Typology of Road Accidents Related to the Default of Signaling: A Case Study of the Yaoundé-Douala Highway, Southern Cameroon ()
1. Introduction
Road accidents are a real threat to the world. They affect every country and every strata of the society. In 2010, 1.3 million people across the world died of road accidents [1] . Without appropriate measures, the increase of road traffic may kill about 2.4 million people by 2030 and more than 50 million injured according to the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2009.
Road insecurity should be considered as a goal when it comes to development, particularly the millennium goal aimed at reducing poverty in the world by 2020 [2] .
In fact, the considerable economic and social expenditures induced by road accidents in poor and developing countries are more than the aid they receive from the International Community to alleviate poverty in the world [2] . In these countries, the intense traffic has provoked a strong increase of accidents (21.5%) resulting in the death of 19.5 per 100,000 inhabitants. In developed countries, the policy of preventing road accidents has reduced by half the ratio now to about 10.3 deaths per 100,000 inhabitants [2] .
In Sub-Saharan African countries, roads have become places of all dangers instead of being spaces of exchange and development that they are supposed to be. In Cameroon, between 1992 and 1997, 511,391 road accidents occurred with about 1500 deaths recorded per year. For instance at Ebombe in 2003 (32 deaths), Ngomo in 2006 (36 deaths) and Boumnyebell in 2011 (30 deaths) all reveal increase with time. Statistics for the year 2010 shows that about 1900 people were killed, and more than 6000 injured, posing a lot of worries. From the above mentioned statistics, road accidents constitute the second cause of mortality in Cameroon after malaria [2] .
Several factors favor the occurrence of road accidents. The quality of road signs, the visibility of the latter and their interpretation by drivers amongst others are factors related to road signing, which influence the occurrence of accidents and determine the type of accidents scenarios. Considering the deficiency in road signs along the roads in Cameroon, it is important to examine the incidence of road signs on the occurrence of road accidents. In other words, what could be the types of accident scenarios related to road signs in Cameroon?
This paper aims at establishing the types of accident scenarios related to road signs in Cameroon. At first, we shall characterize the road signs along the Cameroon highways and secondly from these characteristics highlight the profile of road accidents.
2. Literature Review
Several approaches are used to conduct research in the field of road safety. One of the most commonly used approach is that of detailed survey on road accidents [3] . The principle of this approach is the detailed analysis of accidents based on the collection of data aimed at facilitating the understanding of factual progress and the relationship of casualty for each case study.
According to Brenac and Fleury [4] , the detailed surveys approach can produce significant result on the evaluation of new technique measures, the evaluation of hypothesis or the emergence of new hypotheses regarding the occurrence of accidents and the possibility of prevention, when based on a conceptual framework and research explicit objective [3] [5] . However, difficulties are related to the need of implementing a multidisciplinary expertise for a detailed analysis of cases and rely on data collection. Such approaches used in France for detailed accidents surveys programs were implemented since 1980 [6] following a first restricted program realized between 1965 and 1969 [4] .
In this type of research, it is particularly important to review series of case studies, and draw out appropriate conclusions, and more global information about sets of cases. According to Brenac [7] , and Fleury [4] , the overall results are often presented in the form of the frequencies of involvement of various factors of identified casualties. However, given the heterogeneity and the complexity of the phenomenon, it is useful to keep information as a whole, reporting links between aspects of causality event and the sequences in which they fall.
In surveys related to road accidents, several studies on the phenomena of road accident and the methods of road safety studies have led to the concept of accident scenario allowing synthesis and generalization of knowledge resulting from the studied accident cases. We can point out: the pattern of accidents scenario in circulation on highway [8] , or their applications [9] .
3. Methods
Despite the existence of numerous works on road accidents, an exhaustive data base that can enhance the studying of this phenomenon in various environments is still lacking. The studied phenomenon is old in Cameroon. However, research in this domain is still embryonic and cannot help to draw out certainties as yet. The method applied to this study is that of Yin [10] . Though requiring a small number of analysis units, this approach can help to reach a certain degree of understanding of accident phenomena in the studied locality or area.
This method based on police and or constabulary reports is necessary even when it comes to seek information considered simple and related to road accidents [7] . The presentation of the method stands on the justification of choice of the studied road section, the identification of areas with defective or flawed signposts, the definition of the variables of the study, and the classification of accidents from police reports.
3.1. Choice of Road Sample
The road sample is the Yaoundé-Douala highway which is 243 km long. This road has been chosen for its heavy traffic (6000 vehicles/day) due to the economic and political importance of the towns it connects.
The road sample was subdivided into four sections (Figure 1):
Section 1: Yaoundé-Boumnyebel (91 km)
Section 2: Boumnyebel-Pouma (38 km)
Section 3: Pouma-Edea (48 km)
Section 4: Edea-Douala (66 km)
Each section presents a particular geometry and shows specific features of road insecurity. The geometrical analysis highlights the vertical alignment and cross-section, and horizontal alignment as well as the number of lanes. The analysis of road insecurity was measured by the rate of accidents or the rate of road hazards and conflicts covered which include:
The identification and the location of areas of conflict,
The assessment and the hierarchical organization of the hazard of conflict [11] .
This road was built between 1982 and 1985, it was dimensioned to accommodate 2750 vehicles per day, but nowadays it receives more than 6000 vehicles per day. The principal design and geometrical features of the studied section are: length (114 km), width of the roadway (7.40 m), width of the verge (1.50 m), speed limit (110 km/h), horizontal radius of the (500 m), slope (4%) and coating of the verges: double-layered.
Currently, this section shows a lot of defects such as subsidence, wrenching, potholes, reduced verge and range, lack of marks on the roadway and other road signs. These imperfections are due to the lack or poor maintenance works and thus may lead to road accidents.
For each of the afore-mentioned analysis criterion, an examination of the hazard of conflict zones was proceeded in terms of potentiality, severity, visibility and readability. The itinerary method of study therefore
![]()
Figure 1. Yaoundé-Douala highway. Source: Association “Recherche-Santé - Développement” et INSERM.
requires the identification of all potential non comprehensible areas by drivers for they may be invisible or disconnected from their context and the adjoining networks. These zones are potential risk zones. From the identification of failure points, the method aims at giving an assessment by proposing a conflict or risk hierarchy. That is why we describe the results of each analysis separately, while in practice they mutually allow to determine the relationship between road signs and road accidents.
Sections 3 and 4 (total length of 114 km) are selected as a sample for their heavy traffic and especially the availability of police reports in the existing data in the said sections.
3.2. Identification of Areas Requiring Adequate Signing
We analyze and evaluate the existing signposts based on the relationships between groups of data including braking, stopping, visibility distances and the avoidance maneuver along the road sample. Characteristics of the road sample available in the Department of Public Works, enable us to estimate first the speed as a function of radius of both the radius of curvature and the slope, thanks to the formula (1) [12] .
 (1)
(1)
where V85 (Km/h) represents the speed below which 85% of drivers travel (which provides a way of excluding speeds which are considered to be typical or extreme), R(m) the radius of curvature of horizontal alignment and p (%) the slope. The average of the latter peaked by the maximal authorized speed limit along the sample road has allowed to define the speed Vr(Vretained) leading to both the braking and stopping distances (m) by the formulas (2) and (3) respectively.
 (2)
(2)
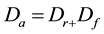 (3)
(3)
v = speed (m/s);
g = acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s2);
cfl = braking force coefficient;
p = longitudinal gradient (%).
Where Dr (m) is the distance of reaction that is, the covered distance during the time interval required for the driver to be aware of the situation and press the brake. This interval of time is about a second [12] .
The velocity Vr (Km/h) has also successively allowed the determination of the avoidance maneuver Devit (m), the maximum overtaking distance dD (m) and the minimum over taking distanced d (m) are given by the Equations (4), (5) and (6) respectively.
 (4)
(4)
 (5)
(5)
 (6)
(6)
we then determine the distance of visibility offered by the technical drafts in consideration of side slopes and vegetation on one hand, and the distance of visibility offered by the vertical alignment on the other hand as shown by the equations (7) and (8) respectively [11] .
 (7)
(7)
 (8)
(8)
where, h0 (m) and hν (m) indicate the height of the driver’s eye and the desired height respectively, and R (m) is the radius of curvature of vertical alignment. These formulas help in the understanding of the geometric parameters of the road environment.
3.3. The Study Variables
From the accident reports, we identified or separated two main concepts: accident type and type of signing (each of them having several variables regrouped in the Table 1) that enable us to assess the phenomenon of accident and to define the relationships between the signing and the occurrence of road accidents.
3.4. Collection and Classification of Accidents from Police Reports
Over a period of three years 2007, 2009 and 2011, we have recorded and classified each accident along the section Douala-Pouma from data obtained from the police or constabulary sources, the residents and the Ministry of Transport. The overall objective of this study is to describe accidents along the Yaoundé-Douala highway. During this period, accidents are distributed as follows (see Table 2).
The approach consisted of: a) collecting a copy of minutes established by the authorized police units of the cases studied during the years 2007, 2009 and 2011; b) making a descriptive analysis of the accident rate using information collected from the messages; c) developing a typology of accidents observed; d) locating and identifying the road sections favorable for accidents e) characterizing accident factors.
3.5. Identification and Development of Typical Accident Scenarios Related to Signing
Amongst the 572 police reports we collected from police stations, 569 were exhaustive and were related to the studied section. Accidents were grouped into scenarios using qualitative methods, regrouping cases judged to be similar in terms of accident process and circumstances from police reports [7] . Field trips allowed the estimation of the visibility and braking distances as well as the avoidance maneuver. It was then possible to describe or analyze the circumstances of accident.
![]()
Table 1. Table of variables and measurements.
Copy of police reports and messages
All the minutes and messages of road accidents along the road sample as well as those of the nearby secondary roads, available at the mobile police unit of Edéa and at the traffic office of the second police region of Cameroon were systematically photocopied. The images were processed by computer and printed.
However, only minutes and messages of accidents along the Pouma-Douala section were used in this study.
Treatment of accident reports
A grid of relevant data from police reports has been implemented from an adaptation of BAAC used in France. A grid was filled for all the police reports of the considered section. A quality control consisted of the cross validation of the pre-filled grid. This process helped to ensure concordance between the information on grids and those on the corresponding minutes and messages.
The encoded information was entered into a designed database and analyzed thanks to SPSS software (SPSS version 11.0).
The retained and significant variables were regrouped in the crossed table (see Table 3). No raised bump, no infrastructure or danger sign, no parking sign and no crossroads sign. Only accidents that have occurred more than five times were considered. It is clear that three cases are significant including: no raised bump (13 accidents in the same direction), no parking sign (9 accidents in the opposite direction and 12 in the same direction) and no crossroads sign (7 accidents in the opposite direction and 10 in the same direction).
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Signing and Road Accidents along the Studied Section
From the above analysis, it comes out that 117 singular points present difficulties to users due to the environment and that 31 points require signing or present default of signing. Here, we referred to them as critical points. Bivariate analysis through SPSS enabled us to develop a significant correlation between the type of accident and the type of sign (Table 4). To enable the analysis of explanatory environmental factors related to accidents, and the identification of the most dangerous sections, segments of 1 to 10 km along the accidents sites were defined. For each type of accident, a reference site has been selected and or chosen at random between 2 and 5 Km from the accident site.
In addition to the geometric characteristics of various sites (accident and reference sites), information were collected on the horizontal and vertical sign, the state of the road, the verge state and the potential obstacles within a radius of about 20 m around the pavement.
Two areas PK 013 and PK 059 were clearly remarkable as hotspots in terms of number of accidents,
Four areas PK 027, PK 043, PK 059 and PK 072 can be considered as hotspots in terms of number of wounded persons,
![]()
Table 3. Crossed table of accident types and types of signing.
And two zones: PK 027 and PK 089 stand out as hotspots with regards to the number of death.
Table 5 presents some results from particular points from the above mentioned information.
Table 5: Data of the calculations of the visibility, braking, stoppage and avoidance distances at selected locations of the studied section, the maximum overtaking distance dD (m) and the minimum overtaking distance dd (m), of the avoidance maneuver Devit (m), Visibility distance in the horizontal alignment DvisTP, Visibility distance in vertical alignment DvisPL. This table is divided into two sections: section 1 and section 2.
The comparison between the visibility and braking distances, the avoidance maneuver as well as the analysis of accident circumstances have led to the identification of 569 accidents cases recorded in our sample for three years, 108 accidents cases due to signing defaults, about 20% of the total number of accidents, which is considerable.
From Figure 2, it appears that frequent accidents along the studied section are those involving vehicles circulating in the same direction (194 cases) and those circulating in opposite direction (132 cases) representing 34.1% and 23.2% of our sample respectively. The diagram below shows the number of accidents according to their frequency and percentage of occurrence. The result obtained is constituted by two numbers: the first being the frequency and the second represents the percentage of occurrence of these accidents respectively.
From the analysis of the variable “types of signing” (Table 6), it appears that accidents not related to signing are the best expressed (455 cases recorded) representing 80% of the sample. However, accidents related to road signs although representing 20% of the sample have to be considered; they are distributed as follows: 36 cases related to lack of raised bump sign; 30 cases occasioned by the lack of parking sign, 30 cases due to the lack of crossroad sign, and 12 cases due to the lack of infrastructure or danger signs.
![]()
Table 4. Pearson’s Chi-squared test.
(a)8 cells (33.3%) with a theoretical number less than 5. The minimum theoretical number is 1.08.
![]() Section 1
Section 1 ![]() Section 2
Section 2
Table 5. Data of the calculations.
![]()
Figure 2. Frequencies and the percentage of the type of accidents.
From the two main defined variables: accidents types and types of signing, we obtained seven (07) accident scenarios (see Table 3). Only accidents occurring more than five times within the same sub-variable were considered. Therefore, the accident scenario 1 defined as that involving vehicles circulating in the same direction with no indication of raised bump yielded 13 accidents. The accident scenario 2 where one vehicle is static and another one in maneuver with no indication of raised bump occasioned 6 accidents. The accident scenario 3 involving others without raised bump sings caused 6 accidents. The accident scenario 4 involving vehicles moving in opposite directions without parking signs caused 9 accidents. The accident scenario 5 where vehicles are circulating in the same direction without parking sign yielded 12 accidents. The accident scenario 6 in which vehicles moved in opposite directions without crossroad sign yielded 7 accidents. The accident scenario 7 where vehicles moved in the same direction without crossroad sign yielded 10 accidents.
Among 108 accidents related to defective signing, 36 (33.33%) are due to the absence of raised bump signs, 30 (27.77%) are related to both the lack of parking and crossroad signs respectively and lastly 12 (11.11%) are linked to the absence of infrastructure or danger signs (see Table 6).
Pearson’s Chi-squared test gives significant links between the variables (see Table 4) (bilateral asymptotique significance of 0.31 and 0.47 for the Pearson’ Chi-squared test and the Probability report respectively).
The analysis of accident circumstances allows the modeling of the type of accident scenarios.
4.2. Development of Typical Accidents Scenarios
Accidents scenarios are described following five situations: driving, accident, emergency, shock situations and accident factors. The typical accident scenarios below are based on the analysis of a sample of representative cases of studied accidents along the road sample. We will randomly present scenarios related to collision on the one hand, and on the other hand, those related to road signs.
Types of accident scenarios related to collision
Table 7 shows the distribution of accidents occurred by collision. Here, it appears that 60 accidents are caused by collision representing 10.5% of the sample.
The analysis was made following each accident case; in addition, only accidents repeated more than five times within the same conditions were retained. Four scenarios were discerned as follows:
Accident scenario N˚1: Collision 1 (06 cases)
Accident scenario N˚2: Collision 2 (8 cases)
Accident scenario N˚3: Collision 3 (20 cases)
Accident scenario No 4: Collision 4 (26 cases)
![]()
Table 7. Description of accident by collision.
Types of accidents scenarios-related to road signs
In this sample, 108 accidents are due to relationships between road signs and road accidents. These accidents were grouped in seven accident scenarios as follows:
Accident scenario Type n˚1: (07 cases)
Accident scenario Type n˚2: (10 cases)
Accident scenario Type n˚3: (06 cases)
Accident scenario Type n˚4: (13 cases)
Accident scenario Type N˚5: (06 cases)
Accident scenario N˚6: (12 cases)
Accident scenario N˚7: (09 cases)
5. Conclusions
The work we have presented aimed at showing that the defaults of road signs have a considerable influence in the occurrence of accidents. We have analyzed and evaluated the signing defaults on the Yaoundé-Douala highway and we have identified and analyzed each accident on the Douala-Pouma section during the years 2007, 2009 and 2011 using the police reports and the messages from constabularies.
From these analysis, it appears that the evaluated defaults and lack of road signs constitute 20% of accidents averagely, which enabled us to identify seven types of accidents scenarios whose accident-factors are: the non signing of cross-roads; the lack of vertical and/or horizontal signing, lack of raised bumps or obstacles and the lack of standard parking or no parking signs at critical points. In addition, we have presented the occurrence of accidents by collision. It comes out that accidents occurring by collision represent 10.5% averagely in 2007, 2009 and 2011. Based on this cumulated information without a direct comparative study, it appears that road signs have a significant impact in the occurrence of road accidents. This should attract the attention of all the actors involved upstream or downstream in the road and traffic management.
The qualitative analysis applied here privileges the rigour and the meticulousness of the obtained information permits the extraction of contents and ideas on the one hand, and on the other hand it allows the categorization of accidents. In such a study, this approach cannot lead to a globalization of the results taken because: It requires the usage of a road section. The nature of the information used is not complete (the absence of the medical certificates in the police report or the statistics does not hold).
Such scenarios enable one to think about the measures of prevention. However, it remains to be consolidated; and a certain number of objectives have to be considered for complementary researches e.g. the problem of the visibility with respect to the road geometry in the Cameroonian highway for instance.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Prof. ELE Pierre (UIT, University of Douala Cameroon), Dr. ONOMO Cyril (ESSEC, University of Douala Cameroon), Dr. KOUSKE Arnaud Patrice and Mrs. KOUMI NGOH (UIT), University of Douala Cameroon) for their critical review and valuable advice which improved the presentation of this paper.