing things that were once done easily?
YES ___ NO ___
4. Becoming confused about the month or season?
YES ___ NO ___
5. Forgetting addresses and phone numbers that were once familiar?
YES ___ NO ___
6. Forgetting what happened just a day or two ago?
YES ___ NO ___
7. Problems remembering what you just said or heard?
YES ___ NO ___
8. Forgetting previous conversations?
YES ___ NO ___
9. Confusing recent events with past events?
YES ___ NO ___
10. Awakening during the night confused about where you are?
YES ___ NO ___