Prediction of Transformation of Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis into Multiple Sclerosis ()

1. Introduction
The most often, ADEM is characterized by the single-phase course accompanied by considerable variations concerning the duration of disease and convalescence. However, also there are relapses of ADEM known already from 1932 year due to van Bogaert who published the paper “ADEM with relapses” [1] . ADEM relapses can be considered as a multi-phases course of this disease or its transformation into multiple sclerosis (see, e.g., the works [2] -[7] ).
ADEM relapses are observed with the following frequencies: in one case from 18 ones for this disease (5.5%) [8] , in 4 of 31 (13%) [9] [10] , in 24 of 132 (18%) [11] , in 7 of 35 (20%) [12] , in 9 of 42 (21%) [13] , in 5 of 21 (24%) [14] .
Appearance of new clinic symptoms in three months after initial signs of this disease is considered as a relapse of ADEM. In the case of this disease relapse, the pathological process comprises new parts of brain and/or spinal cord (which are usually confirmed by clinical investigations and neurovisual methods).
If the relapse appears in a short-time interval after initial signs and is combined with further infection or cancelled hormonal therapy, the term multiphase disseminated encephalomyelitis (MDEM) should be used [15] [16] .
In opinion of researchers, MDEM is characterized by poly-symptomatic presentations of this disease, availability of demyelination focuses in MRT data mainly in subcortical parts of brain, in less degree located periventricularly, with total or partial disappearance of focuses within the convalescent period [17] . The multiphase course of disseminated encephalomyelitis can be diagnosed in the case of disease relapse appearance at least 3 months after its initial presentation [14] [16] -[18] . Appearance of new clinic symptoms and new focuses in MRT data 12 to 18 months after the primary episode of the disease is indicative of its possible transformation into multiple sclerosis [19] .
In literature there is available information about possible options in the course of ADEM. The results of observations aimed at the course of this disease for 40 patients with the ADEM diagnosis show that 14 (35%) of them demonstrate developed clinically confirmed multiple sclerosis one year after the primary ADEM episode [20] . Another investigation showed that 5 (23.8%) from 21 patients demonstrated relapses of disseminated encephalomyelitis, and 2 (9.5%) of these 21 patients had multiple sclerosis. The recent investigations showed that 4 (13%) of 31 patients with ADEM had manifestations of ADEM relapses, while 10 (40%) of 25 patients had clinically confirmed multiple sclerosis [21] . As it follows from the data Schwarz S. et al. [20] [22] , developed multiple sclerosis was found in 14 (35%) of 40 patients in 38-month period of observations (which was confirmed using the Poser criteria). In the Alan investigations, 13 (33.3%) of 39 patients faced the replaces of demyelination disease [9] [21] . For the long period of observations (8 years), only one patient with ADEM of 11 showed new focuses of demyelination in MRT data [20] .
The investigations performed in France indicate that 57% patients with ADEM can acquire multiple sclerosis in 2.9 years, in the average. Investigation of 48 patients with ADEM showed that 10 ones (20.8%) acquire multiple sclerosis in 2.36 years, while 13 (27%)—in 5.64 years [12] .
From the viewpoint of clinical neurology, not only the frequency of the multiphase option in the course of ADEM, but also determination of prognostic risk factors that cause it is of great importance. Prediction of the multiphase course of ADEM and its transformation into disseminated sclerosis is of great importance since it enables to determine the tactics treating the patients and volume of therapeutic measures.
The purpose of this research was to determine the prognostic risk factors of development of transformation of ADEM into multiple sclerosis.
2. Methods
We have examined 101 patients with the diagnosis ADEM, namely: 28 men and 73 women in the age from 17 up to 53 years (average age value 31.7 ± 1.01 years). According to the decision of the Ethics Committee of the O.O. Bogomolets National Medical University (Kyiv city, Ukraine), the investigations described in these articles have been carried out according to modern scientific standards. There have been provided the measures ensuring safety of the patients, respect of their rights and dignity as well as moral and ethical standards in accordance with the human rights principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethics Committee does not have any objections against publishing these articles (protocol number 48 dated 29.09.2010).
All the patients were investigated using magnetic-resonance tomography (MRT) investigations of brain and/or spinal cord as well as estimated the disability degree in accord with the Kurztke Expanded Disability Status Score (EDSS) scale [23] .
All the patients were under observation for 3 years. If during this period we could not mark any replace of demyelination disease, we interpreted it as the single-phase type of the ADEM course. In the case when there arose disease relapses, that, from the clinical viewpoint and after neuro-visual patient examination, had signs of disseminated encephalomyelitis, we considered it as the multi-phase option of its course (MDEM). In the cases of clinically confirmed multiple sclerosis (in accord with the McDonald criteria [24] ), we interpreted it as a transfer of ADEM into multiple sclerosis.
To ascertain the prognostic meaning of clinic-paraclinic indexes for patients with ADEM, we estimated the cumulative part of the absence of relapses by using the Kaplan-Meyer method with the Fisher criterion and the most important clinic-paraclinic data [25] [26] .
3. Results
The total prediction of cumulative parts for transformation of ADEM into disseminated sclerosis is adduced in Figure 1.
As seen from Figure 1, 10% (cumulative part is equal to 0.1) of patients with ADEM show transformation of ADEM into multiple sclerosis 5 months after the first signs of this disease, 25% (cumulative part-0.25)—after 7 months, 50% (cumulative part-0.5)—after 11 months, 75% (cumulative part-0.75)—after 15 months of the period for observation. The cumulative part of patients without transformation of ADEM into multiple sclerosis for the first 6 months was 0.78 (i.e., 78% of all the patients), for 12 months—0.36 (36% of patients), for 24 months—0.04 (4% of patients).
The dynamics of decay in the cumulative part of patients with ADEM but without replaces in its transformation into multiple sclerosis within the three year period of observations is depicted in Figure 2.
As seen in Figure 2, in case of patients with transformation of ADEM into multiple sclerosis, the most pronounced decay in the cumulative part of patients without relapses was observed during the first year of observations (64%) (in particular from 6 to 12 months (42%)), and the least pronounced—during the third year (4%).
Thus, the frequency of replaces changed in dependence on the term of observations for three year period, and it was the highest during the first year and the lowest during the third year.
The prognostic estimate of development for transformation of ADEM into multiple sclerosis in dependence on the age is depicted in Figure 3.
As seen in Figure 3, the best indices of relapses absence were observed in patients of the age 39 to 40 years, however the statistical difference is not reliable (р = 0.78019 (>0.05)).
Prediction of development of transformation of ADEM into multiple sclerosis in dependence on gender did not find any reliable difference between the three year absence of relapses in men and women, but one could observe a tendency for increasing the cumulative part in women (р = 0.15560 (>0.05)) (Figure 4).
Thus, one can draw a conclusion that such prognostic signs as age and gender have no reliable influence on development of transformation of ADEM into multiple sclerosis.
The reliable difference for patients without replaces between the groups of patients with different changes in neurologic status was not found (Figure 5), in other words, presence of some neurologic deficiencies in patients with ADEM does not influence sufficiently on its transformation into multiple sclerosis.
The complex estimate of the status of patients with ADEM by the EDSS scale and its relation to the term of appearance of transformation of ADEM into multiple sclerosis are depicted in Figure 6.
As seen in Figure 6, transformation of ADEM into multiple sclerosis arose later in patients with a slight disability degree by the EDSS scale, as compared to those with a medium or heavy disability degrees; transformation of ADEM into multiple sclerosis arose later in patients with a heavy disability degree, but as far as after 25 months of observation multiple sclerosis arises in 100% of the patients of this group (р = 0.01516 (<0.01)).
Thus, availability of a slight disability degree by the above scale corresponds to a more positive course of ADEM, which is manifested in prolongation of the term of emergence of ADEM transformation into multiple sclerosis.
When analyzing the MRT data taken from patients with ADEM, we ascertained that availability of demyelination focuses with various medium sizes makes an essential effect on prediction of the ADEM course, in particular its transformation into multiple sclerosis, which is adduced in Figure 7.

Figure 1. Dynamics of the cumulative part of patients with ADEM without development of transformation of ADEM into multiple sclerosis for the three-year period of observations (by the Kaplan-Meyer method).
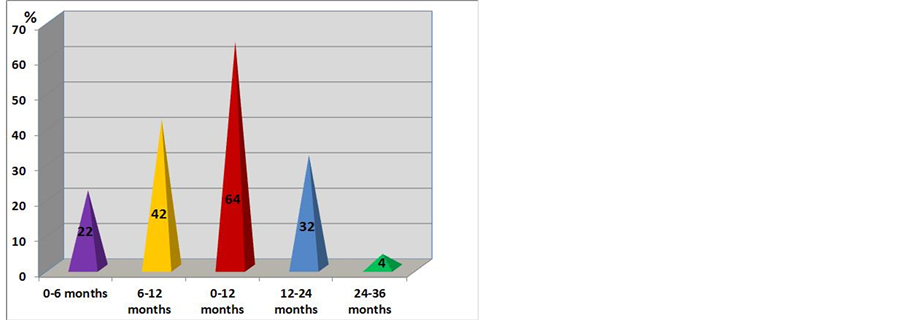
Figure 2. Dynamics of decrease in the cumulative part of patients with ADEM but without development of transformation of ADEM into multiple sclerosis for the three year period of observations (in %).

Figure 3. Dynamics of the cumulative part of patients without replaces by separate age groups (using the Kaplan-Meyer method).

Figure 4. Dynamics of the cumulative part of patients without replaces in dependence on their gender (by the Kaplan-Meyer method).

Figure 5. Dynamics of the cumulative part of patients without relapses in dependence on changes in the neurologic status (by Kaplan-Meyer).

Figure 6. Dynamics of the cumulative part of patients without relapses by the disability degree in accord with the EDSS scale (by Kaplan-Meyer).

Figure 7. Dynamics of the cumulative part of patients without relapses by sizes of demyelination focuses in accord with MRT data (by Kaplan-Meyer).
Thus, the bigger is the medium size of demyelination focuses, the slower is development of transformation of ADEM into multiple sclerosis. (р = 0.01757 (<0.05)).
4. Conclusion
Thus, our analysis of the main clinic-paraclinic indexes by the Kaplan-Meyer method was proved to be reliable and enabled us to find out a number of important prognostic criteria of the ADEM course in the form of its transformation into multiple sclerosis. The reliable influence on development of transformation of ADEM into multiple sclerosis is related to such prognostic signs as disability degree by the EDSS scale and size of demyelination focuses in accord with MRT data. The most favorable criteria for prediction in this disease with later development of transformation into multiple sclerosis are slight degree of disability by the EDSS scale and large size of demyelination focuses (MRT data).