Ethnobotanical Survey of Medicinal Plants Used in Curing Some Diseases in Infants in Abeokuta South Local Government Area of Ogun State, Nigeria ()
1. Introduction
The term ethnobotany was first coined by an American botanist John Harshburger, in 1896, in an attempt to study the plants used by the primitive and aboriginal people. Since then, it has been defined as the traditional knowledge of indigenous communities, about surrounding plant diversity and how various people make use of indigenous plants found in their localities. Ethnobotany involves the study of how communities of a particular region make use of indigenous plants in the region for food, clothing and medicine [1] .
Plants are significant sources of medicines that are used in the treatment of various categories of human dis- eases. Historically all medicinal preparations were derived from plants, whether in the simple form of plant parts or in the more complex form of crude extracts, mixtures, etc. Today a substantial number of drugs are developed from plants which are active against number of diseases [2] .
The majority of these involve the isolation of the active ingredient (chemical compound) found in a particular medicinal plant and its subsequent modification. In the developed countries 25% of the medical drugs are based on plants and their derivatives [2] and the use of medicinal plants is well known among the indigenous people in rural areas of many developing countries. Plants, especially the higher ones have been described as the sleeping giants of drug and these medicinal plants have been screened for their chemicals that are potentially potent [3] . Many of the medicinal plants, especially in Nigeria have been documented [4] . The importance of medicinal plants, and the contribution of phytomedicine to the well-being of a significant number of the world’s population, has attracted interest from a variety of disciplines [5] .
Infancy, a period marked by the most rapid physical growth and development of a person’s life. In Nigeria the need to reduce infant and child morbidity and mortality is one of the greatest challenges confronting the Federal government. It has been estimated that the mortality rate of children below five years of age in Nigeria hovers between 97 and 120 per thousand births [6] [7] . The greatest health challenge to the Federal government of Ni- geria is to reduce this rate to the barest minimum; but despite the efforts of various successive governments to tackle the problem, the results have been dismally poor. Various researchers who are interested in maternal and child health in Nigeria have identified some key factors that may be adduced to this problem and some of these factors include poverty [8] ; ignorance by mothers [9] ; and the lack of political will by the Federal government [10] . For these and other similar reasons, morbidity and mortality from childhood diseases continue their debili- tating effects on the health of young children. The major causes of poor health and premature death among children in the developing world are not rare or exotic diseases. Millions of children in developing countries die each year from common illnesses such as malaria, measles, convulsion, mumps, mouth ulcer, chicken pox, kwashiorkor, small pox, cholera, pertussis (whooping cough), diarrhea, pneumonia, and especially in sub Saha- ran Africa-malaria. Newborns die from delivery complications, cold, tetanus and infections. Thus the aim of this study was to document the medicinal plants used for the treatment of some diseases in infants from Nigeria flora.
2. Materials and Methods
Ethnobotanical survey was carried out between February 2012 and June 2012 to obtain relevant information about medicinal plants used in the treatment of various diseases in infant in Abeokuta South Local Government Area of Ogun State. Data collected was based on oral interview with the aid of semi-structured questionnaire from respondents. Plants specimens indicated in the recipes were collected, pressed, mounted, identified and authenticated using their local names and standard text [11] . Voucher specimens were deposited at forestry and wildlife herbarium of the Federal University of Agriculture Abeokuta.
2.1. Study Area
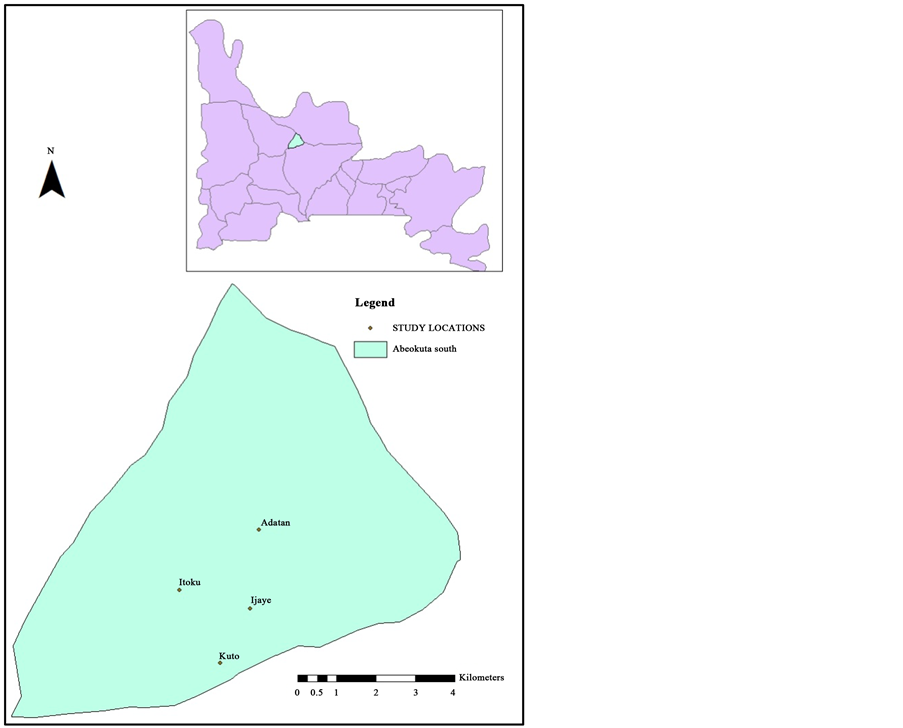
The survey was carried out in Itoku (7.15662˚N, 3.34135˚E), Kuto (7.13943˚N, 3.35074˚E), Adatan (7.17070˚N, 3.35960˚E) and Ijaye (7.15221˚N, 3.35757˚E) all in Abeokuta South Local Government Area of Ogun State, Nigeria. Abeokuta is located within Latitude 7.1608˚N and Longitude 3.3483˚E. Abeokuta is surrounded by large mass of rocks and has a population of about six hundred thousand people [12] . The city covers the geopo- litical areas of Abeokuta North and Abeokuta South Local Government Areas of Ogun State. The Yorubas are the main ethnics in the area but the original settlers are those of the Egba Yoruba dialect who founded the his- toric city. The dialectical groups in the area include Egbado, Ijebu, Egba, Remo, Oyo (Owu), Awori, Ikale and Ilaje. The people are known for traditional arts, carving and sculpturing [13] .
2.2. Ethical Approval
The purpose of the study was explained to the respondents (Herb sellers, traditional medical practitioner and herbalist) in the Local Government Area and informed consent was obtained from each of the respondents.
2.3. Administration of Questionnaire
Fifty-two (52) people were selected from these four study area. 13 people from each location. Ethnobotanical information on the plants was obtained from 50 respondents out of the total selected. These constituted the Tra- ditional Medicinal Practitioners (TMPs), herb sellers and herbalists. The use of semi-structured questionnaire and oral interview were adopted to obtain relevant ethno medicinal data. The questionnaires were administered to the respondents. The questionnaire was divided into three sections.
Section 1 deals with demographic information such as age, sex, religion, nationality, practice specification, duration of practice and educational background.
Section 2 consist of professional experience on the treatment of diseases and includes question such as type of diseases treated, frequency of treatment, use of herbal therapy alone or otherwise, duration of treatment, accom- panied side effects, accompanied verbal instructions, plant part(s) frequently used, availability of plants/plant part(s) and knowledge of treatment.
In Section 3, plants and recipes used in the treatment of common diseases, herbal preparation, arrangement of plant part(s) ingredient, traditional solvent of choice, traditional extraction methods/method of preparation and method of administration were considered.
In terms of educational background, majority of the respondent were not literate. The questionnaire was trans- lated and interpreted to them orally in the local language and responses filled into the questionnaire after each interview.
2.4. Data Analysis
All data were entered and verified using Epi-Info software (version 6.04; Centers for Disease Control Preven- tion, Atlanta, GA) and analyzed using SPSS version 16.0 for windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
3. Results
Demography/Personal Information on Respondents
The survey showed a total of 50 respondents, interviewed through the use of semi-structure questionnaire. The respondents were mainly herb sellers (80%), Traditional Medical Practitioners (TMPs) (12%), TMPs/herb sellers (4%) and herbalists (4%). The demographic survey of respondents was represented in Table 1.
Table 2 showed the professional experience of respondents. The survey showed that only 2% of the respon- dents use other therapies such as incantations to aid treatment of their patients. The survey also showed that (80%) inherited their knowledge of herbal treatment from their ancestors while (10%) got the knowledge from formal training, (8%) both from formal training and ancestors while (2%) claimed that their knowledge was from divination. Also (94%) of the respondents documented no accompanied side effects while (4%) indicated nausea/vomiting as accompanied side effect.
The entire survey revealed that a total of 63 medicinal plant species from 36 families were used by the various practitioners. Botanical names, local names, common names, family, growth form and plant part used were pre- sented in Table 3. Table 4 showed the species distribution according to their families while Table 5 revealed the percentage of plant growth form and plant part used in the treatment of the common diseases in infants. Ta- ble 6 showed the ailments, enumeration of recipes, methods of preparation and mode of administration.
4. Discussion
Plants have been a major source of medicine for human kind. The demand for traditional herbs is increasing very rapidly, mainly because of the harmful effects of synthetic chemical drugs. The global clamor for more herbal ingredients creates possibilities for the local cultivation of medicinal and aromatic crops as well as for the regulated and sustainable harvest of wild plants. Such endeavors could help raise rural employment in the de- veloping countries, boost commerce around the world and perhaps contribute to the health of millions [14] . Ni-
![]()
Table 1. Demographic structure of the respondents on the knowledge of plants used in the treatment infant diseases.
N = number of respondents; % = percentage of respondents.
![]()
Table 2. Professional experience of the respondents on the knowledge of plants used in the treatment infant diseases.
N = number of respondents; % = percentage of respondents.
geria is endowed with an enormous diversity of animals and plants, both domesticated and wild, and an impres- sive variety of habitats and ecosystems. This heritage sustains the food, medicinal, clothing, shelter, spiritual, recreational, and other needs of her population [15] .
Respondents gave local names of plants in recipes used in the treatment of some infant diseases. This was in consonance with Singh (2008) [16] who reported that plants are generally known by their local names in every part of the world. The local names play a vital role in ethnobotanical study of a specific tribe or region. Although local names are not recommended directly for scientific accounts as they lack uniformity and consistency, yet they may certainly be considered as a useful tool for search of new useful plants or new uses of known plants [17] . Local names render a useful service as a means of reference by local people in a particular area.
This work revealed that majority (80%) of the respondents acquired the source of knowledge from their ance- stral via verbal transfer. Ogbole and Ajaiyeoba (2010) [18] had earlier reported that knowledge of the uses of plants, which is sometimes jealously guarded by their owners, is a tradition passed on from one generation to the other by verbal transfer, the changes imposed by modern life on social structures and attitudes now seems to be the cause of the loss or rejection of such indigenous practices.
The study also showed that quite a number of plant parts from the 63 species especially the leaves, roots and stem barks have been found to be efficient in the management of various diseases in infants in the Local Gov- ernment Area. Information gathered from respondents showed that increasing number of people is turning to herbal remedies for prevention and cure of various diseases. The 63 medicinal plants mentioned were repre- sented by all plants forms. Trees were found to be the most used plants followed by shrubs, herbs, underground stem, grass, climber, creeper and weed.
The various plants parts mentioned include bulb, fruit, leaves, rhizome, root, seed, stem bark and whole plants. It was observed that leaves formed the most frequently used (47.62%), followed by stem bark (23.81%), seed (7.93%), roots (6.34%), fruits (4.76%), bulb, rhizome and whole plants (3.17% each). The plant leaves are im- portant ingredient in traditional treatment of various diseases as it features as a component in many herbal prep-
![]()
![]()
Table 3. Enumeration of plants used for the treatment of some common diseases in infants by the people of Abeokuta South Local Government Area.
arations. This finding concurred with other studies such as [19] .
However, most informants opined that there is no side effect in taking herbal recipes.
Some of the plants revealed in the survey have been cited in the ethnobotanical survey of some African coun- tries, for example in the treatment of measles, jaundice, polimylitis, yellow fever, chicken pox [19] , anti malaria [20] . The prominent plant species are Cajanuscajan, Allium sativum, Carica papaya, Momordicacharantia, Garcina kola, Vernonia amygdalina and Aframomum melegueta.
One of the recipes is prepared from a single plant source (Parinari curatellaefolia) while some others are in
![]()
Table 4. Species distribution according to families of plants used for the treatment of some common diseases in infants.
![]()
Table 5. Percentage of plant growth form and plant part used in the treatment of some common diseases in infants by people of Abeokuta South Local Government.
N = number of plant growth form or plant part; % = percentage of plant growth form or plant part.
![]()
![]()
Table 6. Enumeration of recipes, method of preparation, mode of administration used in the treatment of some infant diseases among the residents of Abeokuta South Local Government.
combinations with other common plants. Method of preparation varies decoctions and infusions are the most frequently used methods.
Some of the challenges encountered in the course of this survey include: respondents not willing to give rele- vant information due to fear of losing their major source of their income, some demanded money prior to inter- view as they claimed to have “intellectual properties” stocked with knowledge of medicinal plants, while some castigated government for neglecting them and sending researchers to come and exploit their ethnomedicinal knowledge. Also, some herbalists/TMPs preferred sharing the knowledge on a television programme rather than disseminating ethnomedicinal information to researchers. This they claimed will also help to advertise their names and services.
5. Conclusion
The survey has added more to the existing discoveries of the relevance of plants and its usefulness in the treat- ment of some infant diseases among the residents of Abeokuta South Local Government. The therapeutic claimed recipes incorporated in the study need to be evaluated through phytochemical, pharmacological investi- gation to discover their active compounds.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.