Spring Water Qualitative Assessment in Mountainous Areas, Case Study: Soreq Catchment/Ramallah/West Bank ()
1. Introduction
Improving access to safe drinking-water is of major benefit to the human health and every effort should be made to achieve a drinking-water quality as safe as practicable [1] . Water resources in the West Bank are scarce, due to the fact that the West Bank is lying within an arid region. Groundwater is considered to be the main fresh water resource in the West Bank. This study is considered to be important as there is a lack of detailed information concerning water quality and related issues. This is in spite of the fact that these springs are the major source of water for both domestic and agricultural purposes. The sole source of groundwater in West Bank is in the Mountain Aquifer System, which is divided into three basins: Northeastern, Western and Eastern [2] . The chemical characteristic of the spring water is very important for municipal, agriculture, and drinking water supplies. The chemical composition of water is based on the minerals which have dissolved in it. In addition, the chemical composition of water is modified by ion-exchange equilibrium. There are some environmental conditions affecting the water chemistry such as type of rock, climate, relief, vegetation and time [1] . The growing demand of Palestinians, the lack of sewer systems, the wide distribution of cesspits and septic tanks, the common practice of wastewater disposal into gardens and road ditches, and the uncontrolled disposal of untreated municipal sewage into wadis will cause rapid contamination pollution of aquifer systems through karstic conduits in the area [3] . This study aims at studying the hydrochemical and microbiological parameters to the spring water in Soreq catchment/SW of Ramallah. Twenty two heavy metals are analyzed including Fe2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, Zn2+, Mn2+, B, As2+, Be, Se, Ba, Tl, Cr, Al, V, Co, Cu, Ni, Sr, Bi, Mo, Ag and Li. Chemical changes in spring water between dry and wet seasons were determined to locate possible sources of pollution and their impact on the spring water quality for domestic and agricultural uses.
2. The Study Area
The area of the study is Soreq catchment which is situated in the western part of the West Bank. Its location is within the western catchments (Figure 1) and it has an area of 70 km2. The Soreq catchment borders are: Al Dilb catchment from the North, Quilt catchment from the East, Salman catchment from the West and Mukallak and Nar catchment from the South East. The Palestinian population of Soreq catchment was estimated to be about 125,000 [4] . The climate of the Soreq catchment ranges from arid to semi-arid. The monthly average temperature ranges from 7˚C - 10˚C in winter to 23˚C in the summer. The minimum temperature is −2˚C in January and the maximum is 40˚C in August [5] . Rainfall for Soreq catchment is limited to the winter and spring months, mostly between November and May; summer is completely dry. The rainy days are estimated between 40 - 70 days per year [6] . The average annual rainfall in the eastern part of the district varies from 200 to 450 mm. In the western part of the Soreq catchment, the average annual rainfall is higher than the eastern part; it varies from 350 to 550 mm. In the mountains the average annual rainfalls vary from 550 to 700 mm [7] .
3. Geology of the Study Area
The geological formations of Soreq catchment range in age from lower Cenomanian to Albian. Soreq catchment is mainly covered by sedimentary carbonate rocks of the Cretaceous and Tertiary periods. Lithological composition of these formations consists mainly of limestone, dolomite, marl, chalk, chert and alluvium [8] . The Soreq catchment is underlain by the Western aquifer; many springs emerge in the study area (Table 1).
![]()
Figure 1. Location map of the study area.
4. Methodology
The samples that were collected from springs, in a 1-Liter high density Polyethylene bottles, stabilized with ultrapure nitric acid (0.5% HNO3), preserved in a cool place (about 4˚C). Temperature, pH, electrical conductivity, total dissolved solids were measured in Onsite, using Hanna Field Multimode Meter. Major anions (NO3, SO4, and Cl) were analyzed using HP liquid chromatography. Concentrations of the major cations (Ca, Mg, Na, and K) were determined by ICP-MS. Alkalinity and HCO3 analysis was measured onsite by titration. All chemical analyses were carried out at the Environmental Research Lab. at Al-Quds University―Abu Dis. For Total Coliform and Faecal Coliform tests were collected in sterile 100 ml, glass bottles, then cooling in an ice box and transferred to the laboratory on the same day for biological tests. The spring water samples were analyzed at the laboratory of Birzeit University in Ramallah.
5. Result and Discussion
Results of the physical parameter analysis of spring water samples are represented in Table 2. The results of cations and anions are represented in (Table 3(a) and Table 3(b)).
![]()
Table 1. Springs in the Soreq catchment.
![]()
Table 2. Physical parameters of spring water in Soreq catchment.
TDS is Total Dissolved Solids, T is Temperature, EC is Electric Conductivity.
(a) ![]() (b)
(b) ![]()
Table 3. (a) The anion and cation in ppm of the spring water in Soreq catchment in dry periods; (b) The anion and cation of the spring water in Soreq catchment in wet periods.
6. Hydrochemical Profiles
The spring water quality assessed through the analysis of physiochemical parameters (pH, EC, T, TDS) and major cations (Ca2+, K+, Na+, Mg2+), major anions (Cl−, 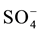 ,
, 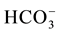 , NO3) and heavy metals (Zn2+, Mn2+, Pb2+, Cd2+, Fe2+, B2+, As2+, Be, Se, Ba, Ti, Cr, Al, V, Co, Cu, Ni, Sr, Bi, Mo, Ag, Li). The spring water in the study area is generally of low alkalinity with (pH) average ranging between 7.8 for dry period and 7.7 for the wet period. The maximum TDS value was 763 recorded in Ein Albalad in March and the minimum is 210 ppm recorded in Ein Abu Zaher, while the maximum TDS value is 561 ppm recorded in the November in Ein Biet Soreq and the minimum is 185 ppm recorded in Ein Katana. EC and TDS averages in wet period are higher than dry period due to dilution process. Depending on TDS values for both periods the spring water in the area is classified as fresh water. The relationship between EC and TDS in the groundwater of the study area is strong and the value of correlation coefficient (R) is close to one. The concentration of Ca2+ is higher than the other major cations and
, NO3) and heavy metals (Zn2+, Mn2+, Pb2+, Cd2+, Fe2+, B2+, As2+, Be, Se, Ba, Ti, Cr, Al, V, Co, Cu, Ni, Sr, Bi, Mo, Ag, Li). The spring water in the study area is generally of low alkalinity with (pH) average ranging between 7.8 for dry period and 7.7 for the wet period. The maximum TDS value was 763 recorded in Ein Albalad in March and the minimum is 210 ppm recorded in Ein Abu Zaher, while the maximum TDS value is 561 ppm recorded in the November in Ein Biet Soreq and the minimum is 185 ppm recorded in Ein Katana. EC and TDS averages in wet period are higher than dry period due to dilution process. Depending on TDS values for both periods the spring water in the area is classified as fresh water. The relationship between EC and TDS in the groundwater of the study area is strong and the value of correlation coefficient (R) is close to one. The concentration of Ca2+ is higher than the other major cations and 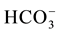 concentration is higher than the other major anions in both seasons (Figure 2).
concentration is higher than the other major anions in both seasons (Figure 2).
EC values are higher in the Ein Beiet Soreq as a result of effect of fertilizers uses in the recharge areas, in addition to agricultural and human activities. Concentrations of cations and anions in wet period are greater than dry period due to the dilution process except bicarbonate ion 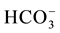 which is lower in the wet period due to
which is lower in the wet period due to
the recharge process, where the carbonate is associated with water converted to 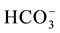 (Table 3(a) & Table 3(b)). The
(Table 3(a) & Table 3(b)). The 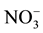 has a mean of 32 mg/L for the samples; nitrate concentration in dry period is greater due to agricultural activities and sewage effect.
has a mean of 32 mg/L for the samples; nitrate concentration in dry period is greater due to agricultural activities and sewage effect.
The analysis of heavy elements in the groundwater of the study area confirm that springs water contains higher values of trace element about WHO like Co, Ni, Cd, Pb, As, Zn, Cr, V, Mn, B, Se, Al, Ti, and Ba (Figure 3) because their concentrations are higher than the permissible limits according to WHO [9] and PWA [10] standard as a result of weathering and solution action, in addition to the effect of the fertilizers and human activities.
Hydrochemical formula shows that most springs of study area have water type of Ca-Mg-HCO3, and the other springs range between Ca-HCO3 for the two periods. However, both spring water types reflect dolomite bearing rock from Albian and sometimes the deeper Cenomanian formations. The spatial distribution of water quality in the study area for both dry and wet periods shows difference in water quality between both periods as a result of recharge and dilution processes in the wet period. The major cations and anions concentrations of the spring water from the sampled springs in the study area are plotted on a piper diagram (Figure 4). The type of spring water in the study area for both periods is “located between the areas of normal earth alkaline water with prevailing bicarbonate and chloride” for the two periods.
![]()
Figure 3. The average concentration of heavy metals in spring in µg/L.
![]()
Figure 4. Piper diagram showing the water types with proportions in the Soreq catchment.
7. Water Quality Parameter (Salinity)
According to the classification in (Figure 5), the spring water samples are plotting in the Wilcox diagram, which representing SAR against the Conductivity and show most samples falling within the field of S1, C2. This means that they are in the zones of medium salinity to low SAR, which is good for agriculture, but the other springs falling within the field of S1, C3. This means that they are in the zones of high salinity to low SAR, which is permissible for agriculture. According to EC and Na% values for the spring water, the springs are good for irrigation in two periods.
8. Total Hardness (TH)
The hardness of water is defined as its content of divalent metallic ions which react with sodium soaps to produce
![]()
Figure 5. Wilcox classification of the water samples.
solid soaps or scummy residue and which react with negative ions when the water is heated in boilers to produce solid boiler scales [11] . In the study area, the lowest value of TH recorded was 223.7 mg/L for Ein Abu Zaher, and the highest value was 599.8 mg/L for Ein Biet Soreq spring in dry season. Water types according to the average TH in the study area range from hard to very hard water with prevailing very hard water in 80% of the samples.
9. Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR)
The sodium adsorption ratio (SAR) indicates sodium concentration in water; (SAR) is considered an important parameter for the evaluation of water suitability for irrigation [11] . Acceptable SAR values for irrigation water depend on the particular water and soil characteristics. According to Winner classification [12] (Figure 6), most of spring water samples in study area fall in the zone of excellent water type for irrigation in both seasons.
10. Soluble Sodium Percentage (SSP) or %Na
Water quality for agricultural purposes in the Soreq catchment shows variation between excellent to good based on Todd classification [11] of soluble sodium percentage (SSP) values, which is defined as:
![]() [12] .
[12] .
where all concentrations are in meq/l. According to EC values for the spring water, the EC of 6 springs (55%) between 750 and 1200 μs/cm, therefore those springs are permissible for irrigation for both seasons while other water springs samples are good for irrigation for both seasons. Depending on Na%, Ein Katana, Ein Beit Soreq, Alsami, Ein Salman, Ein Albalad and Al-Qebleya water springs for both seasons are good for irrigation, while the Ajab, Jefna, Abu Zaher and Aziz spring water is excellent for irrigation.
11. Microbiological Analysis
Water is a good media for microorganism. Groundwater and surface water may contain bacteria, viruses, fungus and algae, which makes water objectionable for domestic purposes and health threatening [9] . In this study, were tested for FC and TC (Table 4). The results obtained from microbiological analysis shown that Ein Al-Balad, Ein Ajab, Ein Biet Soreq and Ein Salman contain uncountable colonies of FC and TC, which reveals contamination from wastewater from sewerage system near Ein Al-Balad and cesspits near Ein Ajab, Ein Biet Soreq and Ein Salman. For Ein Katana, Ein Abu Zaher and Ein Al-Shami spring show uncountable TC, this is referred to sheep herds and manure piles near the spring outlet, especially katana spring, located under farms for cows belonging to the cow farms. It could be concluded that all the springs are contaminated with coliform bacteria; therefore they are not suitable for drinking unless being treated. Boiling, sun disinfection, or chlorination of the water is possible treatment techniques.
12. Conclusion
A hydrochemical study of the spring water in Soreq catchment was conducted to define water types in the study
![]()
Figure 6. Values of (SAR) for water samples of the study area.
![]()
Table 4. The fecal and total coliforms of spring water samples of the studied area.
area and to determine hydrochemical parameters of the aquifer system. Water samples were analyzed within two water sampling campaigns (before and after recharge period), covering all springs in the area. These springs are located close to populated areas and have agricultural activities nearby. The physical properties (temperature and EC) and chemical properties (pH, TDS, major ions, and trace elements) were determined. From the results of this study, the concentrations of most metal, ions and anions are within permissible limits except the few cases discussed. The spring water quality is generally low. Springs are suitable to be used as agricultural and irrigation water source, except some samples which are poor due to high salinity. EC and TDS averages in wet period are higher than those in dry period due to dilution process. Depending on TDS values for both periods the spring water in the area is classified as fresh water. The relationship between EC and TDS in the spring water of the study area is strong and the value of correlation coefficient (R) is close to one by equations (TDS = 0.46 EC + 20.2 with R2 = 0.99). The water of the area is between highly mineralized and excessively mineralized. EC values are higher in Ein Beiet Soreq as a result of the applications of fertilizers uses in the recharge areas, in addition to human activities.